random随机模块,time时间模块
random /随机模块:
作用: 在某个范围内取到每一个值得概率是相通的.
一.随机小数
random.random()
import random
print(random.random()) 0 - 1之内的随机小数.
print(random.random(0, 5)) 0 - 5 之间随机取小数
二.随机整数(重要等级: ***** )
random.randint()
import random
print(random.randint(1, 2))
==> [1, 8] randint的取值区间为左闭右闭形式. 是在包含8在内的范围内随机取整数.
random.randrange()
import random
print(random.randrange(1, 8))
==> [1 , 8) randrange的取值区间为左闭右开,是在不包括8在内的范围内选取整数.
print(random.randrange(1, 8, 2))
是指在不包括8的区间选取奇数.(1,3,5,7 四个数种随机选取一个)
三.随机抽取
随机抽取一个值: random.choice(1)
import random
lst = [1, 2, 4, 'aaa', ('wahaha', 'qq')]
ret = random.choice(lst) # 从列表中随机抽取一个
print(ret) # choice 返回的是一个字符串, chioces 返回的是一个列表
随机抽取多个: random.sample(索取对象的范围, 想要索取的个数)
import random
ret = random.sample(lst, 3)
print(ret) # 得到的结果是个列表, sample里面的的需要处理的对象放第一个参数位置,第二个参数位置放需要取的个数.
四. 打乱顺序
rando.shuffile(lst)
print(lst)
实 例:
生成六位随机验证码:
import random ses = '' # 6位验证码存放位置
for i in range(6): # 迭代6次, 使下面步骤运行6次,从而产生6位验证码
num = str(random.randrange(0, 9, 1))
# 此处是把每个数字取出一个,然后转成字符串形式,
# 数字的话不能直接添加到字符转钟
num1 = chr(random.randrange(65, 91, 1))
# ASCII码中大写字母是从65 - 91,
# 所以在得到准确数字以后再用chr()转成字母
num2 = chr(random.randrange(97, 123, 1))# 此处是小写字母,理论同上.
num3 = [num, num1, num2] # 都先添加到一个列表中,
sum4 = random.choice(num3) #然后再用choice从列表中随机抽取一个ses += sum4 每次得到的 1 位验证码添加到 ses 字符串中
print(ses)注意: 上面这种方法,num3 中出现数字的几率是三分之一.
函数版:
import random
def rand_cone(n = 6):
ses = ''
for i in range(n):
num = str(random.randrange(0, 9, 1))
num1 = chr(random.randrange(65, 91, 1))
num2 = chr(random.randrange(97, 123, 1))
num3 = [num, num1, num2]
sum4 = random.choice(num3)
ses += sum4
print(ses) rand_cone()# 数字/数字+字母
# def rand_code(n=6 , alph_flag = True):
# code = ''
# for i in range(n):
# rand_num = str(random.randint(0,9))
# if alph_flag:
# rand_alph = chr(random.randint(97,122))
# rand_alph_upper = chr(random.randint(65,90))
# rand_num = random.choice([rand_num,rand_alph,rand_alph_upper])
# code += rand_num
# return code
#
# ret = rand_code(n = 4)
# print(ret)# ***** 永远不要创建一个和你知道的模块同名的文件名
time/时间模块
时间模块分为:
1, 时间戳时间,(给机器用的)
格林威治时间,float数据类型 给机器用的
# 英国伦敦的时间 1970.1.1 0:0:0
# 北京时间 1970.1.1 8:0:0
# 1533693120.3467407
2, 结构化时间,(上下两种格式的中间状态)
时间对象 能够通过.属性名来获取对象中的值
3, 格式化时间.(给人看的)
可以根据你需要的格式 来显示时间
1,时间戳时间:
import time
print(time.time())
2, 结构化时间
# time_obj = time.localtime()
# print(time_obj)
# print(time_obj.tm_year)
# print(time_obj.tm_mday)
| 索引(Index) | 属性(Attribute) | 值(Values) |
| 0 | tm_year(年) | 比如2011 |
| 1 | tm_mon(月) | 1 - 12 |
