Deep Learning Specialization 笔记
1. numpy中的几种矩阵相乘:
# x1: axn, x2:nxb
np.dot(x1, x2): axn * nxb
np.outer(x1, x2): nx1*1xn # 实质为: np.ravel(x1)*np.ravel(x2)
np.multiply(x1, x2): [[x1[0][0]*x2[0][0], x1[0][1]*x2[0][1], ...]
2. Bugs' hometown
Many software bugs in deep learning come from having matrix/vector dimensions that don't fit. If you can keep your matrix/vector dimensions straight you will go a long way toward eliminating many bugs.
3. Common steps for pre-processing a new dataset are:
- Figure out the dimensions and shapes of the problem (m_train, m_test, num_px, ...)
- Reshape the datasets such that each example is now a vector of size (num_px \* num_px \* 3, 1)
- "Standardize" the data
4. Unstructured data:
Unstructured data is a generic label for describing data that is not contained in a database or some other type of data structure . Unstructured data can be textual or non-textual. Textual unstructured data is generated in media like email messages, PowerPoint presentations, Word documents, collaboration software and instant messages. Non-textual unstructured data is generated in media like JPEG images, MP3 audio files and Flash video files
5. Chapter of Activation Function:
Choice of activation function:
- If output is either 0 or 1 -- sigmoid for the output layer and the other units on ReLU.
- Except for the output layer, tanh does better than sigmoid.
- ReLU ---level up--> leaky ReLU.
Why are ReLU and leaky ReLU often superior to sigmoid and tanh?
-- The derivatives of the former ones is much bigger than 0, so the learning would be much faster.
A linear hidden layer is more or less useless, yet the activation function is a exception.
6. Regularization:
Initially, \(J(w, b) = \frac{1}{m} * \sum_{i=1}^{m}{L({\hat{Y}^(i), y^{(i)}}) + \frac{\lambda}{2*m}||w||_2^2}\)
L2 regularization: \(\frac{\lambda}{2*m}\sum_{j=1}^{n_x}||w_j||^2 = \frac{\lambda}{2*m}||w||_2\)
One aspect that tanh is better thatn sigmoid(in terms of regularization) -- When x is very close to 0, the derivative of tanh(x) is almost linear, while that of the sigmoid(x) is alomst 0.
Dropout:
Method: Make certain values of weights be zeros randomly, just like -- W= np.multiply(W, C), where C is a 0-1 array.
Matters need attention: Don't use dropout in test procedure -- Time costly, result randomly.
Work principle:
Intuition: Can't rely on any one feature, so have to spread out weights(shrinking weights).
Besides, you can set different rates of "Dropout", like lower ones on more complex layer, which are called "key prop".
- Data augmentation:
Do some operation on your data images, such as flipping, rotation, zooming, etc, without changing their labels, in order to prevent from over-fitting on some aspects, such as the direction of faces, the size of cats.
- Early stopping.
7. Solution to "gradient vanishing or exploding":
Set WL = np.random.randn(shape) * np.sqrt(\(\frac{2}{n^{[L-1]}}\)) if activation_function == "ReLU"
else: np.random.randn(shape) * np.sqrt(\(\frac{1}{n^{[L-1]}}\)) or np.sqrt(\(\sqrt{\frac{2}{n^{[L-1]}+n^{[L]}}}\))(Xavier initialization)
8. Gradient Checking:
for i in range(len(\(\theta\))):
to check if (d\(\theta_{approx}[i] = \frac{J(\theta_1, \theta_2, ..., \theta_i+\epsilon, ...) - J(\theta_1, \theta_2, ..., \theta_i-\epsilon, ...)}{2\epsilon}\)) ?= \(d\theta[i] = \frac{\partial{J}}{\partial{\theta_i}}\)
<==> \(d\theta_{approx} ?= d\theta\)
<==> \(\frac{||d\theta_{approx} - d\theta||_2}{||d\theta_{approx}||_2+||d\theta||_2}\) in an accent range: \(10^{-7}\) is great, and \(10^{-3}\) is wrong.
Tips:
- Only to debug, instead of training.
- If algorithm fails grad check, look at components(\(db^{[L]}, dw^{[L]}\)) to try to identify bug.
- Remember regularization.
- Doesn't work together with dropout.
- Run at random initialization; perhaps again after some training.
9. Exponentially weighted averages:
Definition: let \(V_{t} = {\beta}V_{t-1} + (1 - \beta)\theta_t\) (_V_s are the averages, and the _\(\theta\)_s are the initial discrete data).
and \(V_{t} = \frac{V_{t}}{1 - {\beta}^t}\) (To correct initial bias).
Usage: when it comes to this situation: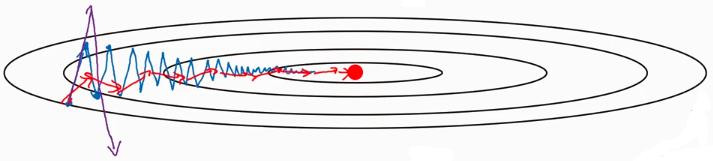
Since the average of the distance vertical movement is almost zeros, you can use EWA to average it, prevent it from divergence.
