数据分析---用pandas进行数据清洗(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)
这里利用ben的项目(https://github.com/ben519/DataWrangling/blob/master/Python/README.md),在此基础上增添了一些内容,来演示数据清洗的主要工作。
以下是一份简单的交易数据,包括交易单号,交易日期,产品序号,交易数量,单价,总价。
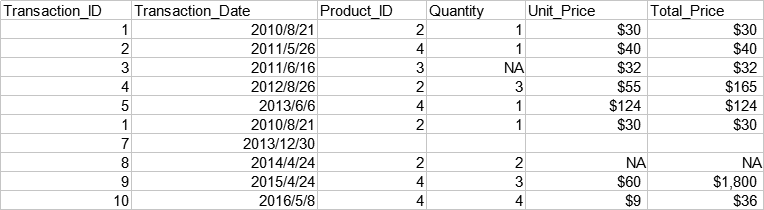
准备工作:导入pandas
import pandas as pd
读取数据: pd.read_excel(), pd.read_csv(), pd.read_json(), pd.read_sql(), pd.read_table()...
transactions=pd.read_excel(r'...\transactions.xlsx')
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
获取数据信息:xx.info()
print(transactions.info())
RangeIndex: 10 entries, 0 to 9
Data columns (total 6 columns):
Transaction_ID 10 non-null int64
Transaction_Date 10 non-null datetime64[ns]
Product_ID 10 non-null object
Quantity 9 non-null object
Unit_Price 9 non-null object
Total_Price 9 non-null object
dtypes: datetime64[ns](1), int64(1), object(4)
memory usage: 560.0+ bytes
None
显示了数据各列的基本信息,比如:Transaction_ID有10个不为空的值,数据类型是int64; Quantity有9个不为空的值(说明有一个缺失值),数据类型是object;等等。
获取数据总行列数信息: xx.shape
print(transactions.shape)
(10, 6)
显示了数据共有10行6列。
获取所有行索引: xx.index.values
print(transactions.index.values)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
获取所有列名: xx.columns.values
print(transactions.columns.values)
['Transaction_ID' 'Transaction_Date' 'Product_ID' 'Quantity' 'Unit_Price'
'Total_Price']
选取某一行: xx.loc[row_index_name, : ] 显式 ; xx.iloc[row_index_from_zero, : ] 隐式
print(transactions.loc[1,:])
Transaction_ID 2
Transaction_Date 2011-05-26 00:00:00
Product_ID 4
Quantity 1
Unit_Price 40
Total_Price 40
Name: 1, dtype: object
选取了数据的第二行。此数据行索引是从0开始一直到9,因此显式选取和隐式选取都一样。
选取某一列: xx['column_name']
print(transactions['Product_ID'])
0 2
1 4
2 3
3 2
4 4
5 2
6
7 2
8 4
9 4
Name: Product_ID, dtype: object
选取连续多行: xx.loc[row_index_name1: row_index_name2, : ] 显式 ; xx.iloc[row_index_from_zero1: row_index_from_zero2, : ] 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[2:4,:])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
选取连续多列: xx.loc[ : , 'column_name1': 'column_name2'] 显式 ; xx.iloc[ : , column_index_from_zero1: column_index_from_zero2] 隐式
print(transactions.loc[:,'Product_ID':'Total_Price'])
Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 2 1 30 30
1 4 1 40 40
2 3 NaN 32 32
3 2 3 55 165
4 4 1 124 124
5 2 1 30 30
6
7 2 2 NaN NaN
8 4 3 60 1800
9 4 4 9 36
选取连续某几行某几列的数据: xx.loc[row_index_name1: row_index_name2, 'column_name1': 'column_name2'] 显式 ; xx.iloc[row_index_from_zero1: row_index_from_zero2, column_index_from_zero1: column_index_from_zero2] 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[2:4,2:4])
Product_ID Quantity
2 3 NaN
3 2 3
选取不连续的多行: xx.loc[[row_index_name1,row_index_name2, ...], :] 显式 ; xx.iloc[[row_index_from_zero1, row_index_from_zero2, ...], :] 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[[1,4]])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
选取不连续的多列: xx.loc[ :, [column_name1, column_name2, ...]] 显式 ; xx.iloc[ :, [column_index_from_zero1, column_index_from_zero2, ...]] 隐式
print(transactions.iloc[:,[1,4]])
Transaction_Date Unit_Price
0 2010-08-21 30
1 2011-05-26 40
2 2011-06-16 32
3 2012-08-26 55
4 2013-06-06 124
5 2010-08-21 30
6 2013-12-30
7 2014-04-24 NaN
8 2015-04-24 60
9 2016-05-08 9
添加行: xx.loc[new_row_index]=[.....]
