Canbus ID filter and mask
CANBUS is a two-wire, half-duplex, bus based LAN system that is ‘collision free’.
Data is BROADCAST onto the bus -THERE IS NO SUCH THNG AS A POINT TO POINT CONNECTION as with data LANs.
All nodes receive all broadcast data and decide whether or not that data is relevant.
A CANBUS B frame consists of a four byte header (containing a 29-bit identifier), followed by up to 8 data bytes.
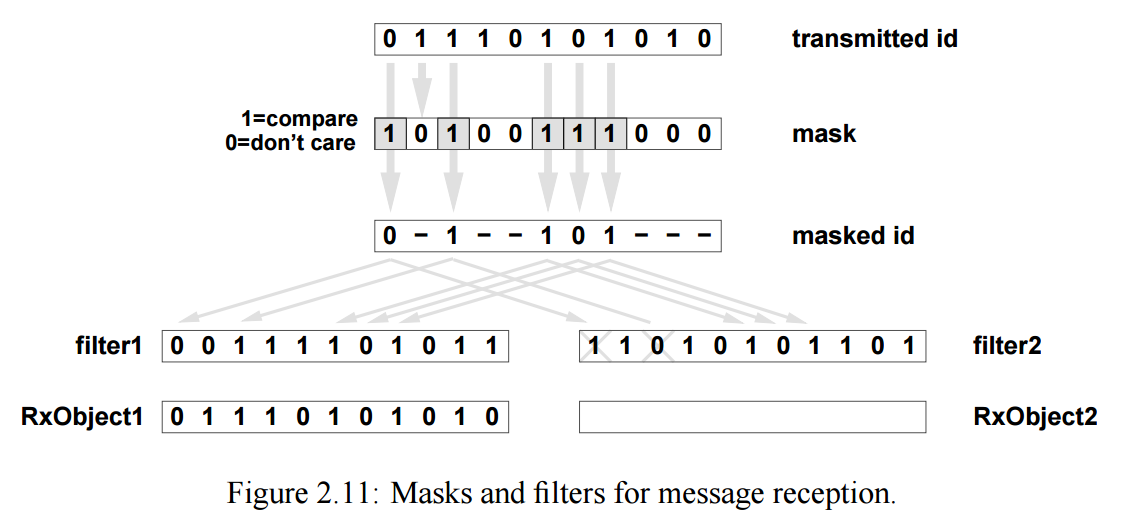
A receiving node would examine the identifier to decide if it was relevant (e.g. waiting for a frame with ID 00001567 which contains data to switch on or off a motor).
It could do this via software (using a C if or case statement); in practice the Canbus interface contains firmware to carry out this task
using the acceptance filter and mask value to filter out unwanted messages.
The filter mask is used to determine which bits in the identifier of the received frame are compared with the filter
If a mask bit is set to a zero, the corresponding ID bit will automatically be accepted, regardless of the value of the filter bit.
If a mask bit is set to a one, the corresponding ID bit will be compare with the value of the filter bit;
if they match it is accepted otherwise the frame is rejected.
A filter matches, when received_can_id & mask == can_id & mask -- Mask=1 : Do Care Bits
Example 1. we wish to accept only frames with ID of 00001567 (hexadecimal values)
set filter to 00001567
set mask to 1FFFFFFF --- Every Bit must match filter
when a frame arrives its ID is compared with the filter and all bits must match; any frame that does not match ID 00001567 is rejected
Example 2. we wish to accept only frames with IDs of 00001560 thru to 0000156F
set filter to 00001560
set mask to 1FFFFFF Low 4 Bits dont care
when a frame arrives its ID is compared with the filter and all bits except bits 0 to 3 must match; any frame other frame is rejected
Example 3. we wish to accept only frames with IDs of 00001560 thru to 00001567
set filter to 00001560
set mask to 1FFFFFF8 Low 3 Bits dont care
when a frame arrives its ID is compared with the filter and all bits except bits 0 to 2 must match; any frame other frame is rejected
Example 4. we wish to accept any frame
set filter to 0
set mask to 0 --- Every Bits dont care
all frames are accepted
In practice Canbus interfaces tends to have a number of filters and masks so combinations of IDs can be accepted,
e.g. a module that carries out a number of different tasks.// mask bit n | filter bit n | message ID bit n | result
// Mask Filter ID
// 0 x x accept
// 1 0 0 accept
// 1 0 1 reject
// 1 1 0 reject
// 1 1 1 accept
Since this filtering is done in hardware it is fairly primitive. Usually the calculation involves two registers a mask and a filter. The equivalent logic in C would be:
/* dsPIC style; mask specifies "do care" bits */
if ((arbitrationId & mask) == filter) {
/* Message accepted; rx interrupt triggered */
} /* Accept all */
mask = ;
filter = ; /* Accept CANopen default connection set (excluding SYNC and NMT) */
mask = 0x7F;
filter = node_id;
/* SJA 1000 style; mask specifies "do not care" bits */
if ((arbitrationId & ~mask) == filter) {
/* Message accepted; rx interrupt triggered */
} /* Accept all */
mask = ~;
filter = ; /* Accept CANopen default connection set (excluding SYNC and NMT) */
mask = ~0x7F;
filter = node_id;
4.1 RAW protocol sockets with can_filters (SOCK_RAW) Using CAN_RAW sockets is extensively comparable to the commonly
known access to CAN character devices. To meet the new possibilities
provided by the multi user SocketCAN approach, some reasonable
defaults are set at RAW socket binding time: - The filters are set to exactly one filter receiving everything
- The socket only receives valid data frames (=> no error message frames)
- The loopback of sent CAN frames is enabled (see chapter 3.2)
- The socket does not receive its own sent frames (in loopback mode) These default settings may be changed before or after binding the socket.