| 2 | tm_mday(日) | 1 - 31 |
| 3 | tm_hour(时) | 0 - 23 |
| 4 | tm_min(分) | 0 - 59 |
| 5 | tm_sec(秒) | 0 - 60 |
| 6 | tm_wday(weekday) | 0 - 6(0表示周一) |
| 7 | tm_yday(一年中的第几天) | 1 - 366 |
| 8 | tm_isdst(是否是夏令时) | 默认为0 |
3,格式化时间:
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))
%y 两位数的年份表示(00-99)
%Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999)
%m 月份(01-12)
%d 月内中的一天(0-31)
%H 24小时制小时数(0-23)
%I 12小时制小时数(01-12)
%M 分钟数(00=59)
%S 秒(00-59)
%a 本地简化星期名称
%A 本地完整星期名称
%b 本地简化的月份名称
%B 本地完整的月份名称
%c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示
%j 年内的一天(001-366)
%p 本地A.M.或P.M.的等价符
%U 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期天为星期的开始
%w 星期(0-6),星期天为星期的开始
%W 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期一为星期的开始
%x 本地相应的日期表示
%X 本地相应的时间表示
%Z 当前时区的名称
%% %号本身python中时间日期格式化符号:
小结:时间戳是计算机能够识别的时间;时间字符串是人能够看懂的时间;元组则是用来操作时间的
几种格式之间的转换
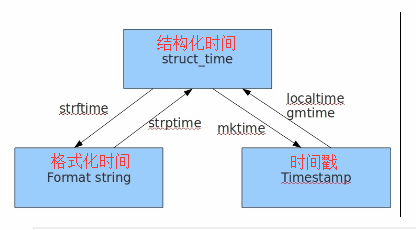
time.gmtime(时间戳) #UTC时间,与英国伦敦当地时间一致
#time.localtime(时间戳) #当地时间。例如我们现在在北京执行这个方法:与UTC时间相差8小时,UTC时间+8小时 = 北京时间
>>>time.gmtime(1500000000)
time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=14, tm_hour=2, tm_min=40, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=195, tm_isdst=0)
>>>time.localtime(1500000000)
time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=14, tm_hour=10, tm_min=40, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=195, tm_isdst=0)
从时间戳时间转化到 格式化时间:
import time
a = time.time()
f = time.localtime(a)
c = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', f)
print(c)# 计算本月一号的时间戳时间
# 结构化时间
# struct_time = time.localtime()
# struct_time = time.strptime('%s-%s-1'%(struct_time.tm_year,struct_time.tm_mon),'%Y-%m-%d')
# print(time.mktime(struct_time))
# 格式化时间
# ret = time.strftime('%Y-%m-1')
# struct_time = time.strptime(ret,'%Y-%m-%d')
# print(time.mktime(struct_time))
random随机模块,time时间模块的更多相关文章
- python常用模块之时间模块
python常用模块之时间模块 python全栈开发时间模块 上次的博客link:http://futuretechx.com/python-collections/ 接着上次的继续学习: 时间模块 ...
- python学习之老男孩python全栈第九期_day019知识点总结——collections模块、时间模块、random模块、os模块、sys模块
一. collections模块 在内置数据类型(dict.list.set.tuple)的基础上,collections模块还提供了几个额外的数据类型:namedtuple.deque.Counte ...
- random、os、时间模块
一.random 模块 1.随机小数 random.random() #产生大于0且小于1之间的小数 random.uniform(1,3) #产生1到3之间的随机小数 2.随机整数 rand ...
- collections模块、时间模块、random模块、os模块、sys模块、序列化模块、subprocess模块
一.collections模块 1.其他数据类型 在内置数据类型(str.dict.list.tuple.set)的基础上,collections模块还提供了了几个额外的数据类型:Counter.de ...
