SHELL脚本编程-普通数组(列表)和关联数组(字典)
SHELL脚本编程-普通数组(列表)和关联数组(字典)
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.数组相关概述
变量:
存储单个元素的内存空间 数组:
存储多个元素的连续的内存空间,相当于多个变量的集合 数组名和索引
索引:编号从0开始,属于数值索引
注意:索引可支持使用自定义的格式,而不仅是数值格式,即为关联索引,bash4.0版本之后开始支持(关联数据使用时必须提前声明类型)
bash的数组支持稀疏格式(索引不连续) 声明数组:
declare -a ARRAY_NAME
declare -A ARRAY_NAME: 关联数组
注意:普通数组不用事先声明就可以使用,但关联数组必须提前声明才能使用,且两者不可相互转换。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash --version
GNU bash, version 4.2.()-release (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu)
Copyright (C) Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html> This is free software; you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash --version
二.数组赋值
1>.一次只赋值一个元素及引用数组详解
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -a title #使用数组变量时建议提前声明
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[]=CEO #逐一对数组进行赋值
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[]=COO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[]=CTO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[]=CFO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[]=devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo $title #如果不加下标则默认打印数组的第一个元素。
CEO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[]} #查看指定的元素下标
COO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[]}
CFO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]} #查看数组中的所有元素
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]} #同上
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]} #查看数组的长度
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[*]} #同上
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[${#title[*]}]="bigdata" #在数组的末尾添加一个元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]}
CEO COO CTO CFO devops bigdata
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset title[] #删除索引为1的元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]}
CEO CTO CFO devops bigdata
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]} [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset title #删除整个数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]} #由于数组依旧被删除了,长度自然也就为0啦~ [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]} #内容也被随之清空了 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
2>.一次赋值全部元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title=(CEO COO CTO CFO devops) #一次性赋值多个元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]}
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset title
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
3>.只赋值特定元素(稀疏格式)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title=([]=CEO []=CTO []=devops)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[@]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
CEO CTO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset title
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
4>.交互式数组值对赋值
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# read -a title #通过交互式对数组title进行赋值,各个元素用空格分开即可。
CTO CEO COO CTO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
CTO CEO COO CTO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[*]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset title
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${#title[*]}
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
5>.显示所有数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student[]="jason"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student[]="yinzhengjie"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -a #显示当前shell中识别的所有数组
declare -a BASH_ARGC='()'
declare -a BASH_ARGV='()'
declare -a BASH_LINENO='()'
declare -ar BASH_REMATCH='()'
declare -a BASH_SOURCE='()'
declare -ar BASH_VERSINFO='([0]="4" [1]="2" [2]="46" [3]="2" [4]="release" [5]="x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu")'
declare -a DIRSTACK='()'
declare -a FUNCNAME='()'
declare -a GROUPS='()'
declare -a PIPESTATUS='([0]="0")'
declare -a student='([0]="jason" [1]="yinzhengjie")'
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
三.遍历数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat shell/title_array.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: yinzhengjie
#QQ:
#Date: --
#FileName: shell/title_array.sh
#URL: http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie
#Description: The test script
#Copyright notice: original works, no reprint! Otherwise, legal liability will be investigated.
#******************************************************************** declare -a title
title[]=CEO
title[]=COO
title[]=CTO
title[]=CFO
title[]=devops count=`seq $[${#title[*]}-]` for i in $count
do
echo Title is ${title[$i]}
done
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/title_array.sh
Title is CEO
Title is COO
Title is CTO
Title is CFO
Title is devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
四.数组数据处理
1>.引用数组中的元素(数组切片)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title=(CEO COO CTO CFO devops) #定义数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]} #查看数组的内容
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]::} #跳过第一个元素并取出后续2个元素
COO CTO
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]:} #跳过前2个元素,后面的元素全都要
CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
2>.向数组中追加元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[*]}
CEO COO CTO CFO devops
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# title[${#title[*]}]="bigdata" #在数组的末尾添加一个元素
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${title[@]}
CEO COO CTO CFO devops bigdata
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
3>.关联数组(在其它编程语言称之为"字典"或者"map")
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -a student_info #声明为普通数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student_info["name"]="尹正杰"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student_info["age"]=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${student_info["name"]} #我们发现查询结果和咱们预期的不符哟! [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${student_info["age"]} [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# unset student_info #将上面的普通数组删除掉,然后使用关联数组来保存数据。
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# declare -A student_info #声明为关联数组
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student_info["name"]="尹正杰"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# student_info["age"]=
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${student_info["name"]} #发现关联数组的确可以保存咱们的变量呢
尹正杰
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# echo ${student_info["age"]} [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
五.小试牛刀
1>.生成10个随机数保存于数组中,并找出其最大值和最小值
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat shell/max_min.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: yinzhengjie
#QQ:
#Date: --
#FileName: shell/max_min.sh
#URL: http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie
#Description: The test script
#Copyright notice: original works, no reprint! Otherwise, legal liability will be investigated.
