Spark2 Linear Regression线性回归
回归正则化方法(Lasso,Ridge和ElasticNet)在高维和数据集变量之间多重共线性情况下运行良好。
数学上,ElasticNet被定义为L1和L2正则化项的凸组合:
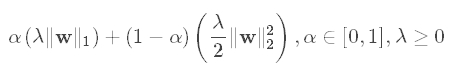
通过适当设置α,ElasticNet包含L1和L2正则化作为特殊情况。例如,如果用参数α设置为1来训练线性回归模型,则其等价于Lasso模型。另一方面,如果α被设置为0,则训练的模型简化为ridge回归模型。
RegParam:lambda>=0
ElasticNetParam:alpha in [0, 1]
导入包
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
import org.apache.spark.sql.Column
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrameReader
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.encoders.ExpressionEncoder
import org.apache.spark.sql.Encoder
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrameStatFunctions
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._ import org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vectors
import org.apache.spark.ml.feature.VectorAssembler
import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.RegressionEvaluator
import org.apache.spark.ml.regression.LinearRegression
导入样本数据
// Population人口,
// Income收入水平,
// Illiteracy文盲率,
// LifeExp,
// Murder谋杀率,
// HSGrad,
// Frost结霜天数(温度在冰点以下的平均天数) ,
// Area州面积
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("Spark Linear Regression").config("spark.some.config.option", "some-value").getOrCreate() // For implicit conversions like converting RDDs to DataFrames
import spark.implicits._ val dataList: List[(Double, Double, Double, Double, Double, Double, Double, Double)] = List(
(3615, 3624, 2.1, 69.05, 15.1, 41.3, 20, 50708),
(365, 6315, 1.5, 69.31, 11.3, 66.7, 152, 566432),
(2212, 4530, 1.8, 70.55, 7.8, 58.1, 15, 113417),
(2110, 3378, 1.9, 70.66, 10.1, 39.9, 65, 51945),
(21198, 5114, 1.1, 71.71, 10.3, 62.6, 20, 156361),
(2541, 4884, 0.7, 72.06, 6.8, 63.9, 166, 103766),
(3100, 5348, 1.1, 72.48, 3.1, 56, 139, 4862),
(579, 4809, 0.9, 70.06, 6.2, 54.6, 103, 1982),
(8277, 4815, 1.3, 70.66, 10.7, 52.6, 11, 54090),
(4931, 4091, 2, 68.54, 13.9, 40.6, 60, 58073),
(868, 4963, 1.9, 73.6, 6.2, 61.9, 0, 6425),
(813, 4119, 0.6, 71.87, 5.3, 59.5, 126, 82677),
(11197, 5107, 0.9, 70.14, 10.3, 52.6, 127, 55748),
(5313, 4458, 0.7, 70.88, 7.1, 52.9, 122, 36097),
(2861, 4628, 0.5, 72.56, 2.3, 59, 140, 55941),
(2280, 4669, 0.6, 72.58, 4.5, 59.9, 114, 81787),
(3387, 3712, 1.6, 70.1, 10.6, 38.5, 95, 39650),
(3806, 3545, 2.8, 68.76, 13.2, 42.2, 12, 44930),
(1058, 3694, 0.7, 70.39, 2.7, 54.7, 161, 30920),
(4122, 5299, 0.9, 70.22, 8.5, 52.3, 101, 9891),
(5814, 4755, 1.1, 71.83, 3.3, 58.5, 103, 7826),
(9111, 4751, 0.9, 70.63, 11.1, 52.8, 125, 56817),
(3921, 4675, 0.6, 72.96, 2.3, 57.6, 160, 79289),
(2341, 3098, 2.4, 68.09, 12.5, 41, 50, 47296),
(4767, 4254, 0.8, 70.69, 9.3, 48.8, 108, 68995),
(746, 4347, 0.6, 70.56, 5, 59.2, 155, 145587),
(1544, 4508, 0.6, 72.6, 2.9, 59.3, 139, 76483),
(590, 5149, 0.5, 69.03, 11.5, 65.2, 188, 109889),
(812, 4281, 0.7, 71.23, 3.3, 57.6, 174, 9027),
(7333, 5237, 1.1, 70.93, 5.2, 52.5, 115, 7521),
(1144, 3601, 2.2, 70.32, 9.7, 55.2, 120, 121412),
(18076, 4903, 1.4, 70.55, 10.9, 52.7, 82, 47831),
(5441, 3875, 1.8, 69.21, 11.1, 38.5, 80, 48798),
(637, 5087, 0.8, 72.78, 1.4, 50.3, 186, 69273),
