Spring-Spring配置-依赖注入
5、Spring配置
5.1、别名
<!--别名,如果添加了别名,我们也可以使用别名获取到这个对象-->
<alias name="user" alias="userAlias"/>
5.2、bean的配置
<!--
id:bean的唯一标识符,也就是相当于我们学的对象名
class:bean对象所对应的全限定名:包名+类名
name:也是别名,而且name可以同时取多个别名
-->
<bean id="userT" class="com.rui.pojo.UserT" name="user2 u2,u3;u4">
</bean>
5.3、import
这个import,一般用于团队开发使用,他可以将多个配置文件,导入合并为一个
假设现在项目中有多个人开发,这三个人负责不同的类开发,不同的类需要注册在不同的bean中,我们可以利用import将所有人的beans.xml合并为一个总的!
- 张三
- 李四
- 王五
- applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="beans.xml"/>
<import resource="beans2.xml"/>
<import resource="beans3.xml"/>
</beans>
使用的时候,直接使用总的配置就可以了
6、依赖注入
6.1、构造器注入
前面已经说过
6.2、Set方式注入【重点】
- 依赖注入:Set注入!
- 依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
- 注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器来注入!
【环境搭建】
复杂类型
package com.rui.pojo; public class Address {
private String address; public String getAddress() {
return address;
} public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
真实测试对象
package com.rui.pojo; import java.util.*; public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info; public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Address getAddress() {
return address;
} public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
} public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
} public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
} public List<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
} public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
} public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
} public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
} public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
} public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
} public String getWife() {
return wife;
} public void setWife(String wife) {
this.wife = wife;
} public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
} public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
", hobbys=" + hobbys +
", card=" + card +
", games=" + games +
", wife='" + wife + '\'' +
", info=" + info +
'}';
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student" class="com.rui.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通注入,value-->
<property name="name" value="尹锐"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
package com.rui; import com.rui.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
