Java并发-ConcurrentModificationException原因源码分析与解决办法
一、异常原因与异常源码分析
对集合(List、Set、Map)迭代时对其进行修改就会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常。这里以ArrayList为例,例如下面的代码:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
//遍历1
for (String s : list){
if (s.equals( "3")) {
list.remove(s); // error
}
}
//遍历2
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
for (; it.hasNext();) {
String value = it.next();
if (value.equals("3")) {
list.remove(value); // error
}
}
ArrayList类中包含了实现Iterator迭代器的内部类Itr,在Itr类内部维护了一个expectedModCount变量,而在ArrayList类中维护一个modCount变量(modCount是ArrayList实现AbstractList类得到成员变量)。其他集合(List、Set、Map)都与之类似。
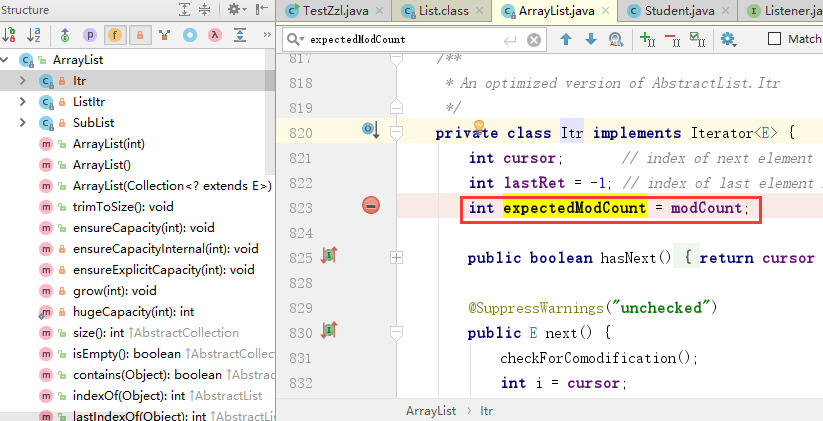
当对集合进行添加或者删除操作时modCount的值都会进行modCount++操作,例如ArrayList中的remove()方法:
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
当集合添加完值后,对集合进行遍历时才会创建Itr对象,这时候会执行int expectedModCount = modCount;操作,也就是说只要是在增加或删除后对集合进行遍历,那expectedModCount 与modCount永远是相等的。
但是如果在遍历的过程中进行增加或删除操作那么modCount++,但是expectedModCount保存的还是遍历前的值,也就是expectedModCount和modCount的值是不相等的。
遍历过程中会调用iterator的next()方法,next()方法方法会首先调用checkForComodification()方法来验证expectedModCount和modCount是否相等,因为之前做了增加或删除操作,modCount的值发生了变化,所以expectedModCount和modCount不相等,抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
二、单线程解决方案
1、迭代器删除
在Itr类中也给出了一个remove()方法,通过调用Itr类的方法就可以实现而且不报错,例如下面代码:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
list.add("4");
list.remove("4");
//遍历2
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
for (; it.hasNext();) {
String value = it.next();
if (value.equals("3")) {
it.remove();
}
}
在Itr类中remove()方法中,执行了expectedModCount = modCount操作,那么执行next()方法时expectedModCount和modCount肯定相等,Itr类中remove()方法的源码:
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
2、其他的方式
// 2 建一个集合,记录需要删除的元素,之后统一删除
List<string> templist = new ArrayList<string>();
for (String value : myList) {
if (value.equals( "3")) {
templist.remove(value);
}
}
// 可以查看removeAll源码,其中使用Iterator进行遍历
myList.removeAll(templist);
System. out.println( "List Value:" + myList.toString()); // 3. 使用线程安全CopyOnWriteArrayList进行删除操作
List<string> myList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<string>();
myList.add( "1");
myList.add( "2");
myList.add( "3");
myList.add( "4");
myList.add( "5"); Iterator<string> it = myList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
String value = it.next();
if (value.equals( "3")) {
myList.remove( "4");
myList.add( "6");
myList.add( "7");
}
}
System. out.println( "List Value:" + myList.toString()); // 4. 不使用Iterator进行遍历,需要注意的是自己保证索引正常
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) {
String value = myList.get(i);
System. out.println( "List Value:" + value);
if (value.equals( "3")) {
myList.remove(value); // ok
i--; // 因为位置发生改变,所以必须修改i的位置
}
}
三、多线程解决方案
1、多线程下异常原因
多线程下ArrayLis用Itr类中remove()方法也是会报异常的,Vector(线程安全)也会出现这种错误,具体原因如下:
Itr是在遍历的时候创建的,也就是每个线程如果遍历都会得到一个expectedModCount ,expectedModCount 也就是每个线程私有的,假若此时有2个线程,线程1在进行遍历,线程2在进行修改,那么很有可能导致线程2修改后导致Vector中的modCount自增了,线程2的expectedModCount也自增了,但是线程1的expectedModCount没有自增,此时线程1遍历时就会出现expectedModCount不等于modCount的情况了。
2、尝试方案
(1) 在所有遍历增删地方都加上synchronized或者使用Collections.synchronizedList,虽然能解决问题但是并不推荐,因为增删造成的同步锁可能会阻塞遍历操作。
(2) 推荐使用ConcurrentHashMap或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
3、CopyOnWriteArrayList使用注意
(1) CopyOnWriteArrayList不能使用Iterator.remove()进行删除。
(2) CopyOnWriteArrayList使用Iterator且使用List.remove(Object);会出现如下异常:
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
list.add("4"); Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
for (; it.hasNext();) {
String value = it.next();
if (value.equals("4")) {
it.remove(); // error
}
} Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList$COWIterator.remove(CopyOnWriteArrayList.java:1040)
at TestZzl.main(TestZzl.java:51)
4、最终解决方案
List<string> myList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<string>();
myList.add( "1");
myList.add( "2");
myList.add( "3");
myList.add( "4");
myList.add( "5"); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override
public void run() {
for (String string : myList) {
System.out.println("遍历集合 value = " + string); try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) {
String value = myList.get(i); System.out.println("删除元素 value = " + value); if (value.equals( "3")) {
myList.remove(value);
i--; // 注意
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
后续会具体分析一下CopyOnWriteArrayList
参考:
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201403/286536.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3933551.html
Java并发-ConcurrentModificationException原因源码分析与解决办法的更多相关文章
- Java并发编程-ReentrantLock源码分析
一.前言 在分析了 AbstractQueuedSynchronier 源码后,接着分析ReentrantLock源码,其实在 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的分析中,已经提到 ...