(10735, 4561, 0.8, 70.82, 7.4, 53.2, 124, 40975),
(2715, 3983, 1.1, 71.42, 6.4, 51.6, 82, 68782),
(2284, 4660, 0.6, 72.13, 4.2, 60, 44, 96184),
(11860, 4449, 1, 70.43, 6.1, 50.2, 126, 44966),
(931, 4558, 1.3, 71.9, 2.4, 46.4, 127, 1049),
(2816, 3635, 2.3, 67.96, 11.6, 37.8, 65, 30225),
(681, 4167, 0.5, 72.08, 1.7, 53.3, 172, 75955),
(4173, 3821, 1.7, 70.11, 11, 41.8, 70, 41328),
(12237, 4188, 2.2, 70.9, 12.2, 47.4, 35, 262134),
(1203, 4022, 0.6, 72.9, 4.5, 67.3, 137, 82096),
(472, 3907, 0.6, 71.64, 5.5, 57.1, 168, 9267),
(4981, 4701, 1.4, 70.08, 9.5, 47.8, 85, 39780),
(3559, 4864, 0.6, 71.72, 4.3, 63.5, 32, 66570),
(1799, 3617, 1.4, 69.48, 6.7, 41.6, 100, 24070),
(4589, 4468, 0.7, 72.48, 3, 54.5, 149, 54464),
(376, 4566, 0.6, 70.29, 6.9, 62.9, 173, 97203)) val data = dataList.toDF("Population", "Income", "Illiteracy", "LifeExp", "Murder", "HSGrad", "Frost", "Area")
建立线性回归模型
val colArray = Array("Population", "Income", "Illiteracy", "LifeExp", "HSGrad", "Frost", "Area")
val assembler = new VectorAssembler().setInputCols(colArray).setOutputCol("features")
val vecDF: DataFrame = assembler.transform(data)
// 建立模型,预测谋杀率Murder
// 设置线性回归参数
val lr1 = new LinearRegression()
val lr2 = lr1.setFeaturesCol("features").setLabelCol("Murder").setFitIntercept(true)
// RegParam:正则化
val lr3 = lr2.setMaxIter(10).setRegParam(0.3).setElasticNetParam(0.8)
val lr = lr3
// Fit the model
val lrModel = lr.fit(vecDF)
// 输出模型全部参数
lrModel.extractParamMap()
// Print the coefficients and intercept for linear regression
println(s"Coefficients: ${lrModel.coefficients} Intercept: ${lrModel.intercept}")
val predictions = lrModel.transform(vecDF)
predictions.selectExpr("Murder", "round(prediction,1) as prediction").show
// Summarize the model over the training set and print out some metrics
val trainingSummary = lrModel.summary
println(s"numIterations: ${trainingSummary.totalIterations}")
println(s"objectiveHistory: ${trainingSummary.objectiveHistory.toList}")
trainingSummary.residuals.show()
println(s"RMSE: ${trainingSummary.rootMeanSquaredError}")
println(s"r2: ${trainingSummary.r2}")
代码执行结果
// 输出模型全部参数
lrModel.extractParamMap()
res15: org.apache.spark.ml.param.ParamMap =
{
linReg_2ba28140e39a-elasticNetParam: 0.8,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-featuresCol: features,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-labelCol: Murder,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-maxIter: 10,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-predictionCol: prediction,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-regParam: 0.3,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-solver: auto,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-standardization: true,
linReg_2ba28140e39a-tol: 1.0E-6
} // Print the coefficients and intercept for linear regression
println(s"Coefficients: ${lrModel.coefficients} Intercept: ${lrModel.intercept}")
Coefficients: [1.36662199778084E-4,0.0,1.1834384307116244,-1.4580829641757522,0.0,-0.010686434270049252,4.051355050528196E-6] Intercept: 109.589659881471 val predictions = lrModel.transform(vecDF)
