(转载)C#使用MemoryStream类读写内存
MemoryStream和BufferedStream都派生自基类Stream,因此它们有很多共同的属性和方法,但是每一个类都有自己独特的用法。这两个类都是实现对内存进行数据读写的功能,而不是对持久性存储器进行读写。
读写内存-MemoryStream类
MemoryStream类用于向内存而不是磁盘读写数据。MemoryStream封装以无符号字节数组形式存储的数据,该数组在创建MemoryStream对象时被初始化,或者该数组可创建为空数组。可在内存中直接访问这些封装的数据。内存流可降低应用程序中对临时缓冲区和临时文件的需要。
下表列出了MemoryStream类的重要方法:
1、Read():读取MemoryStream流对象,将值写入缓存区。
2、ReadByte():从MemoryStream流中读取一个字节。
3、Write():将值从缓存区写入MemoryStream流对象。
4、WriteByte():从缓存区写入MemoytStream流对象一个字节。
Read方法使用的语法如下:
mmstream.Read(byte[] buffer,offset,count)
其中mmstream为MemoryStream类的一个流对象,3个参数中,buffer包含指定的字节数组,该数组中,从offset到(offset +count-1)之间的值由当前流中读取的字符替换。Offset是指Buffer中的字节偏移量,从此处开始读取。Count是指最多读取的字节数。Write()方法和Read()方法具有相同的参数类型。
MemoryStream类的使用实例:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.IO; namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int count;
byte[] byteArray;
char[] charArray;
UnicodeEncoding uniEncoding = new UnicodeEncoding();
// Create the data to write to the stream.
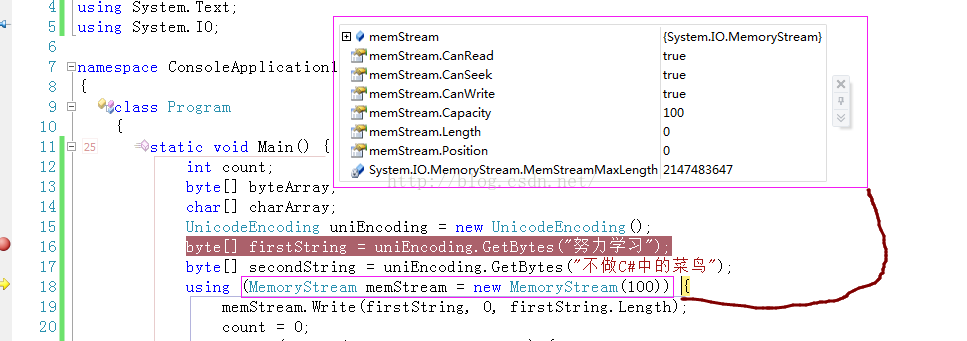
byte[] firstString = uniEncoding.GetBytes("一二三四五");
byte[] secondString = uniEncoding.GetBytes("上山打老虎");
using (MemoryStream memStream = new MemoryStream())
{
// Write the first string to the stream.
memStream.Write(firstString, , firstString.Length); // Write the second string to the stream, byte by byte.
count = ;
while (count < secondString.Length)
{
memStream.WriteByte(secondString[count++]);
} // Write the stream properties to the console.
Console.WriteLine("Capacity={0},Length={1},Position={2}\n", memStream.Capacity.ToString(), memStream.Length.ToString(), memStream.Position.ToString()); // Set the position to the beginning of the stream.
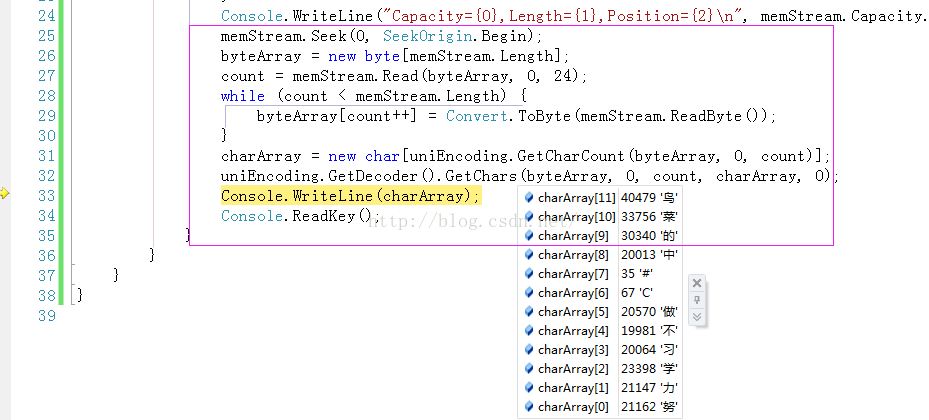
memStream.Seek(, SeekOrigin.Begin); // Read the first 20 bytes from the stream.