- Java并发编程 ReentrantLock 源码分析
ReentrantLock 一个可重入的互斥锁 Lock,它具有与使用 synchronized 方法和语句所访问的隐式监视器锁相同的一些基本行为和语义,但功能更强大. 这个类主要基于AQS(Abst ...
- Java并发编程-AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
简介 提供了一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架.该同步器(以下简称同步器)利用了一个int来表示状态,期望它能够成为实现大部分同步需求的基础.使用的方法是继承,子类通过 ...
- Java并发编程 LockSupport源码分析
这个类比较简单,是一个静态类,不需要实例化直接使用,底层是通过java未开源的Unsafe直接调用底层操作系统来完成对线程的阻塞. package java.util.concurrent.locks ...
- Java并发指南10:Java 读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 源码分析
Java 读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 源码分析 转自:https://www.javadoop.com/post/reentrant-read-write-lock#toc5 ...
- 【死磕 Java 集合】— ConcurrentSkipListMap源码分析
转自:http://cmsblogs.com/?p=4773 [隐藏目录] 前情提要 简介 存储结构 源码分析 主要内部类 构造方法 添加元素 添加元素举例 删除元素 删除元素举例 查找元素 查找元素 ...
- 死磕 java集合之DelayQueue源码分析
问题 (1)DelayQueue是阻塞队列吗? (2)DelayQueue的实现方式? (3)DelayQueue主要用于什么场景? 简介 DelayQueue是java并发包下的延时阻塞队列,常用于 ...
- 死磕 java集合之PriorityBlockingQueue源码分析
问题 (1)PriorityBlockingQueue的实现方式? (2)PriorityBlockingQueue是否需要扩容? (3)PriorityBlockingQueue是怎么控制并发安全的 ...
- 死磕 java集合之CopyOnWriteArraySet源码分析——内含巧妙设计
问题 (1)CopyOnWriteArraySet是用Map实现的吗? (2)CopyOnWriteArraySet是有序的吗? (3)CopyOnWriteArraySet是并发安全的吗? (4)C ...
随机推荐
- 原生js上传文件,使用new FormData()
当创建一个内容较多的表单,表单里面又有了文件上传,文件上传也需要表单提交,单一的上传文件很好操作: <form action="接口" enctype="multi ...
- mysql 的REPLAYCE语句
MySQL数据库insert和update语句引:用于操作数据库的SQL一般分为两种,一种是查询语句,也就是我们所说的SELECT语句,另外一种就是更新语句,也叫做数据操作语句.言外之意,就是对数 ...
- Java学习04 (第一遍)
封装.抽象.继承和多态.封装:在面向对象语言中,封装特性是由类来体现的,我们将现实生活中的一类实体定义成类,其中包括属性和行为(在Java中就是方法),就好像人类,可以具有name,sex,age等属 ...
- oracle 中如何定位重要(消耗资源多)的SQL
链接:http://www.xifenfei.com/699.html 标题:oracle 中如何定位重要(消耗资源多)的SQL 作者:惜分飞©版权所有[文章允许转载,但必须以链接方式注明源地址,否则 ...
- nginx反向代理:两个域名指向不同web服务端口
一台服务器上安装了zabbix服务和jumpserver服务,两个域名zabbix.xxxx.xxxx和jumserver.xxx.xxxx 一.编辑/etc/nginx/conf.d目录下nginx ...
- tomcat中的类加载机制
Tomcat中的类加载机制符合JVM推荐的双亲委派模型,关于JVM的类加载机制不多说,网上很多资料. 1. Tomcat类加载器过程. tomcat启动初始化阶段创建几个类加载器: private v ...
- db2start提示SQL5043,关闭连接终端tty
db2 V10.3启动的时候提示: 问题1: db2start执行后提示: SQL1072C The database manager resources are in an inconsisten ...
- Excel表格如何保护单元格不被修改
Excel如何保护单元格不被修改 有时使用Excel时希望保护单元格不被修改,这可以叫做单元格的“写保护”即把光标定位在一个不允许输入数据的区域内时,是无论如何也无法在里面输入数据的.下面咱们就一起 ...
- UltraEdit窗口布局重新设置
解决办法:工具栏中的视图-->环境-->左边小框里选择“编程员”,再点选择环境 转载:https://blog.csdn.net/u011650048/article/details/18 ...
- 超详细 Nginx 极简教程
什么是Nginx? Nginx (engine x) 是一款轻量级的Web 服务器 .反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器. 什么是反向代理? 反向代理(Reverse Proxy ...
