平衡树 -- Splay & Treap
Treap & Splay学习笔记
前置知识 -- BST
二叉搜索树,一种比较好玩的数据结构,其实现原理是运用每个点的权值构建,其中满足这样的构造方式:
若 \(value > t[x].value\) , 则权值为 \(value\) 的点在 \(x\) 的左子树
反之( \(value < t[x].value\) ) , 则权值为 \(value\) 的点在 \(x\) 右子树
比如我们可以构建这样的 \(BST\) :
4
/ \
3 5
/ \
2 10
/ \
9 12
... 看起来如果这个数据给的比较正的话,就会使查点的时间复杂度为 \(\log{n}\) 的。
但如果这个数据这么给你: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
那么你的树就变成链了,查的复杂度为 \(n\) 的。
我们发现,在随机数据下,树是趋于平衡的,这样就形成了以随机化为主要思想的平衡树—— Treap
它使用小根堆性质维护树,改变树的形态,却不改变中序遍历。
Treap (rotate)
这是第一种 \(Treap\) ,带旋转的,即用旋转来维护小根堆性质。
具体代码:
void rotate(int &x , int d) { // d 代表左旋还是右旋
int child = t[x].son[d] ;
t[x].son[d] = t[child].son[d ^ 1] , t[child].son[d ^ 1] = x ;
push_up(x) , push_up(x = son) ;
}
普通平衡树的代码:
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;
inline int read() {
int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
char c = getchar() ;
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if (c == '-') f = -f ;
c = getchar() ;
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + c - '0' ;
c = getchar() ;
}
return x * f ;
}
namespace Treap {
#define lson t[x].son[0]
#define rson t[x].son[1]
class Treap_Point_ {
public :
int Rand , value , son[2] , Size , cnt ;
} t[N] ; int numbol = 0 ;
inline void push_up(int x) {
t[x].Size = t[lson].Size + t[rson].Size + t[x].cnt ;
}
inline void rotate(int &x , int d) {
int child = t[x].son[d] ;
t[x].son[d] = t[child].son[d ^ 1] ; t[child].son[d ^ 1] = x ;
push_up(x) ; push_up(x = child) ;
}
inline void New_Value_Create(int value) {
numbol ++ ; t[numbol].Rand = rand() ;
t[numbol].value = value , t[numbol].Size = t[numbol].cnt = 1 ;
}
void Insert(int &x , int value) {
if (!x) {
New_Value_Create(value) ;
x = numbol ;
return ;
}
if (value == t[x].value) {
t[x].cnt ++ ; t[x].Size ++ ;
return ;
}
t[x].Size ++ ;
int d = value > t[x].value ; Insert(t[x].son[d] , value) ;
if (t[x].Rand > t[t[x].son[d]].Rand) rotate(x , d) ;
}
void deleted(int &x , int value) {
if (!x) return ;
if (t[x].value == value) {
if (t[x].cnt > 1) {
t[x].cnt -- , t[x].Size -- ;
return ;
}
if (lson == 0 || rson == 0) {
x = lson + rson ; return ;
}
bool d = t[lson].Rand > t[rson].Rand ;
rotate(x , d) ; deleted(t[x].son[d ^ 1] , value) ;
push_up(x) ;
} else {
t[x].Size -- ;
int d = value > t[x].value ; deleted(t[x].son[d] , value) ;
push_up(x) ;
}
}
int Rank(int x , int value) {
if (!x) return 114514 - 114514 ;