byteArray = new byte[memStream.Length];
count = memStream.Read(byteArray, , ); // Read the remaining bytes, byte by byte.
while (count < memStream.Length)
{
byteArray[count++] = Convert.ToByte(memStream.ReadByte());
} // Decode the byte array into a char array
// and write it to the console.
charArray = new char[uniEncoding.GetCharCount(byteArray, , count)];
uniEncoding.GetDecoder().GetChars(byteArray, , count, charArray, );
Console.WriteLine(charArray); Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
}
在这个实例代码中使用了using关键字。注意:
using 关键字有两个主要用途:
1、作为指令,用于为命名空间创建别名或导入其他命名空间中定义的类型。
例如:
using System;
2、作为语句,用于定义一个范围,在此范围的末尾将释放对象。
using(Connection conn=new Connection(connStr))
{
}
//使用using关键字可及时销毁对象
MemoryStream.Capacity 属性 取得或设定配置给这个资料流的位元组数目。
MemoryStream.Position 属性 指定当前流的位置。
MemoryStream.Length 属性获取用字节表示的流长度。
SeekOrigin()是一个枚举类,作用设定流的一个参数。
SeekOrigin.Begin我得理解就是文件的最开始,“0”是偏移,表示跳过0个字节。写2就是跳过2个字节。
MemoryStream类通过字节读写数据。本例中定义了写入的字节数组,为了更好的说明Write和WriteByte的异同,在代码中声明了两个byte数组,其中一个数组写入时调用Write方法,通过指定该方法的三个参数实现如何写入。
另一个数组调用了WriteByte方法,每次写入一个字节,所以采用while循环来完成全部字节的写入。写入MemoryStream后,可以检索该流的容量,实际长度,当前流的位置,将这些值输出到控制台。通过观察结果,可以确定写入MemoryStream流是否成功。
调用Read和ReadByte两种方法读取MemoryStream流中的数据,并将其进行Unicode编码后输出到控制台。

读取内存流中的数据
在.NET中,使用抽象基类System.IO.Stream代表流,它提供Read和Write两个方法。由于数据流的有序性,因此流对象还有一个读写指针,为此,Stream类还有一个Seek方法用于移动读写指针。
字符串与字节数组间的互相转化:
string str = "内存大小";
byte[] temp = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes (str); // 字符串转化为字节数组
string s = Encoding.UTF8.GetString (temp); // 字节数组转化为字符串
Debug.Log (s);
Encoding用法比较简单,如果只是字节和字符的互相转换,GetBytes()和GetChars()这两个方法及它们的重载基本上会满足你所有要求。
GetByteCount()及其重载是得到一个字符串转换成字节时实际的字节个数。
GetCharCount()及其重载是得到一个字节数组转换成字符串的大小。
Decoder.GetChars 方法
Java里一个byte取值范围是-128~127, 而C#里一个byte是0~255.
