java深入探究12-框架之Structs
注意每次修改配置文件后必须项目重启
Structs2=structs1+xwork
Struct2框架预先实现了一些功能:
1.请求数据的封装;2.文件上传的功能3.对国际化功能的简化4.文件效验功能
1.开发Structs框架的步骤:
1)引入8大jar包
commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar 【文件上传相关包】
commons-io-2.0.1.jar
struts2-core-2.3.4.1.jar 【struts2核心功能包】
xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar 【Xwork核心包】
ognl-3.0.5.jar 【Ognl表达式功能支持表】
commons-lang3-3.1.jar 【struts对java.lang包的扩展】
freemarker-2.3.19.jar 【struts的标签模板库jar文件】
javassist-3.11.0.GA.jar 【struts对字节码的处理相关jar】
2)配置web.xml
主要配置filter Struct过滤器,StructsPrepareAndExecuteFilter核心过滤器
//引入struct核心过滤器
<filter>
<filter-name>struct2</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struct2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
3)开发Action
方法满足:无参数,放回值为String,public修饰
编写普通类1.继承ActionSupport有数据效验时必须继承;2.或者实现action接口
3.什么都不写,直接return ”success”再从structs.xml中找到对应的返回页面
例如:
public String register() {
System.out.println("register()" + userName);
return "register";
}
再配置文件中配置
<action name="register" class="cn.itcast.a_config.UserAction" method="register">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
可以使用通配符优化配置
<!-- 使用通配符优化上面的步骤 -->
<!-- http://localhost:8080/struts02/user_login -->
<action name="user_*" class="cn.itcast.a_config.UserAction" method="{1}">
<result name="{1}">/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
public class HelloAction extends ActionSupport {
// 处理请求
public String execute() throws Exception {}
}
4)配置struct.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<!--
package 定义一个包。 包作用,管理action。
(通常,一个业务模板用一个包)
name 包的名字; 包名不能重复;
extends 当前包继承自哪个包
在struts中,包一定要继承struts-default
struts-default在struts-default.xml中定的包
abstract
表示当前包为抽象包; 抽象包中不能有action的定义,否则运行时期报错
abstract=true 只有当当前的包被其他包继承时候才用!
如:
<package name="basePackage" extends="struts-default" abstract="true"></package>
<package name="user" extends="basePackage">
namespace 名称空间,默认为"/"
作为路径的一部分
访问路径= http://localhost:8080/项目/名称空间/ActionName action 配置请求路径与Action类的映射关系
name 请求路径名称
class 请求处理的aciton类的全名
method 请求处理方法
result
name action处理方法返回值
type 跳转的结果类型
标签体中指定跳转的页面 -->
<package name="user" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="login" class="cn.itcast.b_execute.UserAction" method="login">
<result name="login">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
</package> </struts>
2.访问流程:
tomcat服务器启动-》读取web,xml-》读取struct2核心过滤器-》初始化过滤器-》init方法(这里分别读取了struct-default.xml核心功能初始化有拦截器等;struct-plugin.xml:struct相关插件;struct.xml用户编写的xml)-》读取到struct.xml后找到action类-》读取structs.properties用户自定义配置文件会覆盖Structs.xml中的常量设置-》加载到内存中等待访问再实例化action类
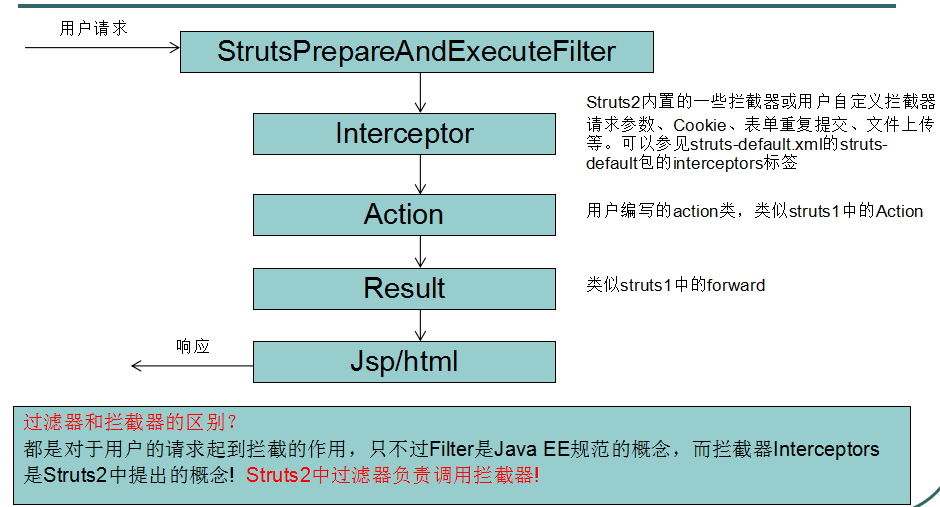
3.一些配置文件详解
struct-default.xml
目录:struts2-core-2.3.4.1.jar/ struts-default.xml
内容:
1. bean节点指定struts在运行的时候创建的对象类型
2.指定struts-default包 【用户写的package(struts.xml)一样要继承此包 】
package struts-default 包中定义了:
a. 跳转的结果类型
dispatcher 转发,不指定默认为转发
redirect 重定向
redirectAction 重定向到action资源
stream (文件下载的时候用)
b. 定义了所有的拦截器
定义了32个拦截器!
为了拦截器引用方便,可以通过定义栈的方式引用拦截器,
此时如果引用了栈,栈中的拦截器都会被引用! defaultStack
默认的栈,其中定义默认要执行的18个拦截器! c. 默认执行的拦截器栈、默认执行的action
<default-interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
<default-class-ref class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport" /> <interceptor
name="prepare" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.PrepareInterceptor"/>
<interceptor
name="params" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ParametersInterceptor"/>
自己的struct。xml配置
1)两种方便访问action的方法“通配符”“动态配置”
通配符:可以使用* 和{1}来优化配置
动态配置:这个访问方式action名字!action类中的需要访问的方法名例如:hello!add.action
/struct2/hello!add.action:用这个只有在常量设置中设置
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="false"/>
<action name="user_*_*" class="" method="{1}{2}">
<result name="{1}">/{1}.jsp</result>
</action>
2)路径匹配原则
/Struts2_01/hello_a/a/b/helloWorld.action
/Struts2_01/hello_a/a/b找package->没找到/Struts2_01/hello_a/a-》没找到/Struts2_01/hello_a没找到/Struts2_01/-报404错
