Cookie和Session的介绍与认识
Cookie:
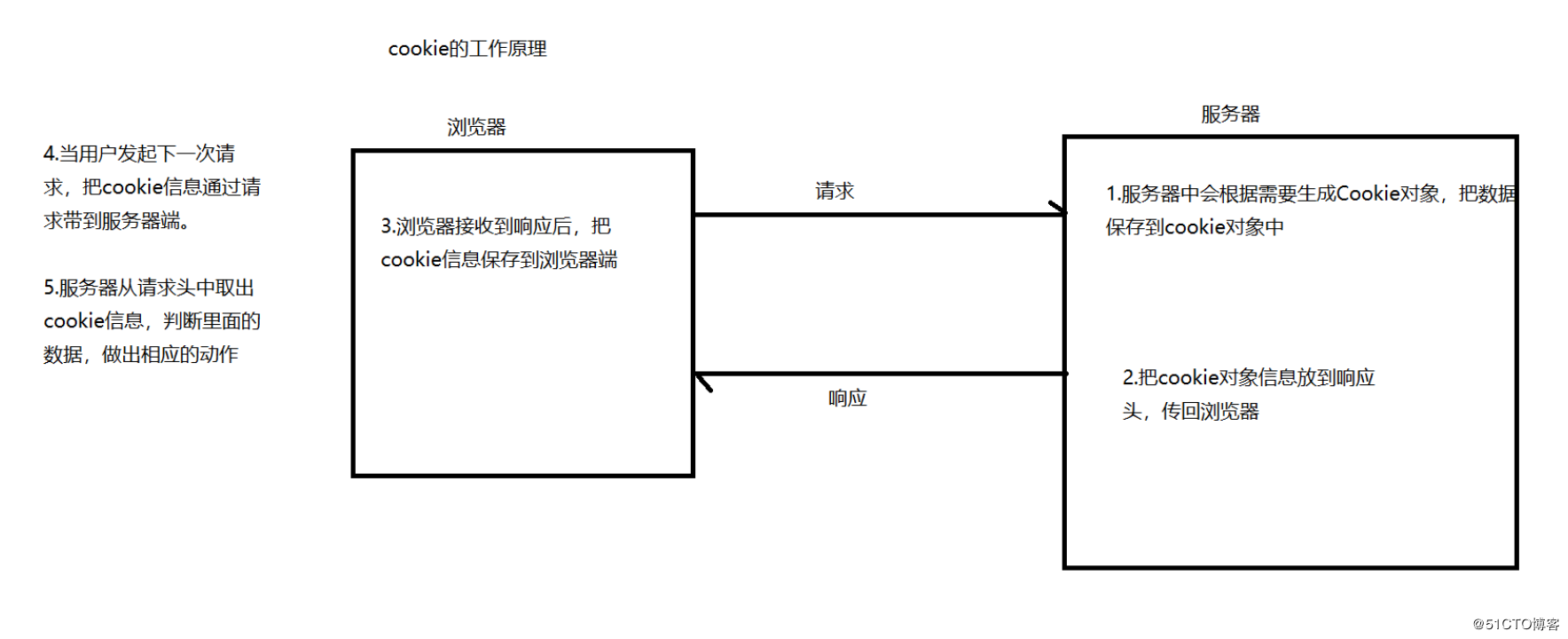
cookie是一种客户端的状态管理技术。
当浏览器向服务器发送请求的时候,服务器会将少量的数据以set-cookie消息头的方式发送给浏览器,当浏览器再次访问服务器时,会将这些数据以cookie消息头的方式发送给服务器.
