Go runtime 调度器精讲(五):调度策略
原创文章,欢迎转载,转载请注明出处,谢谢。
0. 前言
在 第四讲 我们介绍了 main goroutine 是如何运行的。其中针对 main goroutine 介绍了调度函数 schedule 是怎么工作的,对于整个调度器的调度策略并没有介绍,这点是不完整的,这一讲会完善调度器的调度策略部分。
1. 调度时间点
runtime.schedule 实现了调度器的调度策略。那么对于调度时间点,查看哪些函数调用的 runtime.schedule 即可顺藤摸瓜理出调度器的调度时间点,如下图:
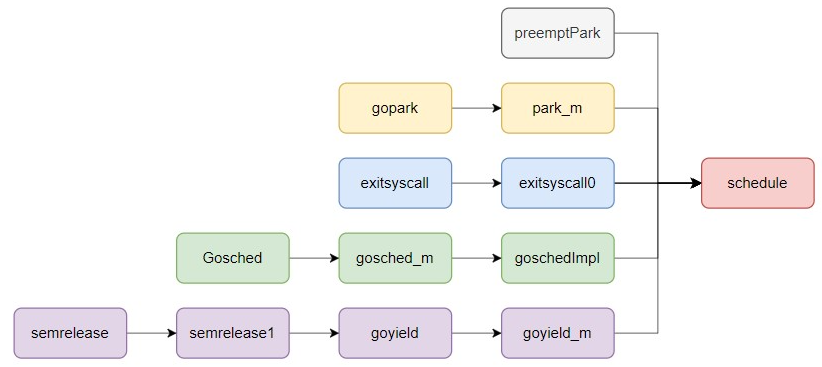
调度时间点不是本讲的重点,这里有兴趣的同学可以顺藤摸瓜,摸摸触发调度时间点的路径,这里就跳过了。
2. 调度策略
调度策略才是我们的重点,进到 runtime.schedule:
// One round of scheduler: find a runnable goroutine and execute it.
// Never returns.
func schedule() {
mp := getg().m // 获取当前执行线程
top:
pp := mp.p.ptr() // 获取执行线程绑定的 P
pp.preempt = false
// Safety check: if we are spinning, the run queue should be empty.
// Check this before calling checkTimers, as that might call
// goready to put a ready goroutine on the local run queue.
if mp.spinning && (pp.runnext != 0 || pp.runqhead != pp.runqtail) {
throw("schedule: spinning with local work")
}
gp, inheritTime, tryWakeP := findRunnable() // blocks until work is available
...
execute(gp, inheritTime) // 执行找到的 goroutine
}
runtime.schedule 的重点在 findRunnable()。findRunnable() 函数很长,为避免影响可读性,这里对大部分流程做了注释,后面在有重点的加以介绍。进入 findRunnable():
// Finds a runnable goroutine to execute.
// Tries to steal from other P's, get g from local or global queue, poll network.
// tryWakeP indicates that the returned goroutine is not normal (GC worker, trace
// reader) so the caller should try to wake a P.
func findRunnable() (gp *g, inheritTime, tryWakeP bool) {
mp := getg().m // 获取当前执行线程
top:
pp := mp.p.ptr() // 获取线程绑定的 P
...
// Check the global runnable queue once in a while to ensure fairness.
// Otherwise two goroutines can completely occupy the local runqueue
// by constantly respawning each other.
if pp.schedtick%61 == 0 && sched.runqsize > 0 {
lock(&sched.lock)
gp := globrunqget(pp, 1)
unlock(&sched.lock)
if gp != nil {
return gp, false, false
}
}
// local runq
if gp, inheritTime := runqget(pp); gp != nil { // 从 P 的本地队列中获取 goroutine
return gp, inheritTime, false
}
// global runq
if sched.runqsize != 0 { // 如果本地队列获取不到就判断全局队列中有无 goroutine
lock(&sched.lock) // 如果有的话,为全局变量加锁
gp := globrunqget(pp, 0) // 从全局队列中拿 goroutine
unlock(&sched.lock) // 为全局变量解锁
if gp != nil {
return gp, false, false
}
}
// 如果全局队列中没有 goroutine 则从 network poller 中取 goroutine
if netpollinited() && netpollWaiters.Load() > 0 && sched.lastpoll.Load() != 0 {
...
}
// 如果 network poller 中也没有 goroutine,那么尝试从其它 P 中偷 goroutine
// Spinning Ms: steal work from other Ps.
//
// Limit the number of spinning Ms to half the number of busy Ps.