On iteration t:
Compute dW on the current mini-batch
\(v_{dW} = {\beta}v_{dW} + (1 - \beta)dW\)
\(v_{db} = {\beta}v_{db} + (1 - \beta)db\)
\(W = W - {\alpha}v_{dW}, b = b - {\alpha}v_{db}\)
Hyperparameters: \(\alpha\), \({\beta}(=0.9)\)
Deep Learning Specialization 笔记的更多相关文章
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(四)CNN卷积神经网络推导和实现(转)
Deep Learning论文笔记之(四)CNN卷积神经网络推导和实现 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文, ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(八)Deep Learning最新综述
Deep Learning论文笔记之(八)Deep Learning最新综述 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文,但老感觉看完 ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(六)Multi-Stage多级架构分析
Deep Learning论文笔记之(六)Multi-Stage多级架构分析 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些 ...
- 【deep learning学习笔记】注释yusugomori的DA代码 --- dA.h
DA就是“Denoising Autoencoders”的缩写.继续给yusugomori做注释,边注释边学习.看了一些DA的材料,基本上都在前面“转载”了.学习中间总有个疑问:DA和RBM到底啥区别 ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(一)K-means特征学习
Deep Learning论文笔记之(一)K-means特征学习 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文,但老感 ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(三)单层非监督学习网络分析
Deep Learning论文笔记之(三)单层非监督学习网络分析 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文,但老感 ...
- Spectral Norm Regularization for Improving the Generalizability of Deep Learning论文笔记
Spectral Norm Regularization for Improving the Generalizability of Deep Learning论文笔记 2018年12月03日 00: ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(四)CNN卷积神经网络推导和实现
https://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/9993371 自己平时看了一些论文,但老感觉看完过后就会慢慢的淡忘,某一天重新拾起来的时候又好像没有看过一 ...
- [置顶]
Deep Learning 学习笔记
一.文章来由 好久没写原创博客了,一直处于学习新知识的阶段.来新加坡也有一个星期,搞定签证.入学等杂事之后,今天上午与导师确定了接下来的研究任务,我平时基本也是把博客当作联机版的云笔记~~如果有写的不 ...
随机推荐
- 如何将1rpx转为1rem
最近我在开发的过程中,出现了一个需求,我需要把开发好的小程序倒模成H5页面,这里就涉及一个布局单位问题,我们小程序用的单位都rpx,是按照750rpx铺满整个页面来算的,可H5又不支持rpx单位,这里 ...
- java实现Excel定制导出(基于POI的工具类)
我的需求: 项目中有一些工程表格需要导出,设计到行列合并,定制样式,原有工具类冗余,内聚性强.所以想写一个可以随意定制excel的工具类,工具类满足需求: 对于常用的工程表格有模板格式,可以任意插拔. ...
- python工业互联网应用实战3—Django Admin列表
Django Admin笔者使用下来可以说是Django框架的开发利器,业务model构建完成后,我们就能快速的构建一个增删查改的后台管理框架.对于大量的企业管理业务开发来说,可以快速的构建一个可发布 ...
- echarts图表X轴文字过长解决解决方案:根据文字长度自动旋转
Echarts 标签中文本内容太长的时候怎么办 ? 关于这个问题搜索一下,有很多解决方案.无非就是 省略(间隔显示).旋转文字方向.竖排展示 前面两种解决方案,就是echarts暴露的: { ax ...
- https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/CommonMistakes
CommonMistakes https://golang.org/doc/faq#closures_and_goroutines Why is there no goroutine ID? ¶ Go ...
- windows.open、 window.location.href
windows.open("URL","窗口名称","窗口外观设定");打开新窗口,window对象的方法 不一定打开新窗口,只要有窗口的名 ...
- vim自动添加C C++ sh文件头
set foldenable set foldmethod=manual set fencs=utf-8,ucs-bom,shift-jis,gb18030,gbk,gb2312,cp936 set ...
- 秒啊,速来get这9个jupyter实用技巧
1 简介 jupyter notebook与jupyter lab作为广受欢迎的ide,尤其适合开展数据分析相关工作,而掌握它们相关的一些实用技巧,势必会大大提升日常工作效率.而今天我就来给大家介绍9 ...
- 《C++ Primer Plus》啃书计 第1~4章
<C++ Primer Plus>啃书计 第1~4章 第一章 预备知识 1.1-1.3略过 1.4 程序创建的技巧 1. cfront,它将C++源代码翻译成C源代码,然后再使用标准C编译 ...
- SQL(replace)替换字段中指定的字符
语法:update 表名 set 字段名=REPLACE(字段名,'修改前的字符','修改后的字符') 例 Product商品表中Name 名字字段中描述中将'AAA' 修改成 'BBB' SQL语句 ...