predictions: org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame = [Population: double, Income: double ... 8 more fields] predictions.selectExpr("Murder", "round(prediction,1) as prediction").show
+------+----------+
|Murder|prediction|
+------+----------+
| 15.1| 11.9|
| 11.3| 11.0|
| 7.8| 9.5|
| 10.1| 8.6|
| 10.3| 9.6|
| 6.8| 4.3|
| 3.1| 4.2|
| 6.2| 7.5|
| 10.7| 9.3|
| 13.9| 12.3|
| 6.2| 4.7|
| 5.3| 4.6|
| 10.3| 8.8|
| 7.1| 6.6|
| 2.3| 3.5|
| 4.5| 3.9|
| 10.6| 8.9|
| 13.2| 13.2|
| 2.7| 6.3|
| 8.5| 7.8|
+------+----------+
only showing top 20 rows // Summarize the model over the training set and print out some metrics
val trainingSummary = lrModel.summary
trainingSummary: org.apache.spark.ml.regression.LinearRegressionTrainingSummary = org.apache.spark.ml.regression.LinearRegressionTrainingSummary@68a83d76 println(s"numIterations: ${trainingSummary.totalIterations}")
numIterations: 11 println(s"objectiveHistory: ${trainingSummary.objectiveHistory.toList}")
objectiveHistory: List(0.49000000000000016, 0.3919242806809093, 0.19908078426904946, 0.1901453492751914, 0.17981874256031405, 0.17878173084286247, 0.1787617816935607, 0.17875431854661641, 0.1
7874702637141196, 0.17874512271568685, 0.1787449876896829)
trainingSummary.residuals.show()
+--------------------+
| residuals|
+--------------------+
| 3.2200068116713023|
| 0.2745518816306607|
| -1.6535887417767414|
| 1.485762696757325|
| 0.6509766532389172|
| 2.457688146554534|
| -1.0675250558261182|
| -1.2879164685248439|
| 1.3672723619868314|
| 1.6125000289597242|
| 1.532060517905248|
| 0.6931301635074645|
| 1.5163001982000175|
| 0.46227066807431605|
| -1.2044058248740273|
| 0.6032541157521649|
| 1.7201545753635|
|-0.01942937427384...|
| -3.632947522687547|
| 0.7077675962948007|
+--------------------+
only showing top 20 rows println(s"RMSE: ${trainingSummary.rootMeanSquaredError}")
RMSE: 1.6663615527314546 println(s"r2: ${trainingSummary.r2}")
r2: 0.7920794990832152
模型调优,用Train-Validation Split
val colArray = Array("Population", "Income", "Illiteracy", "LifeExp", "HSGrad", "Frost", "Area")
val vecDF: DataFrame = new VectorAssembler().setInputCols(colArray).setOutputCol("features").transform(data)
val Array(trainingDF, testDF) = vecDF.randomSplit(Array(0.9, 0.1), seed = 12345)
// 建立模型,预测谋杀率Murder,设置线性回归参数
val lr = new LinearRegression().setFeaturesCol("features").setLabelCol("Murder").fit(trainingDF)
// 设置管道
val pipeline = new Pipeline().setStages(Array(lr))
// 建立参数网格
val paramGrid = new ParamGridBuilder().addGrid(lr.fitIntercept).addGrid(lr.elasticNetParam, Array(0.0, 0.5, 1.0)).addGrid(lr.maxIter, Array(10, 100)).build()
// 选择(prediction, true label),计算测试误差。
// 注意RegEvaluator.isLargerBetter,评估的度量值是大的好,还是小的好,系统会自动识别
val RegEvaluator = new RegressionEvaluator().setLabelCol(lr.getLabelCol).setPredictionCol(lr.getPredictionCol).setMetricName("rmse")
val trainValidationSplit = new TrainValidationSplit().setEstimator(pipeline).setEvaluator(RegEvaluator).setEstimatorParamMaps(paramGrid).setTrainRatio(0.8) // 数据分割比例
// Run train validation split, and choose the best set of parameters.
