B. Mishka and trip
time limit per test1 second
memory limit per test256 megabytes
inputstandard input
outputstandard output
Little Mishka is a great traveller and she visited many countries. After thinking about where to travel this time, she chose XXX — beautiful, but little-known northern country.
Here are some interesting facts about XXX:
- XXX consists of n cities, k of whose (just imagine!) are capital cities.
- All of cities in the country are beautiful, but each is beautiful in its own way. Beauty value of i-th city equals to ci.
- All the cities are consecutively connected by the roads, including 1-st and n-th city, forming a cyclic route 1 — 2 — ... — n — 1. Formally, for every 1 ≤ i < n there is a road between i-th and i + 1-th city, and another one between 1-st and n-th city.
- Each capital city is connected with each other city directly by the roads. Formally, if city x is a capital city, then for every 1 ≤ i ≤ n, i ≠ x, there is a road between cities x and i.
- There is at most one road between any two cities.
- Price of passing a road directly depends on beauty values of cities it connects. Thus if there is a road between cities i and j, price of passing it equals ci·cj.
Mishka started to gather her things for a trip, but didn't still decide which route to follow and thus she asked you to help her determine summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX. Formally, for every pair of cities a and b (a < b), such that there is a road betweena and b you are to find sum of products ca·cb. Will you help her?
InputThe first line of the input contains two integers n and k (3 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of cities in XXX and the number of capital cities among them.
The second line of the input contains n integers c1, c2, ..., cn (1 ≤ ci ≤ 10 000) — beauty values of the cities.
The third line of the input contains k distinct integers id1, id2, ..., idk (1 ≤ idi ≤ n) — indices of capital cities. Indices are given in ascending order.
OutputPrint the only integer — summary price of passing each of the roads in XXX.
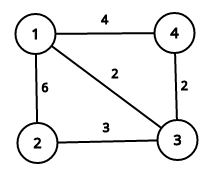
Examplesinput4 1
2 3 1 2
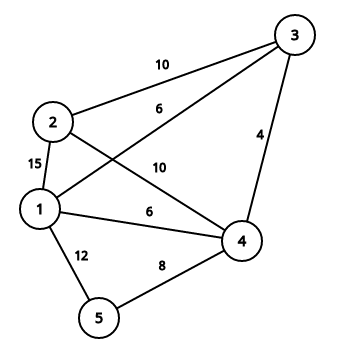
3output17input5 2
3 5 2 2 4
1 4output71NoteThis image describes first sample case:
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 17.
This image describes second sample case:
It is easy to see that summary price is equal to 71.
水完A题艰难的刷出了B,看到10e5整个人都不好了 这难度梯度也太大了吧摔! 后来想到了乘法分配律O(n)暴力....

首先记录首都节点 然后非首都节点每次连接下一个城市,首都节点则连接除自己和前一个城市外的所有城市,注意重复的情况和i==1,i==n的情况。
附AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std; int a[];
int v[]; int main(){
int n,k;
memset(a,,sizeof(a));
memset(v,,sizeof(v));//初始化为0
cin>>n>>k;
long long sum1=,sum2=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
sum1+=a[i];//所有点值的和
}
int x;
for(int i=;i<k;i++){
cin>>x;
v[x]=;//记录首都节点
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
if(v[i]){//判断是否是首都
if(i==){//1和n时特判
sum2+=a[]*(sum1-a[n]-a[]);
if(v[n]){
sum2+=a[]*a[n];
}
}
else{//连接除自身和前一个点外的所有点
sum2+=a[i]*(sum1-a[i]-a[i-]);
if(v[i-]){//若前一个点也为首都则连接两点
sum2+=a[i]*a[i-];
}
}
sum1-=a[i];//减掉已全连过的首都节点 避免重复
}
else{//连接自己和下一个点 n时特判
if(i==n){
sum2+=a[]*a[n];
}
else{
sum2+=a[i]*a[i+];
}
}
}
cout<<sum2<<endl;
return ;
}
B. Mishka and trip的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #365 (Div. 2) Mishka and trip
Mishka and trip 题意: 有n个城市,第i个城市与第i+1个城市相连,他们边的权值等于i的美丽度*i+1的美丽度,有k个首都城市,一个首都城市与每个城市都相连,求所有边的权值. 题解: ...