完善注入信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.rui.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="杭州"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.rui.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通注入,value-->
<property name="name" value="尹锐"/>
<!--第二种,Bean注入,ref-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--数组注入,ref-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>红楼梦</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>三国演义</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>听歌</value>
<value>敲代码</value>
<value>看电影</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Map-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份证" value="111222333344445555"/>
<entry key="银行卡" value="11123123123123123123"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--Set-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOL</value>
<value>COC</value>
<value>BOB</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--null-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!--Properties-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="driver">171030338</prop>
<prop key="url">171030338</prop>
<prop key="username">171030338</prop>
<prop key="password">171030338</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
6.3、拓展方式注入
我们可以使用p命名空间和c命名空间进行注入
官方解释: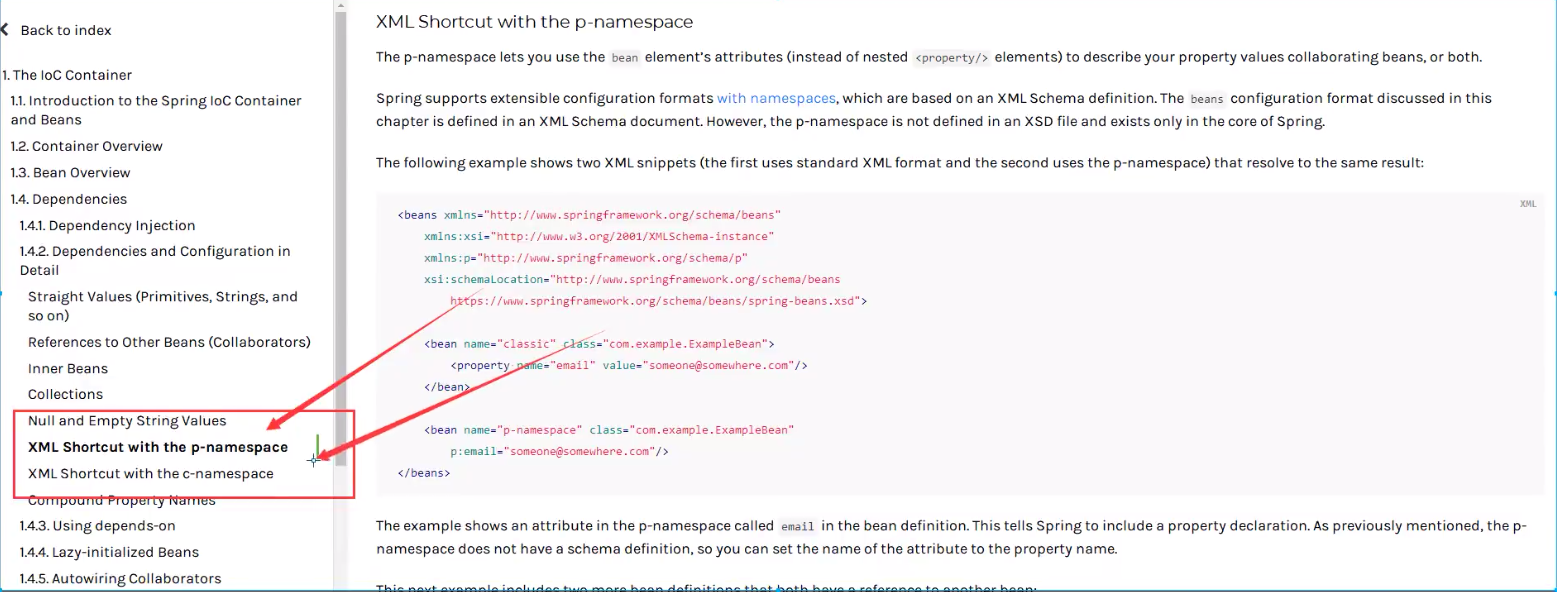
xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--p命名空间注入,可以直接注入属性的值:property-->
<bean id="user" class="com.rui.pojo.User" p:name="尹锐" p:age="18"/>
<!--c命名空间注入,通过构造器注入:construct-args-->
<bean id="user2" class="com.rui.pojo.User" c:age="18" c:name="尹锐"/>
</beans>
测试:
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("userbeans.xml");
User user = (User) context.getBean("user2");
System.out.println(user);
}
注意点:p命名空间和c命名空间不能直接使用,需要导入xml约束!
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
6.4、bean的作用域
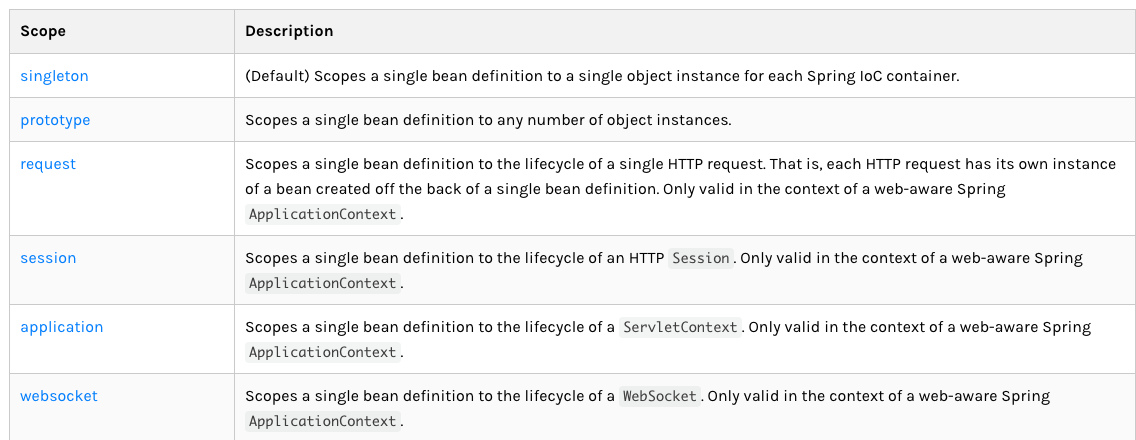
单例模式(Spring默认机制)
<bean id="user2" class="com.rui.pojo.User" c:age="18" c:name="尹锐" scope="singleton"/>
原型模式:每次从容器中get的时候,都会产生一个新对象
<bean id="user2" class="com.rui.pojo.User" c:age="18" c:name="尹锐" scope="prototype"/>其余的request、session、application、这些只能在web开发中用到!
Spring-Spring配置-依赖注入的更多相关文章
- Spring Framework------>version4.3.5.RELAESE----->Reference Documentation学习心得----->Spring Framework的依赖注入和控制反转
Dependency Injection and Inversion of Control 1.概述: 1.1相关概念 bean:由IoC容器所管理的对象,也即各个类实例化所得对象都叫做bean 控制 ...
