keras系列︱迁移学习:利用InceptionV3进行fine-tuning及预测、完美案例(五)
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72982230
之前在博客《keras系列︱图像多分类训练与利用bottleneck features进行微调(三)》一直在倒腾VGG16的fine-tuning,然后因为其中的Flatten层一直没有真的实现最后一个模块的fine-tuning。
看到github上有一份InceptionV3的fine-tuning并且可以实现。我看到的keras微调的方式分为以下两种:
fine-tuning方式一:使用预训练网络的bottleneck特征
fine-tuning方式二:要调整权重,并训练
.
整个流程分为以下几个步骤:
- 一、定义函数以及加载模块
- 二、数据准备
- 三、 fine-tuning方式一:使用预训练网络的bottleneck特征
- 四、fine-tuning方式二:要调整权重,并训练
- 五、画图函数
- 六、预测
.
Keras系列:
1、keras系列︱Sequential与Model模型、keras基本结构功能(一)
2、keras系列︱Application中五款已训练模型、VGG16框架(Sequential式、Model式)解读(二)
3、keras系列︱图像多分类训练与利用bottleneck features进行微调(三)
4、keras系列︱人脸表情分类与识别:opencv人脸检测+Keras情绪分类(四)
5、keras系列︱迁移学习:利用InceptionV3进行fine-tuning及预测、完整案例(五)
一、定义函数以及加载模块
其中的get_nb_files函数为得到文件数量,个数。
其中,from keras.applications.inception_v3_matt import InceptionV3中,我有自己改,不然就会每次都从网上下载。
import os
import sys
import glob
import argparse
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras import __version__
# from keras.applications.inception_v3 import InceptionV3, preprocess_input
from keras.applications.inception_v3_matt import InceptionV3, preprocess_input
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Dense, GlobalAveragePooling2D
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.optimizers import SGD
def get_nb_files(directory):
"""Get number of files by searching directory recursively"""
if not os.path.exists(directory):
return 0
cnt = 0
for r, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for dr in dirs:
cnt += len(glob.glob(os.path.join(r, dr + "/*")))
return cnt
# get_nb_files('/home/ubuntu/keras/animal5/train').
二、数据准备
数据放在不同的文件夹下即可,很方便。本文实践的数据是我上次博客的数据《keras系列︱图像多分类训练与利用bottleneck features进行微调(三)》的第二节。
同时原作者在.flow_from_directory函数中,好像漏写了class_mode=’categorical’,一开始导致最后训练的时候,val_acc一直在0.2徘徊。
# 数据准备
IM_WIDTH, IM_HEIGHT = 299, 299 #InceptionV3指定的图片尺寸
FC_SIZE = 1024 # 全连接层的节点个数
NB_IV3_LAYERS_TO_FREEZE = 172 # 冻结层的数量
train_dir = '/home/ubuntu/keras/animal5/train' # 训练集数据
val_dir = '/home/ubuntu/keras/animal5/validation' # 验证集数据
nb_classes= 5
nb_epoch = 3
batch_size = 16
nb_train_samples = get_nb_files(train_dir) # 训练样本个数
nb_classes = len(glob.glob(train_dir + "/*")) # 分类数
nb_val_samples = get_nb_files(val_dir) #验证集样本个数
nb_epoch = int(nb_epoch) # epoch数量
batch_size = int(batch_size)
# 图片生成器
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input,
rotation_range=30,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True
)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input,
rotation_range=30,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True
)
# 训练数据与测试数据
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(IM_WIDTH, IM_HEIGHT),
batch_size=batch_size,class_mode='categorical')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
val_dir,
target_size=(IM_WIDTH, IM_HEIGHT),
batch_size=batch_size,class_mode='categorical')
.
三、 fine-tuning方式一:使用预训练网络的bottleneck特征
# 添加新层
def add_new_last_layer(base_model, nb_classes):
"""
添加最后的层
输入
base_model和分类数量
输出
新的keras的model
"""
x = base_model.output
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = Dense(FC_SIZE, activation='relu')(x) #new FC layer, random init
predictions = Dense(nb_classes, activation='softmax')(x) #new softmax layer
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=predictions)
return model
# 冻上base_model所有层,这样就可以正确获得bottleneck特征
def setup_to_transfer_learn(model, base_model):
"""Freeze all layers and compile the model"""
for layer in base_model.layers:
layer.trainable = False
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 定义网络框架
base_model = InceptionV3(weights='imagenet', include_top=False) # 预先要下载no_top模型
model = add_new_last_layer(base_model, nb_classes) # 从基本no_top模型上添加新层
setup_to_transfer_learn(model, base_model) # 冻结base_model所有层
# 模式一训练
history_tl = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
nb_epoch=nb_epoch,
samples_per_epoch=nb_train_samples,
validation_data=validation_generator,
nb_val_samples=nb_val_samples,
class_weight='auto')训练时候报错:
main:15: UserWarning: Update your Model call to the Keras 2 API: Model(outputs=Tensor("de..., inputs=Tensor("in...)