3)常量
所有的初始化全局变量配置都在Structs-core-2.3.4-1.jar/org.apache.structs/default.properities
#
# $Id: default.properties 1132110 2011-06-05 08:45:32Z lukaszlenart $
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
# distributed with this work for additional information
# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
# software distributed under the License is distributed on an
# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
# specific language governing permissions and limitations
# under the License.
#
### START SNIPPET: complete_file ### Struts default properties
###(can be overridden by a struts.properties file in the root of the classpath)
### ### Specifies the Configuration used to configure Struts
### one could extend org.apache.struts2.config.Configuration
### to build one's customize way of getting the configurations parameters into Struts
# struts.configuration=org.apache.struts2.config.DefaultConfiguration ### This can be used to set your default locale and encoding scheme
# struts.locale=en_US
struts.i18n.encoding=UTF-8 ### if specified, the default object factory can be overridden here
### Note: short-hand notation is supported in some cases, such as "spring"
### Alternatively, you can provide a com.opensymphony.xwork2.ObjectFactory subclass name here
# struts.objectFactory = spring ### specifies the autoWiring logic when using the SpringObjectFactory.
### valid values are: name, type, auto, and constructor (name is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire = name ### indicates to the struts-spring integration if Class instances should be cached
### this should, until a future Spring release makes it possible, be left as true
### unless you know exactly what you are doing!
### valid values are: true, false (true is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.useClassCache = true ### ensures the autowire strategy is always respected.
### valid values are: true, false (false is the default)
struts.objectFactory.spring.autoWire.alwaysRespect = false ### if specified, the default object type determiner can be overridden here
### Note: short-hand notation is supported in some cases, such as "tiger" or "notiger"
### Alternatively, you can provide a com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ObjectTypeDeterminer implementation name here
### Note: By default, com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.DefaultObjectTypeDeterminer is used which handles type detection
### using generics. com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.GenericsObjectTypeDeterminer was deprecated since XWork 2, it's
### functions are integrated in DefaultObjectTypeDeterminer now.
### To disable tiger support use the "notiger" property value here.
#struts.objectTypeDeterminer = tiger
#struts.objectTypeDeterminer = notiger ### Parser to handle HTTP POST requests, encoded using the MIME-type multipart/form-data
# struts.multipart.parser=cos
# struts.multipart.parser=pell
struts.multipart.parser=jakarta
# uses javax.servlet.context.tempdir by default
struts.multipart.saveDir=
struts.multipart.maxSize=2097152 ### Load custom property files (does not override struts.properties!)
# struts.custom.properties=application,org/apache/struts2/extension/custom ### How request URLs are mapped to and from actions
#struts.mapper.class=org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.mapper.DefaultActionMapper ### Used by the DefaultActionMapper
### You may provide a comma separated list, e.g. struts.action.extension=action,jnlp,do
### The blank extension allows you to match directory listings as well as pure action names
### without interfering with static resources, which can be specified as an empty string
### prior to a comma e.g. struts.action.extension=, or struts.action.extension=x,y,z,,
struts.action.extension=action,, ### Used by FilterDispatcher
### If true then Struts serves static content from inside its jar.
### If false then the static content must be available at <context_path>/struts
struts.serve.static=true ### Used by FilterDispatcher
### This is good for development where one wants changes to the static content be
### fetch on each request.
### NOTE: This will only have effect if struts.serve.static=true
### If true -> Struts will write out header for static contents such that they will
### be cached by web browsers (using Date, Cache-Content, Pragma, Expires)
### headers).
### If false -> Struts will write out header for static contents such that they are
### NOT to be cached by web browser (using Cache-Content, Pragma, Expires
### headers)
struts.serve.static.browserCache=true ### Set this to false if you wish to disable implicit dynamic method invocation
### via the URL request. This includes URLs like foo!bar.action, as well as params
### like method:bar (but not action:foo).
### An alternative to implicit dynamic method invocation is to use wildcard
### mappings, such as <action name="*/*" method="{2}" class="actions.{1}">
struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation = true ### Set this to true if you wish to allow slashes in your action names. If false,
### Actions names cannot have slashes, and will be accessible via any directory
### prefix. This is the traditional behavior expected of WebWork applications.
### Setting to true is useful when you want to use wildcards and store values
### in the URL, to be extracted by wildcard patterns, such as
### <action name="*/*" method="{2}" class="actions.{1}"> to match "/foo/edit" or
### "/foo/save".
struts.enable.SlashesInActionNames = false ### use alternative syntax that requires %{} in most places
### to evaluate expressions for String attributes for tags
struts.tag.altSyntax=true ### when set to true, Struts will act much more friendly for developers. This
### includes:
### - struts.i18n.reload = true
### - struts.configuration.xml.reload = true
### - raising various debug or ignorable problems to errors
### For example: normally a request to foo.action?someUnknownField=true should
### be ignored (given that any value can come from the web and it
### should not be trusted). However, during development, it may be
### useful to know when these errors are happening and be told of
### them right away.
struts.devMode = false ### when set to true, resource bundles will be reloaded on _every_ request.
### this is good during development, but should never be used in production
struts.i18n.reload=false ### Standard UI theme
### Change this to reflect which path should be used for JSP control tag templates by default
struts.ui.theme=xhtml
struts.ui.templateDir=template
#sets the default template type. Either ftl, vm, or jsp
struts.ui.templateSuffix=ftl ### Configuration reloading
### This will cause the configuration to reload struts.xml when it is changed
struts.configuration.xml.reload=false ### Location of velocity.properties file. defaults to velocity.properties
struts.velocity.configfile = velocity.properties ### Comma separated list of VelocityContext classnames to chain to the StrutsVelocityContext
struts.velocity.contexts = ### Location of the velocity toolbox
struts.velocity.toolboxlocation= ### used to build URLs, such as the UrlTag
struts.url.http.port = 80
struts.url.https.port = 443
### possible values are: none, get or all
struts.url.includeParams = none ### Load custom default resource bundles
# struts.custom.i18n.resources=testmessages,testmessages2 ### workaround for some app servers that don't handle HttpServletRequest.getParameterMap()
### often used for WebLogic, Orion, and OC4J
struts.dispatcher.parametersWorkaround = false ### configure the Freemarker Manager class to be used
### Allows user to plug-in customised Freemarker Manager if necessary
### MUST extends off org.apache.struts2.views.freemarker.FreemarkerManager
#struts.freemarker.manager.classname=org.apache.struts2.views.freemarker.FreemarkerManager ### Enables caching of FreeMarker templates
### Has the same effect as copying the templates under WEB_APP/templates
struts.freemarker.templatesCache=false ### Enables caching of models on the BeanWrapper
struts.freemarker.beanwrapperCache=false ### See the StrutsBeanWrapper javadocs for more information
struts.freemarker.wrapper.altMap=true ### maxStrongSize for MruCacheStorage for freemarker
struts.freemarker.mru.max.strong.size=100 ### configure the XSLTResult class to use stylesheet caching.
