Timeseries Prediction Demo base on LSTM
示例代码
import json
import time
import datetime
import requests as req
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM, Dense def date2ts(date_str, layout="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"):
date_struct=time.strptime(date_str, layout)
return int(time.mktime(date_struct)) # 画图之前转换成北京时间
def to_beijing_time(datetime_index):
return datetime_index.tz_localize('UTC').tz_convert('Asia/Shanghai') # 载入原始数据
with open("dataset_2014.json", "r") as rf:
c = rf.read()
d = json.loads(c)
data = {}
for i in range(288*3):
ts = date2ts(d['data']['datetime'][i])
data[ts] = d['data']['count'][i] # 将字典转换为 DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(list(data.items()), columns=['timestamp', 'value'])
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['timestamp'], unit='s')
df.set_index('datetime', inplace=True)
df.drop('timestamp', axis=1, inplace=True) # 确保数据按时间顺序排序
df = df.sort_index() # 重新采样为 5 分钟间隔,填充缺失值
df = df.resample('5T').mean()
df.interpolate(method='linear', inplace=True) # 数据标准化
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
df_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(df)
print("Original Data:\n", df)
print("Scaled Data:\n", df_scaled) # 创建数据集函数
def create_dataset(data, time_step=1):
X, y = [], []
for i in range(len(data) - time_step - 1):
X.append(data[i:(i + time_step), 0])
y.append(data[i + time_step, 0])
return np.array(X), np.array(y) time_step = 10 # 设定用于输入的时间步长
X, y = create_dataset(df_scaled, time_step) # 拆分训练和测试数据集
train_size = int(len(X) * 0.7)
test_size = len(X) - train_size
X_train, X_test = X[:train_size], X[train_size:]
y_train, y_test = y[:train_size], y[train_size:] # 转换为 LSTM 输入格式
X_train = X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0], X_train.shape[1], 1)
X_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0], X_test.shape[1], 1) # 构建 LSTM 模型
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(50, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(time_step, 1)))
model.add(LSTM(50, return_sequences=False))
model.add(Dense(25))
model.add(Dense(1)) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mean_squared_error')
model.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size=1, epochs=10) # 预测
train_predict = model.predict(X_train)
test_predict = model.predict(X_test) # 反标准化预测结果
train_predict = scaler.inverse_transform(train_predict)
test_predict = scaler.inverse_transform(test_predict) # 反标准化实际值
df_inv_scaled = scaler.inverse_transform(df_scaled)
# print("Inverse Scaled Data:\n", df_inv_scaled) # 创建用于绘制图像的空数组
train_predict_plot = np.empty_like(df_scaled)
train_predict_plot[:, :] = np.nan
train_predict_plot[time_step:len(train_predict) + time_step, :] = train_predict # 计算测试预测结果的起始和结束点
