springboot国际化与@valid国际化支持
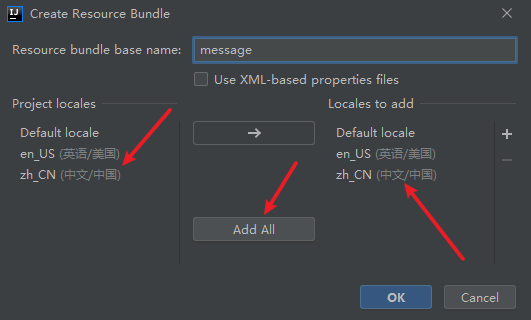
springboot国际化

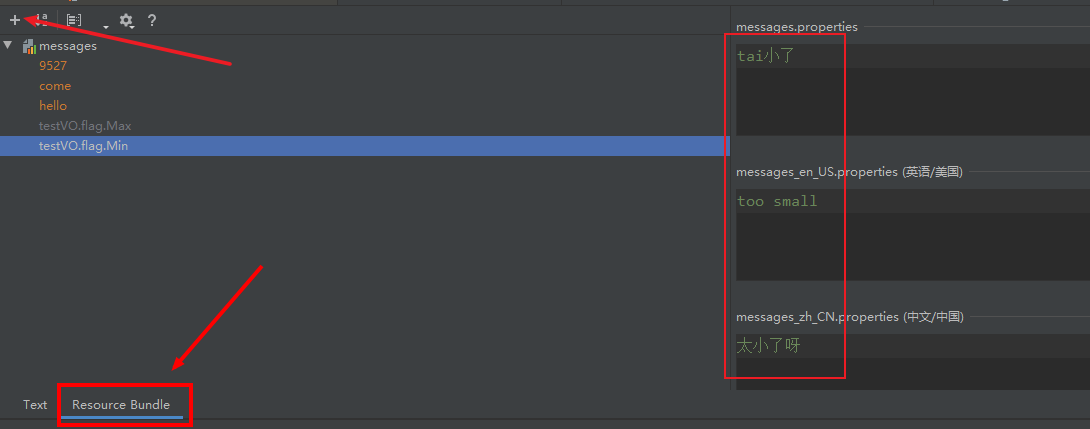
9527=bojack
come=来吧
hello=你好
testVO.flag.Max=tai大了呀
testVO.flag.Min=tai小了9527=jack
come=come
hello=hello
testVO.flag.Max=too big
testVO.flag.Min=too small9527=杰克
come=来吧
hello=你好
testVO.flag.Max=太多了呀
testVO.flag.Min=太小了呀spring:
messages:
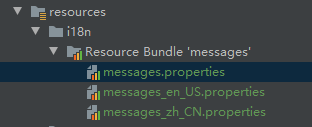
basename: i18n/messages # 多个文件用逗号分隔 /**
* 设置默认语言
* @return
*/
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver acceptHeaderLocaleResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
acceptHeaderLocaleResolver.setDefaultLocale(Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE);
return acceptHeaderLocaleResolver;
}### 简体中文
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: zh-CN
### 美国英语
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: en-USpackage com.springmvc.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("i18n")
public class I18nController {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@GetMapping("test")
public Object test() {
Locale locale = LocaleContextHolder.getLocale();
String displayName = locale.getDisplayName();
System.out.println("displayName = " + displayName);
String hello = messageSource.getMessage("hello", null, locale);
System.out.println("hello = " + hello);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("hello", hello);
map.put("displayName", displayName);
map.put("locale", locale);
String come= messageSource.getMessage("come", null, locale);
map.put("come", come);
String c9527= messageSource.getMessage("9527", null, locale);
map.put("9527", c9527);
return map ;
}
}@valid 参数校验与国际化
/**
* The name of the default message bundle.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_VALIDATION_MESSAGES = "org.hibernate.validator.ValidationMessages";
package com.springmvc.demo.vo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;//MethodArgumentNotValidException
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
@Data
public class TestVO {
@Min(value = 3)//这里不用写messages了,因为要支持国际化
@Max(value = 10)
private Integer flag;
@NotNull
private Integer age;
}testVO.flag.Max=too big
testVO.flag.Min=too smallspring:
messages:
basename: i18n/messages
mvc:
message-codes-resolver-format: postfix_error_codepackage com.springmvc.demo.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.api.R;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class GlobalExceptionHandlerResolver {
@Autowired
MessageSource messageSource;
@ExceptionHandler({MethodArgumentNotValidException.class, BindException.class})
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public R handleBodyValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException exception) {
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<String, String>();
//得到所有的属性错误
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = exception.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors();
//将其组成键值对的形式存入map
for (FieldError fieldError : fieldErrors) {
String[] str= fieldError.getField().split("\\.");
if(str.length>1){
errors.put(str[1], fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}else {
errors.put(fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
String message = messageSource.getMessage(fieldError, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
return R.failed(message);
}
log.error("参数绑定异常,ex = {}", errors);
return R.failed("haha");
}
}###