transactions.loc[10]=[11,"2018-9-9",1,4,2,8]
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 00:00:00 2 1 30
1 2 2011-05-26 00:00:00 4 1 40
2 3 2011-06-16 00:00:00 3 NaN 32
3 4 2012-08-26 00:00:00 2 3 55
4 5 2013-06-06 00:00:00 4 1 124
5 1 2010-08-21 00:00:00 2 1 30
6 7 2013-12-30 00:00:00
7 8 2014-04-24 00:00:00 2 2 NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 00:00:00 4 3 60
9 10 2016-05-08 00:00:00 4 4 9
10 11 2018-9-9 1 4 2 Total_Price
0 30
1 40
2 32
3 165
4 124
5 30
6
7 NaN
8 1800
9 36
10 8
添加列:xx['new_column_name']=[.....]
transactions['Unit_Profit']=[3,5,8,20,9,4,"",33,5,1]
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36 Unit_Profit
0 3
1 5
2 8
3 20
4 9
5 4
6
7 33
8 5
9 1
在指定位置插入列: xx.insert(column_index, 'new_column_name',[...])
transactions.insert(5,'Unit_Profit',[3,5,8,20,9,4,"",33,5,1])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Unit_Profit \
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 3
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 5
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 8
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 20
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 9
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 4
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN 33
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 5
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 1 Total_Price
0 30
1 40
2 32
3 165
4 124
5 30
6
7 NaN
8 1800
9 36
删除行:xx.drop(row_index_from_zero,axis=0)
transactions=transactions.drop(8,axis=0)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
删除列: xx.drop('column_name',axis=1)
transactions=transactions.drop('Total_Price',axis=1)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9
数据转置: xx.T
print(transactions.T)
\
Transaction_ID
Transaction_Date -- :: -- ::
Product_ID
Quantity
Unit_Price
Total_Price \
Transaction_ID
Transaction_Date -- :: -- ::
Product_ID
Quantity NaN
Unit_Price
Total_Price \
Transaction_ID
Transaction_Date -- :: -- ::
Product_ID
Quantity
Unit_Price
Total_Price \
Transaction_ID
Transaction_Date -- :: -- ::
Product_ID
Quantity
Unit_Price NaN
Total_Price NaN Transaction_ID
Transaction_Date -- :: -- ::
Product_ID
Quantity
Unit_Price
Total_Price
有时候需要把行和列进行交换,数据才更容易看懂(尽管这里不需要)。
查找重复值: xx.duplicated()
print(transactions.duplicated())
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 False
4 False
5 True
6 False
7 False
8 False
9 False
dtype: bool
数据第6行(索引为5)是重复的(需要每列的数据都重复)。
删除重复值: xx.drop_duplicates()
transactions=transactions.drop_duplicates()
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
数据第6行已被删除。
查找缺失值: xx.isnull() ; xx.notnull()
print(transactions[transactions['Unit_Price'].isnull()])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 NaN NaN
显示了Unit_Price有缺失值的一行数据。
删除缺失值: xx.dropna(how=..., axis=...) 注:how="any"或"all", axis=0或1
transactions=transactions.dropna(axis=0)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
填补缺失值: xx.fillna(value=..., axis=...) 注:axis=0或1
