POJ-3436 ACM Computer Factory(网络流EK)
As you know, all the computers used for ACM contests must be identical, so the participants compete on equal terms. That is why all these computers are historically produced at the same factory.
Every ACM computer consists of P parts. When all these parts are present, the computer is ready and can be shipped to one of the numerous ACM contests.
Computer manufacturing is fully automated by using N various machines. Each machine removes some parts from a half-finished computer and adds some new parts (removing of parts is sometimes necessary as the parts cannot be added to a computer in arbitrary order). Each machine is described by its performance (measured in computers per hour), input and output specification.
Input specification describes which parts must be present in a half-finished computer for the machine to be able to operate on it. The specification is a set of P numbers 0, 1 or 2 (one number for each part), where 0 means that corresponding part must not be present, 1 — the part is required, 2 — presence of the part doesn’t matter.
Output specification describes the result of the operation, and is a set of P numbers 0 or 1, where 0 means that the part is absent, 1 — the part is present.
The machines are connected by very fast production lines so that delivery time is negligibly small compared to production time.
After many years of operation the overall performance of the ACM Computer Factory became insufficient for satisfying the growing contest needs. That is why ACM directorate decided to upgrade the factory.
As different machines were installed in different time periods, they were often not optimally connected to the existing factory machines. It was noted that the easiest way to upgrade the factory is to rearrange production lines. ACM directorate decided to entrust you with solving this problem.
Input
Input file contains integers P N, then N descriptions of the machines. The description of ith machine is represented as by 2 P + 1 integers Qi Si,1 Si,2…Si,P Di,1 Di,2…Di,P, where Qi specifies performance, Si,j — input specification for part j, Di,k — output specification for part k.
Constraints
1 ≤ P ≤ 10, 1 ≤ N ≤ 50, 1 ≤ Qi ≤ 10000
Output
Output the maximum possible overall performance, then M — number of connections that must be made, then M descriptions of the connections. Each connection between machines A and B must be described by three positive numbers A B W, where W is the number of computers delivered from A to B per hour.
If several solutions exist, output any of them.
Sample Input
3 4
15 0 0 0 0 1 0
10 0 0 0 0 1 1
30 0 1 2 1 1 1
3 0 2 1 1 1 1
3 5
5 0 0 0 0 1 0
100 0 1 0 1 0 1
3 0 1 0 1 1 0
1 1 0 1 1 1 0
300 1 1 2 1 1 1
2 2
100 0 0 1 0
200 0 1 1 1
Sample Output
25 2
1 3 15
2 3 10
4 5
1 3 3
3 5 3
1 2 1
2 4 1
4 5 1
0 0
—————————————————–分割线——————————————————–
题意,有N个机器,每个机器对P个部分进行加工,但是每个机器对加工的对象都有要求,题中input specification 代表机器加工的对象必须满足的条件,其中为0的部分绝对不能存在,为1的部分必须存在,为2的部位存在与不存在都可以。Output specification 代表机器加工完成后的对象, 其中为0的部分代表加工后不存在,为1的部分代表加工后存在。用这些机器将全为0的零件加工成全为1的电脑。给出每个机器的加工速度,加工对象和加工后对象,求最快的加工速度。
解释案例:
3 4
15 0 0 0 0 1 0
10 0 0 0 0 1 1
30 0 1 2 1 1 1
3 0 2 1 1 1 1
有四个机器,每个机器对三个地方加工。
一开始的板子是空的,所以只能用0 0 0 开始的机器来加工,所以一开始只有1号和2号机子可以用,用1号机子后变成0 1 0 然后拿去三号机子,变成1 1 1,这一条路加工速度为15。用2号机子加工变成0 1 1,然后拿去三号机子加工,这条路加工为10,所以总的速度是25。
思路:对于每个点先要把点分割开,把点分开成两部分的意义在于,不能让最大流量超过本身的生产量。这是因为每个点我都需要一进一出,而我自己又有自己最大的生产量,所以我要保证在网络流图上跑的时候不仅不会超过前一个点带来的流量,也不会超过自己本身所可以承受的流量。如图:
