netty(三)---NioEventLoop分析
问题 :
- NioEventLoop 作用到底是什么?是在哪里用到的?
- NioEventLoop 和我们开头创建的 ServerBootstrap 和 EventLoopGroup 是什么关系 ?
- NioEventLoop 和 NioChannel 怎么传递的(按合理,一个channel应该分配一个NioEventLoop)
- NioEventLoop 工作原理
概述
要知道 NioEventLoop 就必须从 EventLoopGroup 说起,以下是它们的类结构图。
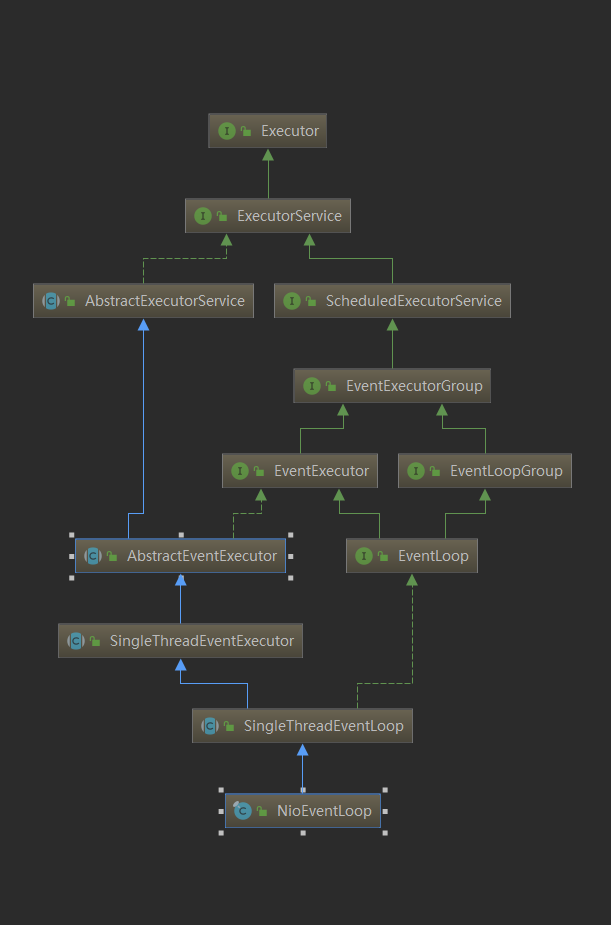 我们在分析 netty 服务端处理的过程中,有一个 createChannel() 的过程,然后调用 group().next() 方法返回一个 NioEventLoop ,剩下的东西就交给这个 NioEventLoop 来处理了,实际中 EventLoopGroup 包含这一个 NioEventLoop 数组,它们是执行处理的实施者。
我们在分析 netty 服务端处理的过程中,有一个 createChannel() 的过程,然后调用 group().next() 方法返回一个 NioEventLoop ,剩下的东西就交给这个 NioEventLoop 来处理了,实际中 EventLoopGroup 包含这一个 NioEventLoop 数组,它们是执行处理的实施者。
源码分析
EventLoopGroup 的父类 MultithreadEventLoopGroup分析
public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup implements EventLoopGroup {
private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(MultithreadEventLoopGroup.class);
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
//默认EventLoopThreads处理线程数
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2));
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);
}
}
/**
* @see {@link MultithreadEventExecutorGroup#MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int, Executor, Object...)}
*/
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
/**
* @see {@link MultithreadEventExecutorGroup#MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int, ThreadFactory, Object...)}
*/
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, threadFactory, args);
}
@Override
protected ThreadFactory newDefaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(getClass(), Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
}
@Override
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
@Override
protected abstract EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
}
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup 类
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
//接受到任务,交给children 执行
private final EventExecutor[] children;
private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren;
private final AtomicInteger childIndex = new AtomicInteger();
private final AtomicInteger terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger();
private final Promise<?> terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
/**
* Create a new instance.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads that will be used by this instance.
* @param threadFactory the ThreadFactory to use, or {@code null} if the default should be used.
* @param args arguments which will passed to each {@link #newChild(Executor, Object...)} call
*/
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory == null ? null : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(threadFactory), args);
}
/**
* Create a new instance.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads that will be used by this instance.
* @param executor the Executor to use, or {@code null} if the default should be used.
* @param args arguments which will passed to each {@link #newChild(Executor, Object...)} call
*/
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
protected ThreadFactory newDefaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(getClass());
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
return children[Math.abs(childIndex.getAndIncrement() % children.length)];
}
...