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: zh
###
GET localhost:8080/i18n/test
Accept-Language: en-US
###
POST localhost:8080/test
Content-Type: application/json
{
"flag": 2,
"age": 22
}
###
POST localhost:8080/test
Content-Type: application/json
Accept-Language: en-US
{
"flag": 5
} /**
* Parse request locales.
*/
protected void parseLocales() {
localesParsed = true;
// Store the accumulated languages that have been requested in
// a local collection, sorted by the quality value (so we can
// add Locales in descending order). The values will be ArrayLists
// containing the corresponding Locales to be added
TreeMap<Double, ArrayList<Locale>> locales = new TreeMap<>();
Enumeration<String> values = getHeaders("accept-language");
while (values.hasMoreElements()) {
String value = values.nextElement();
parseLocalesHeader(value, locales);
}
// Process the quality values in highest->lowest order (due to
// negating the Double value when creating the key)
for (ArrayList<Locale> list : locales.values()) {
for (Locale locale : list) {
addLocale(locale);
}
}
} @Override
public final String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException {
String[] codes = resolvable.getCodes();
if (codes != null) {
for (String code : codes) {
String message = getMessageInternal(code, resolvable.getArguments(), locale);
if (message != null) {
return message;
}
}
}
String defaultMessage = getDefaultMessage(resolvable, locale);
if (defaultMessage != null) {
return defaultMessage;
}
throw new NoSuchMessageException(!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(codes) ? codes[codes.length - 1] : "", locale);
} private String resolveMessage(String message, Locale locale) {
String resolvedMessage = message;
ResourceBundle userResourceBundle = userResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
ResourceBundle constraintContributorResourceBundle = contributorResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
ResourceBundle defaultResourceBundle = defaultResourceBundleLocator
.getResourceBundle( locale );
String userBundleResolvedMessage;
boolean evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce = false;
do {
// search the user bundle recursive (step 1.1)
userBundleResolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
resolvedMessage, userResourceBundle, locale, true
);
// search the constraint contributor bundle recursive (only if the user did not define a message)
if ( !hasReplacementTakenPlace( userBundleResolvedMessage, resolvedMessage ) ) {
userBundleResolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
resolvedMessage, constraintContributorResourceBundle, locale, true
);
}
// exit condition - we have at least tried to validate against the default bundle and there was no
// further replacements
if ( evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce && !hasReplacementTakenPlace( userBundleResolvedMessage, resolvedMessage ) ) {
break;
}
// search the default bundle non recursive (step 1.2)
resolvedMessage = interpolateBundleMessage(
userBundleResolvedMessage,
defaultResourceBundle,
locale,
false
);
evaluatedDefaultBundleOnce = true;
} while ( true );
return resolvedMessage;
}springboot国际化与@valid国际化支持的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot添加对Log4j2的支持
1.在添加对Log4j2的支持前,需要先把SpringBoot默认使用的Logback日志框架排除,修改pom.xml文件: <dependency> <groupId>org ...
- SpringBoot添加对Mybatis的支持
1.修改maven配置文件pom.xml,添加对mybatis的支持: <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</gr ...