To use the referenced definitions of the socket options for CAN_RAW
sockets, include <linux/can/raw.h>. 4.1.1 RAW socket option CAN_RAW_FILTER The reception of CAN frames using CAN_RAW sockets can be controlled
by defining 0 .. n filters with the CAN_RAW_FILTER socket option. The CAN filter structure is defined in include/linux/can.h: struct can_filter {
canid_t can_id;
canid_t can_mask;
}; A filter matches, when <received_can_id> & mask == can_id & mask
which is analogous to known CAN controllers hardware filter semantics.
The filter can be inverted in this semantic, when the CAN_INV_FILTER
bit is set in can_id element of the can_filter structure. In
contrast to CAN controller hardware filters the user may set 0 .. n
receive filters for each open socket separately: struct can_filter rfilter[2]; rfilter[0].can_id = 0x123;
rfilter[0].can_mask = CAN_SFF_MASK;
rfilter[1].can_id = 0x200;
rfilter[1].can_mask = 0x700; setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, &rfilter, sizeof(rfilter)); To disable the reception of CAN frames on the selected CAN_RAW socket: setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, NULL, 0); To set the filters to zero filters is quite obsolete as to not read
data causes the raw socket to discard the received CAN frames. But
having this 'send only' use-case we may remove the receive list in the
Kernel to save a little (really a very little!) CPU usage. 4.1.1.1 CAN filter usage optimisation The CAN filters are processed in per-device filter lists at CAN frame
reception time. To reduce the number of checks that need to be performed
while walking through the filter lists the CAN core provides an optimized
filter handling when the filter subscription focusses on a single CAN ID. For the possible 2048 SFF CAN identifiers the identifier is used as an index
to access the corresponding subscription list without any further checks.
For the 2^29 possible EFF CAN identifiers a 10 bit XOR folding is used as
hash function to retrieve the EFF table index. To benefit from the optimized filters for single CAN identifiers the
CAN_SFF_MASK or CAN_EFF_MASK have to be set into can_filter.mask together
with set CAN_EFF_FLAG and CAN_RTR_FLAG bits. A set CAN_EFF_FLAG bit in the
can_filter.mask makes clear that it matters whether a SFF or EFF CAN ID is
subscribed. E.g. in the example from above rfilter[0].can_id = 0x123;
rfilter[0].can_mask = CAN_SFF_MASK; both SFF frames with CAN ID 0x123 and EFF frames with 0xXXXXX123 can pass. To filter for only 0x123 (SFF) and 0x12345678 (EFF) CAN identifiers the
filter has to be defined in this way to benefit from the optimized filters: struct can_filter rfilter[2]; rfilter[0].can_id = 0x123;
rfilter[0].can_mask = (CAN_EFF_FLAG | CAN_RTR_FLAG | CAN_SFF_MASK);
rfilter[1].can_id = 0x12345678 | CAN_EFF_FLAG;
rfilter[1].can_mask = (CAN_EFF_FLAG | CAN_RTR_FLAG | CAN_EFF_MASK); setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, &rfilter, sizeof(rfilter)); 4.1.2 RAW socket option CAN_RAW_ERR_FILTER As described in chapter 3.4 the CAN interface driver can generate so
called Error Message Frames that can optionally be passed to the user
application in the same way as other CAN frames. The possible
errors are divided into different error classes that may be filtered
using the appropriate error mask. To register for every possible
error condition CAN_ERR_MASK can be used as value for the error mask.
