混沌工程之ChaosToolkit使用之一删除K8s POD
今天我们来玩一下混沌工程的开源工具chaostoolkit 。
它的目标是提供一个免费,开放,社区驱动的工具集以及api。
官方源码链接:https://github.com/chaostoolkit/chaostoolkit
要想了解这个工具就必须知道混沌工程原则中提到的要点。如下所示:
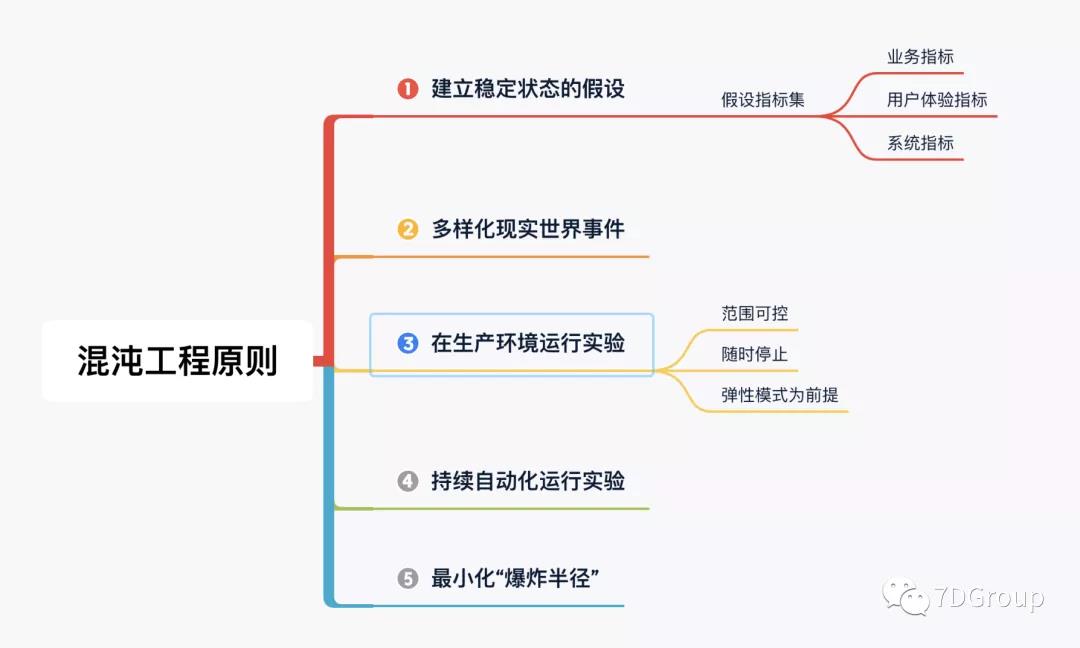
记往这里提到的第一个要点,建立稳态假设。
在运行这个工具之前,我们先来看一下它的架构。
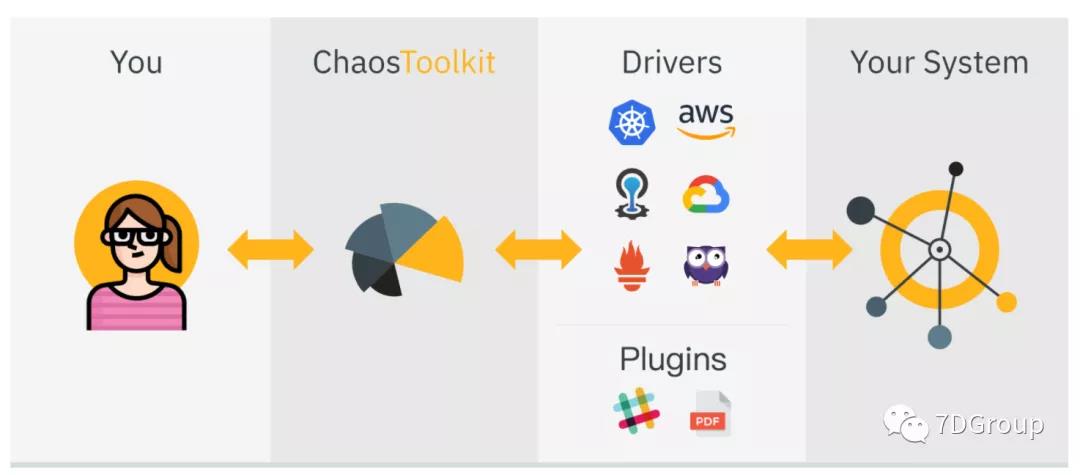
简单来解释一下,就是ChaosToolkit通过Drivers来操作你的被测系统。
它的功能点包括如下部分:

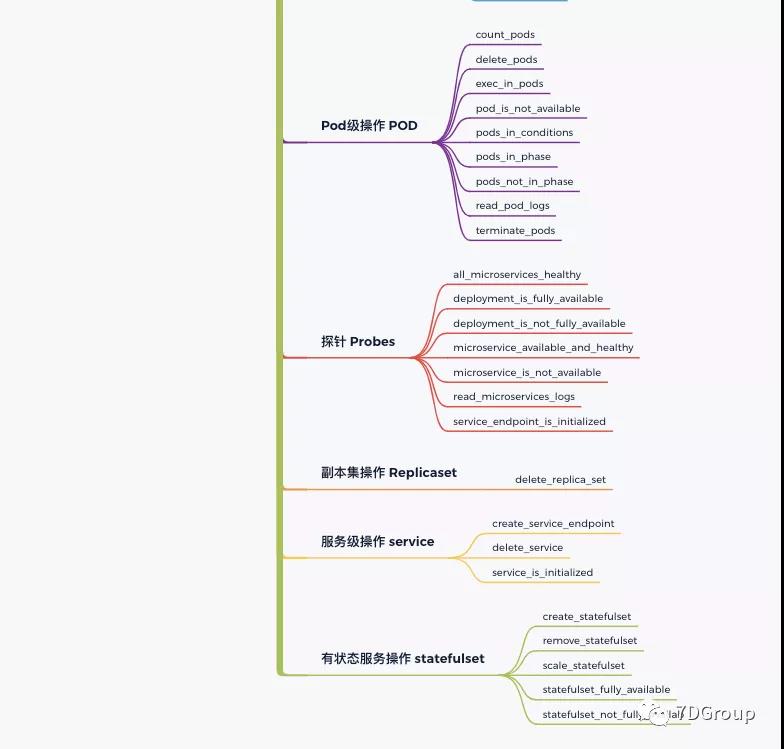
下面我们把工具装起来玩一下。
环境说明:CentOS7.8、k8s 1.19.5、示例应用
安装python3
sudo yum install python3 python3-venv
安装pipenv
gaolou@GaoMacPro ~ % pip3 install pipenv
安装chaos-toolkit 的k8s扩展和报告模块
pip3 install -U chaostoolkit
pip3 install -U chaostoolkit-kubernetes
pip3 install -U chaostoolkit-reporting
如果你需要操作其他平台,也可以安装相应扩展。
创建虚拟环境
python3 -m venv .bundler
source .bundler/bin/activate
为了不影响其他环境,我们这里用python的虚拟环境操作。
以上安装过程是在k8s的master机器上执行的,如果你不是在k8s上安装的,可以配置相应的k8s上下文,具体操作请参考:https://chaostoolkit.org/drivers/kubernetes/。
chaos discover 探索试验
首先执行discover命令,chaostoolkit会根据./kube/config中的内容生成discovery.json文件,这个文件中会包括所有可以对k8s执行的操作集合。执行成功的结果如下:
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]# chaos discover chaostoolkit-kubernetes
[2021-06-23 12:18:07 INFO] Attempting to download and install package 'chaostoolkit-kubernetes'
[2021-06-23 12:18:08 INFO] Package downloaded and installed in current environment
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Discovering capabilities from chaostoolkit-kubernetes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for probes in chaosk8s.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.deployment.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.deployment.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.node.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.node.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.pod.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for probes in chaosk8s.pod.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.replicaset.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.service.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.service.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.statefulset.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for probes in chaosk8s.statefulset.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for actions in chaosk8s.crd.actions
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Searching for probes in chaosk8s.crd.probes
[2021-06-23 12:18:09 INFO] Discovery outcome saved in ./discovery.json
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]#
chaos init 生成试验
执行初始化命令,可以根据提示创建一个混沌试验。
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]# chaos init
You are about to create an experiment.
This wizard will walk you through each step so that you can build
the best experiment for your needs.
