java递归之“二叉树”
物有本末,事有始终,知所先后,则近道矣。-----题记。
BotWong半路入行it做码农,也就半年时间,竟“不知天高地厚”地来到了深圳闯天下。一口气投了百个简历,一周后终于有公司邀约面试,除了基础的java语法和开发经验,大一点的公司都会出几道题给你做(算法题)。BotWong是一头雾水,而且心里很生气!气!气!气!以前自己学的是“人类心理学理论与实践”专业,唯一的计算机基础也就是用过word、excel给客户报过价。自己硬着头皮把java语法和javaEE框架学了一遍,像我这样的个例已经算是出类拔萃的了,为什么还要对我这么苛刻,哼!BotWong从那以后就开始讨厌那些喜欢考试的公司,并发誓以后再也不去那样的公司面试!
我和BotWong是好朋友,他提出了自己的困惑:到底要不要学这些看着“没用”的算法,问我该怎么看待这件事,该如何做。好在BotWang还是个头脑清醒的人,要不然也不会问这样的问题了。我看他挺有诚意,就把自己以前写的一些代码,其中就包含一些算法,拿出来泛泛地说了一遍,建议他自己都去实现一遍。BotWang消失了三月,再见之时,已能感知其功力大涨,已非三月前的那个BotWong了。我心甚慰,特此将自己以前写过的集合类都贴出来,方便自己和网上的宝宝们随时翻看,随时补充能量。
一、二叉树类:
package tree;
/**
* 二叉树数据载体类
* @author tery
*
* @param <T>
*/
public class BinaryTreeNode<T> {
private T data;//权值
private BinaryTreeNode<T> left;//左孩子
private BinaryTreeNode<T> right;//右孩子
public BinaryTreeNode(T data){
this.data=data;
left=right=null;
}
public T getData(){
return this.data;
}
public void setData(T data){
this.data=data;
}
public BinaryTreeNode<T> getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(BinaryTreeNode<T> left) {
this.left = left;
}
public BinaryTreeNode<T> getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(BinaryTreeNode<T> right) {
this.right = right;
}
/**
*插入权值
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public BinaryTreeNode<T> insert(BinaryTreeNode<T> node,Integer data){
if(node==null){
return new BinaryTreeNode<T>((T)data);
}
//如果当前节点的权值大于data,那么插入到左孩子节点上
if(Integer.valueOf(node.getData().toString())>data){
node.left=insert(node.getLeft(),data);
}
//如果当前节点的权值大于data,那么插入到左孩子节点上
if(Integer.valueOf(node.getData().toString())<data){ node.right=insert(node.getRight(),data); }
//相等抛异常
if(Integer.valueOf(node.getData().toString())==data){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("the data:"+data+"is already exsist in the tree");
}
return node;
}
}
insert方法中涉及到的递归:
: aload_1
: ifnonnull
: new # // class tree/BinaryTreeNode
: dup
: aload_2
: invokespecial # // Method "<init>":(Ljava/lang/Object;)V
: areturn
: aload_1
: getfield # // Field data:Ljava/lang/Object;
: aload_2
: if_icmple
: getfield # // Field left:Ltree/BinaryTreeNode;
: aload_2
: invokevirtual # // Method insert:(Ltree/BinaryTreeNode;Ljava/lang/Object;)Ltree/BinaryTreeNode;