// This is necessary to prevent excessive CPU consumption when
// GOMAXPROCS>>1 but the program parallelism is low.
// 如果下面两个条件至少有一个满足,则进入偷 goroutine 逻辑
// 条件 1: 当前线程是 spinning 自旋状态
// 条件 2: 当前活跃的 P 要远大于自旋的线程,说明需要线程去分担活跃线程的压力,不要睡觉了
if mp.spinning || 2*sched.nmspinning.Load() < gomaxprocs-sched.npidle.Load() {
if !mp.spinning { // 因为是两个条件至少满足一个即可,这里首先判断当前线程是不是自旋状态
mp.becomeSpinning() // 如果不是,更新线程的状态为自旋状态
}
gp, inheritTime, tnow, w, newWork := stealWork(now) // 偷 goroutine
if gp != nil {
// Successfully stole.
return gp, inheritTime, false // 如果 gp 不等于 nil,表示偷到了,返回偷到的 goroutine
}
if newWork {
// There may be new timer or GC work; restart to
// discover.
goto top // 如果 gp 不等于 nil,且 network 为 true,则跳到 top 标签重新找 goroutine
}
now = tnow
if w != 0 && (pollUntil == 0 || w < pollUntil) {
// Earlier timer to wait for.
pollUntil = w
}
}
...
if sched.runqsize != 0 { // 偷都没偷到,还要在找一遍全局队列,防止偷的过程中,全局队列又有 goroutine 了
gp := globrunqget(pp, 0)
unlock(&sched.lock)
return gp, false, false
}
if !mp.spinning && sched.needspinning.Load() == 1 { // 在判断一遍,如果 mp 不是自旋状态,且 sched.needspinning == 1 则更新 mp 为自旋,调用 top 重新找一遍 goroutine
// See "Delicate dance" comment below.
mp.becomeSpinning()
unlock(&sched.lock)
goto top
}
// 实在找不到 goroutine,表明当前线程多, goroutine 少,准备挂起线程
// 首先,调用 releasep 取消线程和 P 的绑定
if releasep() != pp {
throw("findrunnable: wrong p")
}
...
now = pidleput(pp, now) // 将解绑的 P 放到全局空闲队列中
unlock(&sched.lock)
wasSpinning := mp.spinning // 到这里 mp.spinning == true,线程处于自旋状态
if mp.spinning {
mp.spinning = false // 设置 mp.spinning = false,这是要准备休眠了
if sched.nmspinning.Add(-1) < 0 { // 将全局变量的自旋线程数减 1,因为当前线程准备休眠,不偷 goroutine 了
throw("findrunnable: negative nmspinning")
}
...
}
stopm() // 线程休眠,直到唤醒
goto top // 能执行到这里,说明线程已经被唤醒了,继续找一遍 goroutine
}
看完线程的调度策略我都要被感动到了,何其的敬业,穷尽一切方式去找活干,找不到活,休眠之前还要在找一遍,真的是劳模啊。
大致流程是比较清楚的,我们把其中一些值得深挖的部分在单拎出来。
首先,从本地队列中找 goroutine,如果找不到则进入全局队列找,这里如果看 gp := globrunqget(pp, 0) 可能会觉得疑惑,从全局队列中拿 goroutine 为什么要把 P 传进去,我们看这个函数在做什么:
// Try get a batch of G's from the global runnable queue.
// sched.lock must be held. // 注释说的挺清晰了,把全局队列的 goroutine 放到 P 的本地队列
func globrunqget(pp *p, max int32) *g {
assertLockHeld(&sched.lock)
if sched.runqsize == 0 {
return nil
}
n := sched.runqsize/gomaxprocs + 1 // 全局队列是线程共享的,这里要除 gomaxprocs 平摊到每个线程绑定的 P
if n > sched.runqsize {
n = sched.runqsize // 执行到这里,说明 gomaxprocs == 1
}
if max > 0 && n > max {
n = max
}
if n > int32(len(pp.runq))/2 {
n = int32(len(pp.runq)) / 2 // 如果 n 比本地队列长度的一半要长,则 n == len(P.runq)/2
}
sched.runqsize -= n // 全局队列长度减 n,准备从全局队列中拿 n 个 goroutine 到 P 中
gp := sched.runq.pop() // 把全局队列队头的 goroutine 拿出来,这个 goroutine 是要返回的 goroutine
n-- // 拿出了一个队头的 goroutine,这里 n 要减 1
for ; n > 0; n-- {
gp1 := sched.runq.pop() // 循环拿全局队列中的 goroutine 出来
runqput(pp, gp1, false) // 将拿出的 goroutine 放到全局队列中
}
return gp
}
调用 globrunqget 说明本地队列没有 goroutine 要从全局队列拿,那么就可以把全局队列中的 goroutine 放到 P 中,提高了全局队列 goroutine 的优先级。
如果全局队列也没找到 goroutine,在从 network poller 找,如果 network poller 也没找到,则准备进入自旋,从别的线程的 P 那里偷活干。我们看线程是怎么偷活的:
// stealWork attempts to steal a runnable goroutine or timer from any P.