Cookie是由HTTP服务器设置的,保存在浏览器中,但HTTP协议是一种无状态协议,在数据交换完毕后,服务器端和客户端的链接就会关闭,每次交换数据都需要建立新的链接。
实际上就是在客户端与服务端交换的一小段数据(一个name/string对)。
示例图:
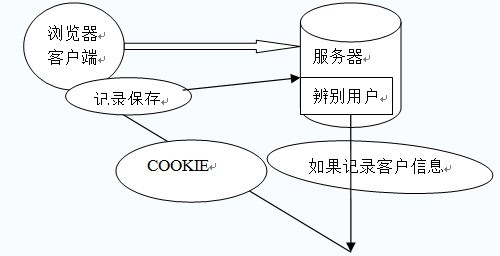
Cookie中的常用方法:
Cookie cookie=new Cookie(String name,String value) 构造一个cookie对象
response.addCookie(Cookie cookie) 是将一个cookie对象传入客户端。
request.getCookies() 得到所有的cookie对象
cookie.getName() 得到此cookie对象的名字
cookie.getValue() 得到对应名称的cookie的值
cookie.setMaxAge() 设置过期时间
Cookie技术的在web应用程序中的一般实现:
实例代码:
package gac.xdp.cookie; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /**
* @author gacl
* cookie实例:获取用户上一次访问的时间
*/
public class CookieDemo01 extends HttpServlet { public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//设置服务器端以UTF-8编码进行输出
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//设置浏览器以UTF-8编码进行接收,解决中文乱码问题
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//获取浏览器访问访问服务器时传递过来的cookie数组
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
//如果用户是第一次访问,那么得到的cookies将是null
if (cookies!=null) {
out.write("您上次访问的时间是:");
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
Cookie cookie = cookies[i];
if (cookie.getName().equals("lastAccessTime")) {
Long lastAccessTime =Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date date = new Date(lastAccessTime);
out.write(date.toLocaleString());
}
}
}else {
out.write("这是您第一次访问本站!");
} //用户访问过之后重新设置用户的访问时间,存储到cookie中,然后发送到客户端浏览器
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("lastAccessTime", System.currentTimeMillis()+"");//创建一个cookie,cookie的名字是lastAccessTime
//将cookie对象添加到response对象中,这样服务器在输出response对象中的内容时就会把cookie也输出到客户端浏览器
response.addCookie(cookie);
} public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
} }
Session:
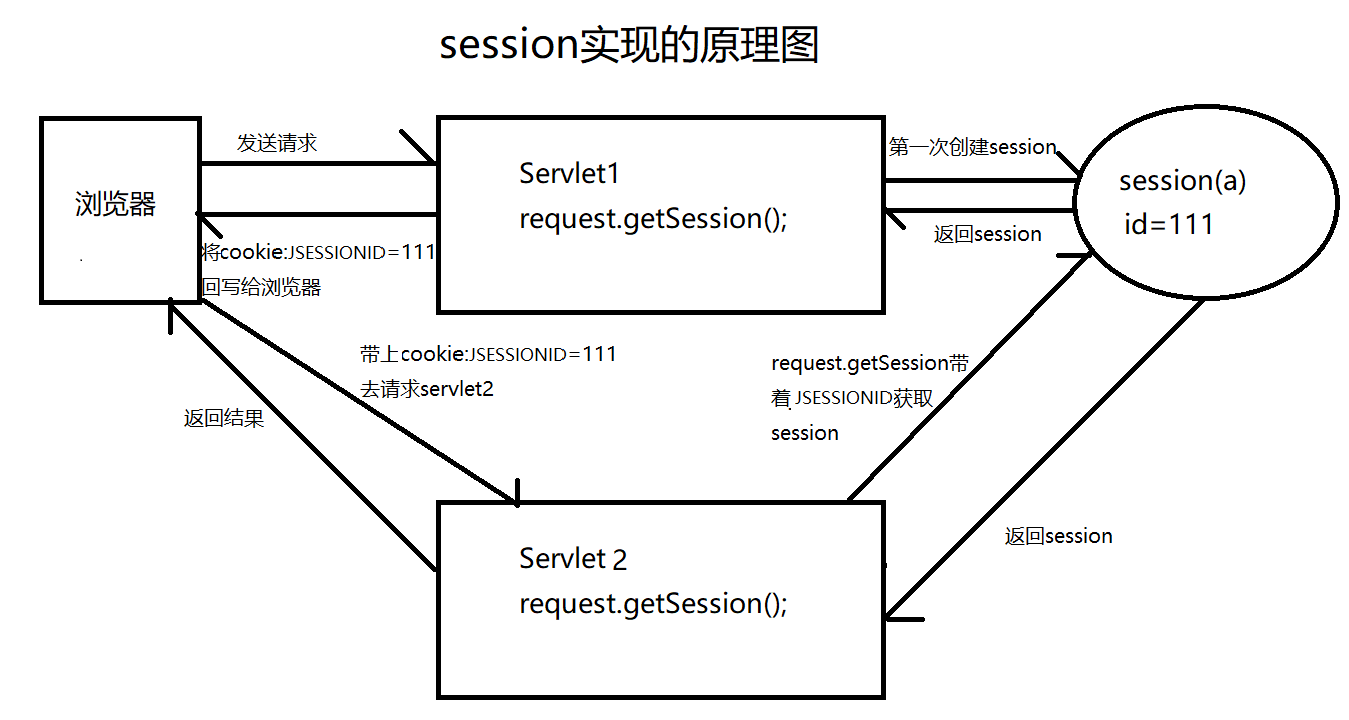
session是一种服务器端的状态管理技术。
session是基于cookie的技术。当浏览器访问服务器时,服务器会创建一个session对象(该对象有一个唯一的id号,称之为sessionId)服务器在默认的情况下,会将sessionId以cookie的方式,发送给浏览器,浏览器会将sessionId保存到内存中。当浏览器再次访问服务器时,会将sessionId发送给服务器,服务器依据sessionId就可以找到之间创建的session对象。
示例图:
Session的简单案例:
