Python中的passed by assignment与.NET中的passing by reference、passing by value
Python文档中有一段话:
Remember that arguments are passed by assignment in Python. Since assignment just creates references to objects, there’s no alias between an argument name in the caller and callee, and so no call-by-reference per se.
我们常说参数的传递分为按值传递与按引用传递,Python中的passed by assignment该如何理解?
argument vs parameter
stackoverflow上关于paramter 和 argument的解释:
A parameter is a variable in a method definition. When a method is called, the arguments are the data you pass into the method's parameters.
- PARAMETER → PLACEHOLDER (This means a placeholder belongs to the function naming and be used in the function body)
- ARGUMENT → ACTUAL VALUE (This means an actual value which is passed by the function calling)

.NET中类型分为值类型和引用类型两种,默认使用值传递,若使用引用传递,需明确使用
ref、in、out关键字。In C#, arguments can be passed to parameters either by value or by reference. Passing by reference enables function members, methods, properties, indexers, operators, and constructors to change the value of the parameters and have that change persist in the calling environment. To pass a parameter by reference with the intent of changing the value, use the
ref, oroutkeyword. To pass by reference with the intent of avoiding copying but not changing the value, use theinmodifier.
Passing Reference-Type Parameters
When you pass a reference-type parameter by value, it is possible to change the data belonging to the referenced object, such as the value of a class member. However, you cannot change the value of the reference itself; for example, you cannot use the same reference to allocate memory for a new object and have it persist outside the method. To do that, pass the parameter using the ref or out keyword. For simplicity, the following examples use ref.
Passing Reference Types by Value
class PassingRefByVal
{
static void Change(int[] pArray)
{
pArray[] = ; // This change affects the original element.
pArray = new int[] {-, -, -, -, -}; // This change is local.
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside the method, the first element is: {0}", pArray[]);
} static void Main()
{
int[] arr = {, , };
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside Main, before calling the method, the first element is: {0}", arr []); Change(arr);
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside Main, after calling the method, the first element is: {0}", arr []);
}
}
/* Output:
Inside Main, before calling the method, the first element is: 1
Inside the method, the first element is: -3
Inside Main, after calling the method, the first element is: 888
*/
In the preceding example, the array, arr, which is a reference type, is passed to the method without the ref parameter. In such a case, a copy of the reference, which points to arr, is passed to the method. The output shows that it is possible for the method to change the contents of an array element, in this case from 1 to 888. However, allocating a new portion of memory by using the new operator inside the Change method makes the variable pArray reference a new array. Thus, any changes after that will not affect the original array, arr, which is created inside Main. In fact, two arrays are created in this example, one inside Main and one inside the Change method.
Passing Reference Type by Reference
The following example is the same as the previous example, except that the ref keyword is added to the method header and call. Any changes that take place in the method affect the original variable in the calling program.
class PassingRefByRef
{
static void Change(ref int[] pArray)
{
// Both of the following changes will affect the original variables:
pArray[] = ;
pArray = new int[] {-, -, -, -, -};
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside the method, the first element is: {0}", pArray[]);
} static void Main()
{
int[] arr = {, , };
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside Main, before calling the method, the first element is: {0}", arr[]); Change(ref arr);
System.Console.WriteLine("Inside Main, after calling the method, the first element is: {0}", arr[]);
}
}
/* Output:
Inside Main, before calling the method, the first element is: 1
Inside the method, the first element is: -3
Inside Main, after calling the method, the first element is: -3
*/
All of the changes that take place inside the method affect the original array in Main. In fact, the original array is reallocated using the new operator. Thus, after calling the Change method, any reference to arr points to the five-element array, which is created in the Change method.
⚠️Do not confuse the concept of passing by reference with the concept of reference types. The two concepts are not the same. A method parameter can be modified by
refregardless of whether it is a value type or a reference type. There is no boxing of a value type when it is passed by reference.
Passing Value-Type Parameters
Passing a value-type variable to a method by value means passing a copy of the variable to the method. Any changes to the parameter that take place inside the method have no affect on the original data stored in the argument variable. If you want the called method to change the value of the argument, you must pass it by reference, using the ref or out keyword. You may also use the in keyword to pass a value parameter by reference to avoid the copy while guaranteeing that the value will not be changed. For simplicity, the following examples use ref.
