activiti主要组件解析
Activiti内部实现中,各主要部件关系

对外,提供Service服务,它是无状态的。
这些Service包括:
- protected RepositoryService repositoryService = new RepositoryServiceImpl();
- protected RuntimeService runtimeService = new RuntimeServiceImpl();
- protected HistoryService historyService = new HistoryServiceImpl();
- protected IdentityService identityService = new IdentityServiceImpl();
- protected TaskService taskService = new TaskServiceImpl();
- protected FormService formService = new FormServiceImpl();
- protected ManagementService managementService = new ManagementServiceImpl();
对service提供的服务,基本上每一个需要执行具体任务的方法,都有一个对应的Command实现与之对应。
- 一般来说,一个Command对应一个完整事物;
- 调用Command之前,都会经过CommandInterceptor,这个在初始化时就确定了,如:LogInterceptor >> CommandContextInterceptor >> CommandInvoker
如果Command不涉及节点相关内容,而是直接对数据库进行操作,则直接关联DB,入DbSqlSession的缓存;
否则,一般会通过ExecutionEntity来完成具体的操作,这里,封装了一些基本的原子操作,它们都是AtomicOperation的接口实现:
流程实例类:
- AtomicOperationProcessStart
- AtomicOperationProcessStartInitial
- AtomicOperationProcessEnd
流程活动类:
- AtomicOperationActivityStart
- AtomicOperationActivityExecute
- AtomicOperationActivityEnd
流程活动流转类:
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerEnd
- AtomicOperationTransitionDestroyScope
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerTake
- AtomicOperationTransitionCreateScope
- AtomicOperationTransitionNotifyListenerStart
流程执行树清理类:
- AtomicOperationDeleteCascade
- AtomicOperationDeleteCascadeFireActivityEnd
其中,活动执行时,具体动作是由ActivityBehavior的实现类来决定的:
关于默认ID生成器
Activiti的默认生成器是DbIdGenerator,实际是一次从数据库中取一块数据,然后慢慢用,用完后再取。
/**
* @author Tom Baeyens
*/
public class DbIdGenerator implements IdGenerator { protected int idBlockSize;
protected long nextId = 0;
protected long lastId = -1; protected CommandExecutor commandExecutor;
protected CommandConfig commandConfig; public synchronized String getNextId() {
if (lastId<nextId) {
getNewBlock();
}
long _nextId = nextId++;
return Long.toString(_nextId);
} protected synchronized void getNewBlock() {
IdBlock idBlock = commandExecutor.execute(commandConfig, new GetNextIdBlockCmd(idBlockSize));
this.nextId = idBlock.getNextId();
this.lastId = idBlock.getLastId();
}
- 在ProcessEngineConfiguration中定义的块默认大小100;
- 在ProcessEngineComfigurationImpl中,完成初始化:
// id generator /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
protected void initIdGenerator() {
if (idGenerator==null) {
CommandExecutor idGeneratorCommandExecutor = null;
if (idGeneratorDataSource!=null) {
ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = new StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration();
processEngineConfiguration.setDataSource(idGeneratorDataSource);
processEngineConfiguration.setDatabaseSchemaUpdate(DB_SCHEMA_UPDATE_FALSE);
processEngineConfiguration.init();
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = processEngineConfiguration.getCommandExecutor();
} else if (idGeneratorDataSourceJndiName!=null) {
ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = new StandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration();
processEngineConfiguration.setDataSourceJndiName(idGeneratorDataSourceJndiName);
processEngineConfiguration.setDatabaseSchemaUpdate(DB_SCHEMA_UPDATE_FALSE);
processEngineConfiguration.init();
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = processEngineConfiguration.getCommandExecutor();
} else {
idGeneratorCommandExecutor = getCommandExecutor();
}
DbIdGenerator dbIdGenerator = new DbIdGenerator();
dbIdGenerator.setIdBlockSize(idBlockSize);
dbIdGenerator.setCommandExecutor(idGeneratorCommandExecutor);
dbIdGenerator.setCommandConfig(getDefaultCommandConfig().transactionRequiresNew());
idGenerator = dbIdGenerator;
}
}
注意:此处对getNextId()方法加了synchronize关键字,它在单机部署下,确定不会出现网上分析的什么ID重复问题。
关于task的start_time_字段取值问题
在TaskEntity中:
/** creates and initializes a new persistent task. */
public static TaskEntity createAndInsert(ActivityExecution execution) {
TaskEntity task = create();
task.insert((ExecutionEntity) execution);
return task;
} public void insert(ExecutionEntity execution) {
CommandContext commandContext = Context.getCommandContext();
DbSqlSession dbSqlSession = commandContext.getDbSqlSession();
dbSqlSession.insert(this); if(execution != null) {
execution.addTask(this);
} commandContext.getHistoryManager().recordTaskCreated(this, execution);
} /*
* 。。。。
*/ /** Creates a new task. Embedded state and create time will be initialized.
