浅谈Objeact.clone克隆(纯个人理解,如有错误请指正)
现在先来看一下jdk给出的Object.clone源码和注释
/**
* Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
* will be true, and that the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
* <p>
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
* <p>
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
* need to be modified.
* <p>
* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
* <p>
* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
* @return a clone of this instance.
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@code clone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
*/
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
克隆对象需要继承Cloneable接口并重写Object.clone()方法,看一下bean的代码
public class TestBean implements Cloneable{
private Long id;
private String code;
private String msg;
private TestCloneBean testCloneBean = new TestCloneBean();
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public TestCloneBean getTestCloneBean() {
return testCloneBean;
}
public void setTestCloneBean(TestCloneBean testCloneBean) {
this.testCloneBean = testCloneBean;
}
@Override
protected TestBean clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (TestBean)super.clone();
}
}
克隆一个全新的对象,接下来看一下原本对象和新的克隆对象有什么区别
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TestBean bean = new TestBean();
TestBean copyBean = bean.clone();
System.out.println("==判断:" + (bean == copyBean));
System.out.println("class判断:" + (bean.getClass() == copyBean.getClass()));
System.out.println("hasCode判断:" + (bean.hashCode() == copyBean.hashCode()));
System.out.println("equals判断:" + (bean.equals(copyBean)));
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
看一下结果
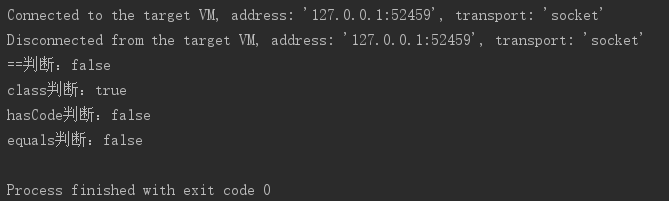
除了.getClass()相等,其余皆是不一样的,是一个全新的对象。
-----------------------------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------------------------
那克隆对象里面包含对象呢?我们来看一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TestBean bean = new TestBean();
TestCloneBean testCloneBean = new TestCloneBean(1L,"1","测试");
bean.setTestCloneBean(testCloneBean);
TestBean copyBean = (TestBean) bean.clone();
System.out.println("==判断:" + (bean.getTestCloneBean() == copyBean.getTestCloneBean()));
System.out.println("class判断:" + (bean.getTestCloneBean().getClass() == copyBean.getTestCloneBean().getClass()));
System.out.println("hasCode判断:" + (bean.getTestCloneBean().hashCode() == copyBean.getTestCloneBean().hashCode()));
System.out.println("equals判断:" + (bean.getTestCloneBean().equals(copyBean.getTestCloneBean())));
System.out.println("bean:{"+bean.getTestCloneBean().toString()+"}");
System.out.println("bean:{"+copyBean.getTestCloneBean().toString()+"}");
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
#1 属性testCloneBean未重写clone方法,结果是

#2 当对象属性也重写了clone方法后
@Override
public TestCloneBean clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (TestCloneBean) super.clone();
}
结果是
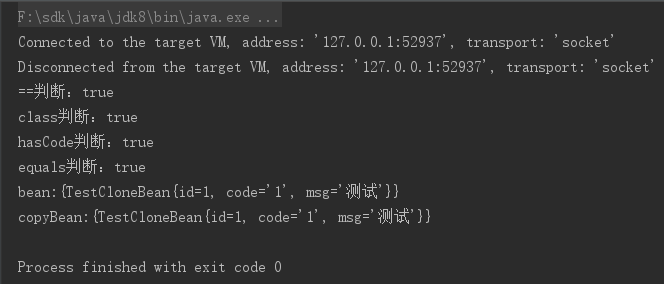
很诧异,还是原来的地址,说明对象属性是没有被克隆的,那是不是对象没有序列化呢?等我加上序列化试一下
额~事实证明,序列化还是一样的,被克隆的对象属性是一样的!
浅谈Objeact.clone克隆(纯个人理解,如有错误请指正)的更多相关文章
- 浅谈MySQL引擎(纯个人理解,如有错误请指正)
MySQL有很多引擎,MyISAM.InnoDB.MERGE.MEMORY(HEAP).BDB(BerkeleyDB).EXAMPLE.FEDERATED...等等 比较常用的就是InnoDB和MyI ...
- [原创]浅谈在创业公司对PMF的理解
[原创]浅谈在创业公司对PMF的理解 在创业时,大多数人都常谈一个词叫"MVP“,但PMF谈的比较少,PMF在创业公司尤为重要,以下谈谈个人一些看法. 1.什么是PMF? 创业公司:一种是找 ...