transactions['Unit_Price']=transactions['Unit_Price'].fillna(value=35)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
1 2 2011-05-26 4 1 40 40
2 3 2011-06-16 3 NaN 32 32
3 4 2012-08-26 2 3 55 165
4 5 2013-06-06 4 1 124 124
5 1 2010-08-21 2 1 30 30
6 7 2013-12-30
7 8 2014-04-24 2 2 35 NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4 3 60 1800
9 10 2016-05-08 4 4 9 36
去除空格: 先把空格替换成NaN,再提取没有缺失值的数据
import numpy as np
transactions=transactions.applymap(lambda x: np.NaN if str(x).isspace() else x)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
2 3 2011-06-16 3.0 NaN 32.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
6 7 2013-12-30 NaN NaN NaN
7 8 2014-04-24 2.0 2.0 NaN
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price
0 30.0
1 40.0
2 32.0
3 165.0
4 124.0
5 30.0
6 NaN
7 NaN
8 1800.0
9 36.0
注:如果替换某行或某列的空格,用apply;如果替换整体数据的空格,则用applymap
转换数据类型:xx.astype(data_type_to_be_transferred_to) 注:可转换的数据类型有:int, str, float ... ; 转换成时间序列: pd.to_datetime(...)
transactions['Transaction_Date']=pd.to_datetime(transactions['Transaction_Date'])
注:需要先把数据内的缺失值处理干净,否则会产生错误
使用掩码进行条件筛选: xx[mask] 注:一些条件表示方法:&(and) ,|(or),~(not),.isin(in)
print(transactions[(transactions['Quantity']==1) & (transactions['Unit_Price']>100)])
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 Total_Price
4 124.0
这里选取了交易数量为1并且单价超过100的数据(删除了所有缺失值后)。
条件筛选后选取符合条件的某一列数据: xx.loc[xx[mask],'column_name']
print(transactions.loc[((transactions['Quantity']==1) & (transactions['Unit_Price']>100)),'Product_ID'])
4 4.0
Name: Product_ID, dtype: float64
这里选取了交易数量为1并且单价超过100的物品的Produxt_ID(删除了所有缺失值后)。
查找异常值: 通过掩码过滤,在这里以Upper Quartile+1.5*IQR和Lower Quartile-1.5*IQR为上下限
print(transactions.describe())
upper_extrme=144.5+1.5*(144.5-33)
lower_extrme=33-1.5*(144.5-33)
print(transactions.loc[((transactions['Total_Price']>upper_extrme) | (transactions['Total_Price']<lower_extrme))])
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price Total_Price
count 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000
mean 4.571429 3.142857 2.000000 49.714286 317.857143
std 3.690399 1.069045 1.290994 36.926568 655.752095
min 1.000000 2.000000 1.000000 9.000000 30.000000
25% 1.500000 2.000000 1.000000 30.000000 33.000000
50% 4.000000 4.000000 1.000000 40.000000 40.000000
75% 7.000000 4.000000 3.000000 57.500000 144.500000
max 10.000000 4.000000 4.000000 124.000000 1800.000000
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 Total_Price
8 1800.0
先通过describe函数查看数据整体分布情况,然后计算出Total_Price的上下限,通过掩码选取Total_Price超过上限或低于下限的行。在这里可以看到,有一个异常值1800,原因是多写了一个0。
替换异常值: xx.replace(to_replace, new_value, inplace=True)
transactions['Total_Price'].replace(1800,180,inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price
0 30.0
1 40.0
3 165.0
4 124.0
5 30.0
8 180.0
9 36.0
把上面查找出来的异常值1800替换成了180。
累计: 累计方法有:count(), mean(), median(), min(), max(), std(), prod(), sum(), ... 注:参数axis=0表示按行进行计算,axis=1表示按列进行计算,默认axis=1
print(transactions['Total_Price'].sum())
2225.0
显示了Total_Price的合计数目。
数据分组:xx.groupby(...)
