利用反射及jdbc元数据实现通用的查询方法
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.customer类:
package com.lanqiao.javatest;
import java.sql.Date;
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Date birth;
public Customer() {
super();
}
public Customer(int id, String name, String email, Date birth) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.birth = birth;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", email=" + email + ", birth=" + birth + "]";
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
student类:
package com.lanqiao.javatest;
public class Student {
/*
* FlowID:int,流水号
* type:int ,英语四六级
* IDcard:varchar(18),身份证号码
* examcard:varchar(15),考试证号
* studentname:varchar(20),学生姓名
* localtion:varchar(20),区域
* grade:int,成绩
*/
private int flowId;
private int type;
private String idCard;
private String examCard;
private String studentName;
private String localtion;
private int grade;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(int flowId, int type, String idCard, String examCard, String studentName, String localtion,
int grade) {
super();
this.flowId = flowId;
this.type = type;
this.idCard = idCard;
this.examCard = examCard;
this.studentName = studentName;
this.localtion = localtion;
this.grade = grade;
}
public int getFlowId() {
return flowId;
}
public void setFlowId(int flowId) {
this.flowId = flowId;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getIdCard() {
return idCard;
}
public void setIdCard(String idCard) {
this.idCard = idCard;
}
public String getExamCard() {
return examCard;
}
public void setExamCard(String examCard) {
this.examCard = examCard;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getLocaltion() {
return localtion;
}
public void setLocaltion(String localtion) {
this.localtion = localtion;
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [flowId=" + flowId + ", type=" + type + ", idCard=" + idCard + ", examCard=" + examCard
+ ", studentName=" + studentName + ", localtion=" + localtion + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
反射方法:
package com.lanqiao.javatest;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
/**
* 反射的 Utils 函数集合
* 提供访问私有变量, 获取泛型类型 Class, 提取集合中元素属性等 Utils 函数
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ReflectionUtils {
/**
* 通过反射, 获得定义 Class 时声明的父类的泛型参数的类型
* 如: public EmployeeDao extends BaseDao<Employee, String>
* @param clazz
* @param index
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static Class getSuperClassGenricType(Class clazz, int index){
Type genType = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
if(!(genType instanceof ParameterizedType)){
return Object.class;
}
Type [] params = ((ParameterizedType)genType).getActualTypeArguments();
if(index >= params.length || index < 0){
return Object.class;
}
if(!(params[index] instanceof Class)){
return Object.class;
}
return (Class) params[index];
}
/**
* 通过反射, 获得 Class 定义中声明的父类的泛型参数类型
* 如: public EmployeeDao extends BaseDao<Employee, String>
* @param <T>
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static<T> Class<T> getSuperGenericType(Class clazz){
return getSuperClassGenricType(clazz, 0);
}
/**
* 循环向上转型, 获取对象的 DeclaredMethod
* @param object
* @param methodName
* @param parameterTypes
* @return
*/
public static Method getDeclaredMethod(Object object, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes){
for(Class<?> superClass = object.getClass(); superClass != Object.class; superClass = superClass.getSuperclass()){
try {
//superClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
return superClass.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
//Method 不在当前类定义, 继续向上转型
}
//..
