Notes for uc/OS-III User Guide
1. Architecture
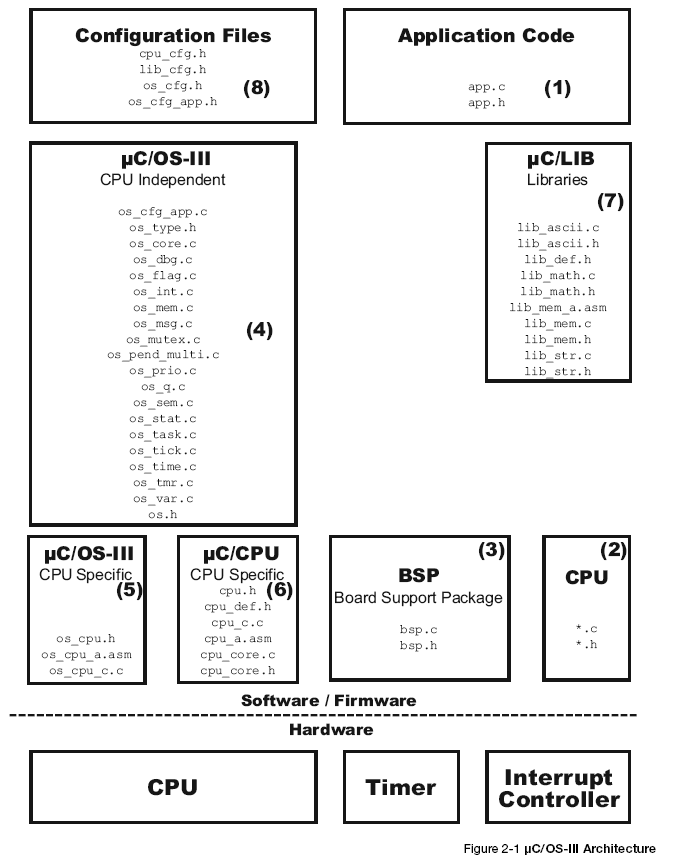
F2-1(1) The application code consists of project or product files. For convenience, these are simply called app.c and app.h, however an application can contain any number of files that do not have to be called app.*. The application code is typically where one would find the main().
F2-1(2) Semiconductor manufacturers often provide library functions in source form for accessing the peripherals on their CPU or MCU. These libraries are quite useful and often save valuable time. Since there is no naming convention for these files, *.c and *.h are assumed.
F2-1(3) The Board Support Package (BSP) is code that is typically written to interface to peripherals on a target board. For example such code can turn on and off LEDs, turn on and off relays, or read switches, temperature sensors, and more.
F2-1(4) This is the μC/OS-III processor-independent code. This code is written in highly portable ANSI C.
F2-1(5) This is the μC/OS-III code that is adapted to a specific CPU architecture and is called a port. μC/OS-III has its roots in μC/OS-II and benefits from being able to use most of the 45 or so ports available for μC/OS-II. μC/OS-II ports, however, will require small changes to work with μC/OS-III. These changes are described in Appendix C, “Migrating from μC/OS-II to μC/OS-III” on page 697.
F2-1(6) At Micriμm, we encapsulate CPU functionality. These files define functions to disable and enable interrupts, CPU_??? data types to be independent of the CPU and compiler used, and many more functions.
F2-1(7) μC/LIB is of a series of source files that provide common functions such as memory copy, string, and ASCII-related functions. Some are occasionally used to replace stdlib functions provided by the compiler. The files are provided to ensure that they are fully portable from application to application and especially, from compiler to compiler. μC/OS-III does not use these files, but μC/CPU does.
F2-1(8) Configuration files are used to define μC/OS-III features (os_cfg.h) to include in the application, specify the size of certain variables and data structures expected by μC/OS-III (os_cfg_app.h), such as idle task stack size, tick rate, size of the message pool, configure the μC/CPU features available to the application programmer (cpu_cfg.h) and also configure μC/LIB options (lib_cfg.h).
Notes for uc/OS-III User Guide的更多相关文章
- uc/os iii移植到STM32F4---IAR开发环境
也许是先入为主的原因,时钟用不惯Keil环境,大多数的教程都是拿keil写的,尝试将官方的uc/os iii 移植到IAR环境. 1.首先尝试从官网上下载的官方移植的代码,编译通过,但是执行会报堆栈溢 ...
- uC/OS - III 移植 IAR平台
关于移植uC/OS-III 网上已经有很多教程了此处只是做个记录 首先下载源码然后解压得到下面的文件: 然后在模版工程里新建各种文件夹: 最后全部都添加进工程: OK了,编译一下,惊呆了,竟然 0错误 ...
