【中英】【吴恩达课后测验】Course 5 - 序列模型 - 第三周测验 - 序列模型与注意力机制
【中英】【吴恩达课后测验】Course 5 - 序列模型 - 第三周测验 - 序列模型与注意力机制
上一篇:【课程5 - 第二周编程作业】※※※※※ 【回到目录】※※※※※下一篇:【待撰写-课程5 - 第三周编程作业】
想一想使用如下的编码-解码模型来进行机器翻译:
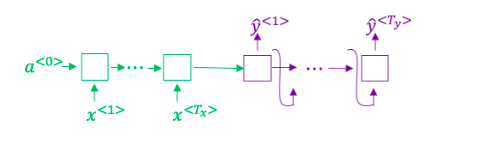
这个模型是“条件语言模型”,编码器部分(绿色显示)的意义是建模中输入句子x的概率- 正确
- 错误
在集束搜索中,如果增加集束宽度\(b\),以下哪一项是正确的?
- 集束搜索将运行的更慢。
- 集束搜索将使用更多的内存。
- 集束搜索通常将找到更好地解决方案(比如:在最大化概率\(P(y|x\))上做的更好)。
- 集束搜索将在更少的步骤后收敛。
在机器翻译中,如果我们在不使用句子归一化的情况下使用集束搜索,那么算法会输出过短的译文。
- 正确
- 错误
假设你正在构建一个能够让语音片段\(x\)转为译文\(y\)的基于RNN模型的语音识别系统,你的程序使用了集束搜索来试着找寻最大的\(P(y|x)\)的值\(y\)。在开发集样本中,给定一个输入音频,你的程序会输出译文\(\hat{y} =\) "I'm building an A Eye system in Silly con Valley.",人工翻译为\(y^* =\) "I'm building an AI system in Silicon Valley."
在你的模型中,
\(P(\hat{y} \mid x) = 1.09*10^{-7}\)
\(P(y^* \mid x) = 7.21*10^{-8}\)
那么,你会增加集束宽度\(B\)来帮助修正这个样本吗?
不会,因为 \(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\) 说明了这个锅要丢给RNN,不能让搜索算法背锅。
不会,因为 \(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\) 说明了这个锅要丢给搜索算法,凭什么让RNN背锅?
会的,因为 \(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\) 说明了都是RNN的错,咱不能冤枉搜索算法。
会的,因为 \(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\) 说明了千错万错都是搜索算法的错,可不能惩罚RNN啊~
博主注:皮这一下好开心~(~ ̄▽ ̄)~
接着使用第4题那里的样本,假设你花了几周的时间来研究你的算法,现在你发现,对于绝大多数让算法出错的例子而言,\(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\),这表明你应该将注意力集中在改进搜索算法上,对吗?
- 嗯嗯~
- 不对
回想一下机器翻译的模型:
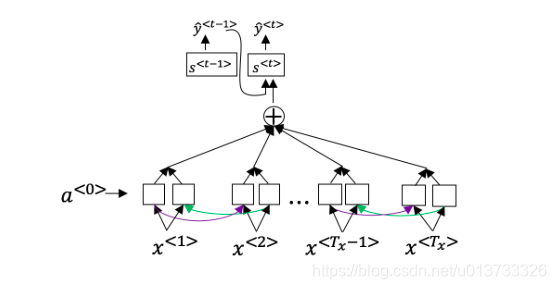
除此之外,还有个公式 \(a^{<t,t'>} = \frac{\text{exp}(e^{<t,t'>})}{\sum^{T_x}_{t'=1}\text{exp}(e^{<t,t'>})}\)下面关于 \(\alpha^{<t,t’>}\) 的选项那个(些)是正确的?
- 对于网络中与输出\(y^{<t>}\)高度相关的 \(\alpha^{<t'>}\) 而言,我们通常希望 \(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\)的值更大。(请注意上标)
- 对于网络中与输出\(y^{<t>}\)高度相关的 \(\alpha^{<t>}\) 而言,我们通常希望 \(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\)的值更大。(请注意上标)
- \(\sum_{t} \alpha^{<t,t'>} = 1\) (注意是和除以t.)
- \(\sum_{t'} \alpha^{<t,t'>}=1\) (注意是和除以t′.)