//
// If newWork is true, new work may have been readied.
//
// If now is not 0 it is the current time. stealWork returns the passed time or
// the current time if now was passed as 0.
func stealWork(now int64) (gp *g, inheritTime bool, rnow, pollUntil int64, newWork bool) {
pp := getg().m.p.ptr() // pp 是当前线程绑定的 P
ranTimer := false
const stealTries = 4 // 线程偷四次,每次都要随机循环一遍所有 P
for i := 0; i < stealTries; i++ {
stealTimersOrRunNextG := i == stealTries-1
for enum := stealOrder.start(fastrand()); !enum.done(); enum.next() { // 为保证偷的随机性,随机开始偷 P。随机开始,后面每个 P 都可以轮到
...
p2 := allp[enum.position()] // 从 allp 中获取 P
if pp == p2 {
continue // 如果获取的是当前线程绑定的 P,则继续循环下一个 P
}
...
// Don't bother to attempt to steal if p2 is idle.
if !idlepMask.read(enum.position()) { // 判断拿到的 P 是不是 idle 状态,如果是,表明 P 还没有 goroutine,跳过它,偷下一家
if gp := runqsteal(pp, p2, stealTimersOrRunNextG); gp != nil { // P 不是 idle,调用 runqsteal 偷它!
return gp, false, now, pollUntil, ranTimer
}
}
}
}
// No goroutines found to steal. Regardless, running a timer may have
// made some goroutine ready that we missed. Indicate the next timer to
// wait for.
return nil, false, now, pollUntil, ranTimer
}
线程随机的偷一个可偷的 P,偷 P 的实现在 runqsteal,查看 runqsteal 怎么偷的:
// Steal half of elements from local runnable queue of p2
// and put onto local runnable queue of p.
// Returns one of the stolen elements (or nil if failed). // 给宝宝饿坏了,直接偷一半的 goroutine 啊,够狠的!
func runqsteal(pp, p2 *p, stealRunNextG bool) *g {
t := pp.runqtail // t 指向当前 P 本地队列的队尾
n := runqgrab(p2, &pp.runq, t, stealRunNextG) // runqgrab 把 P2 本地队列的一半 goroutine 拿到 P 的 runq 队列中
if n == 0 {
return nil
}
n--
gp := pp.runq[(t+n)%uint32(len(pp.runq))].ptr() // 把偷到的本地队列队尾的 goroutine 拿出来
if n == 0 {
return gp // 如果只偷到了这一个,则直接返回。有总比没有好
}
h := atomic.LoadAcq(&pp.runqhead) // load-acquire, synchronize with consumers
if t-h+n >= uint32(len(pp.runq)) {
throw("runqsteal: runq overflow") // 如果 t-h+n >= len(p.runq) 表示偷多了...
}
atomic.StoreRel(&pp.runqtail, t+n) // 更新 P 的本地队列的队尾
return gp
}
这个偷就是把“地主家”(P2)的余粮 (goroutine) 给它抢一半过来,没办法我也要吃饭啊。
如果连偷都没偷到(好吧,太惨了点...),那就准备休眠了,不干活了还不行嘛。不干活之前在去看看全局队列有没有 goroutine 了(口是心非的 M 人)。还是没活,好吧,准备休眠了。
准备休眠,首先解除和 P 的绑定:
func releasep() *p {
gp := getg()
if gp.m.p == 0 {
throw("releasep: invalid arg")
}
pp := gp.m.p.ptr()
if pp.m.ptr() != gp.m || pp.status != _Prunning {
print("releasep: m=", gp.m, " m->p=", gp.m.p.ptr(), " p->m=", hex(pp.m), " p->status=", pp.status, "\n")
throw("releasep: invalid p state")
}
...
gp.m.p = 0
pp.m = 0
pp.status = _Pidle
return pp
}
就是指针的解绑操作,代码很清晰,连注释都不用,我们也不讲了。
解绑之后,pidleput 把空闲的 P 放到全局空闲队列中。
接着,更新线程的状态,从自旋更新为非自旋,调用 stopm 准备休眠:
// Stops execution of the current m until new work is available.