print(transactions.groupby('Product_ID')['Quantity'].sum())
Product_ID
2.0 5.0
4.0 9.0
Name: Quantity, dtype: float64
显示了按照Product_ID分组的交易数量的总和。(注:transactions.groupby('Product_ID')是一个数据分组的对象,它实际上还没有进行任何计算,只是一个暂时存储的容器,要使用累计方法后才会进行计算。因此,groupby一般与累计函数搭配使用。)
如果需要对特定Series使用两个及以上的累计方法,请使用agg()。如果需要对整个DataFrame使用自定义的累计方法,请使用apply()。
print(transactions.groupby('Product_ID')['Quantity'].agg(['sum','mean']))
sum mean
Product_ID
2.0 5.0 1.666667
4.0 9.0 2.250000
计数: xx.value_counts()
print(transactions['Product_ID'].value_counts())
4.0 4
2.0 3
Name: Product_ID, dtype: int64
更改某个列名: xx.rename(columns={'old_column_name':'new_column_name'}, inplace=True)
transactions.rename(columns={'Unit_Price':'UP'},inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity UP Total_Price
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0 40.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0 165.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0 30.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0 1800.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 36.0
批量更改列名:例如把所有列名中的下划线换成空格:xx.columns.str.replace('_', ' ')
更改索引: xx.set_index()
transactions.set_index('Transaction_Date',inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
Transaction_Date
2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0
2011-05-26 2 4.0 1.0 40.0
2012-08-26 4 2.0 3.0 55.0
2013-06-06 5 4.0 1.0 124.0
2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0
2015-04-24 9 4.0 3.0 60.0
2016-05-08 10 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price
Transaction_Date
2010-08-21 30.0
2011-05-26 40.0
2012-08-26 165.0
2013-06-06 124.0
2010-08-21 30.0
2015-04-24 1800.0
2016-05-08 36.0
以交易日期为索引。
按索引排序: xx.sort_index()
transactions.sort_index(ascending=False, inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
Transaction_Date
2016-05-08 10 4.0 4.0 9.0
2015-04-24 9 4.0 3.0 60.0
2013-06-06 5 4.0 1.0 124.0
2012-08-26 4 2.0 3.0 55.0
2011-05-26 2 4.0 1.0 40.0
2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0
2010-08-21 1 2.0 1.0 30.0 Total_Price
Transaction_Date
2016-05-08 36.0
2015-04-24 1800.0
2013-06-06 124.0
2012-08-26 165.0
2011-05-26 40.0
2010-08-21 30.0
2010-08-21 30.0
以交易日期为索引,倒序排列。
按内容排序: xx.sort_values()
transactions.sort_values(by=['Quantity','Total_Price'], inplace=True)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price
0 30.0
5 30.0
1 40.0
4 124.0
3 165.0
8 1800.0
9 36.0
更新索引: xx.reset_index()
transactions.reset_index(inplace=True)
index Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
2 1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
3 4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
4 3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
5 8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
6 9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price
0 30.0
1 30.0
2 40.0
3 124.0
4 165.0
5 1800.0
6 36.0
上面按内容排序后,索引顺序变乱了,如果数据就需要按此顺序排列,那么可以更新索引。
透视表: pd.pivot_table(xx, values=..., index=..., columns=..., aggfunc=...)
