Memory-mapped I/O vs port-mapped I/O
关于MMIO和PIO,我看到的解释最清楚的文章,原文在这里:Memory-mapped I/O vs port-mapped I/O - 2015
Microprocessors normally use two methods to connect external devices: memory mapped or port mapped I/O. However, as far as the peripheral is concerned, both methods are really identical.
Memory mapped I/O is mapped into the same address space as program memory and/or user memory, and is accessed in the same way.
Port mapped I/O uses a separate, dedicated address space and is accessed via a dedicated set of microprocessor instructions.
The difference between the two schemes occurs within the microprocessor. Intel has, for the most part, used the port mapped scheme for their microprocessors and Motorola has used the memory mapped scheme.
As 16-bit processors have become obsolete and replaced with 32-bit and 64-bit in general use, reserving ranges of memory address space for I/O is less of a problem, as the memory address space of the processor is usually much larger than the required space for all memory and I/O devices in a system.
Therefore, it has become more frequently practical to take advantage of the benefits of memory-mapped I/O. However, even with address space being no longer a major concern, neither I/O mapping method is universally superior to the other, and there will be cases where using port-mapped I/O is still preferable.
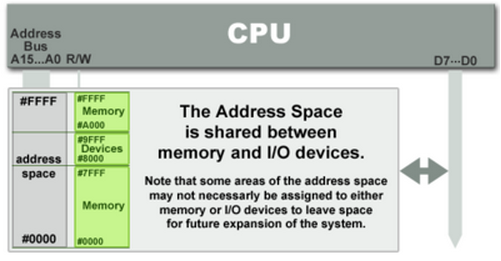
I/O
devices are mapped into the system memory map along with RAM and ROM.
To access a hardware device, simply read or write to those 'special'
addresses using the normal memory access instructions.
The advantage to this method is that every instruction which can access memory can be used to manipulate an I/O device.
The
disadvantage to this method is that the entire address bus must be
fully decoded for every device. For example, a machine with a 32-bit
address bus would require logic gates to resolve the state of all 32
address lines to properly decode the specific address of any device.
This increases the cost of adding hardware to the machine.
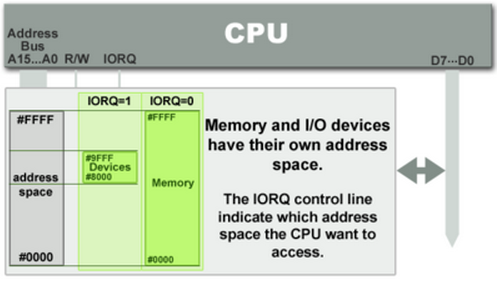
Picture source : IO Devices
I/O
devices are mapped into a separate address space. This is usually
accomplished by having a different set of signal lines to indicate a
memory access versus a port access. The address lines are usually shared
between the two address spaces, but less of them are used for accessing
ports. An example of this is the standard PC which uses 16 bits of port
address space, but 32 bits of memory address space.
The
advantage to this system is that less logic is needed to decode a
discrete address and therefore less cost to add hardware devices to a
machine. On the older PC compatible machines, only 10 bits of address
space were decoded for I/O ports and so there were only 1024 unique port
locations; modern PC's decode all 16 address lines. To read or write
from a hardware device, special port I/O instructions are used.
From a software perspective, this is a slight disadvantage because more
instructions are required to accomplish the same task. For instance, if
we wanted to test one bit on a memory mapped port, there is a single
instruction to test a bit in memory, but for ports we must read the data
into a register, then test the bit.
Comparison - Memory-mapped vs port-mapped
| Memory-mapped IO | Port-mapped IO |
|---|---|
| Same address bus to address memory and I/O devices | Different address spaces for memory and I/O devices |
| Access to the I/O devices using regular instructions | Uses a special class of CPU instructions to access I/O devices |
| Most widely used I/O method | x86 Intel microprocessors - IN and OUT instructions |
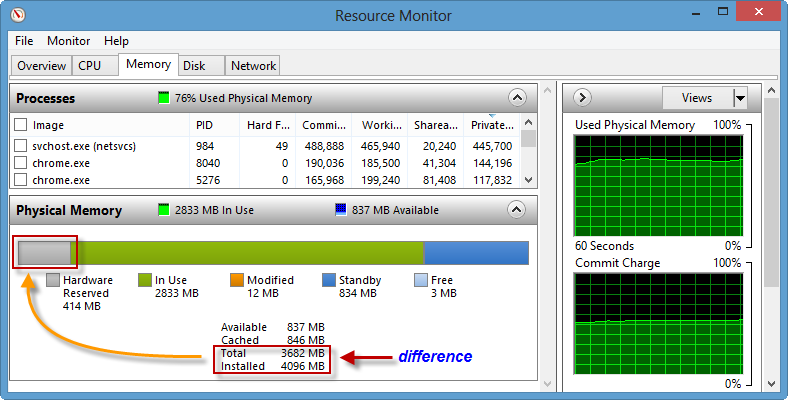
We can check the reserved memory address space from the Resource Monitor via our desktop's Task Manager.