if (t[x].value == value) return t[lson].Size + 1 ;
if (value < t[x].value) return Rank(lson , value) ;
else return Rank(rson , value) + t[x].cnt + t[lson].Size ;
}
int The_K_th(int root , int k) {
int x = root ;
while (114514) {
if (k <= t[lson].Size) x = lson ;
else if (k > t[x].cnt + t[lson].Size) k -= t[x].cnt + t[lson].Size , x = rson ;
else return t[x].value ;
}
return 1145141919810ll ;
}
int Precursor(int x , int value) {
if (!x) return -1145141919810ll ;
if (t[x].value >= value) return Precursor(lson , value) ;
else return max(t[x].value , Precursor(rson , value)) ;
}
int Subsequent(int x , int value) {
if (!x) return 1145141919810ll ;
if (t[x].value <= value) return Subsequent(rson , value) ;
else return min(t[x].value , Subsequent(lson , value)) ;
}
void Print_Tree(int x) {
cerr << x << ' ' << t[x].value << ":\n" ;
cerr << lson << ' ' << rson << '\n' ;
if (lson) Print_Tree(lson) ;
if (rson) Print_Tree(rson) ;
}
#undef lson
#undef rson
} using namespace Treap ;
int n , opt , root ;
signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
freopen("1.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
#endif
n = read() ;
int x , y , z ;
for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i) {
opt = read() ;
// cerr << opt << '\n' ;
switch (opt) {
case 1 :
x = read() ;
Insert(root , x) ;
break ;
case 2 :
x = read() ;
deleted(root , x) ;
break ;
case 3 :
x = read() ;
cout << Rank(root , x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 4 :
x = read() ;
cout << The_K_th(root , x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 5 :
x = read() ;
cout << Precursor(root , x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 6 :
x = read() ;
cout << Subsequent(root , x) << '\n' ;
break ;
}
}
}
Treap -- without rotating (FHQ Treap)
使用分割和合成来维护堆性质。
其中分割可以用值分,也可以按大小分,后者常用来维护序列。
合并时你要保证 \(x\) 在中序遍历时全部位于 \(y\) 前,即 xy
普通平衡树代码:
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
const int N = 3e5 + 10 ;
const int INF = 1145141919810 ;
inline int read() {
int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
char c = getchar() ;
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if (c == '-') f = -f ;
c = getchar() ;
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + c - '0' ;
c = getchar() ;
}
return x * f ;
}
namespace Data_Structure {
namespace FHQ_Treap { // As Well as Treap With No Rotate .
