Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置(转)
用过spring框架进行开发的人,多多少少会使用过它的AOP功能,都知道有@Before、@Around和@After等advice。最近,为了实现项目中的输出日志和权限控制这两个需求,我也使用到了AOP功能。我使用到了@Before、@Around这两个advice。但在,使用过程中,却对它们的执行顺序并不清楚。为了弄清楚在不同情况下,这些advice到底是以怎么样的一个顺序进行执行的,我作了个测试,在此将其记录下来,以供以后查看。
前提
- 对于AOP相关类(aspect、pointcut等)的概念,本文不作说明。
- 对于如何让spring框架扫描到AOP,本文也不作说明。
情况一: 一个方法只被一个Aspect类拦截
当一个方法只被一个Aspect拦截时,这个Aspect中的不同advice是按照怎样的顺序进行执行的呢?请看:
添加 PointCut类
该pointcut用来拦截test包下的所有类中的所有方法。
package test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
public class PointCuts {
@Pointcut(value = "within(test.*)")
public void aopDemo() {
}
}
- package test; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; public class PointCuts { @Pointcut(value = "within(test.*)") public void aopDemo() { } }
添加Aspect类
该类中的advice将会用到上面的pointcut,使用方法请看各个advice的value属性。
package test; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
@Aspect
public class Aspect1 { @Before(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect1] before advise");
} @Around(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("[Aspect1] around advise 1");
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("[Aspect1] around advise2");
} @AfterReturning(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect1] afterReturning advise");
} @AfterThrowing(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect1] afterThrowing advise");
} @After(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect1] after advise");
}
}
添加测试用Controller
添加一个用于测试的controller,这个controller中只有一个方法,但是它会根据参数值的不同,会作出不同的处理:一种是正常返回一个对象,一种是抛出异常(因为我们要测试@AfterThrowing这个advice)
package test; import test.exception.TestException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/aop")
public class AopTestController { @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Result test(@RequestParam boolean throwException) {
// case 1
if (throwException) {
System.out.println("throw an exception");
throw new TestException("mock a server exception");
} // case 2
System.out.println("test OK");
return new Result() {{
this.setId(111);
this.setName("mock a Result");
}};
} public static class Result {
private int id;
private String name; public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
}
测试 正常情况
在浏览器直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=false我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect1] around advise 1
[Aspect1] before advise
test OK
[Aspect1] around advise2
[Aspect1] after advise
[Aspect1] afterReturning advise
测试 异常情况
在浏览器中直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=true
我们会看到输出的结果是:
- [Aspect1] around advise 1
- [Aspect1] before advise
- throw an exception
- [Aspect1] after advise
- [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise
结论
在一个方法只被一个aspect类拦截时,aspect类内部的 advice 将按照以下的顺序进行执行:
正常情况: 

情况二: 同一个方法被多个Aspect类拦截
此处举例为被两个aspect类拦截。
有些情况下,对于两个不同的aspect类,不管它们的advice使用的是同一个pointcut,还是不同的pointcut,都有可能导致同一个方法被多个aspect类拦截。那么,在这种情况下,这多个Aspect类中的advice又是按照怎样的顺序进行执行的呢?请看:
pointcut类保持不变
添加一个新的aspect类
package test; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
@Aspect
public class Aspect2 { @Before(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect2] before advise");
} @Around(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("[Aspect2] around advise 1");
pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("[Aspect2] around advise2");
} @AfterReturning(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect2] afterReturning advise");
} @AfterThrowing(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect2] afterThrowing advise");
} @After(value = "test.PointCuts.aopDemo()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("[Aspect2] after advise");
}
}
测试用Controller也不变
还是使用上面的那个Controller。但是现在 aspect1 和 aspect2 都会拦截该controller中的方法。
下面继续进行测试!