没有关系。
有过这样的报错 :
Epoch 1/3
25/25 [==============================] - 37s - loss: 12.6398 - acc: 0.1900 - val_loss: 12.8990 - val_acc: 0.1997
Epoch 2/3
25/25 [==============================] - 34s - loss: 12.8945 - acc: 0.2000 - val_loss: 12.8718 - val_acc: 0.2014
Epoch 3/3
25/25 [==============================] - 34s - loss: 12.8945 - acc: 0.2000 - val_loss: 12.8877 - val_acc: 0.2004
一般是我在设置错了分类时候会出现的情况
出错在:之前少加了class_mode
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size=(IM_WIDTH, IM_HEIGHT),
batch_size=batch_size,class_mode=’categorical’)
.
四、fine-tuning方式二:要调整权重,并训练
那么fine-tuning模式一与模式二区别在于,模式一冻结了base_model所有层,只有新添加的层才能训练,调整权重。但是模式二,在base_model内开放了一部分。
类似的可以看到官方VGG16的两种模式的区别: 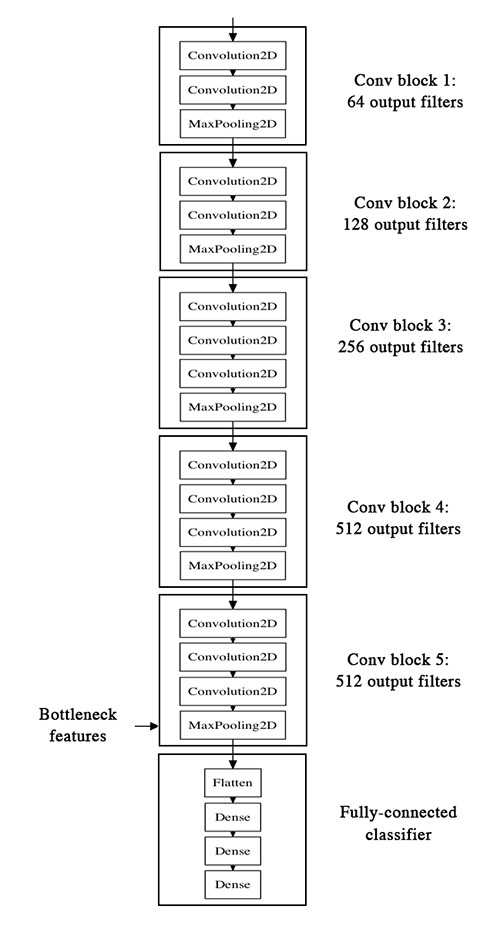
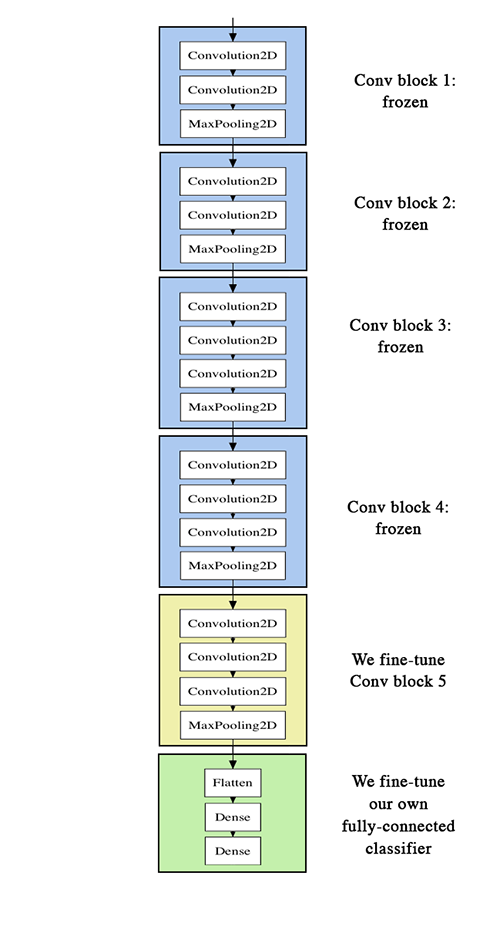
第一张图就是模式一,冻结了base_model层;第二张图就是模式二,base_model一些层都开放了。
# 冻上NB_IV3_LAYERS之前的层
def setup_to_finetune(model):
"""Freeze the bottom NB_IV3_LAYERS and retrain the remaining top layers.