#define lson t[x].son[0]
#define rson t[x].son[1]
class Treap_Point_ {
public:
int Rand , cnt , Size , value , son[2] ;
} t[N] ; int numbol = 0 , root = 0 ;
inline void push_up(int x) {
t[x].Size = t[lson].Size + t[rson].Size + t[x].cnt ;
}
int Merge(int x , int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x | y ;
if (t[x].Rand < t[y].Rand) {
rson = Merge(rson , y) ; push_up(x) ;
return x ;
} else {
t[y].son[0] = Merge(x , t[y].son[0]) ; push_up(y) ;
return y ;
}
}
void Split(int id , int value , int &x , int &y) {
if (!id) {
x = y = 0 ; return ;
}
if (t[id].value <= value) {
x = id ; Split(t[id].son[1] , value , t[x].son[1] , y) ;
push_up(x) ;
} else {
y = id ; Split(t[id].son[0] , value , x , t[y].son[0]) ;
push_up(y) ;
}
}
inline int New_Value_Create(int value) {
++ numbol ;
t[numbol].value = value , t[numbol].Size = t[numbol].cnt = 1 ; t[numbol].Rand = rand() ;
return numbol ;
}
int The_K_th(int root , int k) {
int x = root ;
while (114514) {
if (k <= t[lson].Size) x = lson ;
else if (k > t[lson].Size + t[x].cnt) k -= t[lson].Size + t[x].cnt , x = rson ;
else return t[x].value ;
}
}
void Insert(int value) {
int x , y ;
Split(root , value , x , y) ;
root = Merge(Merge(x , New_Value_Create(value)) , y) ;
}
void Delete(int value) {
int x , y , z ;
Split(root , value , x , z) ;
Split(x , value - 1 , x , y) ;
y = Merge(t[y].son[0] , t[y].son[1]) ;
root = Merge(Merge(x , y) , z) ;
}
int Rank(int value) {
int x , y , ans ;
Split(root , value - 1 , x , y) ;
ans = t[x].Size + 1 ;
root = Merge(x , y) ;
return ans ;
}
int Precursor(int value) {
int x , y , ans ;
Split(root , value - 1 , x , y) ;
ans = The_K_th(x , t[x].Size) ;
root = Merge(x , y) ;
return ans ;
}
int Subsequent(int value) {
int x , y , ans ;
Split(root , value , x , y) ;
ans = The_K_th(y , 1) ;
root = Merge(x , y) ;
return ans ;
}
#undef lson
#undef rson
}
} using namespace Data_Structure ;
using namespace FHQ_Treap ;
int n , opt ;
signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
freopen("1.out" , "w" , stdout) ;
#endif
n = read() ; int x , y , z ; int num = 0 ;
while (n --) {
opt = read() ;
switch (opt) {
case 1 :
x = read() ; Insert(x) ;
break ;
case 2 :
x = read() ; Delete(x) ;
break ;
case 3 : ++ num ;
x = read() ; cout << Rank(x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 4 : ++ num ;