### Set to true for developers and false for production.
struts.xslt.nocache=false ### Whether to always select the namespace to be everything before the last slash or not
struts.mapper.alwaysSelectFullNamespace=false ### Whether to allow static method access in OGNL expressions or not
struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess=false ### Whether to throw a RuntimeException when a property is not found
### in an expression, or when the expression evaluation fails
struts.el.throwExceptionOnFailure=false ### Logs as Warnings properties that are not found (very verbose)
struts.ognl.logMissingProperties=false ### Caches parsed OGNL expressions, but can lead to memory leaks
### if the application generates a lot of different expressions
struts.ognl.enableExpressionCache=true
### END SNIPPET: complete_file
1.Struct中默认访问后缀
Struct1:.do;Struct2:.action
2.在Struct.xml通过常量修改
<constant name="struct.action.extension" value="action,do,"></constant>
指定访问后缀为action/do/没有访问后缀都可以
value="action,do,"不带后缀
value="action,do"访问后缀action或do
value="action" 后缀只能是action
3.常量在struct.xml中配置
<!-- 1.常量 -->
<!-- 指定默认编码集,作用于HttpServletRequest的setCharacterEncoding方法 和freemarker 、velocity的输出 -->
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<!-- 自定义后缀修改常量 -->
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="do"/>
<!-- 设置浏览器是否缓存静态内容,默认值为true(生产环境下使用),开发阶段最好关闭 -->
<constant name="struts.serve.static.browserCache" value="false"/>
<!-- 当struts的配置文件修改后,系统是否自动重新加载该文件,默认值为false(生产环境下使用),开发阶段最好打开 -->
<constant name="struts.configuration.xml.reload" value="true"/>
<!-- 开发模式下使用,这样可以打印出更详细的错误信息 -->
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />
<!-- 默认的视图主题 -->
<constant name="struts.ui.theme" value="simple" />
<!-- 与spring集成时,指定由spring负责action对象的创建 -->
<constant name="struts.objectFactory" value="spring" />
<!-- 该属性设置Struts 2是否支持动态方法调用,该属性的默认值是true。如果需要关闭动态方法调用,则可设置该属性
为 false -->
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="false"/>
<!-- 上传文件的大小限制 -->
<constant name="struts.multipart.maxSize" value="10701096"/>
4)resultType
1.在action中想要获得request对象:
ServletActionContext.getRequest();ServletActionContext是action重要对象

2.其中type的设置有

3.result全局结果
当多个action中使用了相同的result,为了避免result的重复,我们可以设置全局结果;但是局部权限大于全局
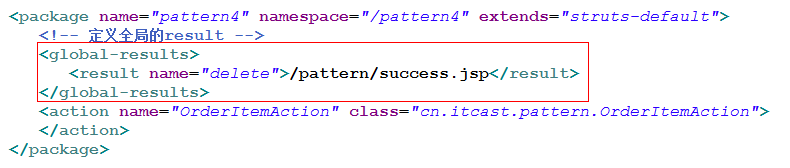
4.数据封装
1)struts对数据封装,当访问action时,参与核心过滤器,访问default-struts.xml->strut.xml,在default-struts.xml中有32个拦截器,其中Parameters拦截器对数据进行封装
2)String-》基本数据类型转换是自动的
String-》Date日期类型的转换是有条件的
3)转换原理过程
1.表单中的name值自动映射到Action中的一个属性;2.还可以映射到一个集合
3.Struts对HttpServetRequest,HttpSession,ServletContext进行了封装,构造了三个Map对象,可通过ServletActionContext来访问三个对象
4)在action中两种获得数据的方法
1.ServletApi 2.通过ServletActionContext获得ActionContext对象得到三个封装好的Map对象3.实现三个接口RequestAware, SessionAware, ApplicationAwar也可以
方式一:通过Servlet Api
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
ServletContext application = ServletActionContext.getServletContext();
// 操作
request.setAttribute("request_data", "request_data1");
session.setAttribute("session_data", "session_data1");
application.setAttribute("application_data", "application_data1");
方式二:推荐这个方法
// Struts中对数据操作,方式2: 通过ActionContext类
ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext();
// 得到Struts对HttpServletRequest对象进行了封装,封装为一个map
// 拿到表示request对象的map
Map<String,Object> request = ac.getContextMap();
// 拿到表示session对象的map
Map<String, Object> session = ac.getSession();
// 拿到表示servletContext对象的map
Map<String, Object> application = ac.getApplication(); // 数据
request.put("request_data", "request_data1_actionContext");
session.put("session_data", "session_data1_actionContext");
application.put("application_data", "application_data1_actionContext");
/**
* 数据处理, 方式3: 实现接口的方法
* @author Jie.Yuan
*
*/
public class DataAction extends ActionSupport implements RequestAware, SessionAware, ApplicationAware{ private Map<String, Object> request;
private Map<String, Object> session;
private Map<String, Object> application; // struts运行时候,会把代表request的map对象注入 public void setRequest(Map<String, Object> request) {
this.request = request;
} // 注入session public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) {
this.session = session;
} // 注入application public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) {
this.application = application;
} public String execute() throws Exception { // 数据
/*
*
// Struts中对数据操作,方式1: 直接拿到ServletApi, 执行操作
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
ServletContext application = ServletActionContext.getServletContext();
// 操作
request.setAttribute("request_data", "request_data1");
session.setAttribute("session_data", "session_data1");
application.setAttribute("application_data", "application_data1");
*/ // 【推荐:解耦的方式实现对数据的操作】
// Struts中对数据操作,方式2: 通过ActionContext类
ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext();
// 得到Struts对HttpServletRequest对象进行了封装,封装为一个map
// 拿到表示request对象的map
Map<String,Object> request = ac.getContextMap();
// 拿到表示session对象的map
Map<String, Object> session = ac.getSession();
// 拿到表示servletContext对象的map
Map<String, Object> application = ac.getApplication(); // 数据
request.put("request_data", "request_data1_actionContext");
session.put("session_data", "session_data1_actionContext");
application.put("application_data", "application_data1_actionContext");
//
return SUCCESS;
} }
5.类型转换
前面说了数据转换String->基本类型类型自动的,日期需要条件
1)是Parameters拦截器做的类似于: Beanutils工具
2)自定义类型转换器
1.继承StrutsTypeConverter
2.全局转换,局部转换配置
例子:
/**
* 自定义类型转换器类
*
* @author Jie.Yuan
*
*/
public class MyConverter extends StrutsTypeConverter { // 新需求: 要求项目中要支持的格式,如: yyyy-MM-dd/yyyyMMdd/yyyy年MM月dd日.. // 先定义项目中支持的转换的格式
DateFormat[] df = { new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"),