// Returns with acquired P.
func stopm() {
gp := getg() // 当前线程执行的 goroutine
...
lock(&sched.lock)
mput(gp.m) // 将线程放到全局空闲线程队列中
unlock(&sched.lock)
mPark()
acquirep(gp.m.nextp.ptr())
gp.m.nextp = 0
}
stopm 将线程放到全局空闲线程队列,接着调用 mPark 休眠线程:
// mPark causes a thread to park itself, returning once woken.
//
//go:nosplit
func mPark() {
gp := getg()
notesleep(&gp.m.park) // notesleep 线程休眠
noteclear(&gp.m.park)
}
func notesleep(n *note) {
gp := getg()
if gp != gp.m.g0 {
throw("notesleep not on g0")
}
ns := int64(-1)
if *cgo_yield != nil {
// Sleep for an arbitrary-but-moderate interval to poll libc interceptors.
ns = 10e6
}
for atomic.Load(key32(&n.key)) == 0 { // 这里通过 n.key 判断线程是否唤醒,如果等于 0,表示未唤醒,线程继续休眠
gp.m.blocked = true
futexsleep(key32(&n.key), 0, ns) // 调用 futex 休眠线程,线程会“阻塞”在这里,直到被唤醒
if *cgo_yield != nil {
asmcgocall(*cgo_yield, nil)
}
gp.m.blocked = false // “唤醒”,设置线程的 blocked 标记为 false
}
}
// One-time notifications.
func noteclear(n *note) {
n.key = 0 // 执行到 noteclear 说明,线程已经被唤醒了,这时候线程重置 n.key 标志位为 0
}
线程休眠是通过调用 futex 进入操作系统内核完成线程休眠的,关于 futex 的内容可以参考 这里。
线程的 n.key 是休眠的标志位,当 n.key 不等于 0 时表示有线程在唤醒休眠线程,线程从休眠状态恢复到正常状态。唤醒休眠线程通过调用 notewakeup(&nmp.park) 函数实现:
func notewakeup(n *note) {
old := atomic.Xchg(key32(&n.key), 1)
if old != 0 {
print("notewakeup - double wakeup (", old, ")\n")
throw("notewakeup - double wakeup")
}
futexwakeup(key32(&n.key), 1) // 调用 futexwakeup 唤醒休眠线程
}
首先,线程是怎么找到休眠线程的?线程通过全局空闲线程队列找到空闲的线程,并且将空闲线程的休眠标志位 m.park 传给 notewakeup,最后调用 futexwakeup 唤醒休眠线程。
值得一提的是,唤醒的线程在唤醒之后还是会继续找可运行的 goroutine 直到找到:
func stopm() {
...
mPark() // 如果 mPark 返回,表示线程被唤醒,开始正常工作
acquirep(gp.m.nextp.ptr()) // 前面休眠前,线程已经和 P 解绑了。这里在给线程找一个 P 绑定
gp.m.nextp = 0 // 线程已经绑定到 P 了,重置 nextp
}
基本这就是调度策略中很重要的一部分,线程如何找 goroutine。找到 goroutine 之后调用 gogo 执行该 goroutine。
3. 小结
本讲继续丰富了调度器的调度策略,下一讲,我们开始非 main goroutine 的介绍。
Go runtime 调度器精讲(五):调度策略的更多相关文章
- mybatis精讲(五)--映射器组件
目录 前言 标签 select insert|update|delete 参数 resultMap cache 自定义缓存 # 加入战队 微信公众号 前言 映射器之前我们已经提到了,是mybatis特 ...
- Python_装饰器精讲_33
from functools import wraps def wrapper(func): #func = holiday @wraps(func) def inner(*args,**kwargs ...
- 第一次作业:基于Linux 4.5的进程模型与调度器分析
1.操作系统是怎么组织进程的? 1.1什么是线程,什么是进程: 刚接触时可能经常会将这两个东西搞混.简单一点的说,进程是一个大工程,线程则是这个大工程中每个小地方需要做的东西(在linux下看作&qu ...
- Linux调度器 - deadline调度器
一.概述 实时系统是这样的一种计算系统:当事件发生后,它必须在确定的时间范围内做出响应.在实时系统中,产生正确的结果不仅依赖于系统正确的逻辑动作,而且依赖于逻辑动作的时序.换句话说,当系统收到某个请求 ...