: putfield # // Field left:Ltree/BinaryTreeNode;
: aload_1
: areturn
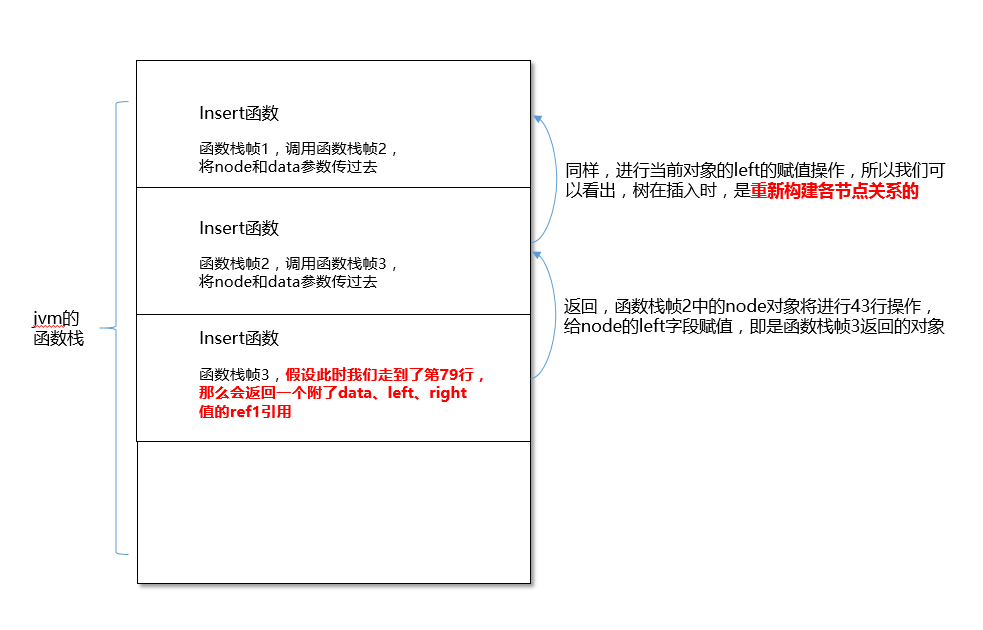
上面是insert方法的jvm执行的指令,我摘抄了部分关键点说明一下递归是怎么做的:
insert函数栈中的局部变量表中的参数:第一个是当前树节点对象(暂且称为ref0),第二个是函数中传进来的node对象的引用(称为ref1),第三个是传进来的常量data(在常量池中#20)
0: aload_1 将第一个引用类型局部变量推送至栈顶,那个引用也就是insert方法中的node对象的引用(ref1)
1 : ifnonnull 13 如果ref1不为空,则跳到13行执行
4-12 : 如果是空,则此节点即是我们要插入的节点,调用它的构造函数<init>方法,将data值赋给它,然后areturn(将这个新生成的对象引用返回)
13 : aload_1 将ref1压入栈顶
14:getfield 将常量池中当前对象ref1的data的值压入栈顶
23:aload_2 将传入的data值压入栈顶
30:if_icmple 79,如果传入的data值小于ref1的权值,那么就跳到79执行
36:getfield #24 ,将常量池中#24,即left压入栈中,即left常量的引用
39:aload_2 将data值压入栈中。实际上36、39两步的指令都是在为下面40行做准备,40行调用insert方法,传递给它需要的参数
40:invokevirtrual #53,调用insert方法,将36、39行准备的两个参数带过去
43:putfield #24 ,给当前实例ref1的left字段赋值
79:aload_1 ,将当前实例ref1压入栈中
80:areturn ,将栈顶的ref1返回
如果你不太懂,我还给你画了个图,帮助你理解:

假设jvm只执行了在左边树插入的递归步骤:
上面的字节码指令和图解是截取了部分关键点进行讲解的,如果想进一步探讨的宝宝们,可以联系我详细讨论。
三、二叉树工具类:
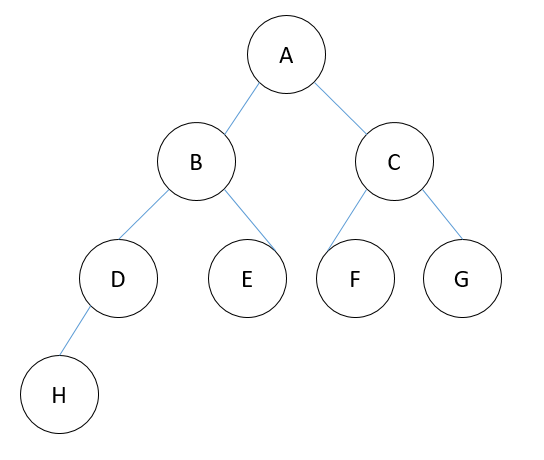
1. 前根序遍历:先遍历根结点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。(ABDHECFG)
2.中根序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历根结点,最后遍历右子树。(HDBEAFCG)
3.后根序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点(HDEBFGCA)
package tree; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack; public class BinaryTreeUtil { /**
* 用递归的方式实现二叉树的前序遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static<T> List<T> preOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> root){
List<T> result=new ArrayList<>();
preOrderVisit(root,result);
return result;
}
private static<T> void preOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> node, List<T> result) {
//如果节点为空,返回
if(node==null){
return;
}
//不为空,则加入节点的值
result.add(node.getData());
//先递归左孩子
preOrderVisit(node.getLeft(),result);
//再递归右孩子
preOrderVisit(node.getRight(),result);
}
/**
* 用递归的方式实现二叉树的中序遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static<T> List<T> inOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> root){
List<T> result=new ArrayList<T>();
inOrderVisit(root,result);
return result;
}
private static<T> void inOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> node, List<T> result) {
