day13 面向对象练习
//1

public class Area_interface
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Rect r = new Rect(15, 12);
Circle c = new Circle(8);
System.out.println(r.getArea());
System.out.println(c.getArea());
}
} interface Areable{
double getArea();
} class NotValueException extends RuntimeException{
NotValueException(String message){
super(message);
}
} // 矩形
class Rect implements Areable{
private int length,width;
public Rect(int length,int width) {
if (length <= 0 || width <= 0){
throw new NotValueException("数值非法!");
}
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double getArea()
{
return length*width;
}
} // 圆形
class Circle implements Areable{
private int radius;
private static final double PI = 3.14;
public Circle(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getArea()
{
return PI*radius*radius;
}
}
//2

public int search_char(char[] chs, char key)
{
if(chs==null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组为空");
}
for(int x = 0;x < chs.length;x++){
if(key==chs[x]){
return x;
}
}
return -1;
}
//3
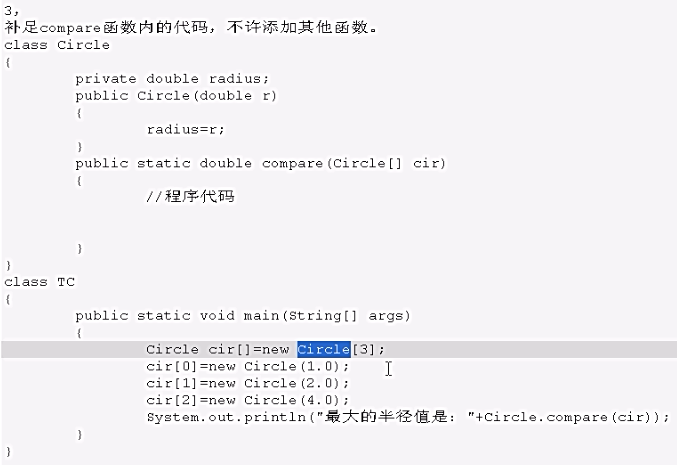
//first method
int max = 0; //初始化为数组中的任意一个角标
for(int x = 1; x < cir.length; x++){
if(cir[x].radius > cir[max].radius){
max = x;
}
}
return cir[max].radius; //second
double max = cir[0].radius; //初始化为数组任意一个元素的半径
for(int x = 1; x < cir.length; x++){
if(cir[x].radius >max){
max = cir[x].radius;
}
}
return max;
//4

class Person{
private int age;
private String name;
public Person(int age, String name) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public void say()
{
System.out.println(name+" "+age);
}
//下面两个都是通过右键搞定的
//get和set方法
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
//hashcode和equals方法
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Person other = (Person) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
equals方法通过eclipse自动生成

//5

public boolean equals(Object other){
if( !(other instanceof Circle) ){
throw new ClassCastException(other.getClass().getName+"类型错误");
}
Circle c = (Circle)other;
return c.radius==this.radius;
}
day13 面向对象练习的更多相关文章
- Java相关英语单词
day1 Java概述 掌握 .JDK abbr. Java开发工具包(Java Developer's Kit) (abbr.缩写) .JRE abbr. Java运行环境(Java Runtime ...
- js下 Day13、面向对象
一.对象 什么是对象: 一组无序的属性集合 创建对象两种方式: 对象字面量: var obj = {} 实例化: var obj = new Object() 对象取值: **[] ( ** 中括号) ...
- Python之路Day13
day13主要内容:JavaScript.DOM.jQuery 武Sir blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5369773.html JavaS ...
- python开发学习-day13(js、jQuery)
s12-20160409-day13 *:first-child { margin-top: 0 !important; } body>*:last-child { margin-bottom: ...
- Python之路day13 web 前端(JavaScript,DOM操作)
参考链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5433893.html day13 1. CSS示例 2. JavaScript 3. DOM操作 上节内容 ...
- angular2系列教程(六)两种pipe:函数式编程与面向对象编程
今天,我们要讲的是angualr2的pipe这个知识点. 例子
- 一起学 Java(二)面向对象
一.方法函数 函数也称为方法,就是定义在类中的具有特定功能的一段独立代码.用于定义功能,提高代码的复用性. 函数的特点1> 定义函数可以将功能代码进行封装,便于对该功能进行复用:2> 函数 ...
- js面向对象学习 - 对象概念及创建对象
原文地址:js面向对象学习笔记 一.对象概念 对象是什么?对象是“无序属性的集合,其属性可以包括基本值,对象或者函数”.也就是一组名值对的无序集合. 对象的特性(不可直接访问),也就是属性包含两种,数 ...
- 前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(二)构造函数与原型
前端开发:面向对象与javascript中的面向对象实现(二)构造函数与原型 前言(题外话): 有人说拖延症是一个绝症,哎呀治不好了.先不说这是一个每个人都多多少少会有的,也不管它究竟对生活有多么大的 ...
随机推荐
- awk常用命令总结
awk工具,主要将一行分成“字段”来处理. awk '条件类型1{动作1} 条件类型2{动作2}...‘ filename awk主要是处理每一行的字段内的数据,而默认的字段的分隔符为空格键或[tab ...
- Javascript的构造函数和constructor属性
原型链 function Foo() { this.value = 42;}Foo.prototype = { method: function() {}}; function Bar() {} // ...
- [转]Supporting OData Query Options in ASP.NET Web API 2
本文转自:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/web-api/overview/odata-support-in-aspnet-web-api/suppor ...
- 手机UA识别
整理手机UA识别如下: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&qu ...
- [android] 实现返回键操作思路
记录用户点击的操作历史,使用栈数据结构,频繁的操作栈顶(添加,获取,删除),使用LinkedList 捕获用户的返回键操作,响应返回键,返回上一个界面 MainActivity.java /** * ...
- 前端定位Position属性四个值
1.static(静态定位):默认值.没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中. 2.relative(相对定位):生成相对定位的元素,通过top,bottom,left,right的设置相对于其正常(原先本身 ...
- 重构指南 - 为布尔方法命名(Rename boolean method)
如果一个方法中包含多个布尔类型的参数,一是方法不容易理解,二是调用时容易出错. 重构前代码 public class BankAccount { public void CreateAccount(C ...
- Create a soft keyboard
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; usin ...
- log在无法调试代码时的妙用
1. 如果修改源代码 通过加入log打印日志 可以判断程序走的流程 找到需要自定义修改的位置(如修改java编写的项目 ApacheDS ) 2. 如果java调用dll文件 出错了 排错的方式也可以 ...
- [国家集训队2012]middle(陈立杰)
我是萌萌的传送门 我是另一个萌萌的传送门 脑残错误毁一下午…… 其实题解早就烂大街了,然而很久之前我只知道是二分答案+主席树却想不出来这俩玩意儿怎么一块儿用的……今天又翻了几篇题解才恍然大悟,是把权值 ...
