Spring Bean 生命周期测试
Bean的生命周期是开始创建到销毁的过程。需要实现相关的类BeanNameAware ,DisposableBean, InitializingBean ,并注册InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor。
Bean类实现BeanNameAware ,DisposableBean, InitializingBean 接口
package com.bean.life.entity; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class User implements BeanFactoryAware
, BeanNameAware
, InitializingBean
, DisposableBean
{
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware setBeanFactory");
} @Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("BeanNameAware接口: setBeanName = " + s);
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean接口: afterPropertiesSet");
} @Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean接口: destroy"); }
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("PostConstruct");
} @PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("PreDestroy");
}
}
注册InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口。
这里的InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter是 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的子孙类。
package com.bean.life.entity; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; @Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter { public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
super();
} @Override
public Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: determineCandidateConstructors: " + beanName);
} return super.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName);
} @Override
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: getEarlyBeanReference: " + beanName);
} return super.getEarlyBeanReference(bean, beanName);
} @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessBeforeInstantiation: " + beanName);
} return super.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
} @Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessAfterInstantiation : " + beanName);
} return super.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bean, beanName);
} @Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessPropertyValues: " + beanName);
}
return super.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, pds, bean, beanName);
} @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessBeforeInitialization: " + beanName);
} return super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("user")){
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessAfterInitialization: " + beanName);
} return super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
输出
MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor --- BeanFactoryPostProcessor
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessBeforeInstantiation: user
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: determineCandidateConstructors: user
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessAfterInstantiation : user
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessPropertyValues: user
BeanNameAware接口: setBeanName = user
BeanFactoryAware setBeanFactory
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessBeforeInitialization: user
PostConstruct
InitializingBean接口: afterPropertiesSet
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口: postProcessAfterInitialization: user PreDestroy
DisposableBean接口: destroy
生命周期图解
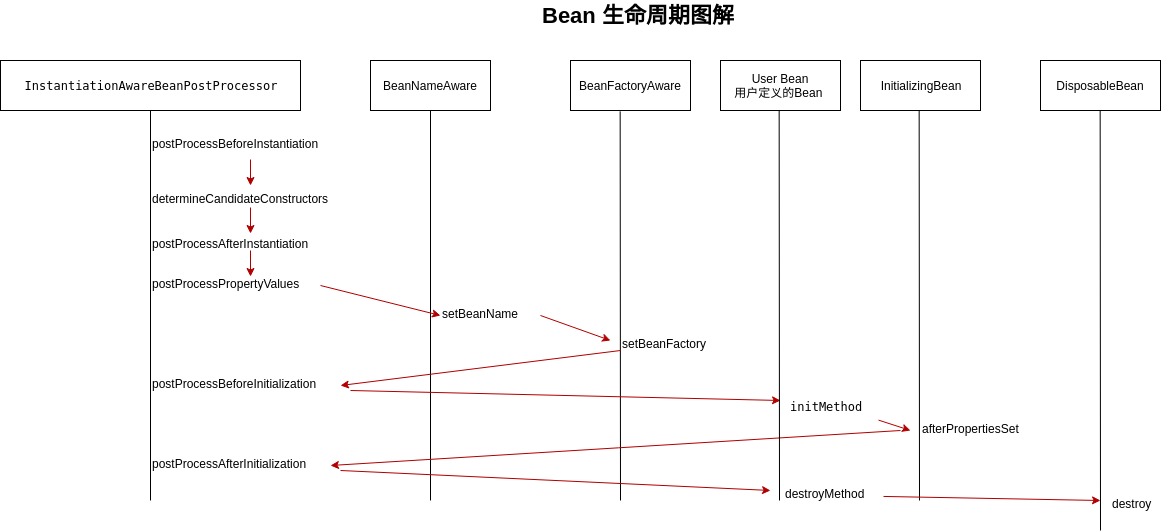
Spring 实现按 init-method 和destory-method的三种方式
- 方式1:xml配置方式
package com.bean.life.entity; public class User
{ public void init(){
System.out.println("PostConstruct");
} public void destory(){
System.out.println("PreDestroy");
}
}
<bean id="user" class="com.bean.life.entity" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
</bean>
- 方式2:注解配置
添加@PostConstruct 和@PreDestroy进行指定
package com.bean.life.entity; @Component
public class User
{ @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("PostConstruct");
} @PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("PreDestroy");
}
}
- 方式3: 使用注解@Bean
public @interface Bean {
@AliasFor("name")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] name() default {};
Autowire autowire() default Autowire.NO;
String initMethod() default "";
String destroyMethod() default "(inferred)";
}
@Configuration
public class UserConfig{ @Bean(initMethod="init",destoryMethod="destory")
public User user(){
return new User();
} }
Spring Bean 生命周期测试的更多相关文章
- Spring点滴四:Spring Bean生命周期
Spring Bean 生命周期示意图: 了解Spring的生命周期非常重要,我们可以利用Spring机制来定制Bean的实例化过程. -------------------------------- ...