#******************************************************************** declare -i min max
declare -a nums for ((i=;i<;i++));do
nums[$i]=$RANDOM
[ $i -eq ] && min=${nums[$i]} && max=${nums[$i]}&& continue
[ ${nums[$i]} -gt $max ] && max=${nums[$i]}
[ ${nums[$i]} -lt $min ] && min=${nums[$i]}
done echo "All numbers are ${nums[*]}"
echo "Max is $max"
echo "Min is $min"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
参考案例1
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat shell/max_min.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: yinzhengjie
#QQ:
#Date: --
#FileName: shell/max_min.sh
#URL: http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie
#Description: The test script
#Copyright notice: original works, no reprint! Otherwise, legal liability will be investigated.
#******************************************************************** declare -i min max
declare -a nums for ((i=;i<;i++));do
nums[$i]=$RANDOM
if [ $i -eq ];then
max=${nums[$i]}
min=${nums[$i]}
else
if [ "$max" -lt "${nums[$i]}" ];then
max=${nums[$i]}
elif [ "$min" -gt "${nums[$i]}" ];then
min=${nums[$i]}
else
true
fi
fi
done echo "All numbers are ${nums[*]}"
echo "Max is $max"
echo "Min is $min"
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/max_min.sh
All numbers are
Max is
Min is
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
参考案例2
2>.编写脚本,定义一个数组,数组中的元素对应的值是/var/log目录下所有以.log结尾的文件;统计出其下标为奇数的文件中的行数之和
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# cat shell/log_wc.sh
#!/bin/bash
#
#********************************************************************
#Author: yinzhengjie
#QQ:
#Date: --
#FileName: shell/log_wc.sh
#URL: http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie
#Description: The test script
#Copyright notice: original works, no reprint! Otherwise, legal liability will be investigated.
#******************************************************************** declare -a files
files=(/var/log/*.log)
declare -i lines=0 for i in $(seq 0 $[${#files[*]}-1]); do
if [ $[$i%2] -eq 1 ];then
let lines+=$(wc -l ${files[$i]} | cut -d' ' -f1)
fi
done echo "Lines: $lines."
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# ll /var/log/*.log
-rw-------. 2 root root 0 Nov 28 07:41 /var/log/boot.log
-rw-------. 1 root root 15539 Nov 23 07:04 /var/log/yum.log
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# wc -l /var/log/boot.log
0 /var/log/boot.log
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# wc -l /var/log/yum.log
256 /var/log/yum.log
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]# bash shell/log_wc.sh
Lines: 256.
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn ~]#
参考案例
3>.输入若干个数值存入数组中,采用冒泡算法进行升序或降序排序
4>.打印杨辉三角形
5>.将下图所示,实现转置矩阵matrix.sh
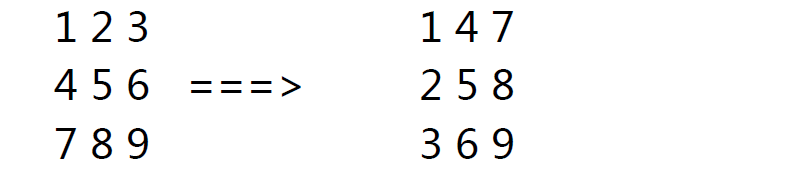
SHELL脚本编程-普通数组(列表)和关联数组(字典)的更多相关文章
- centos shell脚本编程1 正则 shell脚本结构 read命令 date命令的用法 shell中的逻辑判断 if 判断文件、目录属性 shell数组简单用法 $( ) 和${ } 和$(( )) 与 sh -n sh -x sh -v 第三十五节课
centos shell脚本编程1 正则 shell脚本结构 read命令 date命令的用法 shell中的逻辑判断 if 判断文件.目录属性 shell数组简单用法 $( ) 和$ ...
- Linux Shell脚本编程-数组和字符串处理
数组 1.数组的定义及声明 变量:存储单个元素的内存空间 数组:存储多个元素的连续的内存空间,相当于多个变量的集合 数组名:整个数组只有一个名字 索引:编号从0开始,属于数值索引:bash的数组支持 ...