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd"),
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日") }; /**
* 把String转换为指定的类型 【String To Date】
*
* @param context
* 当前上下文环境
* @param values
* jsp表单提交的字符串的值
* @param toClass
* 要转换为的目标类型
*/
@Override
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass) { // 判断: 内容不能为空
if (values == null || values.length == ) {
return null;
}
// 判断类型必须为Date
if (Date.class != toClass) {
return null;
} // 迭代:转换失败继续下一个格式的转换; 转换成功就直接返回
for (int i=; i<df.length; i++) {
try {
return df[i].parse(values[]);
} catch (ParseException e) {
continue;
}
}
return null;
} @Override
public String convertToString(Map context, Object o) {
return null;
} }
局部配置:在自定义转化器添加(自定义转换器名字-conversion.properties):MyConverter-conversion.properties
在其中写:需要转换的字段名=自定义转换器类的权限定名birth=type.MyConverter
全局配置:在项目src目录下建立固定文件xwork-conversion.properties
在其中写:需要转换的类类型=转换器类的权限定名 :java.util.Date=type.MyConverter(java.util.Date是birth的类型)
3)struts-default.xml <interceptor name="conversionError" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.StrutsConversionErrorInterceptor"/>
该拦截器负责对错误信息处理
6.文件支持
1)文件上传
1.核心类:FileItemFactory;ServletFileUpload;FileItem
2.struts处理上传文件:
获得上传文件的file,对应的fileName,fileContextType,之后再execute中执行对上传文件的处理;
上传文件默认都是被缓存到.me_tcat\work\Catalina\localhost\struts02\upload_5bd0b60c_15c3369eeb3__8000_00000005.tmp中
我们要做的是把文件得到存到我们指定的位置
3.配置action:在action子栏中添加。。。等信息
在default-struts中有拦截器fileUpload,而在ServletFileUpload类中文件属性我们都可以在自己写的拦截器中添加
<!-- 限制运行上传的文件的类型 -->
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"> <!-- 限制运行的文件的扩展名 -->
<param name="fileUpload.allowedExtensions">txt,jpg,jar</param>
<param name="fileUpload.maximumSize"></param>
<!-- 限制运行的类型 【与上面同时使用,取交集】
<param name="fileUpload.allowedTypes">text/plain</param>
--> </interceptor-ref>
当文件上传错误时,会自动放回字符串input,我们可以在action中配置跳转到指定页面,这个页面想要显示错误信息可以通过引用struts标签,显示
4.上传例子
.jsp
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/fileUploadAction" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
用户名:<input type="text" name="userName"><br/>
文件:<input type="file" name="file1"><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传">
</form>
.action
public class FileUpload extends ActionSupport { /**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 对应表单:<input type="file" name="file1">
private File file1;
// 文件名
private String file1FileName;
// 文件的类型(MIME)
private String file1ContentType;
public void setFile1(File file1) {
this.file1 = file1;
}
public void setFile1FileName(String file1FileName) {
this.file1FileName = file1FileName;
}
public void setFile1ContentType(String file1ContentType) {
this.file1ContentType = file1ContentType;
}
//上面的代码是通过拦截器对数据自动封装到这三个属性中的 @Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
/******拿到上传的文件,进行处理******/
// 把文件上传到upload目录 System.out.println(file1FileName);
System.out.println(file1ContentType);
// 获取上传的目录路径
String path = ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
System.out.println(path);
// 创建目标文件对象
File destFile = new File(path,file1FileName);
// 把上传的文件,拷贝到目标文件中
FileUtils.copyFile(file1, destFile); return SUCCESS;
}
}
2)文件下载
访问连接down_down.action就是到down_list的action中找到类,对应的list方法,下面的例子是list方法返回list字符串在action中就找到对于的result放回到list.jsp中,在这里通过点击下载-》又发送连接down_down?fileName=文件名.txt-》找到down_down的action找到对应的类里面的down方法开始下载-》随后在对应的action中找到result,这个result的为属于下载业务功能,需要特殊设置:
type="stream";之后在子项中添加四个param子标签
<!-- 下载操作 -->
<result name="download" type="stream">
<!-- 运行下载的文件的类型:指定为所有的二进制文件类型 -->
<param name="contentType">application/octet-stream</param> <!-- 对应的是Action中属性: 返回流的属性【其实就是getAttrInputStream()】 -->
<param name="inputName">attrInputStream</param> <!-- 下载头,包括:浏览器显示的文件名 -->
<param name="contentDisposition">attachment;filename=${downFileName}</param> <!-- 缓冲区大小设置 -->
<param name="bufferSize"></param>
</result>
之后我们需要在action类中再写 1.放回流属性的getAttrInputStream()方法放回要下载文件的流;
2.返回下载头包含浏览器显示的文件名:getDownFileName()
上传下载的整体例子
上传
.file.xml中的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="file" extends="struts-default" namespace="/">
<action name="FileUploadAction" class="fileupload.FileUpload">
<!-- 文件上传有拦截器我们自己定义下,在defaultStrack中的一些定义好的元素会别创建我们可以对他们属性设置 -->
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack">
<param name="fileUpload.allowedExtension">txt,jpg,jar</param>
<param name="fileUpload.maximumSize"></param>
</interceptor-ref>
<result name="success">/e/success.jsp</result>
<result name="input">/e/error.jsp</result>
</action> <action name="down_*" class="fileupload.DownAction" method="{1}">
<!-- 列表显示 -->
<result name="list">e/list.jsp</result>
<!-- 下载操作 -->
<result name="download" type="stream">
<!-- 运行下载的文件的类型:指定为所有的二进制文件类型 -->
<param name="contentType">application/octet-stream</param> <!-- 对应的是Action中属性: 返回流的属性【其实就是getAttrInputStream()】 -->
<param name="inputName">attrInputStream</param> <!-- 下载头,包括:浏览器显示的文件名 -->
<param name="contentDisposition">attachment;filename=${downFileName}</param> <!-- 缓冲区大小设置 -->
<param name="bufferSize"></param>
</result>
</action>
</package> </struts>
.FileUpload.java代码
package fileupload; import java.io.File; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; /**
* 文件上传
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class FileUpload extends ActionSupport{
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private File file1;
private String file1FileName;
//上面的代码是通过拦截器对数据自动封装到这三个属性中的 public void setFile1(File file1) {
this.file1 = file1;
} public void setFile1FileName(String file1FileName) {
this.file1FileName = file1FileName;
} @Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
String path=ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File destDir=new File(path,file1FileName);