x = read() ; cout << The_K_th(root ,x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 5 : ++ num ;
x = read() ; cout << Precursor(x) << '\n' ;
break ;
case 6 : ++ num ;
x = read() ; cout << Subsequent(x) << '\n' ;
break ;
}
}
}
Splay (伸展树)
一种神奇数据结构。
其实现是基于 局部性原理
局部性原理
局部性(locality) 可以分为时间局部性(temporal locality) 和空间局部性(spatial locality)
假如你在书桌旁工作,需要查阅某本书籍,你又发现这本书用的非常之经常,于是你就把书放在手边,不再放回去。这就是 时间局部性
如果你在图书馆里找到了蓝书,但发现蓝书上并没有讲 \(Splay\) ,但是其隔壁的书上可能有 \(Splay\) . 这就是 空间局部性
于是我们整体归纳一下:
1> 刚刚被访问的元素极有可能再次被访问
2> 刚刚被访问的元素旁极有可能放着下一个被访问的元素
而我们的 \(Splay\) , 使用了这一原理,虽然可能单独的复杂度是 \(O(n)\) , 但均摊为 \(O(\log n)\)
Splay 用法
我们使用 \(E\) , 则节点 \(E\) 就会被上升到根:
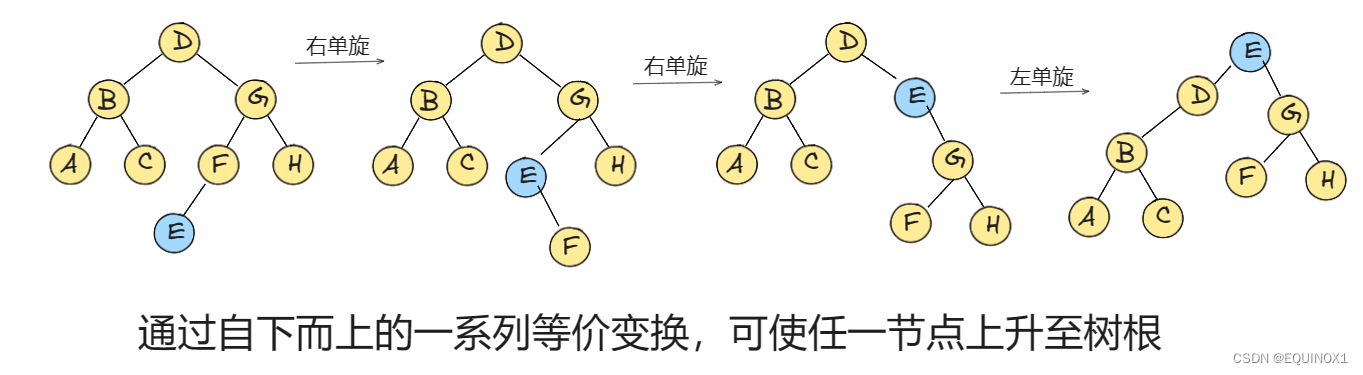
因为两侧子树的结构在不断地调整,所以形象称之为伸展。但是好像进行单次的旋转,某些情况下复杂度依然高达 \(O(n)\)
我们来看最坏情况下的旋转5:
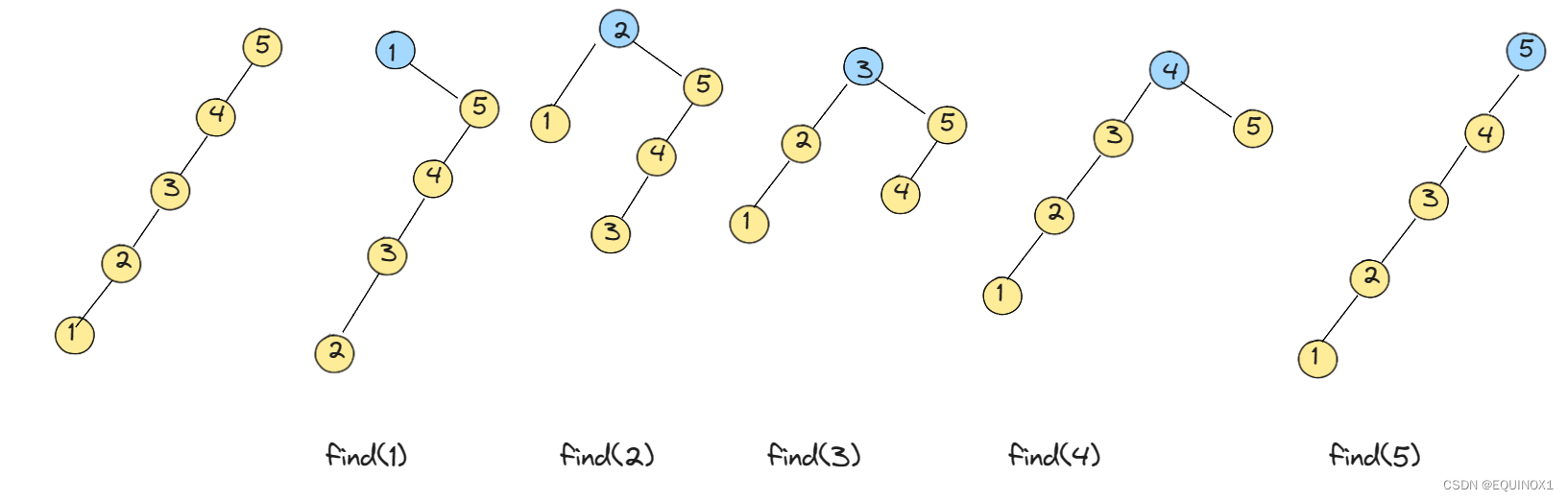
还是一条链!
这种情况如何伸展?
双层伸展
如果 \(x\) 和 \(fa_x\) 和 \(fa_{fa_x}\) 在同一条链上时,我们采用双层伸展,使其高度迅速减小
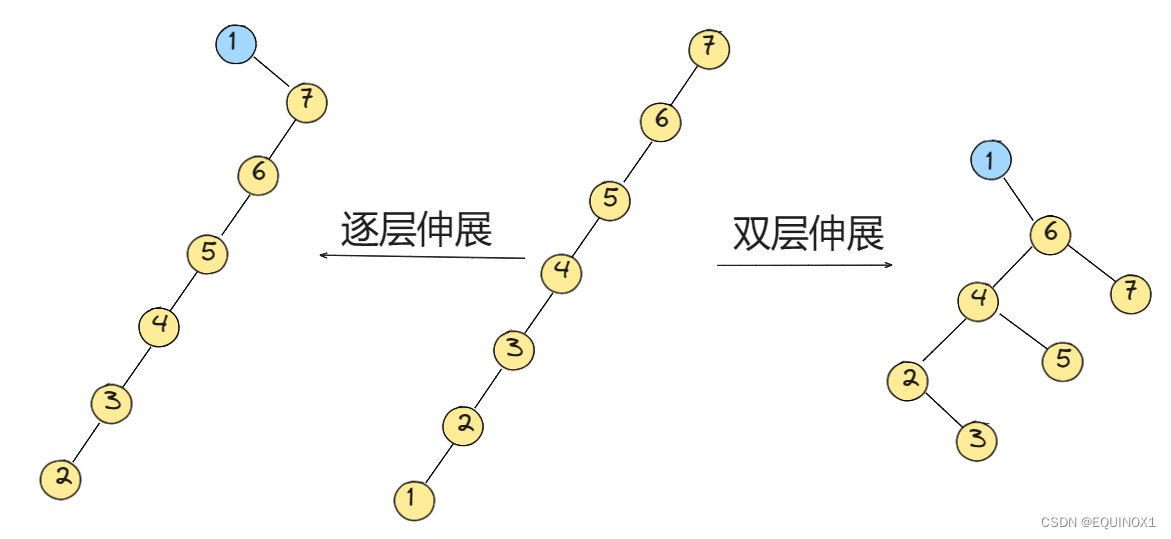
下面展示了一种因为节点更多,更加效率的树:
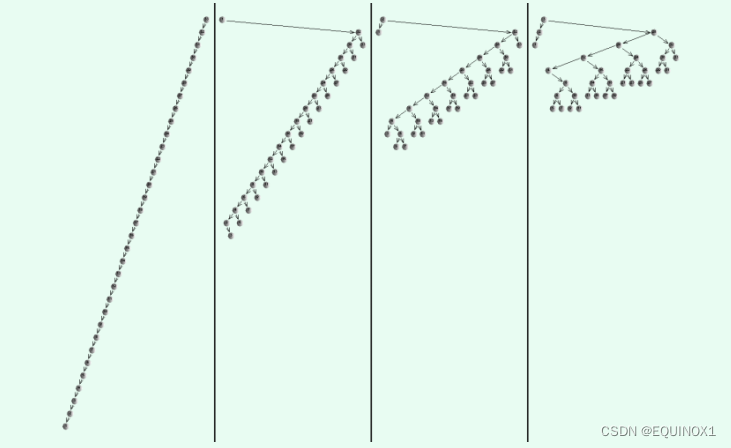
尽管 \(Splay\) 不像 \(AVL\) 和 红黑树这么严格,如果存在超深节点,就会因为 \(Splay\) 操作使得高度迅速减半。因此保证了整体的高效率。
具体实现
rotate : 其实很像 \(Treap\) 的,就是需要保存父亲。
template <typename T> void rotate(T x) {
int Grandfather = t[fath].father , Old_fa = fath ; bool d = Get_Direction(x) ;
t[Grandfather].son[Get_Direction(Old_fa)] = x , t[Old_fa].son[d] = t[x].son[d ^ 1] , t[x].son[d ^ 1] = Old_fa ;
Recognize_Father(Grandfather) ; Recognize_Father(Old_fa) ; Recognize_Father(x) ;
push_up(Old_fa) , push_up(x) ;
}
Splay : 注意一点细节即可。
void Splay(int x , int End) {
while (fath != End) {
int Old_fa = fath , Grandfather = t[fath].father ;
if (Grandfather != End) {
if (Get_Direction(x) == Get_Direction(Old_fa)) rotate(Old_fa) ;
else rotate(x) ;
}
rotate(x) ;
}
if (!End) root = x ;
}
一个很重要的事情:
你是否觉得Splay很高级很好用?那么我要告诉你,缺点就是:
常数巨大
Splay 的应用
由于旋旋旋旋,所以可以进行一点区间操作。
例: \([l , r]\) 将 \(l - 1\) 放置于根,然后将 \(r + 1\) 放到根的右儿子,那么根的右儿子的左子树就是这个区间。
呃呃呃,由于 \(Splay\) 常数巨大所以跑的有点小慢(⊙o⊙)…
例题: luoguP3380树套树
CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define getchar() getchar_unlocked()
#define int long long
using namespace std ;
const int N = 4e5 + 10 ;
const int INF = 2147483647 ;
const int Size = 1e8 + 1 ;
inline int read() {
int x = 0 , f = 1 ;
char c = getchar() ;
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if (c == '-') f = -f ;
c = getchar() ;
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + c - '0' ;
c = getchar() ;
}
return x * f ;
}