测试 正常情况
在浏览器直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=false
我们会看到输出的结果是:
[Aspect2] around advise 1
[Aspect2] before advise
[Aspect1] around advise 1
[Aspect1] before advise
test OK
[Aspect1] around advise2
[Aspect1] after advise
[Aspect1] afterReturning advise
[Aspect2] around advise2
[Aspect2] after advise
[Aspect2] afterReturning advise
但是这个时候,我不能下定论说 aspect2 肯定就比 aspect1 先执行。
不信?你把服务务器重新启动一下,再试试,说不定你就会看到如下的执行结果:
- [Aspect1] around advise 1
- [Aspect1] before advise
- [Aspect2] around advise 1
- [Aspect2] before advise
- test OK
- [Aspect2] around advise2
- [Aspect2] after advise
- [Aspect2] afterReturning advise
- [Aspect1] around advise2
- [Aspect1] after advise
- [Aspect1] afterReturning advise
也就是说,这种情况下, aspect1 和 aspect2 的执行顺序是未知的。那怎么解决呢?不急,下面会给出解决方案。
测试 异常情况
在浏览器中直接输入以下的URL,回车:
http://192.168.142.8:7070/aoptest/v1/aop/test?throwException=true
我们会看到输出的结果是:
- [Aspect2] around advise 1
- [Aspect2] before advise
- [Aspect1] around advise 1
- [Aspect1] before advise
- throw an exception
- [Aspect1] after advise
- [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise
- [Aspect2] after advise
- [Aspect2] afterThrowing advise
同样地,如果把服务器重启,然后再测试的话,就可能会看到如下的结果:
- [Aspect1] around advise 1
- [Aspect1] before advise
- [Aspect2] around advise 1
- [Aspect2] before advise
- throw an exception
- [Aspect2] after advise
- [Aspect2] afterThrowing advise
- [Aspect1] after advise
- [Aspect1] afterThrowing advise
也就是说,同样地,异常情况下, aspect1 和 aspect2 的执行顺序也是未定的。
那么在 情况二 下,如何指定每个 aspect 的执行顺序呢?
方法有两种:
- 实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,实现它的getOrder()方法
- 给aspect添加@Order注解,该注解全称为:org.springframework.core.annotation.Order
不管采用上面的哪种方法,都是值越小的 aspect 越先执行。
比如,我们为 apsect1 和 aspect2 分别添加 @Order 注解,如下:
- @Order(5)
- @Component
- @Aspect
- public class Aspect1 {
- // ...
- }
- @Order(6)
- @Component
- @Aspect
- public class Aspect2 {
- // ...
- }
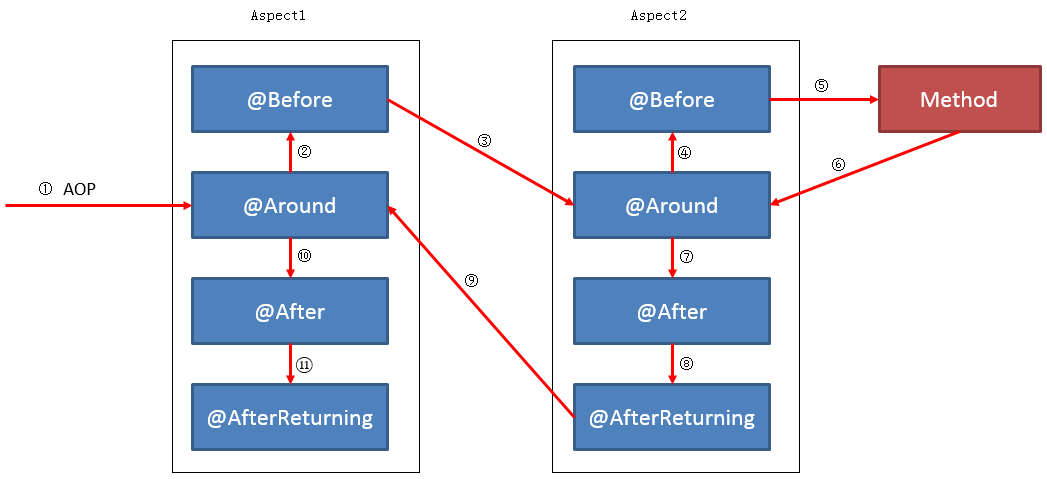
这样修改之后,可保证不管在任何情况下, aspect1 中的 advice 总是比 aspect2 中的 advice 先执行。如下图所示:
注意点
如果在同一个 aspect 类中,针对同一个 pointcut,定义了两个相同的 advice(比如,定义了两个 @Before),那么这两个 advice 的执行顺序是无法确定的,哪怕你给这两个 advice 添加了 @Order 这个注解,也不行。这点切记。
对于@Around这个advice,不管它有没有返回值,但是必须要方法内部,调用一下 pjp.proceed();否则,Controller 中的接口将没有机会被执行,从而也导致了 @Before这个advice不会被触发。比如,我们假设正常情况下,执行顺序为”aspect2 -> apsect1 -> controller”,如果,我们把 aspect1中的@Around中的 pjp.proceed();给删掉,那么,我们看到的输出结果将是:
- [Aspect2] around advise 1
- [Aspect2] before advise
- [Aspect1] around advise 1
- [Aspect1] around advise2
- [Aspect1] after advise
- [Aspect1] afterReturning advise
- [Aspect2] around advise2
- [Aspect2] after advise
- [Aspect2] afterReturning advise
从结果可以发现, Controller 中的 接口 未被执行,aspect1 中的 @Before advice 也未被执行。
参考资料
- Spring 4.3.2.RELEASE 官方资料:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/
- 其中,AOP的执行顺序章节为:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/#aop-ataspectj-advice-ordering
Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置(转)的更多相关文章
- Spring Aop实例@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning@Around 注解方式配置
用过spring框架进行开发的人,多多少少会使用过它的AOP功能,都知道有@Before.@Around和@After等advice.最近,为了实现项目中的输出日志和权限控制这两个需求,我也使用到了A ...
