Vulkan Device Memory
1、通过下面的接口,可以获得显卡支持的所有内存类型;

MemoryType的类型如下:
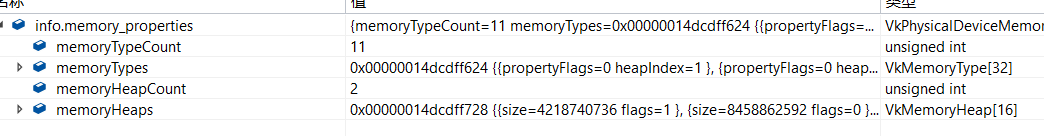
2、引用索引3对内存的描述
我们可以通过调用
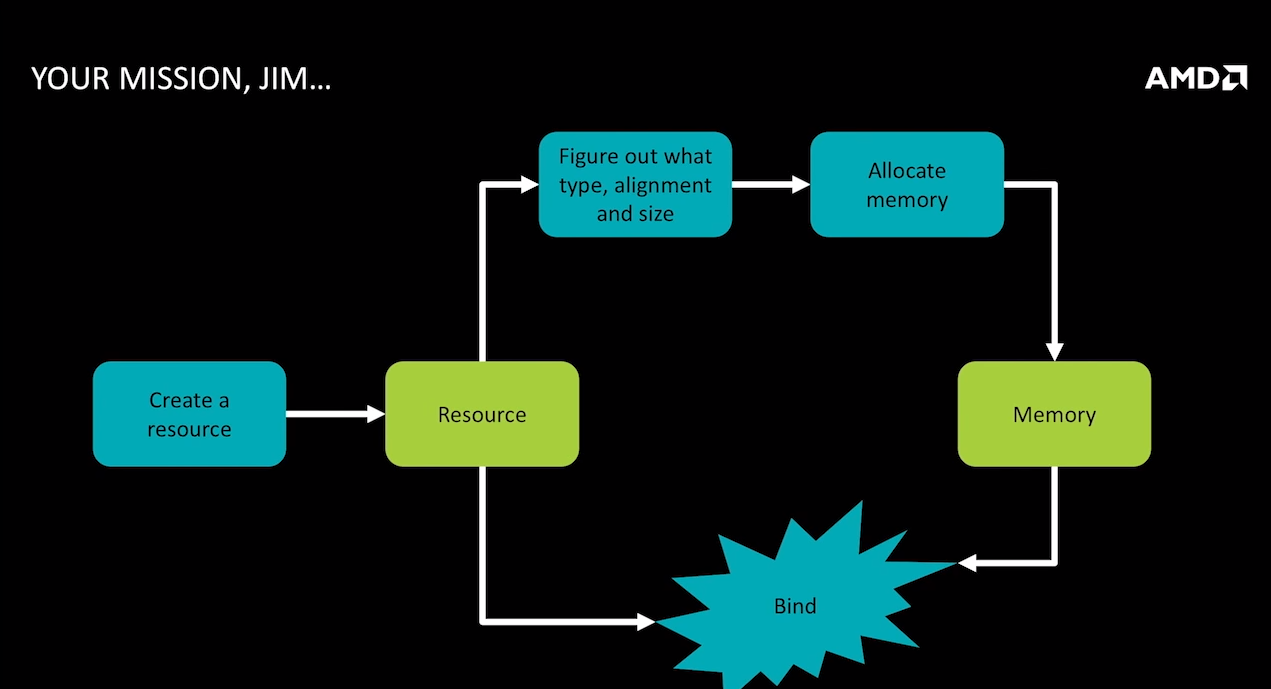
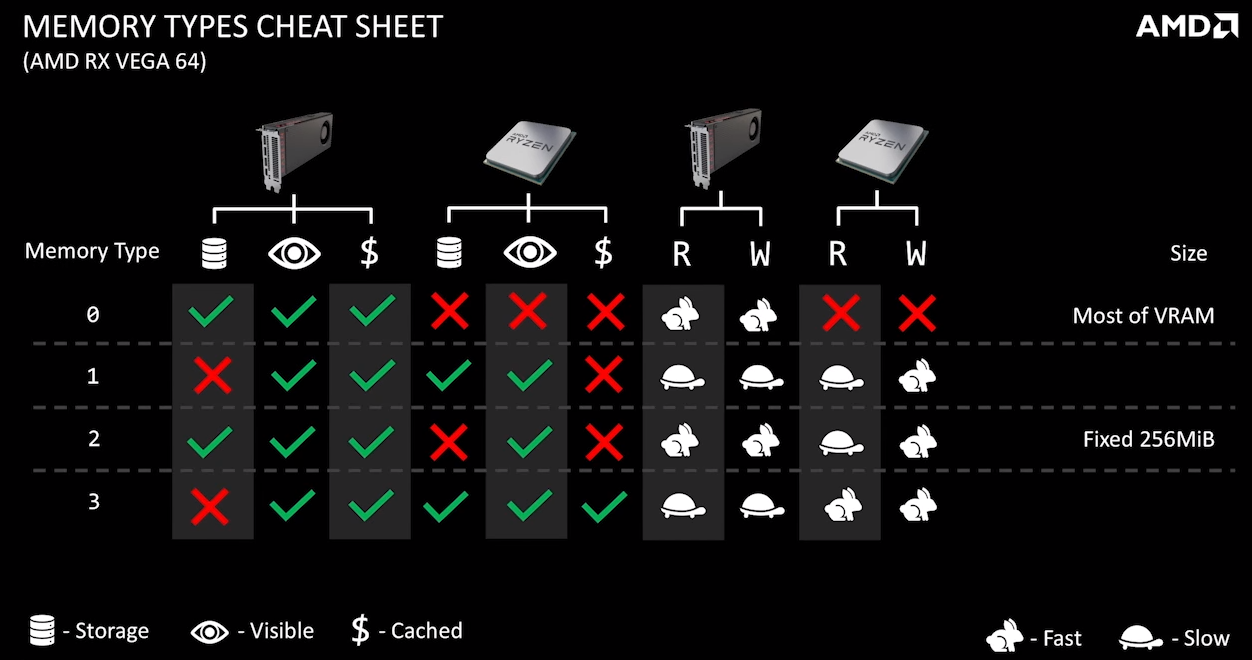
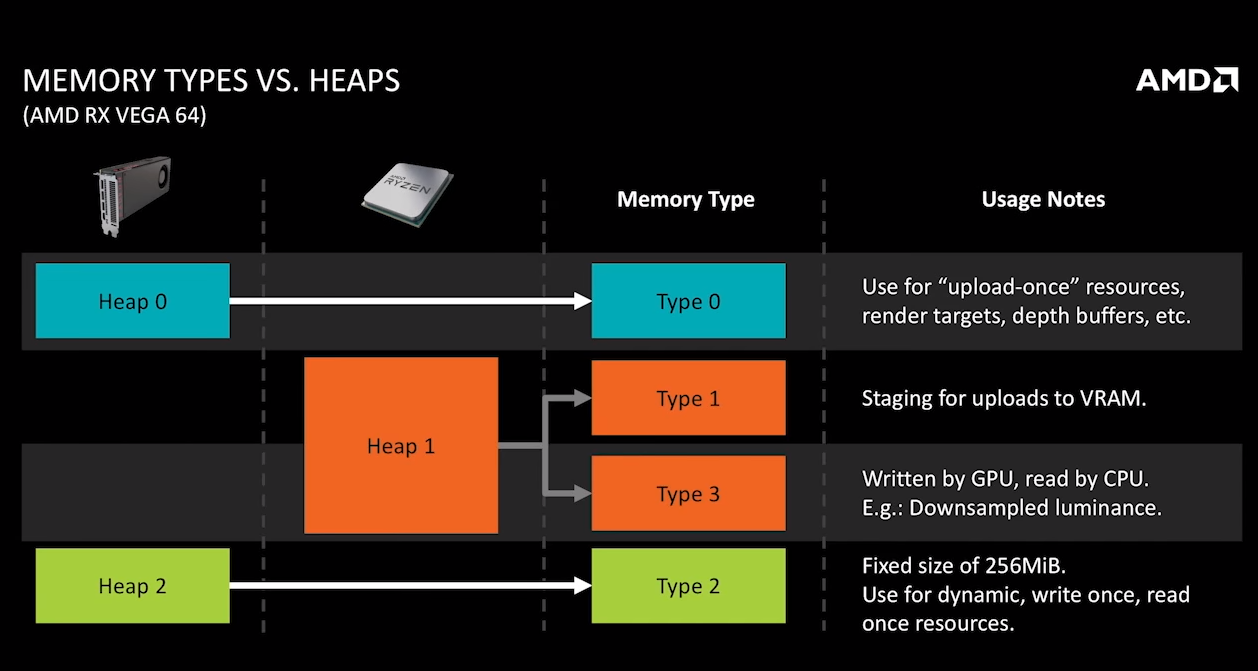
vkGetPhysicalDeviceMemoryProperties查询应用可使用的内存。它会返回请求大小的一个或多个内存堆,或者请求属性的一种或多种内存类型。每种内存类型来自于一个内存堆 - 因此,一个典例就是PC上的一个独立显卡将会有两个堆 - 一个是系统内存,另一个是GPU内存,并且他们各自拥有多种内存类型。内存类型有不同属性。一些内存可以被CPU访问或者不行、GPU和CPU访问一致、有缓存或者无缓存等等。通过调用vkAllocateMemory()可以分配内存,但它需要VkDevice句柄和描述结构体。HostVisibleMemory是可以通过Map方式来完成数据的更新的(vkMapMemory()/vkUnmapMemory())。GL使用者应该熟悉这个概念,但解释给D3D11的用户,vkMapMemory返回的指针可以被hold住被CPU写入当GPU正在使用它们。这些持久化的映射是完全正确的只要你遵守规则并且确定同步了内存访问。
3、VkMemeoryFlagBits
typedef enum VkMemoryHeapFlagBits {
VK_MEMORY_HEAP_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT = 0x00000001,
VK_MEMORY_HEAP_MULTI_INSTANCE_BIT = 0x00000002,
VK_MEMORY_HEAP_MULTI_INSTANCE_BIT_KHR = VK_MEMORY_HEAP_MULTI_INSTANCE_BIT,
VK_MEMORY_HEAP_FLAG_BITS_MAX_ENUM = 0x7FFFFFFF
} VkMemoryHeapFlagBits;
VK_MEMORY_HEAP_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT specifies that the heap corresponds to device local memory.
Device local memory may have different performance characteristics than host local memory,and may support different memory property flags.
• VK_MEMORY_HEAP_MULTI_INSTANCE_BIT specifies that in a logical device representing more than one
physical device, there is a per-physical device instance of the heap memory. By default, an allocation from such a heap will be replicated to each physical device’s instance of the heap.
4、MemoryTypeFlags
typedef enum VkMemoryPropertyFlagBits {