- go语言调度器源代码情景分析之一:开篇语
专题简介 本专题以精心设计的情景为线索,结合go语言最新1.12版源代码深入细致的分析了goroutine调度器实现原理. 适宜读者 go语言开发人员 对线程调度器工作原理感兴趣的工程师 对计算机底层 ...
- Linux核心调度器之周期性调度器scheduler_tick--Linux进程的管理与调度(十八)
我们前面提到linux有两种方法激活调度器:核心调度器和 周期调度器 一种是直接的, 比如进程打算睡眠或出于其他原因放弃CPU 另一种是通过周期性的机制, 以固定的频率运行, 不时的检测是否有必要 因 ...
- Linux 内核调度器源码分析 - 初始化
导语 上篇系列文 混部之殇-论云原生资源隔离技术之CPU隔离(一) 介绍了云原生混部场景中CPU资源隔离核心技术:内核调度器,本系列文章<Linux内核调度器源码分析>将从源码的角度剖析内 ...
- 调度器简介,以及Linux的调度策略
进程是操作系统虚拟出来的概念,用来组织计算机中的任务.但随着进程被赋予越来越多的任务,进程好像有了真实的生命,它从诞生就随着CPU时间执行,直到最终消失.不过,进程的生命都得到了操作系统内核的关照.就 ...
- 第三百五十七节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—利用开源的scrapy-redis编写分布式爬虫代码
第三百五十七节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—利用开源的scrapy-redis编写分布式爬虫代码 scrapy-redis是一个可以scrapy结合redis搭建分布式爬虫的开 ...
- 第三百五十五节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—scrapy信号详解
第三百五十五节,Python分布式爬虫打造搜索引擎Scrapy精讲—scrapy信号详解 信号一般使用信号分发器dispatcher.connect(),来设置信号,和信号触发函数,当捕获到信号时执行 ...
随机推荐
- EasyBPM进销存之物料管理
本文是EasyBPM平台实现进销存系列中的一篇,主要讲述物料的相关的管理. 在ERP系统中,"物料"一词有着广泛的含义,它是所有产品.半成品.在制品.原材料.配套件.协作件.易耗品 ...
- Django集成的密码找回功能
要实现忘记密码功能,您需要进行以下修改: 添加忘记密码链接到登录页面. 创建密码丢失修改页面. 创建密码修改页面. 编写相应的视图函数来处理密码丢失修改和密码修改逻辑. 编写发送验证信息到邮箱的逻辑. ...
- 使用 Doxygen 来生成 Box2d 的 API 文档
对于 Doxygen 以前只听别人说过,而现在使用它也是一个偶然,缘分吧.前两天看 box2d 的官方 sdk 中,发现他有用户手册却没有说明,只是留下了一个 Doxygen 的文件.事情告一段落,然 ...
- MyBatis-Plus文件上传方法
网站的文件上传方法 本地存储上传 // 本地存储方式 MultipartFile接受文件 @PostMapping("/save") public Result save(Stri ...
- 切记:使用nvidia omniverse时一定要用2T的固态硬盘
最近在用nvidia omniverse时突然发现这样的一个问题,那就是这个软件实在是太太了,一个组件就4个多GB大小,如果安装几个组件后那么几十GB的硬盘就没有了,同时由于这个体积太大,因此再启动和 ...
- 如何使用深度学习技术探测代码逻辑死循环 —— 浪潮集团的“公开号CN117271314A”专利
专利公开号: CN117271314A 新闻链接: https://mbd.baidu.com/newspage/data/landingsuper?context={"nid"% ...
- vue之插槽-slot
1.背景 2.slot简单使用 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset ...
- Sy.ExpressionBuilder 动态查询新体验
省流模式,看下对比 //常规查询 var query = users .WhereIf(m => m.UserName.Contains(input.UserName), !string.IsN ...
- 玩转内核链表list_head,3个超级哇塞的的例子
在Linux内核中,提供了一个用来创建双向循环链表的结构 list_head.虽然linux内核是用C语言写的,但是list_head的引入,使得内核数据结构也可以拥有面向对象的特性,通过使用操作li ...
- “从零到一:如何在鸿蒙OS上启动你的第一个项目”
背景与引言 全球操作系统市场现状如何? 长期以来,Android.iOS.Windows等巨头几乎垄断了整个市场,成为人们日常生活中不可或缺的工具.然而,尽管它们在各自领域有着不可否认的成功,却也逐渐 ...