val tvModel = trainValidationSplit.fit(trainingDF)
// 查看模型全部参数
tvModel.extractParamMap()
tvModel.getEstimatorParamMaps.length
tvModel.getEstimatorParamMaps.foreach { println } // 参数组合的集合
tvModel.getEvaluator.extractParamMap() // 评估的参数
tvModel.getEvaluator.isLargerBetter // 评估的度量值是大的好,还是小的好
tvModel.getTrainRatio
// 用最好的参数组合,做出预测
tvModel.transform(testDF).select("features", "Murder", "prediction").show()
调优代码执行结果
// 查看模型全部参数
tvModel.extractParamMap()
res45: org.apache.spark.ml.param.ParamMap =
{
tvs_5de7d3dd1977-estimator: pipeline_062a1dffe557,
tvs_5de7d3dd1977-estimatorParamMaps: [Lorg.apache.spark.ml.param.ParamMap;@60298de1,
tvs_5de7d3dd1977-evaluator: regEval_05204824acb9,
tvs_5de7d3dd1977-seed: -1772833110,
tvs_5de7d3dd1977-trainRatio: 0.8
} tvModel.getEstimatorParamMaps.length
res46: Int = 12 tvModel.getEstimatorParamMaps.foreach { println } // 参数组合的集合
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.5,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.5,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.5,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 0.5,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 1.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 1.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: true,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 1.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 10
}
{
linReg_75628a5554b4-elasticNetParam: 1.0,
linReg_75628a5554b4-fitIntercept: false,
linReg_75628a5554b4-maxIter: 100
} tvModel.getEvaluator.extractParamMap() // 评估的参数
res48: org.apache.spark.ml.param.ParamMap =
{
regEval_05204824acb9-labelCol: Murder,
regEval_05204824acb9-metricName: rmse,
regEval_05204824acb9-predictionCol: prediction
} tvModel.getEvaluator.isLargerBetter // 评估的度量值是大的好,还是小的好
res49: Boolean = false tvModel.getTrainRatio
res50: Double = 0.8 tvModel.transform(testDF).select("features", "Murder", "prediction").show()
+--------------------+------+------------------+
| features|Murder| prediction|
+--------------------+------+------------------+
|[1058.0,3694.0,0....| 2.7| 6.917232043935343|
|[2341.0,3098.0,2....| 12.5|14.760329005533478|
|[472.0,3907.0,0.6...| 5.5| 4.182074651181182|
|[812.0,4281.0,0.7...| 3.3| 4.915905572667441|
|[2816.0,3635.0,2....| 11.6|14.219231061596304|
|[4589.0,4468.0,0....| 3.0| 3.483554528704758|
+--------------------+------+------------------+
Spark2 Linear Regression线性回归的更多相关文章
- Linear Regression(线性回归)(一)—LMS algorithm
(整理自AndrewNG的课件,转载请注明.整理者:华科小涛@http://www.cnblogs.com/hust-ghtao/) 1.问题的引出 先从一个简单的例子说起吧,房地产公司有一些关于Po ...