start_point = len(train_predict) + time_step # 设定起始点位置
end_point = start_point + len(test_predict)
test_predict_plot = np.empty_like(df_scaled)
test_predict_plot[:, :] = np.nan
test_predict_plot[start_point:end_point, :] = test_predict[:df_scaled.shape[0] - start_point, :] # 放置到合适位置 # 将时间戳转换回原始时间格式
original = df.index
original_beijing = to_beijing_time(original)
# 创建 figure 绘图
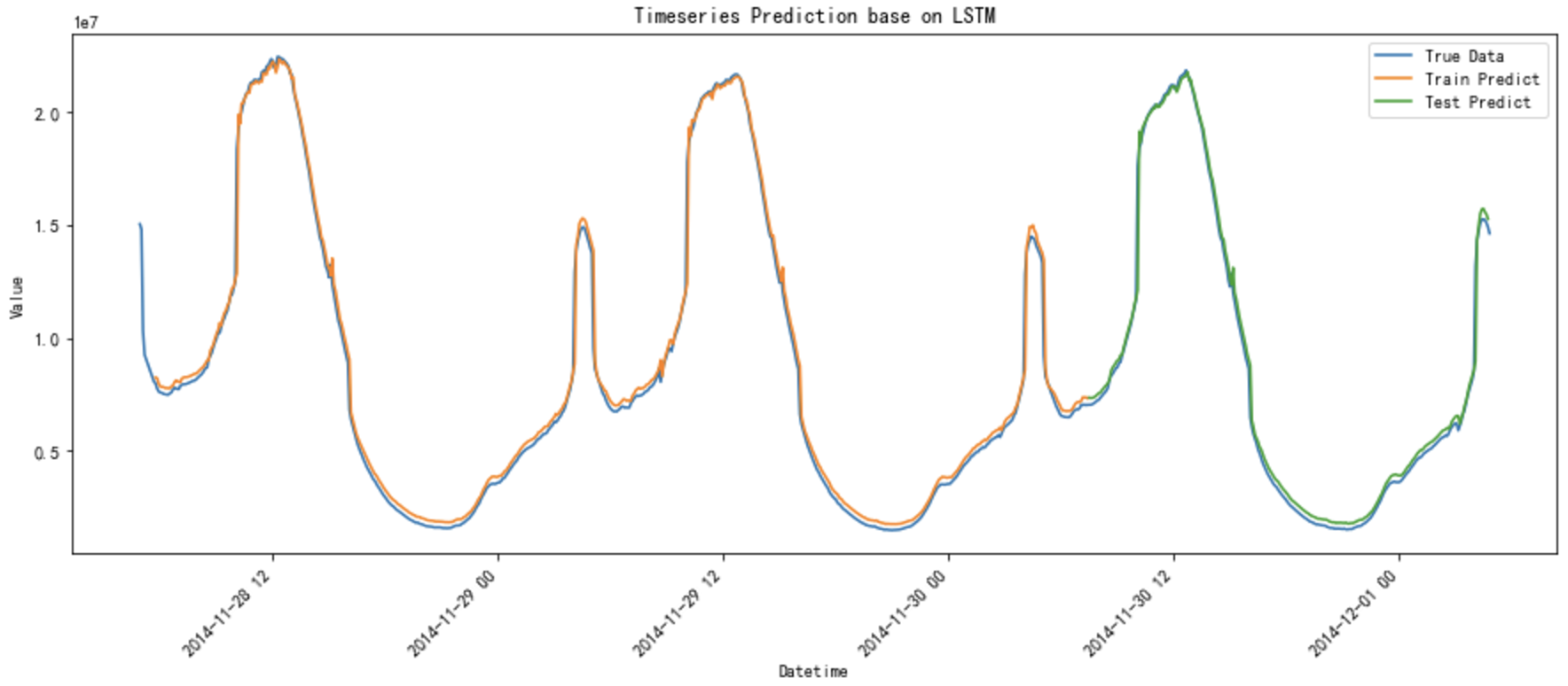
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.title("Timeseries Prediction base on LSTM")
plt.plot(original_beijing, df_inv_scaled, label='True Data') # 确保这里使用适当逆标准化数据
plt.plot(original_beijing, train_predict_plot, label='Train Predict')
plt.plot(original_beijing, test_predict_plot, label='Test Predict')
# 格式化 X 轴,提高可读性
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.HourLocator(interval=12))
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M', tz=original_beijing.tz))
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate(rotation=45)
plt.xlabel('Datetime')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.show() # # 提取最后3天的数据
# last_three_days_mask = original >= (original.max() - pd.Timedelta(days=3))
# filtered_original = original[last_three_days_mask]
# filtered_df_inv_scaled = df_inv_scaled[last_three_days_mask]
# filtered_train_predict_plot = train_predict_plot[last_three_days_mask]
# filtered_test_predict_plot = test_predict_plot[last_three_days_mask]
# # 转换时间为北京时间
# filtered_original_beijing = to_beijing_time(filtered_original) # plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
# plt.title("Timeseries Prediction base on LSTM (last 3 days)")
# plt.plot(filtered_original_beijing, filtered_df_inv_scaled, label='True Data') # 确保这里使用适当逆标准化数据
# plt.plot(filtered_original_beijing, filtered_train_predict_plot, label='Train Predict')
# plt.plot(filtered_original_beijing, filtered_test_predict_plot, label='Test Predict')
# # 格式化 X 轴使用年,并倾斜显示
# plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.HourLocator(interval=4))
# plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M', tz=filtered_original_beijing.tz))
# plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate(rotation=45)
# plt.xlabel('Datetime')
# plt.ylabel('Value')
# plt.legend()
# plt.show()
效果对比
Timeseries Prediction Demo base on LSTM的更多相关文章
- 【转载】Chaotic Time-Series Prediction
原文地址:https://cn.mathworks.com/help/fuzzy/examples/chaotic-time-series-prediction.html?requestedDomai ...
- 用C++调用tensorflow在python下训练好的模型(centos7)
本文主要参考博客https://blog.csdn.net/luoyexuge/article/details/80399265 [1] bazel安装参考:https://blog.csdn.net ...
- 高并发下MySQL出现checking permissions
在某些数据访问层框架中,会使用show full tables from test like 'demo',来检查数据库的状态.当数据库中表的数量较少时,并没有出现严重的问题.但是当数据库中的表数量多 ...