@WebServlet("/SeesionServletDemo1")
public class SeesionServletDemo1 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public SeesionServletDemo1() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
System.out.println(session.getId());
session.setAttribute("name", "zhangsan");
session.setAttribute("student", new Student(1, "zhangsan", 12));
Student stu = (Student) session.getAttribute("student");
stu.setName("lisi");
// 设置过期时间 单位是秒
// session.setMaxInactiveInterval(2);
// 直接销毁session 注销登录
// session.invalidate();
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(Integer id, String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
@WebServlet("/SeesionServletDemo2")
public class SeesionServletDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public SeesionServletDemo2() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建session对象
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
System.out.println(session.getAttribute("name"));
Student stu = (Student) session.getAttribute("student");
System.out.println(stu.getName());
}
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
* response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
doGet(request, response);
}
}
Cookie和Session 的一般差别与联系:
1,session 在服务器端,cookie 在客户端(浏览器)
2,session 默认被存在在服务器的一个文件里(不是内存)
3,session 的运行依赖 session id,而 session id 是存在 cookie 中的,也就是说,如果浏览器禁用了 cookie ,同时 session 也会失效(但是可以通过其它方式实现,比如在 url 中传递 session_id)
4,session 可以放在 文件、数据库、或内存中都可以。
5,用户验证这种场合一般会用 session
Session是在服务端保存的一个数据结构,用来跟踪用户的状态,这个数据可以保存在集群、数据库、文件中。
Cookie是客户端保存用户信息的一种机制,用来记录用户的一些信息,也是实现Session的一种方式。
Cookie和Session的介绍与认识的更多相关文章
- Cookie和Session 简单介绍
cookie : 1.cookie是存在客户端(浏览器)的进程内存中和客户端所在的机器硬盘上 2.cookie只能能够存储少量文本,大概4K大小 3.cookie是不能在不同浏 ...
- cookie和session的介绍
1.cookie和session cookie不属于http协议范围,由于http协议无法保持状态,但实际情况,我们却又需要“保持状态”,因此产生cookie. cookie的工作原理是:由服务器产生 ...
- cookie跟session自我介绍
Cookie是什么? cookie说的直白点就是保存在用户浏览器端的一个键值对,举个例子,你现在登录了京东商城,你把浏览器关闭之后,你再打开京东,你还是可以对你的账户继续操作,已经购买的商品,订单都是 ...