if(node==null){
return;
}
inOrderVisit(node.getLeft(),result);
result.add(node.getData());
inOrderVisit(node.getRight(),result);
}
/**
* 用递归的方式实现二叉树的后遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static<T> List<T> postOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> root){
List<T> result=new ArrayList<T>();
postOrderVisit(root,result);
return result;
}
private static<T> void postOrderVisit(BinaryTreeNode<T> node, List<T> result) {
if(node==null){
return;
}
postOrderVisit(node.getLeft(),result);
postOrderVisit(node.getRight(),result);
result.add(node.getData());
}
/**
* 用非递归的方式实现前序遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static<T> List<T> preOrderVisitWithoutRecursion(BinaryTreeNode<T> root){
List<T> result=new ArrayList<T>();
Stack<BinaryTreeNode<T>> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
BinaryTreeNode<T> node=stack.pop();
result.add(node.getData());
if(node.getRight()!=null){
stack.push(node.getRight());
}
if(node.getLeft()!=null){
stack.push(node.getLeft());
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 用非递归的方式实现中序遍历
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static<T> List<T> inOrderVisitWithoutRecursion(BinaryTreeNode<T> root){
List<T> result=new ArrayList<T>();
Stack<BinaryTreeNode<T>> stack=new Stack<>();
BinaryTreeNode<T> node=root;
while(node!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(node!=null){
stack.push(node);
node=node.getLeft();
}
BinaryTreeNode<T> currentNode=stack.pop();
result.add(currentNode.getData());
node=currentNode.getRight();
}
return result;
}
二叉树部分上面总共列举了15个方法,主要的思想还是用递归。关于递归,为了让宝宝们明白是怎么回事,我也是花了点心思去解释的,请各位再深入思考一下。里面涉及到了jvm函数调用层面的知识,如果不懂,建议大家去看看jvm的书,了解jvm怎么执行代码,那就可以轻轻松松地理解递归到底是怎么执行的了。
java递归之“二叉树”的更多相关文章
- 【数据结构--二叉树】Java递归实现二叉树遍历
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yaobolove/p/6213936.html 这有一棵树: 1.节点对象 package com.tree.mybinarytree; / ...
- java 递归求二叉树深度
给定二叉树,找到它的最大深度. 最大深度是从根节点到最远叶节点的最长路径上的节点数. 注意:叶子是没有子节点的节点. Example: Given binary tree [3,9,20,null,n ...
- JAVA递归、非递归遍历二叉树(转)
原文链接: JAVA递归.非递归遍历二叉树 import java.util.Stack; import java.util.HashMap; public class BinTree { priva ...