An experiment is made up of three elements:
- a steady-state hypothesis [OPTIONAL]
- an experimental method
- a set of rollback activities [OPTIONAL]
Only the method is required. Also your experiment will
not run unless you define at least one activity (probe or action)
within it
Experiment's title: E2 #这里是配置一个试验名
A steady state hypothesis defines what 'normality' looks like in your system
The steady state hypothesis is a collection of conditions that are used,
at the beginning of an experiment, to decide if the system is in a recognised
'normal' state. The steady state conditions are then used again when your experiment
is complete to detect where your system may have deviated in an interesting,
weakness-detecting way
Initially you may not know what your steady state hypothesis is
and so instead you might create an experiment without one
This is why the stead state hypothesis is optional.
Do you want to define a steady state hypothesis now? [y/N]: y # 创建稳态假说,请注意,这个是混沌工程中的重要概念,但是在其他的大部分混沌工具中都看不到这一步
Hypothesis's title: H2
You may now define probes that will determine
the steady-state of your system.
Add an activity
1) all_microservices_healthy
2) deployment_is_fully_available
3) deployment_is_not_fully_available
4) microservice_available_and_healthy
5) microservice_is_not_available
6) read_microservices_logs
7) service_endpoint_is_initialized
8) count_pods
9) pod_is_not_available
10) pods_in_conditions
11) pods_in_phase
12) pods_not_in_phase
13) read_pod_logs
14) statefulset_fully_available
15) statefulset_not_fully_available
16) get_cluster_custom_object
17) get_custom_object
18) list_cluster_custom_objects
19) list_custom_objects
Activity (0 to escape): 1 # 选择稳态假说的判断点,简单来说,这里就是创建一个预期结果
!!!DEPRECATED!!!
1) kill_microservice
2) remove_service_endpoint
Do you want to use this probe? [y/N]: y # 确定是否使用上面选择的探针
A steady-state probe requires a tolerance value, within which
your system is in a reognised `normal` state.
What is the tolerance for this probe?: normal
You now need to fill the arguments for this activity. Default
values will be shown between brackets. You may simply press return
to use it or not set any value.
Argument's value for 'ns' [default]: chaosnamespace # 输入k8s中要操作的命名空间
Do you want to select another activity? [y/N]: y # 是否选择一个的操作动作
Add an activity
1) all_microservices_healthy
2) deployment_is_fully_available
3) deployment_is_not_fully_available
1) kill_microservice
4) microservice_available_and_healthy
5) microservice_is_not_available
6) read_microservices_logs
7) service_endpoint_is_initialized
8) count_pods
9) pod_is_not_available
10) pods_in_conditions
11) pods_in_phase
12) pods_not_in_phase
13) read_pod_logs
14) statefulset_fully_available
15) statefulset_not_fully_available
16) get_cluster_custom_object
17) get_custom_object
18) list_cluster_custom_objects
19) list_custom_objects
Activity (0 to escape): 1 # 选择具体的动作
!!!DEPRECATED!!!
Do you want to use this probe? [y/N]: y # 确定使用上面选择的动作
You now need to fill the arguments for this activity. Default
values will be shown between brackets. You may simply press return
to use it or not set any value.
Argument's value for 'ns' [default]:
Do you want to select another activity? [y/N]: N # 是否要添加另一个试验动作,这里我不再添加了
An experiment's method contains actions and probes. Actions
vary real-world events in your system to determine if your
steady-state hypothesis is maintained when those events occur.
An experimental method can also contain probes to gather additional
information about your system as your method is executed.
Do you want to define an experimental method? [y/N]: y # 选择一个试验具体方法
Add an activity
1) kill_microservice
2) remove_service_endpoint
3) scale_microservice
4) start_microservice
5) all_microservices_healthy
6) deployment_is_fully_available
7) deployment_is_not_fully_available
8) microservice_available_and_healthy
9) microservice_is_not_available
10) read_microservices_logs
11) service_endpoint_is_initialized
12) create_deployment
13) delete_deployment
14) scale_deployment
15) deployment_available_and_healthy
16) deployment_fully_available
17) deployment_not_fully_available
18) cordon_node
19) create_node
20) delete_nodes
21) drain_nodes
22) uncordon_node
23) get_nodes
24) delete_pods
25) exec_in_pods
26) terminate_pods
27) count_pods
28) pod_is_not_available
29) pods_in_conditions
30) pods_in_phase
31) pods_not_in_phase
32) read_pod_logs
33) delete_replica_set
34) create_service_endpoint
35) delete_service
36) service_is_initialized
37) create_statefulset
38) remove_statefulset
39) scale_statefulset
40) statefulset_fully_available
41) statefulset_not_fully_available
42) create_cluster_custom_object
43) create_custom_object
44) delete_cluster_custom_object
45) delete_custom_object
46) patch_cluster_custom_object
47) patch_custom_object
48) replace_cluster_custom_object
49) replace_custom_object
50) get_cluster_custom_object
51) get_custom_object
52) list_cluster_custom_objects
53) list_custom_objects
Activity (0 to escape): 24 # 这里我选择第24个方法:删除一个POD
!!!DEPRECATED!!!