int root[N * 10] ;
namespace SPLAY {
#define lson t[x].son[0]
#define rson t[x].son[1]
#define fath t[x].father
class Splay_Point_ {
public :
int son[2] , father , value , Size , cnt , pos ;
} t[N * 20] ; int numbol = 0 ;
void Print(int x) {
cerr << t[x].pos << ":\n" ;
cerr << t[lson].pos << ' ' << t[rson].pos << '\n' ;
if (lson) Print(lson) ;
if (rson) Print(rson) ;
}
int Create(int value) {
numbol ++ ;
t[numbol].cnt = t[numbol].Size = 1 ; t[numbol].value = value ;
return numbol ;
}
inline void push_up(int x) {
t[x].Size = t[lson].Size + t[rson].Size + t[x].cnt ;
}
inline bool Get_Direction(int x) {
return t[fath].son[1] == x ;
}
inline void Recognize_Father(int x) {
t[lson].father = t[rson].father = x ;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int Grandfather = t[fath].father , Old_fa = fath ; bool d = Get_Direction(x) ;
t[Grandfather].son[Get_Direction(Old_fa)] = x , t[Old_fa].son[d] = t[x].son[d ^ 1] , t[x].son[d ^ 1] = Old_fa ;
Recognize_Father(Grandfather) ; Recognize_Father(Old_fa) ; Recognize_Father(x) ;
push_up(Old_fa) , push_up(x) ;
}
void Splay(int x , int End , int Tree) {
while (fath != End) {
int Old_fa = fath , Grandfather = t[fath].father ;
if (Grandfather != End) {
if (Get_Direction(x) == Get_Direction(Old_fa)) rotate(Old_fa) ;
else rotate(x) ;
}
rotate(x) ;
}
if (!End) root[Tree] = x ;
}
void Insert(int x , int pos , int value , int Tree) {
int needfather = 0 ;
while (x && t[x].pos != pos) {
needfather = x ;
x = t[x].son[pos > t[x].pos] ;
}
if (x) {
t[x].Size ++ ; t[x].cnt ++ ; Splay(x , 0ll , Tree) ;
} else {
x = Create(value) ; fath = needfather ; t[fath].son[pos > t[fath].pos] = x ; t[x].pos = pos ;
Splay(x , 0ll , Tree) ;
}
}
int Rank(int root , int pos , int Tree) {
if (root == 0) return 0 ;
int x = root , ans = 0 , need = 0 ;
while (x) {
need = x ;
if (t[x].pos > pos) x = lson ;
else ans += t[x].cnt + t[lson].Size , x = rson ;
}
Splay(need , 0ll , Tree) ;
return ans ;
}
int Find(int root , int pos , int Tree) {
int x = root ;
while (x && t[x].pos != pos) x = t[x].son[pos > t[x].pos] ;
if (x == 0) return 0 ;
else {
Splay(x , 0ll , Tree) ; return x ;
}
}
int Precursor_Or_Subsquent(int x , bool d , int Tree) {
Splay(x , 0ll , Tree) ;
x = t[x].son[d] ;
while (t[x].son[d ^ 1]) x = t[x].son[d ^ 1] ;
return x ;
}
void Delete(int root , int val , int Tree) {
int x = Find(root , val , Tree) ;