网络通过学习的值\(e^{<t,t'>}\)来学习在哪里关注“关注点”,这个值是用一个小的神经网络的计算出来的:
这个神经网络的输入中,我们不能将 \(s^{<t>}\)替换为\(s^{<t-1>}\)。这是因为\(s^{<t>}\)依赖于\(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\),而\(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\)又依赖于\(e^{<t,t'>}\);所以在我们需要评估这个网络时,我们还没有计算出\(s^{t}\)。
- 正确
- 错误
与题1中的编码-解码模型(没有使用注意力机制)相比,我们希望有注意力机制的模型在下面的情况下有着最大的优势:
- 输入序列的长度\(T_x\)比较大。
- 输入序列的长度\(T_x\)比较小。
9.在CTC模型下,不使用"空白"字符(_)分割的相同字符串将会被折叠。那么在CTC模型下,以下字符串将会被折叠成什么样子?__c_oo_o_kk___b_ooooo__oo__kkk
- cokbok
- cookbook
- cook book
- coookkboooooookkk
- 在触发词检测中, \(x^{<t>}\) 是:
- 时间\(t\)时的音频特征(就像是频谱特征一样)。
- 第\(t\)个输入字,其被表示为一个独热向量或者一个字嵌入。
- 是否在第\(t\)时刻说出了触发词。
- 是否有人在第\(t\)时刻说完了触发词。
Sequence models & Attention mechanism
- Consider using this encoder-decoder model for machine translation.

This model is a "conditional language model" in the sense that the encoder portion (shown in green) is modeling the probability of the input sentence $x$.
- [x] True
- [ ] False
---
2. In beam search, if you increase the beam width BB, which of the following would you expect to be true? Check all that apply.
- [x] Beam search will run more slowly.
- [x] Beam search will use up more memory.
- [x] Beam search will generally find better solutions (i.e. do a better job maximizing P(y \mid x)P(y∣x))
- [ ] Beam search will converge after fewer steps.
----
3. In machine translation, if we carry out beam search without using sentence normalization, the algorithm will tend to output overly short translations.
- [x] True
- [ ] False
---
4. Suppose you are building a speech recognition system, which uses an RNN model to map from audio clip $x$ to a text transcript $y$. Your algorithm uses beam search to try to find the value of $y$ that maximizes $P(y \mid x)$.
On a dev set example, given an input audio clip, your algorithm outputs the transcript $\hat{y} =$ "I’m building an A Eye system in Silly con Valley.", whereas a human gives a much superior transcript $y^* =$ "I’m building an AI system in Silicon Valley.".
According to your model,
$P(\hat{y} \mid x) = 1.09*10^{-7}$
$P(y^∗ \mid x) = 7.21∗10^{−8}$
Would you expect increasing the beam width B to help correct this example?
- [x] No, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
- [ ] No, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
- [ ] Yes, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
- [ ] Yes, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
- Continuing the example from Q4, suppose you work on your algorithm for a few more weeks, and now find that for the vast majority of examples on which your algorithm makes a mistake, \(P(y^∗ \mid x) > P(\hat{y} \mid x)\). This suggest you should focus your attention on improving the search algorithm.
- True
- False
- Consider the attention model for machine translation.

Further, here is the formula for \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\).
\]
Which of the following statements about \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\) are true? Check all that apply.
- We expect \(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\) to be generally larger for values of \(a^{<t'>}\) that are highly relevant to the value the network should output for \(y^{<t>}\). (Note the indices in the superscripts.)
- We expect \(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\) to be generally larger for values of \(a^{<t>}\) that are highly relevant to the value the network should output for \(y^{<t'>}\). (Note the indices in the superscripts.)
- \(\sum_{t} \alpha^{<t,t'>}=1\) (Note the summation is over \(t\).)
- \(\sum_{t'} \alpha^{<t,t'>}=1\) (Note the summation is over \(t'\).)
The network learns where to “pay attention” by learning the values e<t,t′>, which are computed using a small neural network:
We can't replace \(s^{<t-1>}\) with \(s^{<t>}\) as an input to this neural network. This is because \(s^{<t>}\) depends on \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\) which in turn depends on \(e^{<t,t′>}\); so at the time we need to evalute this network, we haven’t computed \(s^{<t>}\) yet.- True
- False
- Compared to the encoder-decoder model shown in Question 1 of this quiz (which does not use an attention mechanism), we expect the attention model to have the greatest advantage when:
- The input sequence length \(T_x\) is large.
- The input sequence length \(T_x\) is small.
- Under the CTC model, identical repeated characters not separated by the "blank" character (_) are collapsed. Under the CTC model, what does the following string collapse to? __c_oo_o_kk___b_ooooo__oo__kkk
- cokbok
- cookbook
- cook book
- coookkboooooookkk
- In trigger word detection, \(x^{<t>}\) is:
- Features of the audio (such as spectrogram features) at time \(t\).
- The \(t\)-th input word, represented as either a one-hot vector or a word embedding.
- Whether the trigger word is being said at time \(t\).
- Whether someone has just finished saying the trigger word at time \(t\).