- Cookie和Session的总结
1.开篇 在之前学习这一段的时候我一直有点没弄清楚,其实对Session这块的理解还可以,但是Cookie感觉始终还是欠缺点火候.之后的很长一段时间都基本上很少用Cookie了,渐渐的也淡忘了这一块的 ...
- 前端Cookie与Session的区别
我们在实际生活中总会遇到这样的事情,我们一旦登录(首次输入用户名和密码)某个网站之后,当我们再次访问的时候(只要不关闭浏览器),无需再次登录.而当我们在这个网站浏览一段时间后,它会产生我们浏览的记录, ...
- 前端页面——Cookie与Session有什么区别
我们在实际生活中总会遇到这样的事情,我们一旦登录(首次输入用户名和密码)某个网站之后,当我们再次访问的时候(只要不关闭浏览器),无需再次登录.而当我们在这个网站浏览一段时间后,它会产生我们浏览的记录, ...
- 【10】Cookie和Session
一.cookie和session的介绍 cookie不属于http协议范围,由于http协议无法保持状态,但实际情况,我们却又需要"保持状态",因此cookie就是在这样一个场景下 ...
- Django(十)COOKIE和session
https://www.cnblogs.com/haiyan123/p/7763169.html from django.shortcuts import render,redirect # Crea ...
- Python框架----cookie和session
一.cookie和session的介绍 cookie不属于http协议范围,由于http协议无法保持状态,但实际情况,我们却又需要“保持状态”,因此cookie就是在这样一个场景下诞生. cookie ...
随机推荐
- 从MySQL大量数据清洗到TiBD说起
从MySQL大量数据清洗到TiBD说起 一.业务场景: 公司主要做的业务是类似贝壳的二手房租售,公司数据库存了上亿级别的房源数据,之前的数据库使用的是 mysql,后面需要将mysql数据库切换成了 ...
- noip18
T1 来自cf原题 考场直接暴力枚举 \(A,B\),15pts. 正解: 首先时间的表达式,\(T=\frac{A}{a_{i}}+\frac{B}{b_{i}}\),然后以\(\frac{1}{a ...
- 分布式redis自增
redis+springboot RedisUtil.java package com.meeno.chemical.common.redis; import java.util.Date; impo ...
- 0x800b010a 证书
无论是装微软的什么应用,只要报这个错误,下载这个证书: http://download.microsoft.com/download/2/4/8/248D8A62-FCCD-475C-85E7-6ED ...
- [C#]c#中数据的同步加锁机制 的几种方法
一,锁定机制最简单的做法就是使用锁定关键字Lock.Lock关键字英文中就是锁的意思,顾名思义就是为操作加上一把锁.它的语法如下: lock(lockObj){//加锁的代码段,一般是操作共同资源的代 ...
- 07.SpringMVC之静态资源
如何你的DispatcherServlet拦截 *.do这样的URL,就不存在访问不到静态资源的问题.如果你的DispatcherServlet拦截"/",拦截了所有的请求,同时对 ...
- Ztree 树插件 树节点名称太长的解决方案
样式允许的情况下 给背景div加滚动条.. 或者使用省略号方法:使用addDiyDom http://blog.csdn.net/zhengbo0/article/details/17759543 ...
- Java锁--Lock实现原理(底层实现)
关于java lock的底层实现原理,讲的有点深,转载学习! 转载自 https://blog.csdn.net/Luxia_24/article/details/52403033 Lock完全用Ja ...
- 【Spring 持久层】Spring 与 Mybatis 整合
持久层整合总述 1.Spring 框架为什么要与持久层技术进行整合? JavaEE开发需要持久层进行数据库的访问操作 JDBC.Hibernate.MyBatis 进行持久开发过程存在大量的代码冗余 ...
- Spring boot中注册Servlet
Spring boot中注册Servlet 如何在spring boot项目中注册Servlet呢? 如何在spring boot项目中注册Servlet呢? 由于没有web.xml,无法直接在xml ...