* But this task still will have to be persisted. See {@link #insert(ExecutionEntity)}. */
public static TaskEntity create() {
TaskEntity task = new TaskEntity();
task.isIdentityLinksInitialized = true;
task.createTime = ClockUtil.getCurrentTime();
return task;
}
由此知道,活动的时间是由ClockUtil.getCurrentTime()决定的。再来看看CockUtil的源码:
/**
* @author Joram Barrez
*/
public class ClockUtil { private volatile static Date CURRENT_TIME = null; public static void setCurrentTime(Date currentTime) {
ClockUtil.CURRENT_TIME = currentTime;
} public static void reset() {
ClockUtil.CURRENT_TIME = null;
} public static Date getCurrentTime() {
if (CURRENT_TIME != null) {
return CURRENT_TIME;
}
return new Date();
} }
注意:
因为可能多线程情况,而且只有set,不会执行类似++,--这样的操作,所以这里用volatile关键字完全满足需要。
默认实现在分布式中问题
在上面介绍了DbIdGenerator以及ClockUtil之后,可以清楚明白他们的原理,那么在分布式部署中,如果还是使用这种默认的实现而不加以改善,会出现什么问题。
1.DbIdGenerator的getNextId()/getNewBlock()两个方法,在分布式主机中,synchronize不能顺利实现锁控制;
2.ClockUtil严重依赖容器所在服务器时间,但是分布式主机的时间不可能达到完全的同步;