The values for the error mask are defined in linux/can/error.h . can_err_mask_t err_mask = ( CAN_ERR_TX_TIMEOUT | CAN_ERR_BUSOFF ); setsockopt(s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_ERR_FILTER,
&err_mask, sizeof(err_mask));
Canbus ID filter and mask的更多相关文章
- 【转】汽车CAN总线
概述 CAN(Controller Area Network)总线协议是由 BOSCH 发明的一种基于消息广播模式的串行通信总线,它起初用于实现汽车内ECU之间可靠的通信,后因其简单实用可靠等特点,而 ...
- [CAN].CAN总线详解
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/cheatscat/article/details/82886889 CAN(Controller Area Network)总线协议是由 BOSCH ...
- PHP Filter
PHP filters are used to validate and sanitize external input. Validating data is determine if the da ...
- 用php自带的filter函数验证、过滤数据 -转载
PHP过滤器包含两种类型 Validation:用来验证验证项是否合法 Sanitization:用来格式化被验证的项目,因此它可能会修改验证项的值,将不合法的字符删除等. input_filters ...
- filter滤镜的使用
刚开始学css,开始遇到filter不懂什么意思后来到网上查了,觉得解释的很全面,就把它抠下来,以便自己经常来看看. CSS滤镜的使用方法:filter:filtername(parameters) ...
- 了不起的 “filter(NULL IS NOT NULL)”
经常会在执行计划中看到很奇怪的"FILTER"操作,然后看对应的执行信息是"filter(NULL IS NOT NULL)". 其实这是优化器非常聪明的“短 ...
- [代码解析]Mask R-CNN介绍与实现(转)
文章来源 DFann 版权声明:如果你觉得写的还可以,可以考虑打赏一下.转载请联系. https://blog.csdn.net/u011974639/article/details/78483779 ...
- csc_滤镜filter和实现透明的两种方式
有这样一个需求,给一个地图实现半透明效果. 使用css滤镜属性可以实现:filter. 下面是属性的所以值 filter: none | blur() | brightness() | contras ...
- vue循环遍历给div添加id
html部分 <div class="img-preview" v-for="(img,i) of list" :key="img.imageK ...
随机推荐
- HDU 2544 最短路 最短路问题
解题报告: 这题就是求两个单源点之间的最小距离,属于最短路问题,由于数据量很小,只有100,所以这题可以用弗洛伊德也可以用迪杰斯特拉,都可以过,但是用迪杰斯特拉会快一点,但用弗洛伊德的代码会稍短一点, ...
- 第10月第4天 Mac g++ sfml opendir
1. g++ OpenGL.cpp -I/Users/temp/Downloads/SFML-2.4.2-osx-clang/include -L/usr/local/lib -framework O ...
- ocky勒索软件恶意样本分析2
locky勒索软件恶意样本分析2 阿尔法实验室陈峰峰.胡进 前言 随着安全知识的普及,公民安全意识普遍提高了,恶意代码传播已经不局限于exe程序了,Locky敲诈者病毒就是其中之一,Locky敲诈者使 ...
- Java Service Wrapper将java程序设置为服务
有时候我们希望我们java写的程序作为服务注册到系统中,Java Service Wrapper(下面简称wrapper)是目前较为流行的将Java程序部署成Windows服务的解决方案, 本文将讨论 ...
- mysqlbinlog 查看mysql bin 日志 mysqlbinlog: unknown variable 'default-character-set=utf8'
mysqlbinlog mysql-bin.000036 | less 查询包含几个字段的语句: mysqlbinlog mysql-bin.000036| egrep '(201103061000 ...
- 公共语言运行库(CLR)开发系列课程(1):Pinvoke 简介 学习笔记
前言 让拖管代码对象和非托管对象协同工作的过程称为互用性(Interoperability),通常简称为 Interop. P/Invoke在托管代码与非托管代码交互式时产生一个事务(Transiti ...
- Python学习五|集合、布尔、字符串的一些特点
#集合本身就像无值的字典 list1 = set([1,2,3,4]) list2 = {1,2,3,4} print('list1 == list2?:',list1==list2)#list1 = ...
- 003_cd pushd popd三个命令的区别
一. It depends. In zsh you can configure cd to push the old directory on the directory stack automati ...
- andriod 自定义来电界面功能
由于近期所做一个项目需要做类似于“来电秀”的功能,所以上网搜索了一些相关资料,加上自己的一些想法,做了一个Demo.一下是我对该功能实现的一些想法,不对的地方欢迎各位指出.最后我会给出Demo 的源代 ...
- PHP-FPM 与 Nginx 的通信机制总结
PHP-FPM 介绍 CGI 协议与 FastCGI 协议 每种动态语言( PHP,Python 等)的代码文件需要通过对应的解析器才能被服务器识别,而 CGI 协议就是用来使解释器与服务器可以互 ...