- cf703B Mishka and trip
B. Mishka and trip time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- 暑假练习赛 003 F Mishka and trip
F - Mishka and trip Sample Output Hint In the first sample test: In Peter's first test, there's on ...
- Codeforces 703B. Mishka and trip 模拟
B. Mishka and trip time limit per test:1 second memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard i ...
- codeforces 703B B. Mishka and trip(数学)
题目链接: B. Mishka and trip time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- CodeForces 703A Mishka and trip
Description Little Mishka is a great traveller and she visited many countries. After thinking about ...
- cf B. Mishka and trip (数学)
题意 Mishka想要去一个国家旅行,这个国家共有个城市,城市通过道路形成一个环,即第i个城市和第个城市之间有一条道路,此外城市和之间有一条道路.这个城市中有个首中心城市,中心城市与每个城市(除了 ...
- Codeforces 703B (模拟) Mishka and trip
题目:这里 题意:n个城市,每个城市有个魅力值vi,首先,有n条路将这n个城市连成一个环,1号城市连2号城市,2号连3号****n号连1号城市,每条路的魅力值是其连接的两个城市 的魅力值的乘积,这n个 ...
- CodeForces 703B Mishka and trip
简单题. 先把环上的贡献都计算好.然后再计算每一个$capital$ $city$额外做出的贡献值. 假设$A$城市为$capital$ $city$,那么$A$城市做出的额外贡献:$A$城市左边城市 ...
随机推荐
- java多线程异步执行
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.ut ...
- 【hibernate spring data jpa】执行了save()方法 sql语句也执行了,但是数据并未插入数据库中
执行了save()方法 sql语句也执行了,但是数据并未插入数据库中 解决方法: 是因为执行了save()方法,也执行了sql语句,但是因为使用的是 @Transactional 注解,不是手动去提 ...
- [Servlet&JSP] 标准标签
在JSP的规范中提供了一些标准标签(Standard Tag),全部的容器都支持这些标签,它能够协助编写JSP时降低Scriptlet的使用. 全部的标准标签都使用jsp:作为前置.这些标准标签是在J ...
- 数组遍历 map()、forEach() 及 字符串切割 split() / 字符串截取 slice()、substring()、substr()
JS数组遍历的几种方式 JS数组遍历,基本就是for,forin,foreach,forof,map等等一些方法,以下介绍几种本文分析用到的数组遍历方式以及进行性能分析对比 第一种:普通for循环 代 ...
- C#面向对象 结构体和类的应用
- [Other]来做一个微信打印机吧 -- 微信打印的设计思路參考
项目源代码地址:https://github.com/callmewhy/why-wechat-printer 近期微信打印机小火了一把.比方印美团.747微信打印机,都是利用微信公共平台实现照片的打 ...
- 程序员笔记|如何编写高性能的Java代码
一.并发 Unable to create new native thread …… 问题1:Java中创建一个线程消耗多少内存? 每个线程有独自的栈内存,共享堆内存 问题2:一台机器可以创建多少线程 ...
- Android_Service详解及实例
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/11952435 http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/art ...
- C语言socket send()数据缓存问题
send()函数默认情况下会使用Nagle算法.Nagle算法通过将未确认的数据存入缓冲区直到积攒到一定数量一起发送的方法.来降低主机发送零碎小数据包的数目.所以假设send()函数发送数据过快的话, ...
- Lambda Architecture
Lambda Architecture » λ lambda-architecture.net http://lambda-architecture.net/ Twitter's tweets ana ...