print(pd.pivot_table(transactions,values='Total_Price',index=['Product_ID','Quantity'],aggfunc='sum'))
Total_Price
Product_ID Quantity
2.0 1.0 60.0
3.0 165.0
4.0 1.0 164.0
3.0 1800.0
4.0 36.0
多级索引行列转换: stack() ; unstack()
print(pd.pivot_table(transactions,values='Total_Price',index=['Product_ID','Quantity'],aggfunc='sum').unstack())
Total_Price
Quantity 1.0 3.0 4.0
Product_ID
2.0 60.0 165.0 NaN
4.0 164.0 1800.0 36.0
将上面的透视表展开。
数据分列: xx.str.split()
假如我们要把交易日期里的年份提取出来,变成单独的列。---> 先把交易日期这一列的数据格式变为str,再按照'-'进行切割,当参数expand为True时,会把切割出来的内容分别当做一列。因此,如果只需要年份,那么就只需要提取第一列。
year=transactions['Transaction_Date'].astype(str).str.split('-',expand=True)[]
transactions['Year']=year
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Year
0 30.0 2010
1 40.0 2011
3 165.0 2012
4 124.0 2013
5 30.0 2010
8 1800.0 2015
9 36.0 2016
这样,以后可以方便按年份或月份进行分组。
数据分区: pd.cut(xx, bins, labels=...) ; pd.qcut(xx, q, labels=...) 注:cut 是根据每个值的大小来进行分区的,qcut 是根据每个值出现的次数来进行分区的。
cut=pd.cut(transactions['Unit_Price'],3,labels=['low','median','high'])
transactions.insert(5,'Price_Range',cut)
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
3 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
8 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
9 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Price_Range Total_Price
0 low 30.0
1 low 40.0
3 median 165.0
4 high 124.0
5 low 30.0
8 median 1800.0
9 low 36.0
在这里把Unit_Price分成了3挡。
合并:
把列作为键进行合并: pd.merge(xx, xx, on=..., how=...)
假设我们现在有另外一张表,记载的是产品序号对应的产品名称。现在把这两张表合并在一起:
product_name=pd.DataFrame({"Product_ID":[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0],"Product_Name":["candy","pen","stapler","toy"]})
merged=pd.merge(transactions,product_name,on='Product_ID',how="inner")
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
2 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
3 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
6 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Product_Name
0 30.0 pen
1 165.0 pen
2 30.0 pen
3 40.0 toy
4 124.0 toy
5 1800.0 toy
6 36.0 toy
假如两张表作为键的列名称不一致,那么可以通过设置left_on和left_on来解决:
product_name=pd.DataFrame({"Product_Identity":[1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0],"Product_Name":["candy","pen","stapler","toy"]})
merged=pd.merge(transactions,product_name,left_on='Product_ID',right_on="Product_Identity",how="inner")
Transaction_ID Transaction_Date Product_ID Quantity Unit_Price \
0 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
1 4 2012-08-26 2.0 3.0 55.0
2 1 2010-08-21 2.0 1.0 30.0
3 2 2011-05-26 4.0 1.0 40.0
4 5 2013-06-06 4.0 1.0 124.0
5 9 2015-04-24 4.0 3.0 60.0
6 10 2016-05-08 4.0 4.0 9.0 Total_Price Product_Identity Product_Name
0 30.0 2.0 pen
1 165.0 2.0 pen
2 30.0 2.0 pen
3 40.0 4.0 toy
4 124.0 4.0 toy
5 1800.0 4.0 toy
6 36.0 4.0 toy
注:how可选"left", "right", "outer", "inner"
"left":类似于SQL的left outer join;
"right":类似于SQL的right outer join;
"outer":并集,类似于SQL的full outer join;
"inner":交集,类似于SQL的inner join;
按索引进行合并: xx.join(xx, on=..., how=...)
假设有另外几张表(t1, t2)记载有交易记录,如果需要把这几张表合并在一起:transactions.join([t1,t2], how="outer")。这里不再做演示。
数据分析---用pandas进行数据清洗(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)的更多相关文章
- 用pandas进行数据清洗(二)(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)
在<用pandas进行数据清洗(一)(Data Analysis Pandas Data Munging/Wrangling)>中,我们介绍了数据清洗经常用到的一些pandas命令. 接下 ...
- Python For Data Analysis -- Pandas
首先pandas的作者就是这本书的作者 对于Numpy,我们处理的对象是矩阵 pandas是基于numpy进行封装的,pandas的处理对象是二维表(tabular, spreadsheet-like ...