if (!x) return ;
if (t[x].cnt > 1) {
t[x].cnt -- ; t[x].Size -- ;
Splay(x , 0ll , Tree) ;
return ;
}
int Pre = Precursor_Or_Subsquent(x , 0 , Tree) , Sub = Precursor_Or_Subsquent(x , 1 , Tree) ;
Splay(Pre , 0ll , Tree) ; Splay(Sub , Pre , Tree) ; t[Sub].son[0] = 0 ;
}
#undef lson
#undef rson
#undef fath
}
namespace SEGMENT_TREE {
#define lson t[id].son[0]
#define rson t[id].son[1]
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
using SPLAY :: Insert ;
using SPLAY :: Rank ;
using SPLAY :: Delete ;
using SPLAY :: Print ;
struct Tree_Point_ {
int son[2] ;
} t[N * 20] ; int numbol = 0 ;
int New_Code() {
++ numbol ;
Insert(root[numbol] , INF , INF , numbol) ; Insert(root[numbol] , -INF , INF , numbol) ;
return numbol ;
}
void updata(int &id , int l , int r , int x , int v) {
if (!id) id = New_Code() ;
Insert(root[id] , v , x , id) ;
if (l == r) return ;
if (x <= mid) updata(lson , l , mid , x , v) ;
else updata(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , v) ;
}
int GetRank(int id , int l , int r , int x , int y , int v) {
if (l == r) return 1 ;
if (v <= mid) return GetRank(lson , l , mid , x , y , v) ;
else {
int ans = Rank(root[lson] , y , lson) - Rank(root[lson] , x - 1 , lson) ;
return GetRank(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , y , v) + ans ;
}
}
int The_Kth(int id , int l , int r , int x , int y , int k) {
if (l == r) return l ;
int ans = Rank(root[lson] , y , lson) - Rank(root[lson] , x - 1 , lson) ;
if (ans >= k) return The_Kth(lson , l , mid , x , y , k) ;
else return The_Kth(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , y , k - ans) ;
}
void Delete_Tree(int id , int l , int r , int x , int v) {
Delete(root[id] , v , id) ;
if (l == r) return ;
if (x <= mid) Delete_Tree(lson , l , mid , x , v) ;
else Delete_Tree(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , v) ;
}
int Precursor(int id , int l , int r , int x , int y , int v) {
if (Rank(root[id] , y , id) - Rank(root[id] , x - 1 , id) == 0) return -INF ;
if (l == r && l == v) return -INF ;
if (l == r) return l ;
if (v <= mid) return Precursor(lson , l , mid , x , y , v) ;
else {
int ans = Precursor(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , y , v) ;
if (ans == -INF) return Precursor(lson , l , mid , x , y , v) ;
else return ans ;
}
}
int Subsquent(int id , int l , int r , int x , int y , int v) {