FileUtils.copyDirectory(file1, destDir);
System.out.println("上传成功");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
.提交上传的表单jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/structs/FileUploadAction" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
文件:<input type="file" name="file1"/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
下载
.DownAction.java
package fileupload; import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.Map; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class DownAction extends ActionSupport{ /**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/************显示所有需要下载的文件*************/
public String list(){
String path=ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getRealPath("/upload");
File file=new File(path);
String[] fileNames = file.list();//得到所有下载的文件名
//保存
ActionContext ac=ServletActionContext.getContext();
Map<String,Object> request=(Map<String, Object>) ac.get("request");
request.put("fileNames", fileNames);
return "list";
} /***************2.文件下载****************/
/*1。获得要下载的文件名字*/
private String fileName;
public void setFileName(String fileName){
//这里提交时get提交存在乱码问题需要解决下
try {
fileName=new String(fileName.getBytes("ISO8859-1"),"UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.fileName=fileName;
}
/*2.下载提交业务*/
public String down(){
return "download";
}
/*3.返回文件流的方法*/
public InputStream getAttrInputStream(){
return ServletActionContext.getServletContext().getResourceAsStream("/upload"+fileName);
} /*4.下载显示的文件名*/
public String getDownFileName(){
//需要中文编码
try {
fileName=URLEncoder.encode(fileName,"UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return fileName;
} }
.显示所有下载文件的list.jsp
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>下载列表</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="">
</head> <body>
list列表
<table border="" align="center" >
<tr>
<td>编号</td>
<td>文件名</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<c:forEach items="${fileNames }" varStatus="vs" var="fileName">
<tr>
<td>${vs.count}</td>
<td>${fileName}</td>
<td>
<!-- 创建一个url -->
<c:url var="url" value="down_down">
<c:param name="fileName" value="${fileName }"></c:param>
</c:url>
<a href="${url }">下载</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html> 。访问方式:先访问list,再下载
6.拦截器
a) 想出拦截器原因
用户想要给action什么功能的时候可以通过拦截器自由组装,基于组件的设计
b) 知识点:拦截器在struts-default中定义了32种拦截器,18中默认拦截器
拦截器栈:组合多个拦截器,默认使用strut-default的18个默认拦截器defaultStack
一旦用户指定哪个拦截器,默认拦截器就不起作用了
c) 拦截器的配置
在struts-default中定义所有的拦截器其中默认拦截器
<interceptor-stack name="defaultStack">
<interceptor-ref name="exception"/>
<interceptor-ref name="alias"/>
<interceptor-ref name="servletConfig"/>
<interceptor-ref name="i18n"/>
<interceptor-ref name="prepare"/>
<interceptor-ref name="chain"/>
<interceptor-ref name="scopedModelDriven"/>
<interceptor-ref name="modelDriven"/>
<interceptor-ref name="fileUpload"/>
<interceptor-ref name="checkbox"/>
<interceptor-ref name="multiselect"/>
<interceptor-ref name="staticParams"/>
<interceptor-ref name="actionMappingParams"/>
<interceptor-ref name="params">
<param name="excludeParams">dojo\..*,^struts\..*,^session\..*,^request\..*,^application\..*,^servlet(Request|Response)\..*,parameters\...*</param>
</interceptor-ref>
<interceptor-ref name="conversionError"/>
<interceptor-ref name="validation">
<param name="excludeMethods">input,back,cancel,browse</param>
</interceptor-ref>
<interceptor-ref name="workflow">
<param name="excludeMethods">input,back,cancel,browse</param>
</interceptor-ref>
<interceptor-ref name="debugging"/>
</interceptor-stack>
自己在struts中定义拦截器
1.定义拦截器和拦截器栈
1.1定义拦截器
<interceptors name=”” class=””></interceptors>
1.2定义拦截器栈
<interceptors-stack name=””>
引用上面的或其他的拦截器
</interceptors-stack>
2.默认执行拦截器(栈)
<default-interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/>
e) 拦截器核心api
Interceptor接口
AbstractInterceptor 拦截器默认实现的抽象类,一般自定义开发继承它就行了
ActionInvacation 拦截器的执行状态,调用下一个拦截器或者action
f) 拦截器和过滤器的区别
g) 拦截器的生命周期
服务器启动-》过滤器创建-》初始化init()创建所有拦截器对象-》客户端访问-》创建action实例-》拦截器interceptor方法拦截-》下一个拦截-》。。。》到达action执行execute()->返回给用户结果
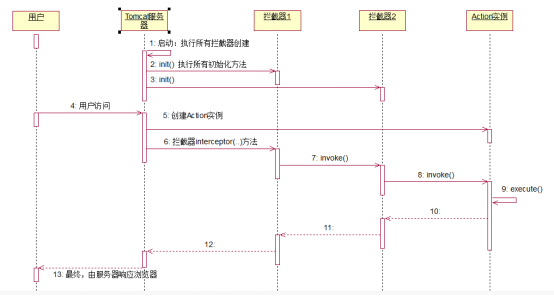
h) 自定义拦截器例子
1.写一个拦截器类
package interceptor; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor; /**
* 拦截器定义
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class HelloInterceptor implements Interceptor{ /**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("销毁。。。。。");
} @Override
public void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("自定义拦截器初始化成功");
}
/**
* 拦截器业务处理:在访问action时执行,在excute之前执行
*/
@Override
public String intercept(ActionInvocation arg0) throws Exception {
System.out.println("拦截器开始执行");
//执行业务逻辑
//执行下一个拦截器
String aa=arg0.invoke();
//拦截器结束
System.out.println("拦截器结束");
return aa;
} }
2.配置struts配置拦截器分3步
a) 定义自定义拦截器<interceptor>
b) 定义我们的拦截器栈<interceptor-stack>:其中引用默认拦截器栈要放在第一位
c) 执行拦截器:<default-interceptor-ref>
<!-- 拦截器配置 -->
<interceptors>
<interceptor name="helloInterceptor" class="interceptor.HelloInterceptor"></interceptor>
<interceptor-stack name="helloStack">
<!-- 引用默认栈 (一定要放到第一行)-->
<interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"></interceptor-ref>
<!-- 引用自定义拦截器 -->
<interceptor-ref name="helloInterceptor"></interceptor-ref>
</interceptor-stack>
</interceptors>
<!-- 执行拦截器 -->
<default-interceptor-ref name="helloStack"></default-interceptor-ref>
<action name="hello" class="interceptor.HelloAction">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
7.国际化
a) Serlvelt中的国际化
- 写资源文件
基础名.properties【默认的语言环境设置】
基础名_语言简称_国家简称.properties
- 读取资源文件再使用
程序:ResourceBundle
Jsp: jstl提供的格式化与国际化标签库。
b) Struts中的国际化
- 写资源文件(同servlet)
- 读取资源文件再使用
程序:ResourceBundle