3.在分布式主机中,对同一个任务,可以同时执行,因为他们都是DbSqlSession缓存,不会立马入库;也就是说,可能存在一个任务被同时自行两次的情况。
对1,2两点分析,基本上是确定会存在的,至于第三点,限于猜想,不知道实际是否有相关的解决策略,目前对activiti关于此处的设置猜想还没有完全弄清楚。
其实之所以那么在乎任务Id以及任务执行时间,主要是在流程跟踪图中,需要根据有序的历史任务结果集模仿重现走过的路径,而做到有序,这两个要素是非常关键的。
对分布式应用,如果同库,那ID的生成问题都会是一个问题,常见的解决方式是把他扔给数据库去解决,比如一个序列、一个类似序列的自定义函数等都是不错的选择。
当然,放到DB中以后,那么频繁访问数据库,activiti中设计的blocksize也就基本失效了,这个也算是衡量的结果吧。
实际问题分析
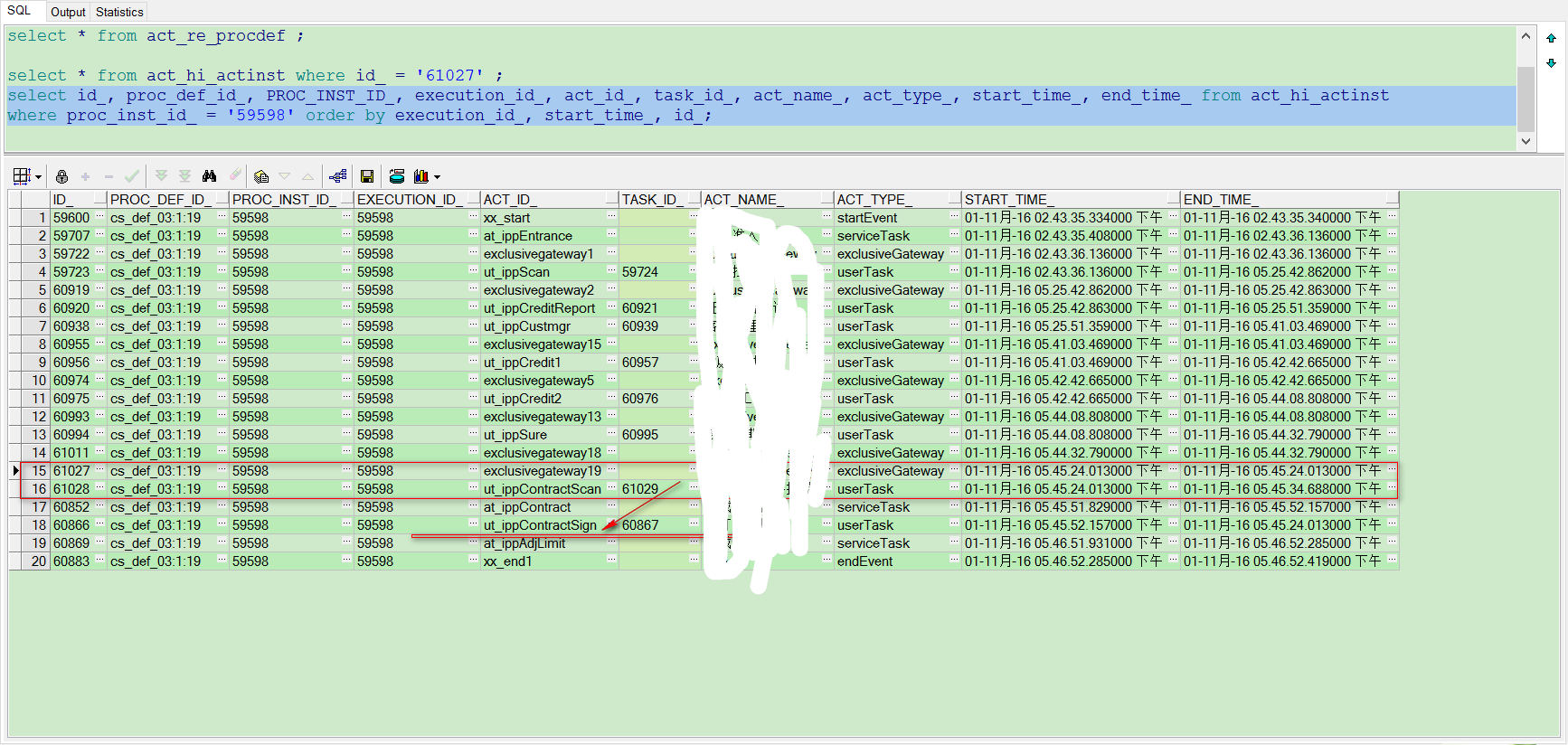
上述数据,是在生产上出现的问题数据,环境是为了负载均衡做了两个应用Server,同时连接一个DB;
从数据可以分析出“活动节点会在双机中运行”;
61011(A) >> 60852(B) >> 60866(B) >> 61022(A) >> 61028(A) >> 60889(B) >> 60893(B)
A机器上的61011执行完毕以后,事件如何转到B机器上的60852,这个还不明白,待解决!!
activiti主要组件解析的更多相关文章
- .NetCore中的日志(1)日志组件解析
.NetCore中的日志(1)日志组件解析 0x00 问题的产生 日志记录功能在开发中很常用,可以记录程序运行的细节,也可以记录用户的行为.在之前开发时我一般都是用自己写的小工具来记录日志,输出目标包 ...
- Ext 常用组件解析
Ext 常用组件解析 Panel 定义&常用属性 //1.使用initComponent Ext.define('MySecurity.view.resource.ResourcePanel' ...
- Ionic 常用组件解析
Ionic 常用组件解析 $ionicModal(弹出窗口): //创建一个窗口 //此处注意目录的起始位置为app $ionicModal.fromTemplateUrl('app/security ...