Memory-mapped I/O vs port-mapped I/O的更多相关文章
- System and method for parallel execution of memory transactions using multiple memory models, including SSO, TSO, PSO and RMO
A data processor supports the use of multiple memory models by computer programs. At a device extern ...
- 【DM642学习笔记六】TI参考文档--DM642 Video Port Mini Driver
这个文档介绍了在DM642EVM板上视频采集和显示微驱动的使用和设计.用EDMA进行存储器和视频端口的数据传输.为了增强代码的复用性和简化设计过程,驱动分为通用视频端口层和特定编解码芯片微驱动层两个 ...
- Anatomy of a Program in Memory
Memory management is the heart of operating systems; it is crucial for both programming and system a ...
- [转]Anatomy of a Program in Memory
Memory management is the heart of operating systems; it is crucial for both programming and system a ...
- Method and apparatus for providing total and partial store ordering for a memory in multi-processor system
An improved memory model and implementation is disclosed. The memory model includes a Total Store Or ...
- Unity3D Optimizing Graphics Performance for iOS
原地址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_72b936d801013ptr.html icense Comparisons http://unity3d.com/unity ...
- linux 查看系统状态方法
Linux下如何查看系统启动时间和运行时间 1.uptime命令输出:16:11:40 up 59 days, 4:21, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.0 ...
- linux包之dmidecode
http://www.dmtf.org/standards/smbios Dmidecode 这款软件允许你在 Linux 系统下获取有关硬件方面的信息.Dmidecode 遵循 SMBIOS/DMI ...
- System Address Map Initialization in x86/x64 Architecture Part 2: PCI Express-Based Systems
原文 http://resources.infosecinstitute.com/system-address-map-initialization-x86x64-architecture-pa ...
- psutil官方文档
psutil documentation¶ Quick links Home page Install Blog Forum Download Development guide What’s new ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ 4868 [Shoi2017]期末考试 ——三分 枚举
考场上xjb三分过掉了. 然后$sdfzyhx$.$silvernebula$ $O(n)$虐掉了. 我还是太菜了 #include <cstdio> #include <cmath ...
- Java防止SQL注入的途径介绍
为了防止SQL注入,最简洁的办法是杜绝SQL拼接,SQL注入攻击能得逞是因为在原有SQL语句中加入了新的逻辑,如果使用PreparedStatement来代替Statement来执行SQL语句,其后只 ...
- 马士兵hadoop第二课:hdfs集群集中管理和hadoop文件操作(转)
马士兵hadoop第一课:虚拟机搭建和安装hadoop及启动 马士兵hadoop第二课:hdfs集群集中管理和hadoop文件操作 马士兵hadoop第三课:java开发hdfs 马士兵hadoop第 ...
- 病毒(bzoj 2938)
Description 二进制病毒审查委员会最近发现了如下的规律:某些确定的二进制串是病毒的代码.如果某段代码中不存在任何一段病毒代码,那么我们就称这段代码是安全的.现在委员会已经找出了所有的病毒代码 ...
- 计算器(bzoj 2242)
Description 你被要求设计一个计算器完成以下三项任务: 1.给定y,z,p,计算Y^Z Mod P 的值: 2.给定y,z,p,计算满足xy≡ Z ( mod P )的最小非负整数: 3.给 ...
- watch watch watch the video! I got almost addicted. Oh what a fuck!!!!
http://v.huya.com/play/574329.html#relate_vid=570467
- linux 中信号量
ctrl-c 发送 SIGINT 信号给前台进程组中的所有进程.常用于终止正在运行的程序.ctrl-z 发送 SIGTSTP 信号给前台进程组中的所有进程,常用于挂起一个进程.ctrl-d 不是发送信 ...
- ZOJ 2619: Generator
类型:概率 + 解方程组(高斯消元法) + KMP(好吧其实我用的是暴力~)题意:你可以等概率的选择大写字母里的前n个字母,在纸上写啊写,一直到出现给定的字符串.问写的字母个数的期望.思路: 期望递推 ...
- 数据结构自己实现——Linklist
//单???链???表??? #include <iostream> using namespace std; typedef char datatype; typedef struct ...
- vue生命周期回调方法
最近在用vue开发一个商品列表页,因需要根据请求回的字段是否有内容来显示隐藏该字段, 但因为vue异步加载导致显示隐藏方法不起作业(主要是判断条件取不到页面渲染内容),围观了vue生命周期后发现upd ...