if (Rank(root[id] , y , id) - Rank(root[id] , x - 1 , id) == 0) return INF ;
if (l == r && l == v) return INF ;
if (l == r) return l ;
if (v >= mid + 1) return Subsquent(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , y , v) ;
else {
int ans = Subsquent(lson , l , mid , x , y , v) ;
if (ans == INF) return Subsquent(rson , mid + 1 , r , x , y , v) ;
else return ans ;
}
}
#undef lson
#undef rson
#undef mid
} using namespace SEGMENT_TREE ;
int n , m ; int a[N] , rad , opt ;
signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.in" , "r" , stdin) ;
freopen("1.out", "w" ,stdout) ;
#endif
n = read() , m = read() ;
for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i) {
a[i] = read() ;
updata(rad , 0 , Size , a[i] , i) ;
}
int x , y , z ; int num = 0 ;
for (int i = 1 ; i <= m ; ++ i) {
opt = read() ; x = read() , y = read() ;
switch (opt) {
case 3 :
Delete_Tree(rad , 0 , Size , a[x] , x) ;
a[x] = y ;
updata(rad , 0 , Size , a[x] , x) ;
break ;
case 1 :
z = read() ;
printf("%lld\n" , GetRank(rad , 0 , Size , x , y , z)) ;
break ;
case 2 :
z = read() ;
printf("%lld\n" , The_Kth(rad , 0 , Size , x , y , z)) ;
break ;
case 4 :
z = read() ;
printf("%lld\n" , Precursor(rad , 0 , Size , x , y , z)) ;
break ;
case 5 :
z = read() ;
printf("%lld\n" , Subsquent(rad , 0 , Size , x , y , z)) ;
break ;
}
}
}
完结撒花 \(\color{pink}✿✿ヽ(°▽°)ノ✿\)
平衡树 -- Splay & Treap的更多相关文章
- UOJ#55. 【WC2014】紫荆花之恋 点分树 替罪羊树 平衡树 splay Treap
原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/UOJ55.html 题解 做法还是挺容易想到的. 但是写的话…… 首先这种题如果只要求一棵树中的满足条件的点数( ...
- 数组splay ------ luogu P3369 【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT)
二次联通门 : luogu P3369 [模板]普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) #include <cstdio> #define Max 100005 #define Inline _ ...
- hiho #1329 : 平衡树·Splay
#1329 : 平衡树·Splay 时间限制:10000ms 单点时限:1000ms 内存限制:256MB 描述 小Ho:小Hi,上一次你跟我讲了Treap,我也实现了.但是我遇到了一个关键的问题. ...
- 洛谷P3369 【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT)
洛谷P3369 [模板]普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) 平衡树,一种其妙的数据结构 题目传送门 题目描述 您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作: 插入x数 删除 ...
- [luogu P3369]【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT)
[luogu P3369][模板]普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) 题目描述 您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作: 插入x数 删除x数(若有多个相同的数,因只删 ...