- uC/OS II原理分析及源码阅读(一)
uC/OS II(Micro Control Operation System Two)是一个可以基于ROM运行的.可裁减的.抢占式.实时多任务内核,具有高度可移植性,特别适合于微处理器和控制器,是和 ...
- uc/os 任务删除
问题描述: uc/os 任务删除 问题解决: uc/os任务删除流程图 具体代码 注: 如上是关中断,以及取消优先级对应的就绪标志 关中断代码为: 取消就绪标志,实际上是将就绪表中指定 ...
- uc/os任务创建
问题描述: uc/os中任务创建 问题解决: 创建一个任务,任务从无到有.任务创建函数分两种, 一种是基本的创建函数OSTaskCreate, 另一种是扩展的任务创建函数OSTaskCrea ...
- uC/OS 的任务调度解析 (转)
uC/OS 的任务调度解析 1.任务调度器启动之后(初始化,主要是TCB的初始化),就可以创建任务,开始任务调度了,实际上第一个任务准确的说不是进行任务切换,而是进行启动当前最高优先级任务.uC/OS ...
- 关于uC/OS的简单学习(转)
1.微内核 与Linux的首要区别是,它是一个微内核,内核所实现的功能非常简单,主要包括: 一些通用函数,如TaskCreate(),OSMutexPend(),OSQPost()等. 中断处理函数, ...
- STM32F40G-EVAL_UC/OS III
micrum官网下载uc/os程序包: 包含文件cotex_M4.h:
- 【原创】uC/OS 中LES BX,DWORD PTR DS:_OSTCBCur的作用及原理
LES BX, DWORD PTR DS:_OSTCBCur ;OSTCBCur->OSTCBStkPtr = SS:SP!!! ], SS ;将当前SS(栈的基地址)寄存器值存放至当前任务控制 ...
- 【原创】uC/OS II 任务切换原理
今天学习了uC/OS II的任务切换,知道要实现任务的切换,要将原先任务的寄存器压入任务堆栈,再将新任务中任务堆栈的寄存器内容弹出到CPU的寄存器,其中的CS.IP寄存器没有出栈和入栈指令,所以只能引 ...
随机推荐
- golang如何使用指针灵活操作内存?unsafe包原理解析
Hi 你好,我是k哥.一个大厂工作6年,还在继续搬砖的后端程序员. 我们都知道,C/C++提供了强大的万能指针void*,任何类型的指针都可以和万能指针相互转换.并且指针还可以进行加减等算数操作.那么 ...
- bs4解析-优美图库
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup url = 'http://www.umeituku.com/bizhitupian/meinvbizhi/ ...
- 升级到 MySQL 8.4,MySQL 启动报错:io_setup() failed with EAGAIN
问题 最近碰到一个 case,一台主机上,部署了多个实例.之前使用的是 MySQL 8.0,启动时没有任何问题.但升级到 MySQL 8.4 后,部分实例在启动时出现了以下错误. [Warning] ...
- package-lock.json 文件
今天有同事找到我说,本地js 编译不过,编译不过的代码如下 const host = window?.location?.host || 'localhost'; 是option chaining, ...
- Nuxt框架中内置组件详解及使用指南(五)
title: Nuxt框架中内置组件详解及使用指南(五) date: 2024/7/10 updated: 2024/7/10 author: cmdragon excerpt: 摘要:本文详细介绍了 ...
- 2 - 【RocketMQ 系列】CentOS 7.6 安装部署RocketMQ
二.开始安装部署RocketMQ 官方网站:https://rocketmq.apache.org/ 各版本要求: 1.版本选取 下载地址: https://github.com/apache/roc ...
- [项目自荐] 交叉编译njs并使用Nginx搭建自由的个人网盘:vList5
这个博客好久没有打理了,最近才想起来 这篇文章是以下 5 篇文章的组合,希望这个免费的项目能实现他的初衷吧 vList5:部署指南 vList5.3 全面加密,从我做起 njs 从入门(交叉编译)到入 ...
- [oeasy]python0079_控制序列_光标位置设置_ESC_逃逸字符_CSI
光标位置 回忆上次内容 上次我们研究的比较杂 类型转化 进制转化 捕获异常 版本控制 生成帮助文档 变量的常用类型 变量的生命周期控制 数据类型主要研究了两个 字符串 str 整型数字 int ...
- oeasy教您玩转vim - 30 - # 屏位行号
屏位行号 回忆上节课内容 上次我们主要讲的翻页 :set scrolloff=2 控制上下留天留地 上下翻页(这个最常用) ctrl + f 向下一屏 ctrl + b 向上一屏 上下移屏一行 c ...
- 深入浅出分析最近火热的Mem0个性化AI记忆层
最近Mem0横空出世,官方称之为PA的记忆层,The memory layer for Personalized AI,有好事者还称这个是RAG的替代者,Mem0究竟为何物,背后的原理是什么,我们今天 ...
