Architecture of SQLite
Introduction
This document describes the architecture of the SQLite library. The information here is useful to those who want to understand or modify the inner workings of SQLite.
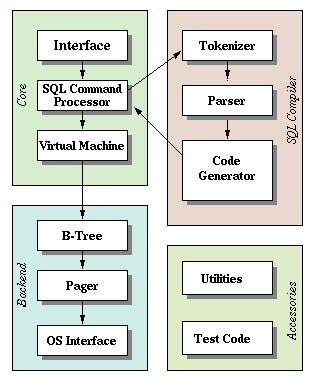
A nearby diagram shows the main components of SQLite and how they interoperate. The text below explains the roles of the various components.
Overview
SQLite works by compiling SQL text into bytecode, then running that bytecode using a virtual machine.
The sqlite3_prepare_v2() and related interfaces act as a compiler for converting SQL text into bytecode. The sqlite3_stmt object is a container for a single bytecode program using to implement a single SQL statement. The sqlite3_step() interface passes a bytecode program into the virtual machine, and runs the program until it either completes, or forms a row of result to be returned, or hits a fatal error, or is interrupted.
Interface
Much of the C-language Interface is found in source files main.c, legacy.c, and vdbeapi.c though some routines are scattered about in other files where they can have access to data structures with file scope. The sqlite3_get_table() routine is implemented in table.c. The sqlite3_mprintf() routine is found in printf.c. The sqlite3_complete() interface is in complete.c. The TCL Interface is implemented by tclsqlite.c.
To avoid name collisions, all external symbols in the SQLite library begin with the prefix sqlite3. Those symbols that are intended for external use (in other words, those symbols which form the API for SQLite) add an underscore, and thus begin with sqlite3_. Extension APIs sometimes add the extension name prior to the underscore; for example: sqlite3rbu_ or sqlite3session_.
Tokenizer
When a string containing SQL statements is to be evaluated it is first sent to the tokenizer. The tokenizer breaks the SQL text into tokens and hands those tokens one by one to the parser. The tokenizer is hand-coded in the file tokenize.c.
Note that in this design, the tokenizer calls the parser. People who are familiar with YACC and BISON may be accustomed to doing things the other way around — having the parser call the tokenizer. Having the tokenizer call the parser is better, though, because it can be made threadsafe and it runs faster.
Parser
The parser assigns meaning to tokens based on their context. The parser for SQLite is generated using the Lemon parser generator. Lemon does the same job as YACC/BISON, but it uses a different input syntax which is less error-prone. Lemon also generates a parser which is reentrant and thread-safe. And Lemon defines the concept of a non-terminal destructor so that it does not leak memory when syntax errors are encountered. The grammar file that drives Lemon and that defines the SQL language that SQLite understands is found in parse.y.
Because Lemon is a program not normally found on development machines, the complete source code to Lemon (just one C file) is included in the SQLite distribution in the "tool" subdirectory.
Code Generator
After the parser assembles tokens into a parse tree, the code generator runs to analyze the parser tree and generate bytecode that performs the work of the SQL statement. The prepared statement object is a container for this bytecode. There are many files in the code generator, including: attach.c, auth.c, build.c, delete.c, expr.c, insert.c, pragma.c, select.c, trigger.c, update.c, vacuum.c, where.c, wherecode.c, andwhereexpr.c. In these files is where most of the serious magic happens. expr.c handles code generation for expressions. where*.c handles code generation for WHERE clauses on SELECT, UPDATE and DELETE statements. The files attach.c, delete.c, insert.c, select.c, trigger.c update.c, and vacuum.c handle the code generation for SQL statements with the same names. (Each of these files calls routines in expr.c and where.c as necessary.) All other SQL statements are coded out of build.c. The auth.c file implements the functionality of sqlite3_set_authorizer().