- cookbook of python for data analysis
打算写讲义,目录已经想好. Content basic of python jupyter 开发环境 python 基本语法 利用python脚本完成工作 numpy for matrix compu ...
- How to use data analysis for machine learning (example, part 1)
In my last article, I stated that for practitioners (as opposed to theorists), the real prerequisite ...
- 《python for data analysis》第五章,pandas的基本使用
<利用python进行数据分析>一书的第五章源码与读书笔记 直接上代码 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# <python for data analysis>第五 ...
- 数据分析03 /基于pandas的数据清洗、级联、合并
数据分析03 /基于pandas的数据清洗.级联.合并 目录 数据分析03 /基于pandas的数据清洗.级联.合并 1. 处理丢失的数据 2. pandas处理空值操作 3. 数据清洗案例 4. 处 ...
- Python for Data Analysis 学习心得(二) - pandas介绍
一.pandas介绍 本篇程序上篇内容,在numpy下面继续介绍pandas,本书的作者是pandas的作者之一.pandas是非常好用的数据预处理工具,pandas下面有两个数据结构,分别为Seri ...
- pandas 之 数据清洗-缺失值
Abstract During the course fo doing data analysis and modeling, a significant amount of time is spen ...
- 数据分析---《Python for Data Analysis》学习笔记【04】
<Python for Data Analysis>一书由Wes Mckinney所著,中文译名是<利用Python进行数据分析>.这里记录一下学习过程,其中有些方法和书中不同 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu Desktop: 备份与还原
Ubuntu Desktop 版本默认自带了图形化的备份/还原工具 Déjà Dup.该工具主要用来备份和还原用户的数据,当然我们也可以用它来备份/还原系统的数据.本文主要介绍 Déjà Dup 的主 ...
- ORM简介 单表添加修改删除表记录
---------------------------------------------------------------目标既定,在学习和实践过程中无论遇到什么困难.曲折都不灰心丧气,不轻易改变 ...
- 美团2016秋招笔试B
1.下述解决死锁的方法中,属于死锁预防策略的是? 资源有序分配法 银行家算法:避免死锁 资源有序分配法:预防死锁 资源分配图化简法:检测死锁 撤销进程法:解决死锁 2. 什么是死锁? 如果一个进 ...
- 关于jsp中jstl-core标签循环遍历的使用
JSP标准标签库(JSTL)是一个JSP标签集合,它封装了JSP应用的通用核心功能. JSTL支持通用的.结构化的任务,比如迭代,条件判断,XML文档操作,国际化标签,SQL标签. 除了这些,它还提供 ...
- Deflation Methods for Sparse PCA
目录 背景 总括 Hotelling's deflation 公式 特点 Projection deflation 公式 特点 Schur complement deflation Orthogona ...
- ElastichSearch漏洞
Ubuntu服务器被黑经历(ElastichSearch漏洞) 起因 最近我们的一台Ubuntu阿里云服务器一直提示有肉鸡行为,提示了好几天,开始并没有关注,然后连续几天后发现应该是个大问题啊.很可能 ...
- Python之发邮件
使用模块yagmail(使用收藏的yagmail,现在的第三方模块不能解决中文乱码问题) import yagmail user='xxx@126.com' password='xxxxxx' #使用 ...
- 百度地图支持https
百度地图SDK, 支持https <script src="http://api.map.baidu.com/api?v=3.0&ak=nbnttGGI6lilllgy2zn ...
- XManager&XShell如何保存登录用户和登录密码
Xshell配置ssh免密码登录 - qingfeng2556的博客 - CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/wuhenzhangxing/article/details/7948 ...
- MySQL数据库性能优化思路与解决方法(一转)
1.选取最适用的字段属性 MySQL可以很好的支持大数据量的存取,但是一般说来,数据库中的表越 小,在它上面执行的查询也就会越快.因此,在创建表的时候,为了获得更好的性能,我们可以将表中字段的宽度设 ...