- 使用递归打印二叉树的左视图 java
使用递归打印二叉树的左视图 java package com.li.jinRiTouTiao; public class PrintLeftView { static class TreeNode{ ...
- 非递归遍历二叉树Java版的实现代码(没写层次遍历)
直接上代码呵呵,里面有注解 package www.com.leetcode.specificProblem; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util ...
- 非递归遍历二叉树Java实现
2018-10-03 20:16:53 非递归遍历二叉树是使用堆栈来进行保存,个人推荐使用双while结构,完全按照遍历顺序来进行堆栈的操作,当然在前序和后序的遍历过程中还有其他的压栈流程. 一.Bi ...
- java数据结构之二叉树遍历的非递归实现
算法概述递归算法简洁明了.可读性好,但与非递归算法相比要消耗更多的时间和存储空间.为提高效率,我们可采用一种非递归的二叉树遍历算法.非递归的实现要借助栈来实现,因为堆栈的先进后出的结构和递归很相似.对 ...
- Java实现查找二叉树&C++的做法
写了个Java的查找二叉树,用递归做的,不用递归的还没弄出来.先贴一下.回头再研究. BTreeTest.java: public class BTreeTest{ class Node{ Node ...
- JAVA递归实现线索化二叉树
JAVA递归实现线索化二叉树 基础理论 首先,二叉树递归遍历分为先序遍历.中序遍历和后序遍历. 先序遍历为:根节点+左子树+右子树 中序遍历为:左子树+根节点+右子树 后序遍历为:左子树+右子树+根节 ...
随机推荐
- python模块之ConfigParser: 用python解析配置文件
在程序中使用配置文件来灵活的配置一些参数是一件很常见的事情,配置文件的解析并不复杂,在python里更是如此,在官方发布的库中就包含有做这件事情的库,那就是ConfigParser,这里简单的做一些介 ...
- git 基础入门操作
前言: 介绍基础的git入门级指令,虽然git指令非常多,但是实际工作中,我们会用到的非常少,小项目中甚至只需要用到2.3个.而且大部分人都会采用gui,而不是每次都打开终端然后输一长串难记的指令. ...
- react native 获取 软键盘高度 和 新增软键盘的组件
import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View, Keyboard, Te ...
- navicat链接mysql 8 出现 2015 authentication plugin 'caching_sha2_password' 错误
使用mysql自带的 MySQL 8.0 Command Line Client - Unicode 登录, 然后使用命令: alter user 'root'@'localhost' identif ...
- ubuntu16.04安装Nvidia显卡驱动、CUDA8.0和cudNN V6
Nvidia显卡驱动安装 在ubuntu搜索框输入 软件更新,打开 "软件和更新" 对话框,在 附加驱动里选择系统检测到的Nvidia驱动,应用更改,重启系统: 安装完成之后查看G ...
- Linux udhcp client (udhcpc) get IP at anytime
/*************************************************************************************** * Linux udh ...
- python print的用法
第一种是格式化的 strHello = "the length of (%s) is %d" %('Hello World',len('Hello World')) import ...
- 项目管理软件选择:redmine or JIRA
个人理解,这两款软件从本质上说是issue tracking,而不是项目管理. 先说些个人的想法 1)从现阶段情况看,都是够用的,毕竟本来就是小团队 2)从扩展而言,根据现在团队的实际情况(基本都是搞 ...
- Linux下编写动态链接库
下面通过一个例子来介绍如何生成一个动态库.这里有一个头文件:so_test.h,三个.c文件:test_a.c.test_b.c.test_c.c,我们将这几个文件编译成一个动态库:libtest.s ...
- 【转】Ubuntu12.04安装YouCompleteMe插件
原文网址:http://m.blog.csdn.net/blog/unhappypeople/19160243 以前用的都是ctags+omnicomplete+acp的方式,这次换成clang自解析 ...