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT = 0x00000001,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT = 0x00000002,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT = 0x00000004,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT = 0x00000008,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_LAZILY_ALLOCATED_BIT = 0x00000010,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_PROTECTED_BIT = 0x00000020,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_COHERENT_BIT_AMD = 0x00000040,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_UNCACHED_BIT_AMD = 0x00000080,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_FLAG_BITS_MAX_ENUM = 0x7FFFFFFF
} VkMemoryPropertyFlagBits;
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT bit specifies that memory allocated with this type is the most efficient for device access. This property will be set if and only if the memory type belongs to a heap with the VK_MEMORY_HEAP_DEVICE_LOCAL_BIT set.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT bit specifies that memory allocated with this type can be mapped for host access using vkMapMemory.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT bit specifies that the host cache management commands vkFlushMappedMemoryRanges and vkInvalidateMappedMemoryRanges are not needed to flush host writes to the device or make device writes visible to the host, respectively.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT bit specifies that memory allocated with this type is cached on the host. Host memory accesses to uncached memory are slower than to cached memory,however uncached memory is always host coherent.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_LAZILY_ALLOCATED_BIT bit specifies that the memory type only allows device access to the memory. Memory types must not have both
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_LAZILY_ALLOCATED_BIT and VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT set.Additionally, the object’s backing memory may be provided by the implementation lazily as specified in Lazily Allocated Memory.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_PROTECTED_BIT bit specifies that the memory type only allows device access to the memory, and allows protected queue operations to access the memory. Memory types must not have VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_PROTECTED_BIT set and any of VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT set, or VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT set, or VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT set.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_COHERENT_BIT_AMD bit specifies that device accesses to allocations of this memory type are automatically made available and visible.
• VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_DEVICE_UNCACHED_BIT_AMD bit specifies that memory allocated with this type is not cached on the device. Uncached device memory is always device coherent.
5、Host memory is memory needed by the Vulkan implementation for non-device-visible storage.This memory may be used to store the implementation’s representation and state
of Vulkan objects.
6. Device memory is memory that is visible to the device — for example the contents of the image or buffer objects, which can be natively used by the device.
Device coherence is a useful property for certain debugging use cases (e.g. crash analysis, where performing separate coherence actions could mean values are not
reported correctly). However, device coherent accesses may be slower than equivalent accesses without device coherence, particularly if they are also device
uncached. For device uncached memory in particular, repeated accesses to the same or neighbouring memory locations over a short time period (e.g. within a
frame) may be slower than it would be for the equivalent cached memory type. As such, it’s generally inadvisable to use device coherent or device uncached memory
except when really needed.