【中英】【吴恩达课后测验】Course 5 - 序列模型 - 第三周测验 - 序列模型与注意力机制的更多相关文章
- 【吴恩达课后测验】Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第二周测验【中英】
[中英][吴恩达课后测验]Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第二周测验 第2周测验 - 神经网络基础 神经元节点计算什么? [ ]神经元节点先计算激活函数,再计算线性函数(z = Wx + ...
- 【吴恩达课后测验】Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第一周测验【中英】
[吴恩达课后测验]Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第一周测验[中英] 第一周测验 - 深度学习简介 和“AI是新电力”相类似的说法是什么? [ ]AI为我们的家庭和办公室的个人设备供电 ...
- 【中文】【deplearning.ai】【吴恩达课后作业目录】
[目录][吴恩达课后作业目录] 吴恩达深度学习相关资源下载地址(蓝奏云) 课程 周数 名称 类型 语言 地址 课程1 - 神经网络和深度学习 第1周 深度学习简介 测验 中英 传送门 无编程作业 编程 ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习1-week4-homework-two-hidden-layer -1
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79767169 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 两层神经网络,和吴恩达课 ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习1-week4-homework-multi-hidden-layer -2
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79767169 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 实现多层神经网络 1.准 ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习2-week1-1 初始化
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79847918 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 初始化.正则化.梯度校验 ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习2-week1-2正则化
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79847918 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 4.正则化 1)加载数据 ...
- 【吴恩达课后编程作业】第二周作业 - Logistic回归-识别猫的图片
1.问题描述 有209张图片作为训练集,50张图片作为测试集,图片中有的是猫的图片,有的不是.每张图片的像素大小为64*64 吴恩达并没有把原始的图片提供给我们 而是把这两个图片集转换成两个.h5文件 ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习2-week3-tensorflow learning-1-例子学习
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79971488 使用TensorFlow构建你的第一个神经网络 我们将会使用TensorFlo ...
- 吴恩达课后作业学习1-week2-homework-logistic
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013733326/article/details/79639509 希望大家直接到上面的网址去查看代码,下面是本人的笔记 搭建一个能够 “识别猫” ...
随机推荐
- 1h玩转kubernetes
学习k8s就跟学习office三件套上,95%的人只会5%,而5%的知识可以干95%的事情,所以不要觉的k8s难 1 kubernetes 1 什么是kubernetes Kubernetes 是一个 ...
- Git Pull Failed:You have not concluded your merge.Exiting because of unfinished merge
前言 在拉取远程代码时,出现 Git Pull Failed:You have not concluded your merge.Exiting because of unfinished merge ...
- 设置git忽略文件
要设置Git忽略文件,你可以使用一个名为.gitignore的特殊文件.在这个文件中,你可以列出需要Git忽略的文件.文件夹.或者匹配模式.当Git执行操作时,它会自动忽略这些被列出的文件. 1. 在 ...
- JDK8-日历类--java进阶day07
JDK7和JDK8之间的时间API比较 1.日历类 1.LocalDateTime LocalDateTime最为齐全,只要掌握这个类,另外两个都是一样的 now方法获取到此刻时间,of方法设置想要的 ...
- 白话kotlin协程
文章同步发布于公众号:移动开发那些事白话kotlin协程 1 什么是协程 Kotlin协程(Coroutine)是一种轻量级的线程管理框架,允许开发者以更简洁,更高效的方式处理异步操作,避免回调地狱和 ...
- FastAPI中的依赖注入与数据库事务管理
title: FastAPI中的依赖注入与数据库事务管理 date: 2025/04/09 00:10:29 updated: 2025/04/09 00:10:29 author: cmdragon ...
- 解释Spring框架中bean的生命周期
一.Bean生命周期的流程图 二.spring的生命周期 spring生命周期中的阶段,包括初始化.使用.销毁. 1.初始化阶段 1)调用bean的构造函数,创建实例: 2)进行参数依赖注入: 3)若 ...
- java基础之数据结构
一.栈:stack,又称堆栈[出口和入口在同一侧],特点:先进后出(即,存进去的元素,要在后它后面的元素依次取出后,才能取出该元素) 例子:子弹压进弹夹,先压进去的子弹在下面,后压进去的子弹在上面,当 ...
- MySQL开启general_log
General_log 详解 1.介绍 开启 general log 将所有到达MySQL Server的SQL语句记录下来. 一般不会开启开功能,因为log的量会非常庞大.但个别情况下可能会临时的开 ...
- Java单例模式:从实战到面试的深度解析
结论先行 饿汉式:线程安全但可能造成资源浪费,推荐在初始化成本低的场景使用 懒汉式:需要解决线程安全问题,推荐使用双重检查锁+volatile优化 静态内部类:最佳实践方案,完美平衡延迟加载与线程安全 ...