Passing Value Types by Value
class PassingValByVal
{
static void SquareIt(int x)
// The parameter x is passed by value.
// Changes to x will not affect the original value of x.
{
x *= x;
System.Console.WriteLine("The value inside the method: {0}", x);
}
static void Main()
{
int n = ;
System.Console.WriteLine("The value before calling the method: {0}", n); SquareIt(n); // Passing the variable by value.
System.Console.WriteLine("The value after calling the method: {0}", n); // Keep the console window open in debug mode.
System.Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
System.Console.ReadKey();
}
}
/* Output:
The value before calling the method: 5
The value inside the method: 25
The value after calling the method: 5
*/
The variable n is a value type. It contains its data, the value 5. When SquareIt is invoked, the contents of n are copied into the parameter x, which is squared inside the method. In Main, however, the value of n is the same after calling the SquareIt method as it was before. The change that takes place inside the method only affects the local variable x.
Passing Value Types by Reference
The following example is the same as the previous example, except that the argument is passed as a ref parameter. The value of the underlying argument, n, is changed when x is changed in the method.
class PassingValByRef
{
static void SquareIt(ref int x)
// The parameter x is passed by reference.
// Changes to x will affect the original value of x.
{
x *= x;
System.Console.WriteLine("The value inside the method: {0}", x);
}
static void Main()
{
int n = ;
System.Console.WriteLine("The value before calling the method: {0}", n); SquareIt(ref n); // Passing the variable by reference.
System.Console.WriteLine("The value after calling the method: {0}", n); // Keep the console window open in debug mode.