The code generator, and especially the logic in where*.c and in select.c, is sometimes called the query planner. For any particular SQL statement, there might be hundreds, thousands, or millions of different algorithms to compute the answer. The query planner is an AI that strives to select the best algorithm from these millions of choices.
Bytecode Engine
The bytecode program created by the code generator is run by a virtual machine.
The virtual machine itself is entirely contained in a single source file vdbe.c. The vdbe.h header file defines an interface between the virtual machine and the rest of the SQLite library and vdbeInt.h which defines structures and interfaces that are private the virtual machine itself. Various other vdbe*.c files are helpers to the virtual machine. The vdbeaux.c file contains utilities used by the virtual machine and interface modules used by the rest of the library to construct VM programs. The vdbeapi.c file contains external interfaces to the virtual machine such as the sqlite3_bind_int() and sqlite3_step(). Individual values (strings, integer, floating point numbers, and BLOBs) are stored in an internal object named "Mem" which is implemented by vdbemem.c.
SQLite implements SQL functions using callbacks to C-language routines. Even the built-in SQL functions are implemented this way. Most of the built-in SQL functions (ex: abs(), count(), substr(), and so forth) can be found in func.c source file. Date and time conversion functions are found in date.c. Some functions such as coalesce() and typeof() are implemented as bytecode directly by the code generator.
B-Tree
An SQLite database is maintained on disk using a B-tree implementation found in the btree.c source file. A separate B-tree is used for each table and index in the database. All B-trees are stored in the same disk file. The file format details are stable and well-defined and are guaranteed to be compatible moving forward.
The interface to the B-tree subsystem and the rest of the SQLite library is defined by the header file btree.h.
Page Cache
The B-tree module requests information from the disk in fixed-size pages. The default page_size is 4096 bytes but can be any power of two between 512 and 65536 bytes. The page cache is responsible for reading, writing, and caching these pages. The page cache also provides the rollback and atomic commit abstraction and takes care of locking of the database file. The B-tree driver requests particular pages from the page cache and notifies the page cache when it wants to modify pages or commit or rollback changes. The page cache handles all the messy details of making sure the requests are handled quickly, safely, and efficiently.
The primary page cache implementation is in the pager.c file. WAL mode logic is in the separate wal.c. In-memory caching is implemented by thepcache.c and pcache1.c files. The interface between page cache subsystem and the rest of SQLite is defined by the header file pager.h.
OS Interface
In order to provide portability between across operating systems, SQLite uses abstract object called the VFS. Each VFS provides methods for opening, read, writing, and closing files on disk, and for other OS-specific task such as finding the current time, or obtaining randomness to initialize the built-in pseudo-random number generator. SQLite currently provides VFSes for unix (in the os_unix.c file) and Windows (in the os_win.c file).
Utilities
Memory allocation, caseless string comparison routines, portable text-to-number conversion routines, and other utilities are located in util.c. Symbol tables used by the parser are maintained by hash tables found in hash.c. The utf.c source file contains Unicode conversion subroutines. SQLite has its own private implementation of printf() (with some extensions) in printf.c and its own pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) in random.c.
Test Code
Files in the "src/" folder of the source tree whose names begin with test are for testing only and are not included in a standard build of the library.
https://sqlite.org/arch.html
Architecture of SQLite的更多相关文章
- SQLite剖析之体系结构
1.通过官方的SQLite架构文档,理清大体的系统层次:Architecture of SQLite 2.阅读SQLite Documentation中Technical/Design Documen ...
- 数据库-SQLite简介
SQLite是D.Richard Hipp用C语言编写的开源嵌入式数据库(轻型数据库). 由于资源占用少.性能良好和零管理成本,嵌入式数据库有了它的用武之地,像Android.iPhone都有内置的S ...
- 实现键值对存储(三):Kyoto Cabinet 和LevelDB的架构比較分析
译自 Emmanuel Goossaert (CodeCapsule.com) 在本文中,我将会逐组件地把Kyoto Cabinet 和 LevelDB的架构过一遍.目标和本系列第二部分讲的差点儿相 ...