Do you want to use this action? [y/N]: y # 确认选择
You now need to fill the arguments for this activity. Default
values will be shown between brackets. You may simply press return
to use it or not set any value.
Argument's value for 'name': DeleteRedisPOD # 给这个方法命名
Argument's value for 'ns' [default]: chaosnamespace # 确定要操作的k8s命名空间
Argument's value for 'label_selector' [name in ({name})]: app=redis # 输入要操作对象的标签,以便可以找到操作对象
Do you want to select another activity? [y/N]: N # 是否添加另一个动作,这里我不再添加
An experiment may optionally define a set of remedial actions
that are used to rollback the system to a given state.
Do you want to add some rollbacks now? [y/N]: N # 是否添加回滚动作,这里我是要删除redis的POD,因为k8s会自动拉起来,所以我不用回滚动作
Experiment created and saved in './experiment.json' # 生成了试验文件
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]#
Chaos Run 执行案例
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]# chaos run experiment.json
[2021-06-28 23:03:23 INFO] Validating the experiment's syntax
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Experiment looks valid
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Running experiment: E2
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Steady-state strategy: default
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Rollbacks strategy: default
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Steady state hypothesis: H2
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Probe: all_microservices_healthy
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 WARNING] all_microservices_healthy function is DEPRECATED and will be removed in the next releases, please use all_pods_healthy instead
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Steady state hypothesis is met!
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Playing your experiment's method now...
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Action: delete_pods
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Steady state hypothesis: H2
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Probe: all_microservices_healthy
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 WARNING] all_microservices_healthy function is DEPRECATED and will be removed in the next releases, please use all_pods_healthy instead
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Steady state hypothesis is met!
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Let's rollback...
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] No declared rollbacks, let's move on.
[2021-06-28 23:03:24 INFO] Experiment ended with status: completed
(.bundler) [root@s5 chaostoolkit_scenarios]#
检查结果
执行试验前:
[root@s5 ~]# kubectl get pods -n chaosnamespace -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
...........................
redis-master-b96c9795b-nqzmr 1/1 Running 0 3d9h 10.100.220.84 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-6r42k 1/1 Running 0 3d9h 10.100.220.86 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-z55m5 1/1 Running 0 3d9h 10.100.53.206 s7 <none> <none>
执行试验后:
[root@s5 ~]# kubectl get pods -n chaosnamespace -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
...............................
redis-master-b96c9795b-92rc6 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s <none> s6 <none> <none>
redis-master-b96c9795b-nqzmr 0/1 Terminating 0 3d9h 10.100.220.84 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-5m2xt 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2s <none> s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-6r42k 1/1 Terminating 0 3d9h 10.100.220.86 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-fj4xc 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s <none> s7 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-z55m5 1/1 Terminating 0 3d9h 10.100.53.206 s7 <none> <none>
POD完全启动后:
[root@s5 ~]# kubectl get pods -n chaosnamespace -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
.......................
redis-master-b96c9795b-92rc6 1/1 Running 0 5m43s 10.100.220.89 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-5m2xt 1/1 Running 0 5m42s 10.100.220.90 s6 <none> <none>
redis-slave-6b8d456947-fj4xc 1/1 Running 0 5m43s 10.100.53.211 s7 <none> <none>
[root@s5 ~]#
从上面的结果可以看到,试验是执行成功的,几个redisPOD都被杀掉并被k8s拉起来了。
今天我们就写这一个试验,你可以根据同样的步骤去生成其他试验。
混沌工程之ChaosToolkit使用之一删除K8s POD的更多相关文章
- FrameWork逆向工程之MotioPI
在BI项目建设的过程中我们一般都是有备份的,而且这个是必须有的!特别是例如ETL Model,还有Data Model这一类的元数据,这些东西如果我们没有备份,而恰好的我们的开发模型又在某一天离我们而 ...