可以看到构造方法,就是创建多个 child (真正处理的执行者)。其中 newChild 交给子类实现,我们看一下NioEventLoopGroup newChild 的实现。
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0]);
}
至此,我们摸清了最终“干活”的人就是 NioEventLoop 。
参考资料
无
netty(三)---NioEventLoop分析的更多相关文章
- Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(三)—NioEventLoop的执行
前面两篇文章Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(一)—NioEventLoop的创建与Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(二)—NioEventLoop的启动中我们对NioEven ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第1节: NioEventLoopGroup之创建线程执行器
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 概述: 通过上一章的学习, 我们了解了Server启动的大致流程, 有很多组件与模块并没有细讲, 从这个章开始, 我们开始详细剖析netty的各个 ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第3节: 初始化线程选择器
Netty源码分析第二章:NioEventLoop 第三节:初始化线程选择器 回到上一小节的MultithreadEventExecutorGroup类的构造方法: protected Multi ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第6节: 执行select操作
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第六节: 执行select操作 分析完了selector的创建和优化的过程, 这一小节分析select相关操作 跟到跟到select操作的入口 ...
- Netty源码分析之NioEventLoop(二)—NioEventLoop的启动
上篇文章中我们对Netty中NioEventLoop创建流程与源码进行了跟踪分析.本篇文章中我们接着分析NioEventLoop的启动流程: Netty中会在服务端启动和新连接接入时通过chooser ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第2节: NioEventLoopGroup之NioEventLoop的创建
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第二节: NioEventLoopGroup之NioEventLoop的创建 回到上一小节的MultithreadEventExecutorG ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第4节: NioEventLoop线程的启动
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第四节: NioEventLoop线程的启动 之前的小节我们学习了NioEventLoop的创建以及线程分配器的初始化, 那么NioEvent ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第5节: 优化selector
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第五节: 优化selector 在剖析selector轮询之前, 我们先讲解一下selector的创建过程 回顾之前的小节, 在创建NioEv ...
- Netty源码分析第2章(NioEventLoop)---->第7节: 处理IO事件
Netty源码分析第二章: NioEventLoop 第七节:处理IO事件 上一小节我们了解了执行select()操作的相关逻辑, 这一小节我们继续学习select()之后, 轮询到io事件的相关 ...
随机推荐
- c#中的强类型、弱类型和泛型
强类型和弱类型的变量都有两个属性:类型和值. 强类型的变量类型是不能改变的,弱类型的变量类型是随需改变的,这是强弱的真正含义. 我们在编写c#代码时,变量类型是明确的,不可更改的,如string就是s ...
- plt/sns draw histgram
当使用如下代码保存使用 plt.savefig 保存生成的图片时,结果打开生成的图片却是一片空白. import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = np.triu(ged) # ...
- C++-数据抽象入门
一.假定数据是如何存储的 隐藏某些实现逻辑时,我们是想要隐藏绘制子弹的细节.我们是通过使用一个可以调用的函数,而不是直接写出绘制子弹到屏幕上的代码来实现的.这里同样可以使用一个函数来隐藏棋盘存储的细节 ...
- 数据库 concat 与 ||
mysql中用concat,oracle中concat和||都有,都是做字符串拼接的 oracle简单实例: 1.建表 CREATE TABLE tab1 (col1 VARCHAR2(6), col ...
- laravel如何A表中包含B表中信息
A表中如何包含B表中的信息 首先看A表的信息 接着看B表的信息 我的需求就是 A表字段name对应B表字段ream_name然后得到B表的对应主键ID要在A表中查询出来 发现问题就是查询出来的id和A ...
- 大数据-SparkStreaming
SparkStreaming SparkStreaming是一种微批处理,准实时的流式框架.数据来源包括:Kafka, Flume,TCP sockets,Twitter,ZeroMQ等 SparkS ...
- 使用imread()函数读取图片的六种正确姿势
OpenCV实践之路——使用imread()函数读取图片的六种正确姿势 opencv里的argv[1]指向的文件在哪里 测试 #include "opencv2/highgui/highgu ...
- 「口胡题解」「CF965D」Single-use Stones
目录 题目 口胡题解 题目 有许多的青蛙要过河,可惜的是,青蛙根本跳不过河,他们最远只能跳 \(L\) 单位长度,而河宽 \(W\) 单位长度. 在河面上有一些石头,距离 \(i\) 远的地方有 \( ...
- MySQL中int(11)的意思
参考文献:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012479448 int(11)中的11代表的是字符的显示宽度,在字段类型为int时,无论你显示宽度设置为多少,int类 ...
- Js选择器总结
一.原生JS选择器 JS选择器常用的有getElementById().getElementsByName().getElementsByTagName().getElementsByClassNam ...