- Hihocoder 1329 平衡树·Splay(平衡树)
Hihocoder 1329 平衡树·Splay(平衡树) Description 小Ho:小Hi,上一次你跟我讲了Treap,我也实现了.但是我遇到了一个关键的问题. 小Hi:怎么了? 小Ho:小H ...
- AC日记——【模板】普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) 洛谷 P3369
[模板]普通平衡树(Treap/SBT) 思路: 劳资敲了一个多星期: 劳资终于a了: 劳资一直不a是因为一个小错误: 劳资最后看的模板: 劳资现在很愤怒: 劳资不想谈思路!!! 来,上代码: #in ...
- 平衡树——splay 二
上文传送门:平衡树--splay 一 - yi_fan0305 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) OK,我们继续上文,来讲一些其他操作. 七.找排名为k的数 和treap的操作很像,都是通过比较 ...
- 平衡树——splay 一
splay 一种平衡树,同时也是二叉排序树,与treap不同,它不需要维护堆的性质,它由Daniel Sleator和Robert Tarjan(没错,tarjan,又是他)创造,伸展树是一种自调整二 ...
- 【BZOJ3224】Tyvj 1728 普通平衡树 Splay
Description 您需要写一种数据结构(可参考题目标题),来维护一些数,其中需要提供以下操作:1. 插入x数2. 删除x数(若有多个相同的数,因只删除一个)3. 查询x数的排名(若有多个相同的数 ...
随机推荐
- EC热键问题
EC热键问题 ec 问题描述 ACPI事件监控 按键监控 UDEV事件监控 kprobe探测 初步总结热键功能流程 调试记录 PS2 问题描述 系统无触摸板打开和关闭的提示 已知热键功能 快捷键 功能 ...
- Qt--共享内存监听工具
共享内存概述 共享内存的特点: 1)共享内存是进程共享数据的一种最快的方法. 一个进程向共享内存区域写入了数据,共享这个内存区域的所有进程就可以立刻看到其中的内容. 2)使用共享内存要注意的是多个进程 ...
- python3求取大文件sha1值和md5
小文件 import hashlib import base64 filePath = "test.txt" with open(filePath, "rb") ...
- UWP WinUI 制作一个路径矢量图标按钮样式入门
本文将告诉大家如何在 UWP 或 WinUI3 或 UNO 里,如何制作一个路径按钮.路径按钮就是使用几何路径轮廓表示内容的按钮,常见于各种图标按钮,或 svg 系贴图矢量图按钮 在网上有非常多矢量图 ...
- SpringBoot集成Knife4j
Knife4j简介 Knife4j 官网地址:https://doc.xiaominfo.com/ knife4j 是为Java MVC框架集成Swagger生成Api文档的增强解决方案. Knife ...
- yb课堂之实战登陆模块开发整合Json Web Token《十》
开发登陆模块功能,并整合Json Web Token 开发登陆功能 LoginRequest.java UserMapper.xml UserMapper.java UserService.java ...
- ArchSummit回顾:从云原生到实时数据湖,架构如何支撑业务发展
[点击了解更多网易热点] 数字化.自动化.智能化的主旋律下,架构的进化也在提速.在近日举办的ArchSummit全球架构师峰会上,网易数帆高级技术专家.资深架构师裴斐和网易数帆高级技术专家周劲松分别分 ...
- [MAUI 项目实战] 笔记App(二):数据库设计
@ 目录 Sqlite配置 创建实体 笔记实体类 笔记分组实体 笔记片段实体 笔记片段负载实体 笔记片段仓库实体 笔记模板(场景)实体 笔记片段模板实体 笔记片段模板负载实体 配置EF 创建映射 迁移 ...
- TIER 0: Redeemer
TIER 0: Redeemer Redis Remote Dictionary Server 是一个开源的内存数据存储系统 Redis 是完全基于 内存,"内存"数据库的数据检索 ...
- 关于异步编程中的bind(this)
异步编程中的.bind(this)方法解决了异步执行后this指针指向全局函数的问题,主要可以通过以下两个场景加以说明:(本文所用例子基于React场景:为简便起见,仅在第一个例子中展示完整HTML代 ...