- 详解SpringBoot 添加对JSP的支持(附常见坑点)
序言: SpringBoot默认不支持JSP,如果想在项目中使用,需要进行相关初始化工作.为了方便大家更好的开发,本案例可直接作为JSP开发的脚手架工程 SpringBoot+War+JSP . 常见 ...
- JavaWeb开发——软件国际化(文本元素国际化)
前几天围绕着JDBC编程进行了系统的学习.现在我们对Java程序数据库操作已经是轻车熟路了.也学会了使用各种框架来帮助我们简化编程. 今天是学习计划的第七天,虽然学习热情没有前几天高涨了.但是,写博客 ...
- springboot 使用i18n进行国际化
1.i18n介绍 i18n(其来源是英文单词 internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数)是“国际化”的简称.在资讯领域,国际化(i18n)指让产品(出版物,软件,硬 ...
- 逐浪web无障碍与国际化以及全民族语言支持白皮书
北京时间2019年5月10日,领先的门户网站与WEB内核服务厂商--上海Zoomla!逐浪CMS团队发布其年度重榜产品:逐浪CMS全民族语言与国际版,体验站点:http://demo2.z01.com ...
- springboot、Thymeleaf、国际化的简单使用
1.项目体系结构 (1)知识体系 springboot:省去了很多繁琐的配置,如:视图解析器.前端控制器等 thymeleaf:获取controller数据逼能够进行展示 集合:用于存储数据,此练习没 ...
- springboot 使用i18n进行国际化乱码解决
方式1.设置国际化的编码和你使用的编译器(IDEA之类)一致,如编译器为UTF-8则在application配置文件中添加 #i18n spring: messages: encoding: UTF- ...
- 国际化之Android设备支持的语种
昨天发了关于iOS支持的语种,文章最后也补了安卓支持语种列表.但最后发现安卓设备支持跟它列的有出入,我重新完全手工整理了一遍. 我将对应的语种在安卓的语言列表里的显示,也全部逐一列出来了,方便大家到时 ...
随机推荐
- (数据科学学习手札112)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——表单控件篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- CSS垂直布局
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="U ...
- 轻量易用的微信Sdk发布——Magicodes.Wx.Sdk
概述 最简洁最易于使用的微信Sdk,包括公众号Sdk.小程序Sdk.企业微信Sdk等,以及Abp VNext集成. GitHub地址:https://github.com/xin-lai/Magico ...
- P1085_不高兴的津津(JAVA语言)
package 顺序与分支; /* * 题目描述 津津上初中了.妈妈认为津津应该更加用功学习,所以津津除了上学之外, 还要参加妈妈为她报名的各科复习班.另外每周妈妈还会送她去学习朗诵.舞蹈和钢琴. 但 ...
- 通过《第一行代码》学习 Android 开发
第一行代码 Android --第 2 版-- 郭霖 著 第 1 章:开始启程--你的第一行 Android 代码 •1.2 手把手带你搭建开发环境 Android Studio 的安装及配置 A ...
- Android Studio 之创建自定义控件
•前言 常用控件和布局的继承结构,如下图所示: 可以看到,我们所用的所有的控件都是直接或者间接的继承自View的: 所用的所有布局都是直接或者间接继承自ViewGroup的: View 是 Andro ...
- 力扣 - 剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
目录 题目 思路 代码 复杂度分析 题目 剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树 思路 序列化其实就是层序遍历 但是,要能反序列化的话,前.中.后.层序遍历是不够的,必须在序列化时候保存所有信息,这样 ...
- 1,turicreate入门 - jupyter & turicreate安装
turicreate入门系列文章目录 1,turicreate入门 - jupyter & turicreate安装 2,turicreate入门 - 一个简单的回归模型 3,turicrea ...
- 【C/C++】malloc和new的区别
malloc和new的区别 malloc是C语言的内存申请函数.new是C++语言的运算符.所以在.c文件中无法使用new. malloc申请空间时,传递的是size.new申请空间时,传递的是typ ...
- Ducci Sequence UVA - 1594
A Ducci sequence is a sequence of n-tuples of integers. Given an n-tuple of integers (a1,a2,···,an ...