- [原创]浅谈在创业公司对MVP的理解
[原创]浅谈在创业公司对MVP的理解 目前自已所处的公司类似一个创业平台,我们内部会不断的去孵化不同方向的产品,产品经理经常谈到的一个词就是MVP,所以有必需要去了解下什么是MVP? 1 什么是MVP ...
- 浅谈对java中锁的理解
在并发编程中,经常遇到多个线程访问同一个 共享资源 ,这时候作为开发者必须考虑如何维护数据一致性,在java中synchronized关键字被常用于维护数据一致性.synchronized机制是给共享 ...
- 浅谈EM算法的两个理解角度
http://blog.csdn.net/xmu_jupiter/article/details/50936177 最近在写毕业论文,由于EM算法在我的研究方向中经常用到,所以把相关的资料又拿出来看了 ...
- 浅谈Javascript 浅拷贝和深拷贝的理解
javascript中存储对象都是存地址的. 浅拷贝:浅拷贝是都指向同一块内存区块,浅拷贝共用同一内存地址,你改值我也变.如果拷贝的对象里面的值是一个对象或者数组,它就是浅拷贝,拷贝的知识引用地址. ...
- 干货,阿里P8浅谈对java线程池的理解(面试必备)
线程池的概念 线程池由任务队列和工作线程组成,它可以重用线程来避免线程创建的开销,在任务过多时通过排队避免创建过多线程来减少系统资源消耗和竞争,确保任务有序完成:ThreadPoolExecutor ...
- 浅谈对ST表的一些理解
今天打了人生第一道ST表题(其实只是ST表跑得最快); ST表是一种用来解决RMQ问题的利器... 大体操作有两步: 第一部分nlogn预处理 第二部分O(1)询问 预处理就是运用倍增+区间动规 ST ...
- 浅谈个人对RAID技术的理解
RAID,字面意思为一种廉价的冗余磁盘阵列,它是通过将大量的磁盘分组,实现了数据冗余,目的是为了保护数据.RAID现已经应用于计算机各个领域.它的优点是降低了工作成本并提高了效率,并且使系统有稳定的运 ...
随机推荐
- java持有对象【2】ArrayList容器续解
此为JDK API1.6.0对ArrayList的解释. ArrayList 使用java泛型创建类很复杂,但是应用预定义的泛型很简单.例如,要想定义用来保存Apple对象的ArrayList,可以声 ...
- AWS CSAA -- 04 AWS Object Storage and CDN - S3 Glacier and CloudFront(三)
021 Storage Gateway 022 Snowball 023 Snowball - Lab 024 S3 Transfer Acceleration
- 用JS实现控制浏览器F12与右键功能
本文出至:新太潮流网络博客 用JS实现控制浏览器F12与右键功能,防止恶意窃取代码,或其他直接复制进去就好 //禁用右键 document.oncontextmenu = function () { ...
- CSS| 解决子级用css float浮动 而父级div没高度不能自适应高度
解决子级用css float浮动 而父级div没高度不能自适应高度 解决子级对象使用css float浮动 而父级div不能自适应高度,不能被父级内容撑开解决方法,父级div没有高度解决方法. 最外层 ...
- 转:asp.net mvc下的多语言方案 包含Html,Javascript和图片
可以不使用微软的Resource文件,而是将所有的词汇放入在一个txt的词典之中,便于维护. 步骤如下: 1)在整个程序的入口处global.asax.cs加入函数 private void Read ...
- 解决:Tomcat 局域网IP地址 访问不了
解决:Tomcat 局域网IP地址 访问不了 2014年10月17日 ⁄ 综合 ⁄ 共 1000字 ⁄ 字号 小 中 大 ⁄ 评论关闭 如果连最基本的localhost:8080都失败的话. 原因就一 ...
- 使用Index()+Match()函数实现更为灵活的VLookUp()
上一篇 http://www.cnblogs.com/-SANG/p/8407017.html 文章中已经介绍了vlookup的用法. 今天要使用index+match实现更为灵活的vlookup 先 ...
- 1-100求和 sum(range(101))
print(sum(range(101))) s = 0for i in range(101): s += iprint(s)
- NOIP2018考前抱佛脚——搜索复习
目录 搜索 DFS 例1 P1101 单词方阵 题目描述 输入输出格式 输入输出样例 标程 例2 P1605 迷宫 题目背景 输入输出格式 输入输出样例 标程 例3 P1019 单词接龙 题目描述 输 ...
- 【Ansible 文档】【译文】动态inventory
Dynamic Inventory 动态inventory 配置管理系统的用户经常想要保存inventory到不同的软件系统中.Ansible提供了一个基本的基于文本的系统,正如inventory中描 ...