- IT四大名著
标题耸人听闻,sorry. CPU.操作系统.编译器和数据库我都不会.我英语也不行,但我认识所有的字母.:-) 万一有人感兴趣呢?https://sqlite.org/doclist.htmlThe ...
- About SQLite
About SQLite See Also... Features When to use SQLite Frequently Asked Questions Well-known Users Boo ...
- sqlite学习1
Architecture  就像编译器一样,结构分为前端.虚拟机.后端 性能和限制(limitations) 使用B树来做indexes,用B+树来做table.和其他数据库一样 由于不需要鉴权.网 ...
- [Architecture Design] 跨平台架构设计
[Architecture Design] 跨平台架构设计 跨越平台 Productivity Future Vision 2011 在开始谈跨平台架构设计之前,请大家先看看上面这段影片,影片内容是微 ...
- [Architecture Design] 3-Layer基础架构
[Architecture Design] 3-Layer基础架构 三层式体系结构 只要是软件从业人员,不管是不是本科系出身的,相信对于三层式体系结构一定都不陌生.在三层式体系结构中,将软件开发所产出 ...
- SQLite入门与分析(一)---简介
写在前面:出于项目的需要,最近打算对SQLite的内核进行一个完整的剖析,在此希望和对SQLite有兴趣的一起交流.我知道,这是一个漫长的过程,就像曾经去读Linux内核一样,这个过程也将是辛苦的,但 ...
随机推荐
- Java 学习笔记 反射与迭代器
反射 使用反射获得类 Class cls = Class.forName("全类名") //包括包名 Class cls = xx.Class;//xx代表类名 使用反射获得构造方 ...
- Android开发过程中的坑及解决方法收录(五)
1. 导入依赖库出现错误 因为使用的sdk版本不同,使用下列代码强制使用最低版本,25.3.1就是我当前使用的版本号,根据自己的情况修改 configurations.all { resolution ...
- word转PDF,PDF转Image,使用oppenOffice注意事项等
最近在电子合同等项目中需要把word或者pdf转换成image,用到了openOffice把word转换pdf,以及把pdf转换成图片 感谢小伙伴张国清花费了三天时间来实现了此功能.下面我将把具体的步 ...
- 【Java每日一题】20170303
20170302问题解析请点击今日问题下方的“[Java每日一题]20170303”查看(问题解析在公众号首发,公众号ID:weknow619) package Mar2017; public cla ...
- mysql启动事件
1.查看时间是否开启 SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'event_scheduler' 若是查看结果为OFF,的话开启ON 2.设置事件开启 SET GLOBAL event_schedul ...
- ASP.NET MVC 使用Jquery异步操作JS代码
$(function () { var ajaxFormSubmit = function () { var $form = $(this); var options = { url: $form.a ...
- struts2框架-----Action
控制器Action Action对象是struts2框架的核心,每个URL映射到特定的Action,其提供处理来自用户的请求所需要的处理逻辑.Action有两个重要的功能,即将数据从请求传递到视图和协 ...
- python笔记之time模块
方法一:time.perf_counter() 说明:返回计时器的精准时间(系统的运行时间),包含整个系统的睡眠时间.由于返回值的基准点是未定义的,所以,只有连续调用的结果之间的差才是有效的. 代码示 ...
- 2018-08-13 Head First OO分析设计一书略读与例子中文化
注: 此笔记仅为个人学习此教程的布局和材料组织之用. 如有兴趣请自行详阅. 第一章是以吉他商店的存货系统作例子. 第二章设计有狗洞的门. 第三章对第二章基础上, 更改需求后对应设计. 第四章继续改进此 ...
- Salesforce 的 package.xml 文件
package.xml文件 在部署元数据(Metadata)的时候,package.xml是很关键的一个文件.此文件中定义了一个XML格式的列表,其中包含了各个元数据组件的定义. Metadata A ...