Jsp: 1)jstl表亲啊 (同servlet)
2)struts标签获取资源文件内容
c) 注意
还可以在页面加载
<s:i18n name="cn.itcast.config.msg">
<s:text> 标签必须放到标签体中。
</s:i18n>
d) 区别
Struts2加载资源文件更加简单!通过常量加载即可!再在jsp页面直接使用
|
à1. 写资源文件 |
|
Msg.properties 默认的语言环境; 找不到配置就找它 |
|
Msg_en_US.properties 美国 |
|
-à2. 加载 |
|
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources" value="cn.itcast.config.msg"></constant> |
|
à3. 使用: 标签name值直接写配置文件中的key |
|
<s:text name="title"></s:text> |
8.Ognl表达式语言与Struts标签
深刻理解Ognl,Struct2传输模式
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7ffb8dd5010141pd.html
.ActionContext装饰OgnlContext
.OgnlValueStack值栈对象包含了OgnlContext,root对象
.OgnlContext中包含了所有域对象,全局属性,action对象等等
.Struts2数据传输DataTransfer的核心对象是OgnlValueStack、 OgnlContext
这里主要需要知道的是“值栈对象”生成过程和内部成员,调用方式
a) Ognl表达式:Object Graphic Navigation Language(对象图导航语言)的缩写是一个开源项
b) 优势:
- 支持对象方法调用,如xxx.doSomeSpecial();
支持类静态的方法调用和值访问,表达式的格式:@[类全名(包括包路径)]@[方法名 | 值名]例如:@java.lang.String@format('foo %s', 'bar')
- 支持赋值操作和表达式串联,如price=100, discount=0.8,calculatePrice(),这个表达式会返回80
- 访问OGNL上下文(OGNL context)和ActionContext;
- 操作集合对象
c) OgnlContext对象
是Ognl表达式的核心
访问Ognl表达式中值Ognl.getValue(ognl表达式,ActionContext ac,ognl的root)
例子:主要看我们对ActionContext上下文对象如何处理,ac中直接添加键值对,创建ognl表达式时要加#,ac添加root时,创建表达式就不需要了
当我们调用工具类的一个方法时,创建ognl表达式:Ognl.parseExpression("@[类名]@[方法调用]")如:@Math@floor(10.9)
1. Ognl表达式语言语言取值,取非根元素的值,必须用#号
public void testOgnl() throws Exception {
// 创建一个Ognl上下文对象
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
// 放入数据
User user = new User();
user.setId();
user.setName("Jack");
// 【往非根元素放入数据, 取值的时候表达式要用"#"】
context.put("user", user);
// 获取数据(map)
// 先构建一个Ognl表达式, 再解析表达式
Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("#user.name");
Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot());
System.out.println(value);
}
2. Ognl表达式语言语言取值,取根元素的值,不用带#号
public void testOgn2() throws Exception {
// 创建一个Ognl上下文对象
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
// 放入数据
User user = new User();
user.setId();
user.setName("Jack");
// 【往根元素放入数据】
context.setRoot(user);
// 获取数据(map)
// 先构建一个Ognl表达式, 再解析表达式
Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("address.province");
Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot());
System.out.println(value);
}
3.Ognl对 静态方法调用的支持
public void testOgn3() throws Exception {
// 创建一个Ognl上下文对象
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
// Ognl表单式语言,调用类的静态方法
//Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("@Math@floor(10.9)");
// 由于Math类在开发中比较常用,所以也可以这样写
Object ognl = Ognl.parseExpression("@@floor(10.9)");
Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognl, context, context.getRoot());
System.out.println(value);
}
4.Ognl运用在jsp页面:数据存到request中后自然就存到OgnlContext中了,在jsp页面通过#request.list就能访问到OgnlContext中的list对象和里面的值,OgnlContext就相当于一个容器,存放了所有的域对象和自己存进去的键值对
map迭代
<s:iterator var="en" value="#request.map" status="st">
<tr>
<td><s:property value="#en.key"/></td>
<td><s:property value="#en.value.name"/></td>
</tr>
</s:iterator>
不是根Obnl的根对象都是用#开头才能访问到
d) ValueStack对象
用户访问action时,创建action对象,之后再将很多信息,action对象、全局属性、域对象、等等存入值栈对象中,之后值栈对象就有了很多内容,我们取值都可以从这里取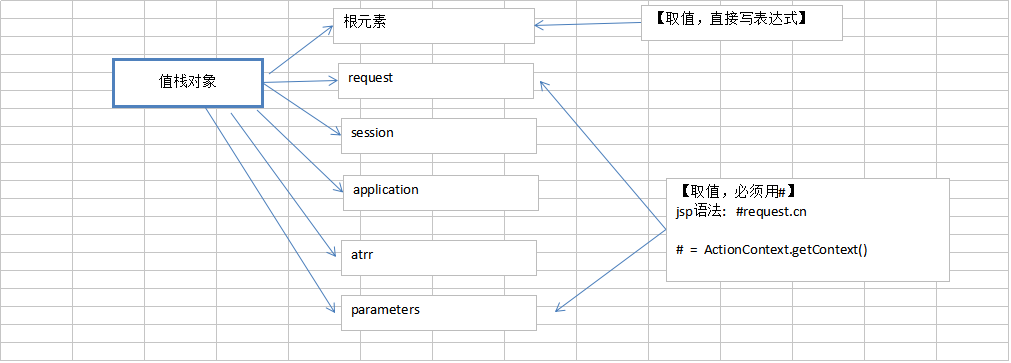

值栈对象,是struts数据存储中心,或者说是中转站
访问action时,创建了action对象、值栈对象、ActionContext对象;将action对象放入值栈对象,再将值栈对象存入request中传到jsp中
ActionContext类装饰OgnlContext类
获取值栈对象2种方式:
1.因为action对象放入值栈对象,值栈对象又存入request对象,所有想要获得ValueStack对象可以从request对象中获得
ValueStack vs1 = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute("struts.valueStack");
2.直接从ActionContext对中获得
ac..getValueStack();
e) Struts标签
Struct标签就是用了Ognl表达式语言
9.验证
代码验证
package validation; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; /**
* 验证需要实现接口或者继承ActionSupport
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class UserAction extends ActionSupport{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//封装数据的请求
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
//重写数据验证的方法
/*public void validateRegister() {
if(user.getUserName()==null||"".equals(user.getUserName())){
//保存错误信息
super.addFieldError("userName","用户名必须重写");
}
// 密码
if (user.getPwd() == null || "".equals(user.getPwd())) {
super.addFieldError("pwd", "密码必填");
}
}*/
//业务方法
public String register(){
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println();
return SUCCESS;
}
//列表展示
public String list(){
return SUCCESS;
}
}
xml验证
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC
"-//Apache Struts//XWork Validator 1.0.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/xwork-validator-1.0.3.dtd">
<validators>
<!-- 验证每一个字段用field表示 -->
<field name="user.userName">
<field-validator type="requiredstring">
<!-- 验证失败的错误提示信息 -->
<message>用户名不能为空</message>
</field-validator>
</field> <!-- 密码不能为空 -->
<field name="user.pwd">
<!-- 非空 -->
<field-validator type="requiredstring">
<message>密码不能为空!</message>
</field-validator>
<!-- 长度 -->
<field-validator type="stringlength">
<param name="minLength"></param>
<param name="maxLength"></param>
<message>密码必须为6-8位!</message>
</field-validator>
</field> <!-- 验证日期 -->
<field name="user.birth">
<field-validator type="date">
<message>日期格式不对!</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
<!-- 验证emil -->
<field name="user.emil">
<field-validator type="email">
<message>邮件格式不对</message> </field-validator>
</field>
</validators>
1)验证原理
通过拦截器验证
<interceptor name="validation" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.validation.AnnotationValidationInterceptor"/>
2)配置验证步骤
写一个类继承ActionSuppert或者实现Validate接口重写validate()方法即可
要注意的是:想要验证指定的方法只需只需验证名称规则:validate+要验证的方法名(public void validateRegister())
3)验证action的方法
1)代码验证
重写验证方法,注意命名规则可以指定特定的方法验证
validate+要验证的方法名
public void validateRegister() {
只会验证当前action的register方法!