- python中from module import * 的一个陷阱
from module import *把module中的成员全部导到了当前的global namespace,访问起来就比较方便了.当然,python style一般不建议这么做,因为可能引起nam ...
- JavaScript 的性能优化:加载和执行
随着 Web2.0 技术的不断推广,越来越多的应用使用 javascript 技术在客户端进行处理,从而使 JavaScript 在浏览器中的性能成为开发者所面临的最重要的可用性问题.而这个问题又因 ...
- Bootstrap 栅格系统(转载)
源地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/linjiqin/p/3559800.html Bootstrap 栅格系统 目录1.简介2.栅格选项3.列偏移4.嵌套列5.列排序 1.简介Bo ...
- python之import机制
1. 标准 import Python 中所有加载到内存的模块都放在 sys.modules .当 import 一个模块时首先会在这个列表中查找是否已经加载了此模块,如果加载了则只是将 ...
- c++ 虚析构函数[避免内存泄漏]
c++ 虚析构函数: 虚析构函数(1)虚析构函数即:定义声明析构函数前加virtual 修饰, 如果将基类的析构函数声明为虚析构函数时,由该基类所派生的所有派生类的析构函数也都自动成为虚析构函数. ...
- springboot学习随笔(四):Springboot整合mybatis(含generator自动生成代码)
这章我们将通过springboot整合mybatis来操作数据库 以下内容分为两部分,一部分主要介绍generator自动生成代码,生成model.dao层接口.dao接口对应的sql配置文件 第一部 ...
- CMake 常用方法
CMake 允许开发者编写平台无关的 CMakeLists.txt 文件来定制整个编译流程,然后再根据目标用户的平台进一步生成所需的本地化 Makefile 和工程文件,如 Linux 的Makefi ...
随机推荐
- 聊聊AI浏览器
提供AI咨询+AI项目陪跑服务,有需要回复1 大模型一直有个难以解决的问题:系统的知识是过时的,他们难以跟进最新的信息. 基于这个原因,ChatGPT以及DeepSeek都提出了联网功能,只不过效果嘛 ...
- Vim编辑器基本用法
热门的Linux操作系统中都会默认安装一款文本编辑器-----Vim.它有三种模式:命令模式,末行模式和编辑模式. 命令模式 控制光标的移动,可对文本进行删除,复制,粘贴. 输入模式 正常的文本录入 ...
- 线下IDC数据中心迁移至阿里云详细方案
一.迁移前准备 1. 迁移规划 资源评估 统计需迁移的数据库类型.版本.数据量(如 MySQL 5.7.SQL Server 2019.文件存储系统等). 评估应用依赖关系,明确停机窗口(建议业务低峰 ...
- Linux下搭建Kafka集群
摘要 Kafka 是一个分布式的基于push-subscribe的消息系统,它具备快速.可扩展.可持久化的特点.由 LinkedIn 开源,用作 LinkedIn 的活动流(Activity Stre ...
- 从Clipto.AI看AI SaaS创业的隐形机会:一个月2500万访问量背后的商业逻辑
最近深度研究了一个让我眼前一亮的产品--Clipto.AI. 这款看似简单的音视频转录工具,月访问量竟然达到了2540万,这个数字让我震惊,也让我重新思考了AI工具的商业化路径. 今天想和大家分享一下 ...
- opencv检测黑色轮廓(矩形)
opencv检测黑色轮廓: import cv2 import numpy as np class ShapeDetector: def __init__(self, image_path): sel ...
- `.NC`文件的读取与使用
.NC文件的读取与使用 前言 NetCDF(network Common Data Form)网络通用数据格式是一种面向数组型并适于网络共享的数据的描述和编码标准.目前,NetCDF广泛应用于大气科学 ...
- 强化PHP安全策略,有效防范网络钓鱼威胁
本文由 ChatMoney团队出品 随着互联网的飞速发展,网络钓鱼攻击已成为网络安全领域的重要威胁之一.网络钓鱼攻击通过伪装成合法网站或企业,诱骗用户进入虚假网站并窃取用户的个人信息.密码等敏感信息. ...
- Web前端入门第 72 问:JavaScript DOM 内容操作常用方法和 XSS 注入攻击
当项目的安全团队找上门告诉您,您开发的项目存在 XSS 安全漏洞,作为一个开发人员,就问您慌不慌?? HTML 内容写入的时候,如果稍不注意就会触发隐藏 BOSS 漏洞 XSS. XSS 漏洞原理就是 ...
- 运行yolo时候,查mmcv各个版本
https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu111/torch1.8.0/index.html