- SSH深度历险(十) AOP原理及相关概念学习+AspectJ注解方式配置spring AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),是面向切面编程的技术.AOP基于IoC基础,是对OOP的有益补充. AOP之所以能得到广泛应用,主要是因为它将应用系统拆分分了2个部分 ...
- Spring AOP 的@Aspect
Spring AOP 的@Aspect 转自:http://blog.csdn.net/tanghw/article/details/3862987 从Spring 2.0开始,可以使用基于sch ...
- 跟着刚哥学习Spring框架--通过注解方式配置Bean(四)
组件扫描:Spring能够从classpath下自动扫描,侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件. 特定组件包括: 1.@Component:基本注解,识别一个受Spring管理的组件 2.@Resposit ...
- spring bean的介绍以及xml和注解的配置方法
5.Bean 下边我们来了解一下Bean的: Bean的作用域Bean的生命周期Bean的自动装配Resources和ResourceLoader 5.1Bean容器的初始化 Bean容器的初始化 两 ...
- Spring声明式事务管理(基于注解方式实现)
----------------------siwuxie095 Spring 声明式事务管理(基于注解方式实现) 以转 ...
- spring学习笔记 星球日two - 注解方式配置bean
注解要放在要注解的对象的上方 @Autowired private Category category; <?xml version="1.0" encoding=" ...
- Spring boot 基于注解方式配置datasource
Spring boot 基于注解方式配置datasource 编辑 Xml配置 我们先来回顾下,使用xml配置数据源. 步骤: 先加载数据库相关配置文件; 配置数据源; 配置sqlSessionF ...
- Spring配置文件中bean标签中init-method和destroy-method和用注解方式配置
Person类: public class Person { private int i = 0; public Person(){ System.o ...
随机推荐
- Python 解LeetCode:606 Construct String from Binary Tree
题目描述:用先序遍历的方式把二叉树转换成字符串,其中结点用括号分割,具体示例见题目链接 思路: 先序遍历,先把根结点的值转化成字符串,然后递归的把左右子树的值转化成字符串 把1中的根结点和左右子结点的 ...
- 路由器设置 WDS 桥接
步骤: 1.先更改路由器LAN口地址,然后重启路由器 2.连接SSID信道名称,先关闭DHCP服务,然后进入无线设置,基本设置,更改SSID号,开启WDS桥接,保存 3.连接新的SSID名称,无线设置 ...
- 关于NumPy中数组轴的理解
参考原文链接(英文版):https://www.sharpsightlabs.com/blog/numpy-axes-explained/:中文版:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ ...
- 硬件实现IIC协议读取EEPROM
我TMD也是服了,反正我板子搞了半天也不成功我也不知道为什么,野火STM32-MINI,一直卡EV5,不管了 先代码沾上 工程目录(板子为野火STM32 MINI) 串口相关代码: bsp_usart ...
- 『Python基础』第2节: Python简介及入门
一. Python介绍 Python是一门高级计算机程序设计语言,1989年,荷兰的Guido von Rossum创造了它.Guido是是一个牛人,1982年,他从阿姆斯特丹大学获得了数学和计算机硕 ...
- JPA扩展(自定义sql)
pom.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="htt ...
- Istio技术与实践03:最佳实践之sidecar自动注入
Istio通过对serviceMesh中的每个pod注入sidecar,来实现无侵入式的服务治理能力.其中,sidecar的注入是其能力实现的重要一环(本文主要介绍在kubernetes集群中的注入方 ...
- Base64编码为什么会使数据量变大
现在工作中把视频转成base64发现数据量过大无法下载. 1.为什么base64编码会使数据量变大呢? Base64编码的思想是是采用64个基本的ASCII码字符对数据进行重新编码.它将需要编码的数据 ...
- web.xml 转 学习!http://www.cnblogs.com/wkrbky/p/5929943.html
1.spring 框架解决字符串编码问题:过滤器 CharacterEncodingFilter(filter-name) 2.在web.xml配置监听器ContextLoaderListener(l ...
- oracle exists和 not exists 的用法
比如 a,b 关联列为 a.id = b.id,现在要取 a 中的数据,其中id在b中也存在: select * from a where exists(select 1 from b where b ...