- 谈谈自己了解的spring.NET的依赖注入
spring.net里实现了控制反转IOC(Inversion of control),也即依赖注入DI(Dependency Injection),以达到解耦的目的,实现模块的组件化.程序 ...
- Spring学习(三)——Spring中的依赖注入的方式
[前面的话] Spring对我太重要了,做个关于web相关的项目都要使用Spring,每次去看Spring相关的知识,总是感觉一知半解,没有很好的系统去学习一下,现在抽点时间学习一下Spring.不知 ...
- spring六种种依赖注入方式
平常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程 ...
- spring.NET的依赖注入
谈谈自己了解的spring.NET的依赖注入 spring.net里实现了控制反转IOC(Inversion of control),也即依赖注入DI(Dependency Injection), ...
- spring 四种依赖注入方式以及注解注入方式
平常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程 ...
- JavaEE开发之Spring中的依赖注入与AOP
上篇博客我们系统的聊了<JavaEE开发之基于Eclipse的环境搭建以及Maven Web App的创建>,并在之前的博客中我们聊了依赖注入的相关东西,并且使用Objective-C的R ...
- JavaEE开发之Spring中的依赖注入与AOP编程
上篇博客我们系统的聊了<JavaEE开发之基于Eclipse的环境搭建以及Maven Web App的创建>,并在之前的博客中我们聊了依赖注入的相关东西,并且使用Objective-C的R ...
- spring几种依赖注入方式以及ref-local/bean,factory-bean,factory-method区别联系
平常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程 ...
- 【Spring IoC】依赖注入DI(四)
平常的Java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法.通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理. Spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程 ...
随机推荐
- JS中根据某个值进行大小排序
//从大到小排序 function compareBigToSmall(property){ return function(a,b){ var value1 = a[property]; var v ...
- Oracle 表的导入与导出
周末任务:将一个表从一个库导到另一个库大致思路:用expdp 将表从一个实例导出 ,再用impdp将导出的 .dmp文件导入到另一个实例1.在实例 orcl 中准备一个用于导出的表: 进入实例为orc ...
- 记crt 在windows与linux服务器之间利用ftp进行文件的上传下载
我们首先来熟悉一些相关的命令以及操作: ls #展示linux服务器当前工作目录[你连接sftp时所处的目录]下的所有文件以及文件夹 lcd F:\niki #绑定你在windo ...
- Sql server 中count() 与 sum() 的区别
一句话概括就是Sum(列) 是求和,把所有列的值进行汇总求和:COUNT(列) 是行数汇总,只要列的值不为Null,就会增加1: 举个例子说明下: --创建临时表结构 CREATE TABLE Tem ...
- Sql 第一行某列减第二行某列
--1. 将结果插入临时表SELECT *INTO xxx FROM( SELECT TOP 1 a.FQTY,a.fseq FROM T_SAL_ORDERENTRY as a WHERE FQTY ...
- StarUML3.1.0版(2019.3.6)生成Java代码
下载官网 StarUML3.1.0(2019.3.6) 步骤 打开StarUML: 点击菜单栏的Tools: 列表中如果有Java,说明已经有这个生成Java代码的扩展了: 列表里如果没有Java: ...
- 防止vi粘贴时自动添加缩进的方法
使用Xshell连接Linux服务器,使用vi打开文件进行粘贴时,会自动在行首添加很多空格,导致格式错乱.可以用如下方法剞劂 在拷贝前输入:set paste (这样的话,vim就不会启动自动缩进,而 ...
- 【爬虫集合】抖音API分析
1. 分析接口 Charles注册码 Registered Name: https://zhile.io License Key: 48891cf209c6d32bf4 抖音API分析 抖音.猫眼网页 ...
- B+Tree的基本介绍
概念 特点 B-Tree有许多变种,其中最常见的是B+Tree,例如MySQL就普遍使用B+Tree实现其索引结构. 与B-Tree相比,B+Tree有以下不同点: 每个节点的指针上限为2d而不是2d ...
- ant Windows下环境变量配置 安装 编译
下载 官网:[http://ant.apache.org/] 其他版本:[http://archive.apache.org/dist/ant/binaries/] 点击这个进入下载页面 Window ...