System.Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit.");
System.Console.ReadKey();
}
}
/* Output:
The value before calling the method: 5
The value inside the method: 25
The value after calling the method: 25
*/
In this example, it is not the value of n that is passed; rather, a reference to n is passed. The parameter x is not an int; it is a reference to an int, in this case, a reference to n. Therefore, when x is squared inside the method, what actually is squared is what x refers to, n.
图解按引用传递
曾在Github上提过一个issue,用几幅图描述了按引用传递的情况。
Python passed by assignment
说了这么多,Python中的passed by assignment该怎么理解?Python中类型没有像.NET那样分为值类型与引用类型。Python中所有类型的值都是对象,这些对象分为可变对象与不可变对象两种:
不可变类型
float、int、str、tuple、bool等可变类型
list、dict、set等
Python中,所有的数据类型都是对象,在传参时,传递的是对象的引用。与.NET中按值传递引用类型类似。对于不可变类型:
num = 9 def changeValue(value: int):
# int类型是不可变类型,改变value的值会让value指向新的对象8,不会改变num
value = 8 print(num)
changeValue(num)
print(num) """
输出:
9
9
"""
对于可变类型:
l = [9, 8, 7] def createNewList(l1: list):
# l1+[0]会创建一个新的list对象,只是改变了局部变量l1的引用地址,不会影响变量l
l1 = l1+[0] def changeList(l1: list):
# 在列表末尾添加一个元素,因为l1和l引用同一个对象,所以l也会改变
l1.append(0) print(l)
createNewList(l)
print(l)
changeList(l)
print(l) """
输出:
[9, 8, 7]
[9, 8, 7]
[9, 8, 7, 0]
"""
小结
按值传递就是拷贝出变量值的一个副本,所有的操作都是针对这个副本的,对原始数据没有影响。
⚠️对于.NET中的值类型,原始数据就是变量的值;对于.NET中的引用类型,原始数据也是值变量的值,只不过这个值存储的是内存地址
从下图中可以看到,按值传递引用类型,变量p2和p在内存中的地址不同,但存储的值相同:
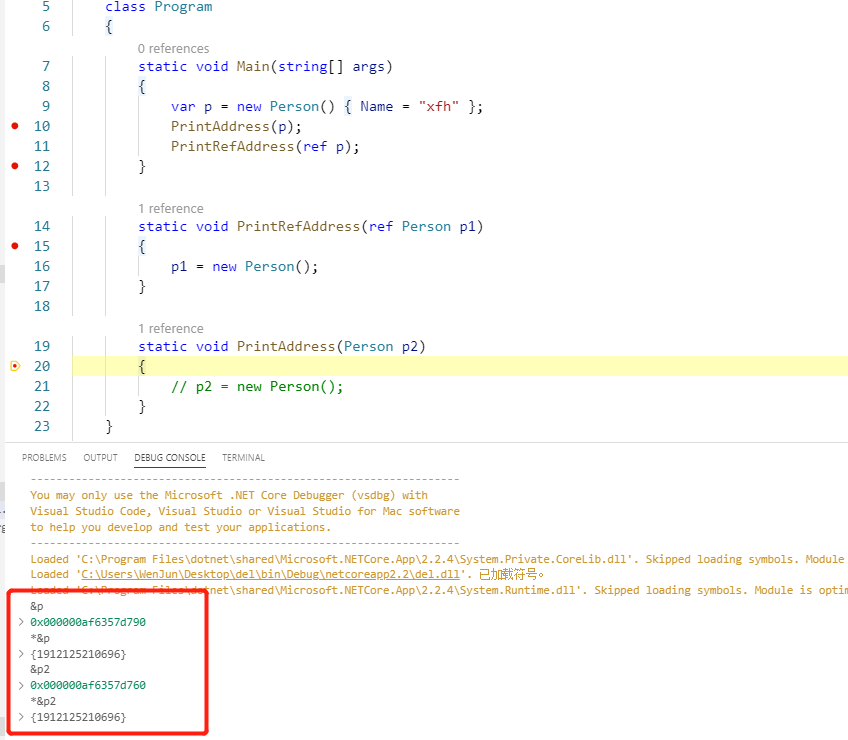
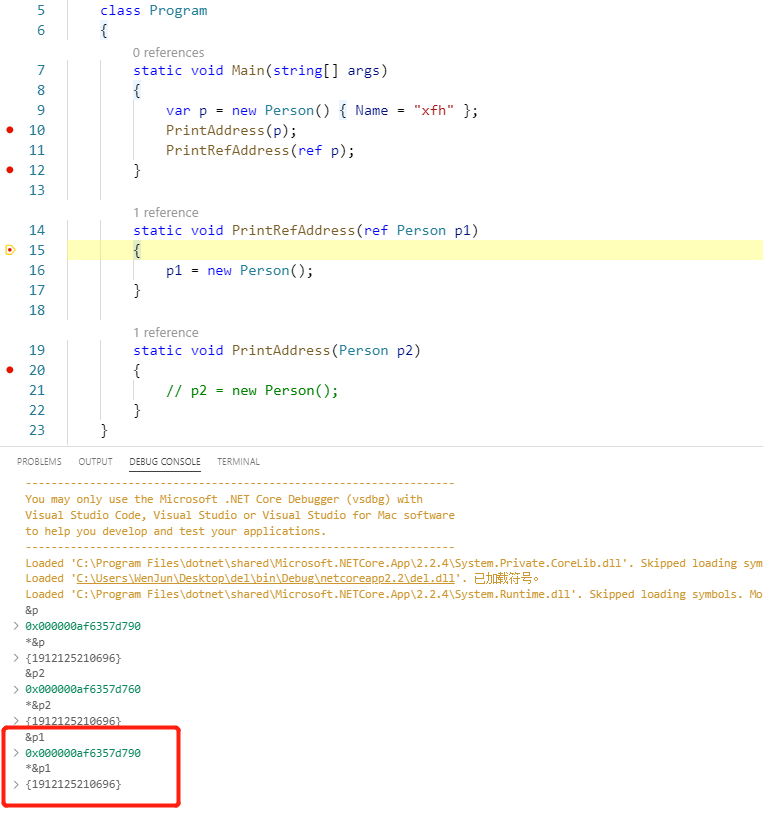

Passing Parameters (C# Programming Guide)
Method Parameters (C# Reference)
Python中的passed by assignment与.NET中的passing by reference、passing by value的更多相关文章
- 【python】实践中的总结——列表『持续更新中』
2016-04-03 21:02:50 python list的遍历 list[a::b] #从list[a] 开始,每b个得到一个元组,返回新的list 举个例子: >>> l ...