首位不同. 但是底层I/O存储的数据是一样的
FileStream对象的数据来自文件,而MemoryStream对象的数据来自内存缓冲区。这两个类都继承自Stream类。
MemoryStream的数据来自内存中的一块连续区域,这块区域称为“缓冲区(Buffer)”。可以把缓冲区看成一个数组,每个数组元素可以存放一个字节的数据。
在创建MemoryStream对象时,可以指定缓冲区的大小,并且可以在需要的时候更改。
//字节数组
byte[] buffer = new byte[];
//填充字节数组
private void CreateExampleData()
{
for(int i=; i<; i++)
{
//byte类型的数最大不能超过255,用256取模实现
buffer[i] = (byte)(i%);
}
}
内存流的基本使用方法:
private void OnTestMemory()
{
//创建测试数据
CreateExampleData(); //创建内存流对象,初始分配50字节的缓冲区
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(); //向内存流中写入字节数组的所有数据
mem.Write(buffer,,buffer.GetLength()); MessageBox.Show("写入数据后的内存流长度:" + mem.Length.ToString());
MessageBox.Show("分配给内存流的缓冲区大小:" + mem.Capacity.ToString()); mem.SetLength(); MessageBox.Show("调用SetLength方法后的内存流长度:" + mem.Length.ToString()); mem.Capacity = ;//此值不能小于Length属性
MessageBox.Show("调用Capacity方法后缓冲区大小:" + mem.Capacity.ToString()); //将读写指针移到距流开头10个字节的位置
mem.Seek(,SeekOrigin.Begin);
MessageBox.Show(mem.ReadByte().ToString());
mem.Close();
}
内存流的Length属性代表了其中存放的数据的真实长度,而Capacity属性则代表了分配给内存流的内存空间大小。
可以使用字节数组创建一个固定大小的MemoryStream,
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer);
这时,无法再设置Capacity属性的大小。
还可以创建只读的内存流对象。
MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(buffer,false); FlieStream用于存取文件。
创建文件并写入内容:
//创建一个新文件
FileStream fsForWrite = new FileStream("test.data",FileMode.Create);
try
{
//写入一个字节
fsForWrite.WriteByte();
CreateExampleData();
//将字节数组写入文件
fsForWrite.Write(buffer,,buffer.GetLength());
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
//关闭文件
fsForWrite.Close();
}
打开文件并读取内容:
private void ReadFromFile()
{
FileStream fsForRead = new FileStream("test.data",FileMode.Open);
try
{
//读入一个字节
MessageBox.Show("文件的第一个字节为:"+fsForRead.ReadByte().ToString());
//读写指针移到距开头10个字节处
fsForRead.Seek(,SeekOrigin.Begin);
byte[] bs = new byte[];
//从文件中读取10个字节放到数组bs中
fsForRead.Read(bs,,);
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
fsForRead.Close(); }
}
如果一个程序退出了,但它打开的文件没有被关闭,将导致其他程序无法修改或删除此文件。
FileStream与MemoryStream间的相互作用:
-----解决方案--------------------
FileStream fs = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open);
byte[] data = new byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read(data, , data.Length);
fs.Close();
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(data);
------解决方案--------------------
///定义并实例化一个内存流,以存放图片的字节数组。
MemoryStream m = new MemoryStream();
///获得当前路径
string strAppPath = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory; //获得可执行文件的路径。
///获得图片路径
string strPath = strAppPath + "img\\default.jpg";
///图片读入FileStream
FileStream f = new FileStream(strPath, FileMode.open);
///把FileStream写入MemoryStream
m.SetLength(f.Length);
f.Read(m.GetBuffer(), , (int)f.Length);
m.Flush();
f.Close();
------解决方案--------------------
FileStream fs = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open);
byte[] MyData = new byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read(MyData, , (int)fs.Length);
fs.Close();
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(MyData);
------解决方案--------------------
MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(File.ReadAllBytes("c:\\1.jpg"));
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/e295166319/article/details/52702461
(转载)C#使用MemoryStream类读写内存的更多相关文章
- C#使用MemoryStream类读写内存
MemoryStream和BufferedStream都派生自基类Stream,因此它们有很多共同的属性和方法,但是每一个类都有自己独特的用法.这两个类都是实现对内存进行数据读写的功能,而不是对持久性 ...
- MemoryStream类读写内存
和FileStream一样,MemoryStream和BufferedStream都派生自基类Stream,因此它们有很多共同的属性和方法,但是每一个类都有自己独特的用法.这两个类都是实现对内存进行数 ...
- c#中@标志的作用 C#通过序列化实现深表复制 细说并发编程-TPL 大数据量下DataTable To List效率对比 【转载】C#工具类:实现文件操作File的工具类 异步多线程 Async .net 多线程 Thread ThreadPool Task .Net 反射学习
c#中@标志的作用 参考微软官方文档-特殊字符@,地址 https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/toke ...