}
return null;
}
/**
* 使 filed 变为可访问
* @param field
*/
public static void makeAccessible(Field field){
if(!Modifier.isPublic(field.getModifiers())){
field.setAccessible(true);
}
}
/**
* 循环向上转型, 获取对象的 DeclaredField
* @param object
* @param filedName
* @return
*/
public static Field getDeclaredField(Object object, String filedName){
for(Class<?> superClass = object.getClass(); superClass != Object.class; superClass = superClass.getSuperclass()){
try {
return superClass.getDeclaredField(filedName);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
//Field 不在当前类定义, 继续向上转型
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 直接调用对象方法, 而忽略修饰符(private, protected)
* @param object
* @param methodName
* @param parameterTypes
* @param parameters
* @return
* @throws InvocationTargetException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
*/
public static Object invokeMethod(Object object, String methodName, Class<?> [] parameterTypes,
Object [] parameters) throws InvocationTargetException{
Method method = getDeclaredMethod(object, methodName, parameterTypes);
if(method == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find method [" + methodName + "] on target [" + object + "]");
}
method.setAccessible(true);
try {
return method.invoke(object, parameters);
} catch(IllegalAccessException e) {
System.out.println("不可能抛出的异常");
}
return null;
}
/**
* 直接设置对象属性值, 忽略 private/protected 修饰符, 也不经过 setter
* @param object
* @param fieldName
* @param value
*/
public static void setFieldValue(Object object, String fieldName, Object value){
Field field = getDeclaredField(object, fieldName);
if (field == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find field [" + fieldName + "] on target [" + object + "]");
makeAccessible(field);
try {
field.set(object, value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
System.out.println("不可能抛出的异常");
}
}
/**
* 直接读取对象的属性值, 忽略 private/protected 修饰符, 也不经过 getter
* @param object
* @param fieldName
* @return
*/
public static Object getFieldValue(Object object, String fieldName){
Field field = getDeclaredField(object, fieldName);
if (field == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find field [" + fieldName + "] on target [" + object + "]");
makeAccessible(field);
Object result = null;
try {
result = field.get(object);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
System.out.println("不可能抛出的异常");
}
return result;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
实现主方法:
package com.lanqiao.javatest;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.management.ReflectionException;
import javax.swing.text.FieldView;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.mysql.jdbc.ResultSetMetaData;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement;
/*
* 建立一个统一的方法可以引用任何类的对象,实现数据库数据的处理
* 通过一个对象获取任何一个数据库数据
* */
public class TestPreparedStatement {
private static final Class<Customer> Customer = null;
private static final Class<Student> Student = null;
=================================================================================
//连接数据库方法
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
//四连接数据必不可少的
String driverClass=null;
String jdbcUrl=null;
String user=null;
String password=null;
InputStream in=
TestPreparedStatement.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//其中getClass与TestConnection.classh互换使用
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass=properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
// System.out.println(driverClass+jdbcUrl+user+password);
Driver driver=(Driver)Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
Properties info=new Properties();
info.put("user", "root");
info.put("password", "lxn123");
Connection connection=driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
return connection;
}
//测试类
public static void testGetConn() throws Exception{
System.out.println(getConnection());
}
====================================================================================
关闭资源的方法
public void close(Connection connection,
PreparedStatement preparedStatement,ResultSet resultSet) throws Exception{
if (resultSet!=null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement!=null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection!=null) {
connection.close();
}
}
===========================================================================================
//student类获取数据
public Student getStudent(String sql,Object...args) throws Exception{
Student student=null;
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=TestPreparedStatement.getConnection();
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//resultset里面的nest()方法,把查询到的数据,student获取
if(resultSet.next()){
student=new Student();
student.setFlowId(resultSet.getInt(1));
student.setType(resultSet.getInt(2));