假设c能承受的流量只有15 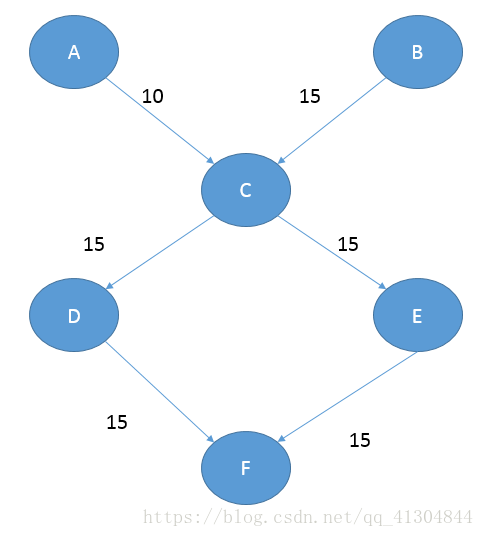
如果按这个图跑,那么我会超出自身可以承受的流量,超出15,使最大流变成30,这显然是不可以的 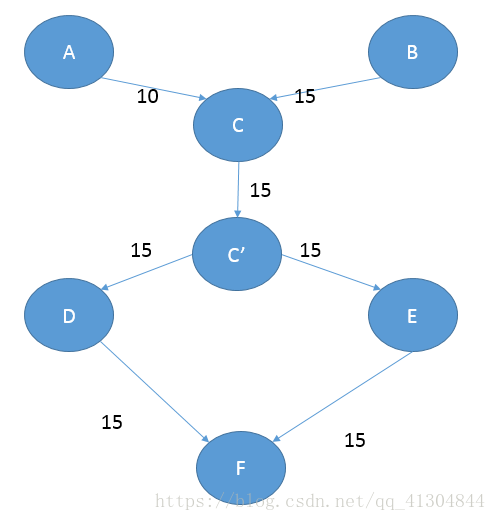
那么我这时候就需要对c点进行拆点,是一条从自身到自身的路的权值是自身的生产量,这样我就保证了我不会超出自身最大可以承受的流量。
同理,在这题中就需要对每个点来进行拆点,然后一个点用来接收流量,一个点用来发送流量,在这两个点之间用本身可以承受的最大流量来将这两个点连接起来,在这题中也就是本身的生产速度。最后跑一边最大流,然后对每条边判断,如果一开始的边比跑完以后的边的权值大,那么就说明有流量经过。
#include<map>
#include<ctime>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm> typedef unsigned long long int ull;
typedef long long int ll;
const double pi = 4.0*atan(1.0);
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = ;
const int maxm = ;
using namespace std; int n, m;
int maps[maxn][maxn];
int flow[maxn];
int pre[maxn];
int tmp[maxn][maxn];
int inp[maxn][maxn];
int oup[maxn][maxn];
int res[maxm][];
queue<int> q; void init() {
memset(inp, , sizeof(inp));
memset(oup, , sizeof(oup));
memset(tmp, , sizeof(tmp));
memset(res, , sizeof(res));
memset(maps, , sizeof(maps));
memset(flow, , sizeof(flow));
} void getmap() {
int src = ;
int des = * m + ;
int val;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++) {
scanf("%d", &val);
maps[i][i+m] = val;
bool flag = true;
for(int j=; j<=n; j++) {
scanf("%d", &inp[i][j]);
if(inp[i][j] == ) flag = false;
}
if(flag)
maps[src][i] = inf;
flag = true;
for(int j=; j<=n; j++) {
scanf("%d", &oup[i][j]);
if(oup[i][j] == ) flag = false;
}
if(flag)
maps[i + m][des] = inf;
}
for(int i=; i<=m; i++) {
for(int j=; j<=m; j++) {
if(i == j) continue;
int flag = true;
for(int k=; k<=n; k++) {
if(oup[i][k] == && inp[j][k] == ) flag = false;
if(oup[i][k] == && inp[j][k] == ) flag = false;
}
if(flag)
maps[i+m][j] = inf;
}
}
} int bfs(int src, int des) {
while(!q.empty()) q.pop();
memset(pre, -, sizeof(pre));
q.push(src);
pre[src] = ;
flow[src] = inf;
while(!q.empty()) {
int index = q.front();
q.pop();
if(index == des) break;
for(int i=src; i<=des; i++) {
if(i != src && maps[index][i] && pre[i] == -) {
pre[i] = index;
flow[i] = min(flow[index], maps[index][i]);
q.push(i);
}
}
}
if(pre[des] == -) return -;
else return flow[des];
} int EK(int src, int des) {
int ans = ;
int val;
while() {
val = bfs(src, des);
if(val == -) break;
int last = des;
while(last != src) {
maps[pre[last]][last] -= val;
maps[last][pre[last]] += val;
last = pre[last];
}
ans += val;
}
return ans;
} int solve() {
int ans = ;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++) {
for(int j=; j<=m; j++) {
if(tmp[i + m][j] - maps[i + m][j] > ) {
res[ans][] = i;
res[ans][] = j;
res[ans][] = tmp[i + m][j] - maps[i + m][j];
ans++;
}
}
}
return ans;
} int main() {
while(~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m)) {
init();
getmap();
int src = ;
int des = * m + ;
/*
for(int i=src; i<=des; i++) {
for(int j=src; j<=des; j++) {
printf("%d%c", maps[i][j], j==des ? '\n' : '\t');
}
}
*/
memcpy(tmp, maps, sizeof(maps));
int ans = EK(src, des);
int tol = solve();
printf("%d %d\n", ans, tol);
for(int i=; i<tol; i++) {
printf("%d %d %d\n", res[i][], res[i][], res[i][]);
}
}
return ;
}
POJ-3436 ACM Computer Factory(网络流EK)的更多相关文章
- POJ - 3436 ACM Computer Factory 网络流
POJ-3436:http://poj.org/problem?id=3436 题意 组配计算机,每个机器的能力为x,只能处理一定条件的计算机,能输出特定的计算机配置.进去的要求有1,进来的计算机这个 ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory (网络流,最大流)
POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory (网络流,最大流) Description As you know, all the computers used for ACM cont ...