- Linear Regression 线性回归
Motivation 问题描述 收集到某一地区的房子面积和房价的数据(x, y)42组,对于一套已知面积的房子预测其房价?   由房价数据可视化图可以看出,可以使用一条直线拟合房价.通过这种假设得 ...
- Linear Regression(线性回归)(二)—正规方程(normal equations)
(整理自AndrewNG的课件,转载请注明.整理者:华科小涛@http://www.cnblogs.com/hust-ghtao/) 在上篇博客中,我们提出了线性回归的概念,给出了一种使代价函数最小的 ...
- 线性回归 Linear regression(3) 线性回归的概率解释
这篇博客从一种方式推导了Linear regression 线性回归的概率解释,内容来自Standford公开课machine learning中Andrew老师的讲解. 线性回归的概率解释 在Lin ...
- Kernel Methods (3) Kernel Linear Regression
Linear Regression 线性回归应该算得上是最简单的一种机器学习算法了吧. 它的问题定义为: 给定训练数据集\(D\), 由\(m\)个二元组\(x_i, y_i\)组成, 其中: \(x ...
- 线性回归、梯度下降(Linear Regression、Gradient Descent)
转载请注明出自BYRans博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 实例 首先举个例子,假设我们有一个二手房交易记录的数据集,已知房屋面积.卧室数量和房屋的交易价格,如下表: ...
- Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7732417 本文为Maching Learning 栏目补充内容,为上几章中所提到单参数线性 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第二讲. 多变量线性回归 Linear Regression with multiple variable
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7700772 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- 机器学习之多变量线性回归(Linear Regression with multiple variables)
1. Multiple features(多维特征) 在机器学习之单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)我们提到过的线性回归中,我们只有一个单一特征量 ...
随机推荐
- C语言的结构体
举例,一个结构体的定义如下: typedef struct _foo { ]; int age; int sex; } foo; 对齐 如果直接对上面的结构体作sizeof()运算: printf( ...
- InnoDB锁问题 & DB事务隔离级别
<参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/jack204/archive/2012/06/09/2542940.html>InnoDB行锁实现方式InnoDB行锁是通过给索引上 ...
- SpringBoot------热部署(Springloaded)
为啥要热部署: 在修改代码的时候,不需要重新启动程序,程序会自动进行编译 注意: 控制器中新增加的方法是不能进行热部署的 方法: 1.在pom.xml文件里面添加下面代码 <project> ...
- SpringBoot------8080端口被占用抛出异常
异常信息: The Tomcat connector configured to listen on port failed to start. The port may already be in ...
- Linux 日常运维
查看用户信息:w 查看系统负载:uptime 查看系统资源使用情况:vmstat 查看进程动态:top 查看网卡流量:sar 查看网卡流量:nload 查看磁盘读写:iostat 查看磁盘读写:iot ...
- samba 服务器
1.apt-get install smaba 2.安装完成后apt-get install smbclient 然后就是配置那个.conf文件,这个到网上搜下ubuntu下配置smaba服务器就可以 ...
- setTag,getTage复用
radioButtons = new RadioButton[rgMain.getChildCount()]; //遍历RadioGroupfor (int i = 0; i < radioBu ...
- ASP/SQL 注入天书
引言 随着 B/S 模式应用开发的发展,使用这种模式编写应用程序的程序员也越来越多.但是由于这个行业的入门门槛不高,程序员的水平及经验也参差不齐,相当大一部分程序员在编写代码的时候,没有对用户输入数据 ...
- 《转》Python学习(17)-python函数基础部分
http://www.cnblogs.com/BeginMan/p/3171977.html 一.什么是函数.方法.过程 推荐阅读:http://www.cnblogs.com/snandy/arch ...
- android基础---->IntentService的使用
这一篇博客,我们开始前台服务与IntentServie源码分析的学习,关于service的生命周期及其简单使用,请参见我的博客:(android基础---->service的生命周期) 目录导航 ...