student.setIdCard(resultSet.getString(3));
student.setExamCard(resultSet.getString(4));
student.setStudentName(resultSet.getString(5));
student.setLocaltion(resultSet.getString(6));
student.setGrade(resultSet.getInt(7));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
return student;
}
========================================================================================
//Customer类获取数据
public Customer getCustomer(String sql,Object...args) throws Exception{
Customer customer=null;
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=TestPreparedStatement.getConnection();
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//resultset里面的nest()方法,把查询到的数据,student获取
if(resultSet.next()){
customer=new Customer();
customer.setId(resultSet.getInt(1));
customer.setName(resultSet.getString(2));
customer.setEmail(resultSet.getString(3));
customer.setBirth(resultSet.getDate(4));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
return customer;
}
=======================================================================================
//一个通用的方法的模板:可利用反射,实现数据库查询,插入值
public <T> T getT(Class <T> clazz,String sql,Object...args) throws Exception{
T entity=null;
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection=TestPreparedStatement.getConnection();
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//得到ResultSetMetaDate对象,获取数据库中的列和列名
ResultSetMetaData rsmd=(ResultSetMetaData) resultSet.getMetaData();
//创建一个Map<String,Object>对象,键:sql查询列的别名;值:列的值;
Map<String, Object> values=new HashMap<String, Object>();
//处理结果集,利用ResultSetMetaDate的方法,填充对应的map的对象
while(resultSet.next()){
//方法getColumnCount(),是获取ResultSetMetaDate对象获取数据库属性的个数
for(int i=0;i<rsmd.getColumnCount();i++){
String columnLabel=rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1);//获取属性,它是字符串
Object columnValues=resultSet.getObject(columnLabel);
// System.out.println(columnValues);
values.put(columnLabel, columnValues);
}
}
//map不为空,利用反射创建clazz的对象
if (values.size()>0) {
entity=clazz.newInstance();
//遍历map,利用反射class对应的对象的属性赋值
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry: values.entrySet()) {
String fieldName=entry.getKey();
Object fieldValues=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(fieldName+":"+fieldValues);
//反射获取属性,并修改 xxxx(entity,fieldName,fieldValues);
ReflectionUtils.setFieldValue(entity, fieldName, fieldValues);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
return entity;
}
//测试getT()方法
@Test
public void testGetT() throws Exception{
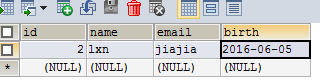
String sql="select id,name,email,birth from customer where id=?";
Customer customer=getT(Customer.class,sql,2);
System.out.println(customer);
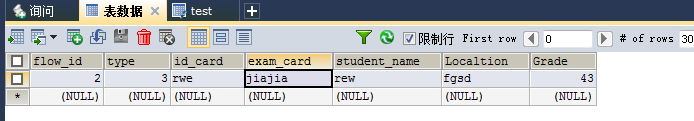
String sql1="SELECT flow_id flowId,type,id_card idCard,"
+ "exam_card examCard,student_name studentName ,"
+ "localtion,grade FROM test WHERE flow_id=?;";
Student student=getT(Student.class,sql1,2);
System.out.println(student);
}
=======================================================================================
//ResultSetMetaDate,是描述ResultSet的元数据对象,即从中可以获取到结果集中有多少列,列名是。。。。。
//用法:调用ResultSet的getMetaDate()方法,
//好用的方法:int getColumnCount(),sql语句中包含那些列
//String getColumnLabel(int column):获取指定列的别名,其中索引从1开始
public void testResultSetMetaDate() throws Exception{
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
String sql="SELECT flow_id flowid,type,id_card idcard,"
+ "exam_card examcard,student_name studentname ,"
+ "localtion,grade FROM test WHERE flow_id=?;";
connection=TestPreparedStatement.getConnection();
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 2);
resultSet=preparedStatement.executeQuery();
Map<String, Object> values=new HashMap<String, Object>();
//1.得到ResultSetMetaDate对象,获取数据库中的列和列名
ResultSetMetaData rsmd= (ResultSetMetaData) resultSet.getMetaData();
while(resultSet.next()){
//2.{}打印每一列的列名
for(int i=0;i<rsmd.getColumnCount();i++){
String columnLabel=rsmd.getColumnLabel(i+1);//获取指定列的别名
Object columnValue=resultSet.getObject(columnLabel);//获取指定列的值
values.put(columnLabel, columnValue);
}
}
System.out.println(values);
//反射获取
Class clazz=Student.class;
Object obj=clazz.newInstance();
//强制for循环
for(Map.Entry<String, Object> entry: values.entrySet()){
String fieldName=entry.getKey();
Object fieldValues=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(fieldName+":"+fieldValues);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
}
数据库图片:
利用反射及jdbc元数据实现通用的查询方法的更多相关文章
- Java -- JDBC_利用反射及 JDBC 元数据编写通用的查询方法
先利用 SQL 进行查询,得到结果集: 利用反射创建实体类的对象:创建对象: 获取结果集的列的别名: 再获取结果集的每一列的值, 结合 3 得到一个 Map,键:列的别名,值:列的值: 再利用反射为 ...
- JDBC学习笔记(5)——利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用的查询方法
JDBC元数据 1)DatabaseMetaData /** * 了解即可:DatabaseMetaData是描述数据库的元数据对象 * 可以由Connection得到 */ 具体的应用代码: @Te ...