2)XML方式验证
1.将错误信息显示在jsp页面:<s:fielderror fieldName="user.userName"></s:fielderror>
2.代码验证缺点:设计很多重复的验证逻辑!例如:非空验证、数值验证、email、日期等。
3.Struts对于常用的验证进行了封装
Struts提供的所有的验证器:xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar/com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators/default.xml
都在这里了
<!-- START SNIPPET: validators-default -->
<validators>
<validator name="required" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="requiredstring" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RequiredStringValidator"/>
<validator name="int" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.IntRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="long" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.LongRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="short" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ShortRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="double" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DoubleRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="date" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.DateRangeFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="expression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ExpressionValidator"/>
<validator name="fieldexpression" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.FieldExpressionValidator"/>
<validator name="email" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.EmailValidator"/>
<validator name="url" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.URLValidator"/>
<validator name="visitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.VisitorFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="conversion" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConversionErrorFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="stringlength" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.StringLengthFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="regex" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.RegexFieldValidator"/>
<validator name="conditionalvisitor" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.validator.validators.ConditionalVisitorFieldValidator"/>
</validators>
<!-- END SNIPPET: validators-default -->
XML文件名称语法:
指定的是所有验证:ActionClassName-validation.xml;
指定特定的方法命名规则:ActionClassName-ActionName-validation.xml
注意:此XML需要与当前要验证的acton同在一个目录
举例:UserAction-validation.xml/UserAction-register-validation.xml
例如:xml中的规则在dtd文件在xwork-core-2.3.4.1.jar下慢慢找吧dtd文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE validators PUBLIC
"-//Apache Struts//XWork Validator 1.0.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/xwork-validator-1.0.3.dtd">
<validators>
<!-- 验证每一个字段用field表示 -->
<field name="user.userName">
<field-validator type="requiredstring">
<!-- 验证失败的错误提示信息 -->
<message>用户名不能为空</message>
</field-validator>
</field> <!-- 密码不能为空 -->
<field name="user.pwd">
<!-- 非空 -->
<field-validator type="requiredstring">
<message>密码不能为空!</message>
</field-validator>
<!-- 长度 -->
<field-validator type="stringlength">
<param name="minLength"></param>
<param name="maxLength"></param>
<message>密码必须为6-8位!</message>
</field-validator>
</field> <!-- 验证日期 -->
<field name="user.birth">
<field-validator type="date">
<message>日期格式不对!</message>
</field-validator>
</field>
<!-- 验证emil -->
<field name="user.emil">
<field-validator type="email">
<message>邮件格式不对</message> </field-validator>
</field>
</validators>
3)验证总结
代码:
重写validate() , 验证action所有方法
Validate方法名(), 验证指定“方法名”的方法
Xml:
验证所有方法: ActionClassName-validation.xml
验证指定方法: ActionClassName-actionName-validation.xml
代码验证,
比较灵活,可以满足所有的需求.
比较繁琐,要写重复的验证判断逻辑!
适合: 表单字段较少的情况用!
XML验证:
通用,但不够灵活; 可以验证特定简单的业务。
适合: 验证表单字段较多,可以大大简化代码!
(配置文件过多)
4)显示错误信息:
.方式一:
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %>
<!-- 显示的是struts在运行时期产生的所有错误 -->
<s:fielderror></s:fielderror>
.方式二:
<!-- 修改struts标签默认的样式: 不让换行 --> 这样弄因为显示错写信息时会自动生成ui,ul标签 <style type="text/css"> ul{display: inline;} ul li{display: inline;color: red;} </style> .修改标签定义的模板 找到fielderror标签定义的模板文件:Struts-core.jar\template\simple\ fielderror.ftl 把修改后的文件放到src/ template/ simple/ fielderror.ftl 这样样式就修改好了
10.struts简单的UI标签
<!-- 服务器标签 : 最终别解析为html标签-->
<s:form action="/user_login" method="post" name="frmLogin" id="frmLogin" theme="simple"> 用户名:<s:textfield name="user.name"></s:textfield>
密码:<s:textfield name="user.pwd"></s:textfield>
<s:submit value="登陆"></s:submit>
</s:form>
<!-- 修改主题 (当前项目所有的标签都用此主题)-->
<constant
name="struts.ui.theme" value="simple"></constant>
11.Struts中几种特殊符号(jsp页面)
#:获取非根元素值、map集合
$:配置文件取值
%:提供一个ognl表示的运行环境
例子:
<body>
<br/>获取request域数据<br/>
<!-- property 标签是对象类型的标签,默认支持ognl表达式, 会从根元素去China名称对应的值 -->
<s:property value="China"/> <br/>
<!-- 如果直接赋值,需要用单引号 -->
<s:property value="'China'"/> <br/>
<s:property value="%{#request.cn}"/> <br/> <!-- 值类型的标签,value值默认就是值类型,不支持ognl表达式 -->