7.



VulkanMemoryAllocator Github 提供了一个专门针对vulkan内存管理的库。
Reference
2、https://gpuopen.com/vulkan-device-memory/
5、Vulkanised 2018 - Memory Management in Vulkan
Vulkan Device Memory的更多相关文章
- [译]Vulkan教程(27)Image
[译]Vulkan教程(27)Image Images Introduction 入门 The geometry has been colored using per-vertex colors so ...
- [译]Vulkan教程(07)物理设备和队列家族
[译]Vulkan教程(07)物理设备和队列家族 Selecting a physical device 选择一个物理设备 After initializing the Vulkan library ...
- Vulkan SDK 之 Depth Buffer
深度缓冲是可选的,比如渲染一个3D的立方体的时候,就需要用到深度缓冲.Swapchain就算有多个images,此时深度缓冲区也只需要一个.vkCreateSwapchainKHR 会创建所有需要的i ...
- ARM: STM32F7: hardfault caused by unaligned memory access
ARM: STM32F7: hardfault caused by unaligned memory access ARM: STM32F7: 由未对齐的内存访问引起的hardfault异常 Info ...
- Android内存管理(4)*官方教程 含「高效内存的16条策略」 Managing Your App's Memory
Managing Your App's Memory In this document How Android Manages Memory Sharing Memory Allocating and ...
- OpenCL memory object 之 Global memory (2)
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2011/12/18/2291584.html 当我们用clCreateBuffer, clCreate ...
- OpenCL memory object 之 Global memory (1)
本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2011/12/17/2291239.html 这篇日志是学习AMD OpenCL文档时候的总结. ...
- OpenCL memory object 之 传输优化
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mikewolf2002/archive/2011/12/18/2291741.html 首先我们了解一些优化时候的术语及其定义: 1.defer ...
- GPU编程--Shared Memory(4)
GPU的内存按照所属对象大致分为三类:线程独有的.block共享的.全局共享的.细分的话,包含global, local, shared, constant, and texture memoey, ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu安装TTF字体
sudo mkdir /usr/share/fonts/ttf sudo cp ~/ttf/* /usr/share/fonts/ttf cd /usr/share/fonts/ttf sudo ch ...
- Derivative Pricing_1_Black
1. Stock Option wih divends 1.1 Task A 1.1.1 Calculate a ECO on a stock. /Ex-dividend dates in 3 and ...
- linux查漏补缺-Linux文件目录结构一览表
FHS 标准 FHS(Filesystem Hierarchy Standard),文件系统层次化标准,该标准规定了 Linux 系统中所有一级目录以及部分二级目录(/usr 和 /var)的用途. ...
- 如何查看python的notebook文件.ipynb
文章中的ipython notebook和jupyter notebook基本可以互换,不过使用ipython notebook会警告您要使用jupyter notebook.其他没有区别. ---- ...
- unity 骨骼 蒙皮
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44350205/article/details/100551233 https://www.jianshu.com/p/d5e2870eb3 ...
- MacBook OSX VMWare Fusion 11安装 Tools For Windows
需要加载对应客户机系统的安装文件,可以在/Applications/VMware\ Fusion.app/Contents/Library/isoimages文件夹下找到: 设置虚拟机的光驱: 在虚拟 ...
- 吴裕雄 Bootstrap 前端框架开发——Bootstrap 辅助类:清除浮动
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Bootstrap .clearfix 实例</title> &l ...
- SQL语言的四种类型
SQL语言共分为四大类:数据查询语言DQL,数据操纵语言DML,数据定义语言DDL,数据控制语言DCL. 1. 数据查询语言DQL 数据查询语言DQL基本结构是由SELECT子句,FROM子句,WHE ...
- is application failed to start because no Qt platform plugin could be initialized. Reinstalling the application may fix this problem
最近试着了解 c++,接触到了QT,写了一个测试程序,在开发环境下正常后移到非开发环境,报错 网上找资料说是少了platforms文件夹中的dll,把里面所有的dll复制到执行程序目录,还是提示,继续 ...
- 运行自己的 DaemonSet【转】
本节以 Prometheus Node Exporter 为例演示如何运行自己的 DaemonSet. Prometheus 是流行的系统监控方案,Node Exporter 是 Prometheus ...