- 【转】JDBC学习笔记(5)——利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用的查询方法
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/ JDBC元数据 1)DatabaseMetaData /** * 了解即可:DatabaseMetaData是描述数据库的元数据对象 ...
- <五>JDBC_利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用的查询方法
此类针对javaBean类写了一个通用的查询方法,List<javaBean> 通用查询更新中...:通过学习,深刻体会到学会反射就等于掌握了java基础的半壁江山! 一.使用JDBC驱动 ...
- MYSQL 之 JDBC(六): 增删改查(四)利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用的查询
1.先利用SQL进行查询,得到结果集2.利用反射创建实体类的对象:创建Student对象3.获取结果集的列的别名:idCard.studentName4.再获取结果集的每一列的值,结合3得到一个Map ...
- JDBC--利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用的查询方法
1.JDBC元数据(ResuleSetMetaData):描述ResultSet的元数据对象,可以从中获取到结果集中的列数和列名等: --使用ResultSet类的getMetaData()方法获得R ...
- java攻城狮之路--复习JDBC(利用BeanUtils、JDBC元数据编写通用的查询方法;元数据;Blob;事务;批量处理)
1.利用BeanUtils的前提得要加入以下两个jar包: commons-beanutils-1.8.0.jar commons-logging-1.1.1.jar package com.shel ...
- 利用反射和JDBC元数据实现更加通用的查询方法
package com.at221.jdbc; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.*; i ...
- 利用反射及JDBC元数据编写通用查询方法
元数据:描述数据的数据,ResultSetMetaData是描述ResultSet的元数据对象,从它可以得到数据集有多少了,每一列的列名... ResultSetMetaData可以通过ResultS ...
随机推荐
- c# 多线程与异步调用
异步操作的本质 在方法调用前为异步方法指定一个回调函数,方法调用后被线程池中的一个线程接管,执行该方法.主线程立即返回,继续执行其他工作或响应用户请求.如果异步方法执行完 毕,回调函数被自动执行,以处 ...
- Java NIO 读数据处理过程
这两天仿hadoop 写java RPC框架,使用PB作为序列号工具,在写读数据的时候遇到一个小坑.之前写过NIO代码,恰好是错误的代码产生正确的逻辑,误以为自己写对了.现在简单整理一下. 使用NIO ...
- Android初体验
上文提到使用genymotion来运行android项目,结果却是令人失望,我这边使用的是代理账户,尽管我在Setting中配置了代理,还是不能登录我注册的账户,郁闷,于是本文采用的是我自己的手机作为 ...
- Wcf Restful Service服务搭建
目的 使用Wcf(C#)搭建一个Restful Service 背景 最近接到一个项目,客户要求使用Restful 方式接收到数据,并对数据提供对数据的统计显示功能,简单是简单,但必须要使用Restf ...
- 使用 CSS 的 :before 和 :after 选择器做一个箭头样式
对于 :before 和 :after 选择器,大家并不陌生,但是很少有人会主动去用它们.先解释下它们的定义和用法: :before 选择器在被选元素的内容前面插入内容,:after 选择器在被选元素 ...
- Nodejs解决2分钟限制
摘要:解决:在nodejs中调用服务,若超过2分钟服务没有返回数据,node会再次请求服务. 加班的日子总算暂时结束了,才发现下午6点钟的天还没有黑!开始我的总结吧... 去年的某个项目用nodej ...
- Adobe Flash CC 安装报错的解决办法
安装FlashCC的时候莫名的报错 ---------------------------Flash.exe - 应用程序错误---------------------------应用程序无法正常启动 ...
- application 统计网站访问人数
参考书<JSP Web 开发案例教程> index.jsp welcome.jsp 显示
- C#: 数据绑定
数据绑定是分离UI和后端主逻辑程序的一种好的办法.这里总结下TextBox, Label, ComboBox, ListBox, DataGridView的数据绑定 数据绑定都是通过DB来和UI控件的 ...
- java正则表达式练习
package shb.java.demo3; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * 正则表达式简 ...