- 大厂高频面试题Spring Bean生命周期最详解
Spring作为当前Java最流行.最强大的轻量级框架.Spring Bean的生命周期也是面试高频题,了解Spring Bean周期也能更好地帮助我们解决日常开发中的问题.程序员应该都知道Sprin ...
- Spring Bean生命周期,好像人的一生。。
大家好,我是老三,上节我们手撸了一个简单的IOC容器五分钟,手撸一个Spring容器!,这节我们来看一看Spring中Bean的生命周期,我发现,和人的一生真的很像. 简单说说IoC和Bean IoC ...
- spring bean 生命周期和 ? 作用域? spirng bean 相互依赖? jvm oom ? jvm 监控工具? ThreadLocal 原理
1. spring bean 生命周期 1. 实例化一个bean ,即new 2. 初始化bean 的属性 3. 如果实现接口 BeanNameAware ,调用 setBeanName 4. Bea ...
- Spring Bean 生命周期之destroy——终极信仰
上一篇文章 Spring Bean 生命周期之我从哪里来 说明了我是谁? 和 我从哪里来? 的两大哲学问题,今天我们要讨论一下终极哲学我要到哪里去? 初始化 Spring Bean 有三种方式: @P ...
- 常见问题:Web/Servlet生命周期与Spring Bean生命周期
Servlet生命周期 init()初始化阶段 Servlet容器加载Servlet(web.xml中有load-on-startup=1;Servlet容器启动后用户首次向Servlet发请求;Se ...
- 睡前聊一聊"spring bean 生命周期"
spring bean 生命周期=实属初销+2个常见接口+3个Aware型接口+2个生命周期接口 实属初销:spring bean生命周期只有四个阶段,即实例化->属性赋值->初始化-&g ...
- Spring Bean 生命周期2
在spring中,从BeanFactory或ApplicationContext取得的实例为Singleton,也就是预设为每一个Bean的别名只能维持一个实例,而不是每次都产生一个新的对象使用Sin ...
- Spring bean 生命周期验证
一.从源码注释看bean生命周期 从JDK源码上看,BeanFactory实现类需要支持Bean的完整生命周期,完整的初始化方法及其标准顺序(格式:接口 方法)为: 1.BeanNameAware s ...
随机推荐
- php curl_errno 60
问题描述 使用curl进行微信统一下单,curl 错误 curl_errno 60 错误码60 因为使用了证书配置项,所以要配置curl证书 解决方法 下载证书并配置php.ini ,配置curl证书 ...
- mybatis整合spring获取配置文件信息出错
描述:mybatis整合spring加载jdbc.properties文件,然后使用里面配置的值来 配置数据源,后来发现用户变成了admin- jdbc.properties的配置: 加载配置: 报错 ...
- HTML5 CSS3 诱人的实例 : 网页加载进度条的实现,下载进度条等
今天给大家带来一个比较炫的进度条,进度条在一耗时操作上给用户一个比较好的体验,不会让用户觉得在盲目等待,对于没有进度条的长时间等待,用户会任务死机了,毫不犹豫的关掉应用:一般用于下载任务,删除大量任务 ...
- springMVC简单的一些操作
SpringMVC的模型-视图-控制器(MVC)框架是围绕一个DispatcherServlet来设计的,这个Servlet会把请求分发给各个处理器进行处理,由DispatcherServlet来统一 ...
- JUC中AQS简介
AQS,在java.util.concurrent.locks包中,AbstractQueuedSynchronizer这个类是并发包中的核心,了解其他类之前,需要先弄清楚AQS.在JUC的很多类中都 ...
- BZOJ_3942_[Usaco2015 Feb]Censoring_KMP
BZOJ_3942_[Usaco2015 Feb]Censoring_KMP Description 有一个S串和一个T串,长度均小于1,000,000,设当前串为U串,然后从前往后枚举S串一个字符一 ...
- BZOJ_3689_异或之_可持久化Trie+堆
BZOJ_3689_异或之_可持久化Trie+堆 Description 给定n个非负整数A[1], A[2], ……, A[n]. 对于每对(i, j)满足1 <= i < j < ...
- ajax封装函数和表单序列化
//表单序列化function iSerialize(form){ var parts={}; for(var i=0;i<form.elements.length;i++){ var file ...
- python的知识统计笔记
python的发展
- java基础系列之ConcurrentHashMap源码分析(基于jdk1.8)
1.前提 在阅读这篇博客之前,希望你对HashMap已经是有所理解的,否则可以参考这篇博客: jdk1.8源码分析-hashMap:另外你对java的cas操作也是有一定了解的,因为在这个类中大量使用 ...