- SHELL脚本编程的常识和VI常用技巧
来源:http://mprc.pku.edu.cn/mentors/training/TrainingCourses/material/ShellProgramming.HTM#_Toc3751808 ...
- 浅谈自底向上的Shell脚本编程及效率优化
作者:沐星晨 出处:http://blog.csdn.net/sosodream/article/details/6276758 浅谈自底向上的Shell脚本编程及效率优化 小论文,大家多批评指导:) ...
- Shell脚本编程30分钟入门
Shell脚本编程30分钟入门 转载地址: Shell脚本编程30分钟入门 什么是Shell脚本 示例 看个例子吧: #!/bin/sh cd ~ mkdir shell_tut cd shell_t ...
- Shell脚本编程具体解释
第12章 Shell脚本编程 l Shell命令行的执行 l 编写.改动权限和运行Shell程序的步骤 l 在Shell程序中使用參数和变量 l 表达式比較.循环结构语句和条件结构语句 l ...
- 30分钟快速学习Shell脚本编程
什么是Shell脚本 示例 看个例子吧: #!/bin/sh cd ~ mkdir shell_tut cd shell_tut for ((i=0; i<10; i++)); do touch ...
- 《Linux命令行与shell脚本编程大全》第二十二章 gawk进阶
gawk是一门功能丰富的编程语言,你可以通过它所提供的各种特性来编写好几程序处理数据. 22.1 使用变量 gawk编程语言支持两种不同类型的变量: 内建变量和自定义变量 22.1.1 内建变量 ga ...
- 《Linux命令行与shell脚本编程大全 第3版》
第一部分 Linux 命令行 第1章 初识Linux she1.1 什么是Linux 21.1.1 深入探究Linux 内核 31.1.2 GNU 工具 61.1.3 Linux 桌面环境 81 ...
随机推荐
- MongoDB开发深入之二:索引
索引分类: 默认索引 单一索引 复合索引 多键索引(数组索引) 全文检索索引 2dsphere 索引 2D索引 ...... 索引属性: 到期TTL 唯一索引 部分索引 稀疏索引 索引通常能够极大的提 ...
- StandardServer.await: Invalid command '' received
tomcat服务运行时 后台提输出警告:StandardServer.await: Invalid command '' received 这个警告是 多个tomcat启动时会出现端口占用的情况, 将 ...
- &和&&的区别?
&运算符有两种用法:(1)按位与:(2)逻辑与.&&运算符是短路与运算.逻辑与跟短路与的差别是非常巨大的,虽然二者都要求运算符左右两端的布尔值都是true整个表达式的值才是tr ...
- openshift 使用curl命令访问apiserver
openshift版本:openshift v3.6.173.0.5 使用oc(同kubectl)命令访问apiserver资源的时候,会使用到/root/.kube/config文件中使用的配置. ...
- Ubuntu16.04 安装PHP7 的 imagick 扩展
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16885135/article/details/78130281 1.从 https://pecl.php.net/package/imagi ...
- javascript中 for in 、for 、forEach 、for of 、Object.keys().
一 .for ..in 循环 使用for..in循环时,返回的是所有能够通过对象访问的.可枚举的属性,既包括存在于实例中的属性,也包括存在于原型中的实例.这里需要注意的是使用for-in返回的属性因各 ...
- Python如何获取系统大小端模式
1. 第一种方法导入sys模块: >>> import sys >>> >>> sys.byteorder 'little' >>&g ...
- CLRS最大子数组问题
今天我们一起来看一下关于最大子数组的一些问题.最大子数组的应用场景可以是这样的:有一天,你搞了一场投资开始炒股,这时你就会想,我怎样才能获得最大的利润呢,最简单的想法就是我在股票的最低价时买入,然后在 ...
- ubuntu 使用阿里云镜像源快速搭建kubernetes 1.15.2集群
一.概述 搭建k8s集群时,需要访问google,下载相关镜像以及安装软件,非常麻烦. 正好阿里云提供了k8s的更新源,国内用户就可以直接使用了. 二.环境介绍 操作系统 主机名 IP地址 功能 配置 ...
- go ---变量数据结构调试利器 go-spew
我们在使用Golang(Go语言)开发的过程中,会通过经常通过调试的方式查找问题的原因,解决问题,尤其是当遇到一个很棘手的问题的时候,就需要知道一段代码在执行的过程中,其上下文的变量对应的数据,以便进 ...