- 《Python自然语言处理》中文版-纠错【更新中。。。】
最近在看<Python自然语言处理>中文版这本书,可能由于是从py2.x到py3.x,加上nltk的更新的原因,或者作者的一些笔误,在书中很多代码都运行不能通过,下面我就整理一下一点有问题 ...
- Python在金融,数据分析,和人工智能中的应用
Python在金融,数据分析,和人工智能中的应用 Python最近取得这样的成功,而且未来似乎还会继续下去,这有许多原因.其中包括它的语法.Python开发人员可用的科学生态系统和数据分析库.易于 ...
- 《Python CookBook2》 第一章 文本 - 检查字符串中是否包含某字符集合中的字符 && 简化字符串的translate方法的使用
检查字符串中是否包含某字符集合中的字符 任务: 检查字符串中是否出现了某个字符集合中的字符 解决方案: 方案一: import itertools def containAny(seq,aset): ...
- python中print()函数的“,”与java中System.out.print()函数中的“+”
python中的print()函数和java中的System.out.print()函数都有着打印字符串的功能. python中: print("hello,world!") 输出 ...
- 用python在excel中读取与生成随机数写入excel中
今天是我第一次发博客,就关于python在excel中的应用作为我的第一篇吧. 具体要求是:在一份已知的excel表格中读取学生的学号与姓名,再将这些数据放到新的excel表中的第一列与第二列,最后再 ...
- python编程中的if __name__ == 'main与windows中使用多进程
if __name__ == 'main 一个python的文件有两种使用的方法,第一是直接作为程序执行,第二是import到其他的python程序中被调用(模块重用)执行. 因此if __name_ ...
- python之匿名函数以及在内置函数中的使用
一. 匿名函数 Python使用 lambda 来创建匿名函数.所谓匿名函数,它与用 def 关键字定义的函数相比,没有函数名称. 1.1 匿名函数定义及特点 语法: lambda [para1, p ...
- Python “No module named” 以及在Python2中可以导入,但在python3中却出现的原因
Python “No module named” 以及在Python2中可以导入,但在python3中却出现的原因 原因之1: 例如有这样的一个包和它的模块: Test __init__.py Mod ...
随机推荐
- 禁止页面被复制和禁止右键,一段样式一段JS就行了,无需复杂设定!
群里小伙伴经常问怎么禁止页面复制和右键,其实这个问题百度一下是很多资料的,我估计小伙伴都懒,所以这里统一回复下: 找到模板里面的</head>,在上面加如下代码就行了 <style ...
- 2.java容器的设计模式
目录 1.collection接口中的迭代器模式 2.迭代器模式 1.collection接口中的迭代器模式 迭代器分析: Iterator接口有hasNext().next(),remove()三个 ...
- 爬取动态html网页,requests+execjs
请求地址:https://g.hongshu.com/content/99269/15382723.html 网页内容为动态执行js所得 1.直接浏览器模拟 不用考虑页面的业务逻辑什么的,直接得到结果 ...
- JS基础语法---数组案例---9个练习
练习1:求数组中所有元素的和 var arr1 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; var sum = 0; for (var i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++ ...
- jsp表单更新数据库
和插入语句相似,表单传值,在另一个页面接收数据并连接数据库进行更新: 语句如下: <% request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); Stri ...
- python : html 调用本地python程序
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="gb2312"> <title> ...
- Microsoft Office自制安装指南 —Nusen_Liu
Microsoft Word 2010 正版下载安装步骤 版权来自:Nusen_Liu 1. 解压文件(推荐解压到当前文件夹,大神也可以自定义的)下载地址在第16步 (*^__^*) 2. 解 ...
- Android框架Volley之:ImageRequest请求实现图片加载
首先我们在项目中导入这个框架: implementation 'com.mcxiaoke.volley:library:1.0.19' 在AndroidManifest文件当中添加网络权限: < ...
- 【Android】Context的使用
Android开发经常需要使用Context来启动Activity,或者打开SharedPreferences,或者构建一个Dialog.最近老是用到getContext(),getApplicati ...
- Windows 10 路由表管理
基本管理命令: route print route命令基本格式: ROUTE [-f] [-p] [-|-] command [destination] [MASK netmask] [gateway ...