- C#中MemoryStream类的介绍
MemoryStream位于System.IO命名空间,为系统内存提供流式的读写操作.常作为其他流数据交换时的中间对象操作. 1.MemoryStream类封装一个字节数组,在构造实例时可以使用一个字 ...
- Linux就这个范儿 第15章 七种武器 linux 同步IO: sync、fsync与fdatasync Linux中的内存大页面huge page/large page David Cutler Linux读写内存数据的三种方式
Linux就这个范儿 第15章 七种武器 linux 同步IO: sync.fsync与fdatasync Linux中的内存大页面huge page/large page David Cut ...
- MemoryStream类
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kissdodog/archive/2013/01/20/2868864.html MemoryStream 是一个特例,MemoryStream中 ...
- 目录_Java内存分配(直接内存、堆内存、Unsafel类、内存映射文件)
1.Java直接内存与堆内存-MarchOn 2.Java内存映射文件-MarchOn 3.Java Unsafe的使用-MarchOn 简单总结: 1.内存映射文件 读文件时候一般要两次复制:从磁盘 ...
- C++类的内存分配
今天面试被问到一个类的内存问题,有些记不清楚了.用了 C++这么年,实在是不应该. 于是上网查了一些资料,并做了实验,整理如下: 所用测试环境为64位mac air,编译器为XCode 1.最简单 c ...
- 虚函数列表: 取出方法 // 虚函数工作原理和(虚)继承类的内存占用大小计算 32位机器上 sizeof(void *) // 4byte
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: A(){} virtual void geta(){ cout < ...
随机推荐
- 初学Python——函数
一.函数定义 def name( parameters): #没有参数括号内可以为空 "函数描述" #其实就是注释 <代码块> return [expression] ...
- 根据成绩输出对应的等级(使用if多分支和switch语句分别实现)
根据成绩输出对应的等级,使用if多分支和switch语句分别实现. a) A级 [90,100] b) B级 [80,90) c) C级 [70, ...
- poj-1330(暴力写的lca)
传送门 一看就是lca的板子题 然而 (写这个的时候我忘了怎么写lca) 于是我就试着写暴力了 本以为会tle结果e了一次后居然a掉了 开心到起飞.嘿嘿嘿 但还是格式输出错误了一次而且在ce之前也de ...
- 5239-回忆京都-洛谷3月赛gg祭
传送门 题目背景 第十五届东方人气投票 音乐部门 106名 第四次国内不知道东方的人对东方原曲的投票调查 51名 回忆京都副歌我tm吹爆,东方文花帖我tm吹爆! 题目描述 射命丸文在取材中发现了一个好 ...
- Java虚拟机垃圾收集器
一.判断对象存活的算法 1.引用计数(Reference Counting)算法 给对象添加一个引用计数器,每当有一个地方引用时,计数器加1.当引用失效时,计数器减1.当计数器的值为0的时候说该对象不 ...
- Spring+Struts2+Hibernate框架整合流程
一:基本步骤 新建Maven项目,导入相关依赖(推荐) 在WEB-INF的web.xml中进行配置 ————–Hibernate配置 —————- 创建entity包,创建数据库相关实体类 根据实体类 ...
- 缓存子系统如何设计(Cachable tag, Memcache/redis support, xml config support, LRU/LFU/本地缓存命中率)
大家对这段代码肯定很熟悉吧: public List<UserInfo> SearchUsers(string userName) { string cacheKey=string.For ...
- 从.Net框架Bug的提交到修复代码成功合并到.NET CoreFX主线
从发现.NET Framework中SmtpClient的Bug并拿出解决方案,然后给微软开发者社区提交Bug开始,总共耗时一个多月,对Bug修复的代码最终被采纳,现已合并到.NET Core Lib ...
- jdk1.8之线程中断
在Core Java中有这样一句话:"没有任何语言方面的需求要求一个被中断的程序应该终止.中断一个线程只是为了引起该线程的注意,被中断线程可以决定如何应对中断 " 线程中断不会使线 ...
- 腾讯AlloyTeam正式发布omi-cli脚手架 - 创建网站无需任何配置
omi-cli omi-cli omi-cli命令 omi框架 用户指南 文件目录 npm 脚本 npm start npm run dist 代码分割 兼容 IE8 插入 CSS 插入组件局部 CS ...