国家:<s:textfield name="txtCountry" value="%{#request.cn}"></s:textfield>
</body>
12.Struts中常用的几个技术
1)数据回显
必须使用struts标签:
进入修改页面时-》将数据信息存入request域Map中,或者存入栈值对中,在jsp页面,通过struts标签就能获得obnl标签值
两种数据存入方式
1.通过request域Map
2.通过ValueStack存入头对象,能直接访问
例子:
Action中:
// 进入修改页面
public String viewUpdate() {
// 模拟一个对象(先获取一个id,再根据id调用service查询,把查到的结果保存到域)
User userInfo = new User();
userInfo.setUserName("Jack");
userInfo.setEmail("yuanjie@itcast.cn"); ActionContext ac = ActionContext.getContext();
// Map<String,Object> request = (Map<String, Object>) ac.get("request");
// request.put("userInfo", userInfo); /************* 数据回显***************/
// 获取值栈
ValueStack vs = ac.getValueStack();
vs.pop();// 移除栈顶元素
vs.push(userInfo); // 入栈 // 进入修改页面
return "viewUpdate";
} JSP页面:
<body>
<%@taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %> <br/>
<!-- 在页面文本框内,显示要修改记录的数据 --> <!-- 手动通过value设置显示的值
<s:form action="#"> 用户名: <s:textfield name="user.userName" value="%{#request.userInfo.userName}"></s:textfield> <br/> 邮箱: <s:textfield name="user.email" value="%{#request.userInfo.email}"></s:textfield> <br/>
</s:form>
--> <!-- 数据回显技术:s:textfield会自动查找根元素数据(Ognl表达式语言取值) -->
<s:form action="#"> 用户名: <s:textfield name="userName"></s:textfield> <br/> 邮箱: <s:textfield name="email"></s:textfield> <br/>
</s:form> <s:debug></s:debug>
</body>
2)模型驱动,属性驱动
模型驱动就是直接将对象封装,属性驱动就是将属性赋值给对象的属性
<interceptor name="modelDriven" class="com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.ModelDrivenInterceptor"/>
@Override
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
Object action = invocation.getAction(); if (action instanceof ModelDriven) {
ModelDriven modelDriven = (ModelDriven) action;
ValueStack stack = invocation.getStack();
Object model = modelDriven.getModel();
if (model != null) {
stack.push(model);
}
if (refreshModelBeforeResult) {
invocation.addPreResultListener(new RefreshModelBeforeResult(modelDriven, model));
}
}
return invocation.invoke();
}
prams拦截器,可以把请求数据自动填充的action的属性中
就是数据封装的关键拦截器
4.表单重复提交拦截器
<interceptor name="token" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.TokenInterceptor"/>
Struts2知识进阶
1.继承了ActionSupport的类,想要给前台页面发送信息处了可以通过域对象发送;还可以通过以下三种方式提交信息
this.addActionMessage("message");
this.addActionError(anErrorMessage);
this.addFieldError(fieldName, errorMessage)
之后在前台界面使用<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<s:actionmessage/>;<s:actionerror/>来显示数据信息
java深入探究12-框架之Structs的更多相关文章
- Java 集合系列 12 TreeMap
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- 第51节:Java当中的集合框架Map
简书作者:达叔小生 Java当中的集合框架Map 01 Map提供了三个集合视图: 键集 值集 键-值 映射集 public String getWeek(int num){ if(num<0 ...
- 第48节:Java当中的集合框架
Java当中的集合框架 01 在我们班里有50位同学,就有50位对象. // 简书作者:达叔小生 Student[] stus = new Student[20]; 结果来了一位插班生,该同学因为觉得 ...
- java io系列12之 BufferedInputStream(缓冲输入流)的认知、源码和示例
本章内容包括3个部分:BufferedInputStream介绍,BufferedInputStream源码,以及BufferedInputStream使用示例. 转载请注明出处:http://www ...
- 2018面向对象程序设计(Java)第12周学习指导及要求
2018面向对象程序设计(Java)第12周学习指导及要求 (2018.11.15-2018.11.18) 学习目标 (1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API: (2) 掌 ...
- (转)java并发编程--Executor框架
本文转自https://www.cnblogs.com/MOBIN/p/5436482.html java并发编程--Executor框架 只要用到线程,就可以使用executor.,在开发中如果需要 ...
- Java中的集合框架-Map
前两篇<Java中的集合框架-Commection(一)>和<Java中的集合框架-Commection(二)>把集合框架中的Collection开发常用知识点作了一下记录,从 ...
- Java中的集合框架-Collection(二)
上一篇<Java中的集合框架-Collection(一)>把Java集合框架中的Collection与List及其常用实现类的功能大致记录了一下,本篇接着记录Collection的另一个子 ...
- 面向对象程序设计(JAVA) 第12周学习指导及要求
2019面向对象程序设计(Java)第12周学习指导及要求 (2019.11.15-2019.11.18) 学习目标 (1) 掌握Vetor.Stack.Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API ...
随机推荐
- linq内联左联
内联:没有into 左联:有into 例子: from GoodsStore in this.GetCurrentDbSession.Tbl_OfficeSupplies_GoodsStoreDLL. ...
- jQuery整理笔记八----jQuery的Ajax
Ajax,我一直读的是"阿贾克斯",据当时大学老师讲该读音出处是依据当年风靡欧洲的荷兰足球俱乐部阿贾克斯的名字来的,我认为说法挺靠谱的. jQuery封装了Ajax的交互过程,用户 ...
- Highway
Highway Accepted : 78 Submit : 275 Time Limit : 4000 MS Memory Limit : 65536 KB Highway In ICPCC ...
- influxDB 变换类函数
1.DERIVATIVE()函数 作用:返回一个字段在一个series中的变化率. InfluxDB会计算按照时间进行排序的字段值之间的差异,并将这些结果转化为单位变化率.其中,单位可以指定,默认为1 ...
- Machine Learning - week 2 - 编程练习
3. % J = COMPUTECOST(X, y, theta) computes the cost of using theta as the % parameter for linear r ...
- 【python】-- Django 分页 、cookie、Session、CSRF
Django 分页 .cookie.Session.CSRF 一.分页 分页功能在每个网站都是必要的,下面主要介绍两种分页方式: 1.Django内置分页 from django.shortcuts ...
- ORACLE日期时间函数
ORACLE日期时间函数大全 TO_DATE格式(以时间:2007-11-02 13:45:25为例) Year: yy two digits 两位年 ...
- standard pbr(三)-BRDF
// Default BRDF to use: #if !defined (UNITY_BRDF_PBS) // allow to explicitly override BRDF in custom ...
- RecyclerView添加分割线
mRecyclerView = findView(R.id.id_recyclerview); //设置布局管理器 mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(layout); // ...
- app开发流程有哪些
app开发流程是需求方和供求方相互协调的过程,一般分为需求分析.功能设计.功能实现.项目测试.上线等几个步骤,下面我们就来一起看看ytkah团队进行app开发各个流程主要做哪些事情,让您对app开发设 ...