- 023.Python的随机模块和时间模块
一 random 随机模块 1.1 获取随机0-1之间的小数(左闭右开) 0<= x < 1 import random res = random.random() print(res) ...
- python语言(四)关键字参数、内置函数、导入第三方模块、OS模块、时间模块
一.可变参数 定义函数时,有时候我们不确定调用的时候会传递多少个参数(不传参也可以).此时,可用包裹(packing)位置参数(*args),或者包裹关键字参数(**kwargs),来进行参数传递,会 ...
- python模块之时间模块
一.time模块 表示时间的方式分为: 1时间戳(timestamp) 2格式化化的时间字符串(format string) 3结构化时间(struct_time) import time print ...
- day17.json模块、时间模块、zipfile模块、tarfile模块
一.json模块 """ 所有的编程语言都能够识别的数据格式叫做json,是字符串 能够通过json序列化成字符串与如下类型: (int float bool str l ...
- 时间模块 time 随机模块random os模块,sys模块
时间模块 time #时间模块 import time #三种格式 #时间戳时间:是一个浮点数,以秒为单位,计算机用语 #结构化时间 :是一个元组 #用于中间转换 #格式化时间:str数据类型, 用 ...
随机推荐
- 129 - Krypton Factor
/*UVa129 - Krypton Factor --回溯问题.看例子可知道确定该字符串是按照从左到右依次考虑每个位置,当前位置填不上所有的字符时,需要回溯. -- */ #define _CRT_ ...
- ubuntu live cd修复grub引导项
1. 通过Ubuntu Live CD(安装盘,选择try Ubuntu)进入Ubuntu系统 打开终端,依次进行如下操作: 1. sudo fdisk -l 出现如下界面: 2. 然后会看到,有好多 ...
- 【OpenGL4.0】GLSL渲染语言入门与VBO、VAO使用:绘制一个三角形 【转】
http://blog.csdn.net/xiajun07061225/article/details/7628146 以前都是用Cg的,现在改用GLSL,又要重新学,不过两种语言很多都是相通的. 下 ...
- Ubuntu启动sshd服务
1.Ubuntu主机安装ssh相关服务 openssh-client openssh-server 方法: sudo apt-get install openssh-client openssh-se ...
- EffectiveJava(12)考虑实现Comparable接口
考虑实现Comparable接口 compareTo方法 Comparable接口的唯一方法,允许进行简单的等同性比较,允许执行顺序比较 Comparable接口被所有值类实现.所以如果一个值类有非常 ...
- Java模式的秘密--java常用的几种模式
要学习设计模式,首先要明白设计模式,就是为实现某一种或某一组功能提供的代码编码方式.它没有固定的套路,只有约定俗成的风格.所有编码者可以根据已有的设计模式开放思维,设计出自己的设计模式,也会在无意中使 ...
- 简单的图片处理servlet
好久没写博客了.近期做了一个比較有趣的商城项目,里面的业务还真的非常复杂,好在做了特殊的处理之后商城也能正常的使用了. 可是没中不足的就是图片目录和项目掺杂在一块,实在有些难以维护.之后找了点资料就搞 ...
- 倍福TwinCAT(贝福Beckhoff)基础教程3.1 TwinCAT如何编写简单的计算器
把编写简单计算器作为入门的第一个范例程序,主要是因为比较简单,而且综合了HMI,数据类型,数据转换,PRG和FBD等功能块的混合等知识,个人认为还是比较适合用来快速上手的.由于是第一个范例,所以视频教 ...
- JAVA Eclipse如何开发Android的多页面程序
Fragment可以认为是Activity的一个界面的组成部分,Fragment必须依存于Activity. 在layout文件夹中新建一个xml文件,布局方式采用RelativeLayout,注 ...
- iOS block用作属性封装代码
@property (copy, nonatomic) void (^actionBlock)(); @property (copy, nonatomic) void (^actionWithPapa ...