- React Native组件(三)Text组件解析
相关文章 React Native探索系列 React Native组件系列 前言 此前介绍了最基本的View组件,接下来就是最常用的Text组件,对于Text组件的一些常用属性,这篇文章会给出简单的 ...
- 2016.11.25 activiti的配置文件解析
参考来自activiti的用户手册. activiti的配置文件解析 1.processEngine的配置 注意,单独创建流程引擎与spring方式创建流程引擎是不一样的,区别在于:process ...
- React Native组件解析(二)之Text
React Native组件解析(二)之Text 1. 概述 Text组件对应于iOS的UILabel,Android的TextView,用来显示文本.但是Text组件的内部使用的并不是flexbox ...
- SpringMVC组件解析
SpringMVC组件解析 1. 前端控制器:DispatcherServlet 用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于 MVC 模式中的 C,DispatcherServlet 是整个流程控制的中心,由 ...
- Sprign-mvc系列之Spring快速入门 什么是sprign-mvc spring-mvc的作用及其基本使用+组件解析+注解解析
Spring-mvc 什么是SpringMvc SpringMvc是一种基于java的实现Mvc设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级web框架,属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spr ...
- 跨平台的.NET邮件协议MailKit组件解析
发起的.NET Core开源组织号召,进展的速度是我自己也没有想到的,很多园友都积极参与(虽然有些人诚心砸场子,要是以我以前的宝脾气,这会应该被我打住院了吧,不过幸好是少数,做一件事总有人说好,也有人 ...
随机推荐
- iOS—— iOS 内存管理:增长+泄漏
1.如果是循环中局部变量data没有释放导致的,给NSData 手动添加释放池 @autoreleasepool { your code } 2.url 转变字典key值的时候出现内存暴增! //设置 ...
- Duplicate spring bean id
问题背景:从本地调用服务器的dubbo接口进行测试 实现思路:基于IDEA+Spring+maven+Dubbo搭建测试项目,从本地直接调用 具体实现思路可参考博客:https://www.cnb ...
- 洛谷P3348 [ZJOI2016]大森林(LCT,虚点,树上差分)
洛谷题目传送门 思路分析 最简单粗暴的想法,肯定是大力LCT,每个树都来一遍link之类的操作啦(T飞就不说了) 考虑如何优化算法.如果没有1操作,肯定每个树都长一样.有了1操作,就来仔细分析一下对不 ...
- USACO Section 1.4 Mother's Milk 解题报告
题目 题目描述 有三个牛奶桶,三个桶的容积分别是A,B,C,最小为1,最大为20.刚开始只有第三个桶里面装满了牛奶,其余两个桶都是空的.我们现在可以将第三个桶中的牛奶往其他两个桶里面倒一些牛奶,然后还 ...
- java 7 升级后,控制面板里找不到java图标了
如果电脑里只装了jre的情况下,好像从java 7 update 9开始,通过java自动升级程序完成升级后,控制面板里的java图标就不见了. 只好重新从java.sun.com上下载最新版的jre ...
- codeblocks编译器
发现网络有些编译器没有MinGW,特此留一文件: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pLltzvH 有时下载codeblocks后编译不了,还要修改MinGW的位置,找到MinGW文件 ...
- Linux上vi编辑文件非正常退出后文件恢复
Vim另存文件的命令为 编辑完文件后Esc,输入以下指令 :w filename 编辑文件时非正常退出,会生成.hello.txt.swp的文件,还有一些其他信息 恢复文件要使用以下命令: [keys ...
- 弹指之间 -- Prerequisites
CHAPTER 1 吉他的分类 Electric Guitar Classic Guitar Folk Guitar CHAPTER 2 吉他各部名称 CHAPTER 3 选购吉他 琴颈弯曲程度 木头 ...
- 枚举类型---java基础代码
package com.mon11.day4; /** * 类说明 :定义枚举 * @author 作者 : chenyanlong * @version 创建时间:2017年11月4日 */ pub ...
- 一个简单的Kubernetes应用部署示例
说明 我们通过一个示例来演示一下kubernetes部署应用的基本配置. 这个示例相对比较简单,就是一个tomcat应用加上一个mysql数据库 在tomcat里运行一个简单的webappp,这个ap ...