- Poj 3436 ACM Computer Factory (最大流)
题目链接: Poj 3436 ACM Computer Factory 题目描述: n个工厂,每个工厂能把电脑s态转化为d态,每个电脑有p个部件,问整个工厂系统在每个小时内最多能加工多少台电脑? 解题 ...
- kuangbin专题专题十一 网络流 POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3436 Sample input 1 3 4 15 0 0 0 0 1 0 10 0 0 0 0 1 1 30 0 1 2 1 ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory 最大流,拆点 难度:1
题目 http://poj.org/problem?id=3436 题意 有一条生产线,生产的产品共有p个(p<=10)零件,生产线上共有n台(n<=50)机器,每台机器可以每小时加工Qi ...
- POJ - 3436 ACM Computer Factory(最大流)
https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3436 题目描述: 正如你所知道的,ACM 竞赛中所有竞赛队伍使用的计算机必须是相同的,以保证参赛者在公平的环境下竞争.这就是所有这些 ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory(最大流+路径输出)
http://poj.org/problem?id=3436 题意: 每台计算机包含P个部件,当所有这些部件都准备齐全后,计算机就组装完成了.计算机的生产过程通过N台不同的机器来完成,每台机器用它的性 ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory (拆点+输出解)
[题意]每台计算机由P个零件组成,工厂里有n台机器,每台机器针对P个零件有不同的输入输出规格,现在给出每台机器每小时的产量,问如何建立流水线(连接各机器)使得每小时生产的计算机最多. 网络流的建图真的 ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory
题意: 为了追求ACM比赛的公平性,所有用作ACM比赛的电脑性能是一样的,而ACM董事会专门有一条生产线来生产这样的电脑,随着比赛规模的越来越大,生产线的生产能力不能满足需要,所以说ACM董事会想 ...
- poj 3436 ACM Computer Factory 最大流+记录路径
题目 题意: 每一个机器有一个物品最大工作数量,还有一个对什么物品进行加工,加工后的物品是什么样.给你无限多个初始都是000....的机器,你需要找出来经过这些机器操作后最多有多少成功的机器(111. ...
随机推荐
- MYSQL mydumper & myloader
第三方逻辑备份工具myduper和myloader | xiaoyu的数据库小窝-技术交流http://www.dbaxiaoyu.com/archives/1643 myloader原理0 - ze ...
- nginx配置ssl证书后无法访问https
一直听说https更安全,要安装证书,一直没试过,今天终于试了试 首先得有个http的域名网站,服务器. 到阿里云的安全-ssl证书管理申请一个免费的,可以绑定一个域名 然后完善资料,照着例子配置一 ...
- [2018.05].NET Core 3 and Support for Windows Desktop Applications
.NET Core 3 and Support for Windows Desktop Applications Richard 微软官网的内容...net 3.0 升级任务 任重道远 https:/ ...
- Quartz框架学习(1)—核心层次结构
Quartz框架学习 Quartz(任务调度)框架的核心组件: job:任务.即任务调度行为中所要调度的对象. trigger:触发器.是什么促使了一个任务的调度?当然是时间.这也算事件驱动类型程序. ...
- js 首次进入弹窗
今天有个需求,首次进入需要弹窗,然后就在网上找了下,虽然看了很多但是说的都不是我想要的,最后终于到了一个合适的. function get_cookie(Name) { var search = Na ...
- Algorithm Visualizer
Algorithm Visualizer https://algorithm-visualizer.org/ https://algorithm-visualizer.org/divide-and-c ...
- Oracle 查询两个时间段内的所有日期列表
1.查询某时间段内日期列表 select level,to_char(to_date('2013-12-31','yyyy-mm-dd')+level-1,'yyyy-mm-dd') as date_ ...
- JUC同步锁(五)
根据锁的添加到Java中的时间,Java中的锁,可以分为"同步锁"和"JUC包中的锁". 一.同步锁--synchronized关键字 通过synchroniz ...
- axis函数
axis函数 axis([xmin xmax ymin ymax]) 用来标注输出的图线的最大值最小值. MATLAB中坐标系的设置函数 MATLAB 函数 axis([XMIN XMAX YMI ...
- Qt QTimer
QTimer类提供了重复和单次触发信号的定时器. QTimer类为定时器提供了一个高级别的编程接口.很容易使用:首先,创建一个QTimer,连接timeout()信号到适当的槽函数,并调用start( ...