- 逆向工程之App脱壳
http://www.cnblogs.com/ludashi/p/5725743.html iOS逆向工程之App脱壳 本篇博客以微信为例,给微信脱壳."砸壳"在iOS逆向工程中是 ...
- k8s pod,pvc,pv无法删除问题
注意步骤: 一般删除步骤为:先删pod再删pvc最后删pv 但是遇到pv始终处于“Terminating”状态,而且delete不掉 pod一直删不掉 [root@hadoop01 nacos-k8s ...
- 记一次k8s pod频繁重启的优化之旅
关键词:k8s.jvm.高可用 1.背景 最近有运维反馈某个微服务频繁重启,客户映像特别不好,需要我们尽快看一下. 听他说完我立马到监控平台去看这个服务的运行情况,确实重启了很多次.对于技术人员来说, ...
- k8s pod 在迁移zookeeper时出现的问题
一次迁移中出现的问题,因为要搬迁机房,集群中的节点服务器分布在两个机房,通过专线打通了,现在需要整体都迁移到其中一个机房,所以pod要进行迁移,机器资源也比较紧张,在迁移中zookeeper迁移出现问 ...
- k8s pod的4种网络模式最佳实战(externalIPs )
[k8s]k8s pod的4种网络模式最佳实战(externalIPs ) hostPort相当于docker run -p 8081:8080,不用创建svc,因此端口只在容器运行的vm ...
- k8s pod节点调度及k8s资源优化
一.k8s pod 在节点间调度控制 k8s起pod时,会通过调度器scheduler选择某个节点完成调度,选择在某个节点上完成pod创建.当需要在指定pod运行在某个节点上时,可以通过以下几种方式: ...
- kubectl cp 从k8s pod 中 拷贝 文件到本地
请查看官方的说明 kubectl cp --help 官方说使用cp , pod里需要有tar命令 从k8s pod 中 拷贝 文件到本地 这是我使用的命令 kubectl exec redis-6c ...
- 记一次删除k8s namespace无法删除的问题
在用longhorn工具做k8s存储卷动态预配的时候,需要修改longhorn.yaml的一个默认参数,修改完成需要重新加载longhorn.yaml,结果重新加载出错了,修改的参数没有生效,于是执行 ...
随机推荐
- CSS中的颜色、长度、角度、时间
一.颜色的表示方法 颜色是通过对红.绿和蓝光的组合来显示的. 1.颜色名 1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 &l ...
- 如何使用ghost备份系统?
如何使用ghost备份系统? 如何使用ghost工具电脑系统备份?需要具体的详细步骤 关注者 11 被浏览 13,197 关注问题写回答 邀请回答 添加评论 分享 1 个回答 默认排 ...
- SPI总线 通俗易懂讲解——(转载)
SPI总线 MOTOROLA公司的SPI总线的基本信号线为3根传输线,即SI.SO.SCK.传输的速率由时钟信号SCK决定,SI为数据输入.SO为数据输出.采用SPI总线的系统如图8-27所示,它包含 ...
- java 文件上传下载
翻新十年前的老项目,文件上传改为调用接口方式,记录一下子~~~ java后台代码: //取配置文件中的上传目录 @Value("${uploadPath}") String pat ...
- 阿里云服务器安装Docker并部署nginx、jdk、redis、mysql
阿里云服务器安装Docker并部署nginx.jdk.redis.mysql 一.安装Docker 1.安装Docker的依赖库 yum install -y yum-utils device-map ...
- conda 按照指定源下载python包
conda 按照指定源下载python包 换成了国内的pip源就可以正常安装了,我使用的是:pip install xlrd -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple --tr ...
- harbor搭建及使用
harbor搭建及使用 1 系统及软件版本 1.1 系统版本 # uname -a Linux localhost.localdomain 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP ...
- RMAN-20208: UNTIL CHANGE is before RESETLOGS change
执行recover操作时: RMAN> recover database; Starting recover at 28-NOV-19 using channel ORA_DISK_1 ...
- Windows家庭版打开或关闭Hyper-V
打开hyper-v 创建open_hyper-v.bat文件 pushd "%~dp0" dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\*Hyper ...
- ubuntu虚拟机安装ssh教程
大家好,这期给大家带来一期Ubuntu虚拟机中ssh的安装教程,话不多说,开整 第一步:输入su后输入密码进入root权限 第二步:在管理员模式下运行apt-get install openssh-s ...