note: NB_IV3_LAYERS corresponds to the top 2 inception blocks in the inceptionv3 arch
Args:
model: keras model
"""
for layer in model.layers[:NB_IV3_LAYERS_TO_FREEZE]:
layer.trainable = False
for layer in model.layers[NB_IV3_LAYERS_TO_FREEZE:]:
layer.trainable = True
model.compile(optimizer=SGD(lr=0.0001, momentum=0.9), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 设置网络结构
setup_to_finetune(model)
# 模式二训练
history_ft = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
samples_per_epoch=nb_train_samples,
nb_epoch=nb_epoch,
validation_data=validation_generator,
nb_val_samples=nb_val_samples,
class_weight='auto')
# 模型保存
model.save(args.output_model_file)
# 正确
Epoch 1/3
25/25 [==============================] - 38s - loss: 0.0589 - acc: 0.9850 - val_loss: 0.0084 - val_acc: 0.9986
Epoch 2/3
25/25 [==============================] - 37s - loss: 0.0196 - acc: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.0150 - val_acc: 0.9965
Epoch 3/3
25/25 [==============================] - 37s - loss: 0.0349 - acc: 0.9875 - val_loss: 0.0101 - val_acc: 0.9979
.
五、画图函数
# 画图
def plot_training(history):
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc))
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'r.')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'r')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'r.')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'r-')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.show()
# 训练的acc_loss图
plot_training(history_ft).
六、预测
# 定义层
import sys
import argparse
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import requests
from io import BytesIO
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.applications.inception_v3 import preprocess_input
# 狂阶图片指定尺寸
target_size = (229, 229) #fixed size for InceptionV3 architecture
# 预测函数
# 输入:model,图片,目标尺寸
# 输出:预测predict
def predict(model, img, target_size):
"""Run model prediction on image
Args:
model: keras model
img: PIL format image
target_size: (w,h) tuple
Returns:
list of predicted labels and their probabilities
"""
if img.size != target_size:
img = img.resize(target_size)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)
x = preprocess_input(x)
preds = model.predict(x)
return preds[0]
# 画图函数
# 预测之后画图,这里默认是猫狗,当然可以修改label
labels = ("cat", "dog")
def plot_preds(image, preds,labels):
"""Displays image and the top-n predicted probabilities in a bar graph
Args:
image: PIL image
preds: list of predicted labels and their probabilities
"""
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure()
plt.barh([0, 1], preds, alpha=0.5)
plt.yticks([0, 1], labels)
plt.xlabel('Probability')
plt.xlim(0,1.01)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 载入模型
model = load_model(args.model)
# 本地图片
img = Image.open(image)
preds = predict(model, img, target_size)
plot_preds(img, preds)
# 图片URL
response = requests.get(image_url)
img = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
preds = predict(model, img, target_size)
plot_preds(img, preds)延伸一:fine-tuning时如何加载No_top的权重
场景:你要用自己的训练完的模型,作为下一个模型初始化的权重,譬如inceptionv3中的no_top版本。
如果你需要加载权重到不同的网络结构(有些层一样)中,例如fine-tune或transfer-learning,你可以通过层名字来加载模型:
model.load_weights(‘my_model_weights.h5’, by_name=True)
例如:
假如原模型为:
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(2, input_dim=3, name="dense_1"))
model.add(Dense(3, name="dense_2"))
...
model.save_weights(fname)# new model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(2, input_dim=3, name="dense_1")) # will be loaded
model.add(Dense(10, name="new_dense")) # will not be loaded
# load weights from first model; will only affect the first layer, dense_1.
model.load_weights(fname, by_name=True)keras系列︱迁移学习:利用InceptionV3进行fine-tuning及预测、完美案例(五)的更多相关文章
- 深度学习应用系列(二) | 如何使用keras进行迁移学习,以训练和识别自己的图片集
本文的keras后台为tensorflow,介绍如何利用预编译的模型进行迁移学习,以训练和识别自己的图片集. 官网 https://keras.io/applications/ 已经介绍了各个基于Im ...
- keras系列︱图像多分类训练与利用bottleneck features进行微调(三)
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72861152 中文文档:http://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/ ...
- keras系列︱Sequential与Model模型、keras基本结构功能(一)
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72857454 中文文档:http://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/ ...
- keras系列︱人脸表情分类与识别:opencv人脸检测+Keras情绪分类(四)
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72885715 人脸识别热门,表情识别更加.但是表情识别很难,因为人脸的微表情很多,本节 ...
- keras系列︱Application中五款已训练模型、VGG16框架(Sequential式、Model式)解读(二)
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72859145 中文文档:http://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/ ...
- 【深度学习系列】迁移学习Transfer Learning
在前面的文章中,我们通常是拿到一个任务,譬如图像分类.识别等,搜集好数据后就开始直接用模型进行训练,但是现实情况中,由于设备的局限性.时间的紧迫性等导致我们无法从头开始训练,迭代一两百万次来收敛模型, ...
- 基于深度学习和迁移学习的识花实践——利用 VGG16 的深度网络结构中的五轮卷积网络层和池化层,对每张图片得到一个 4096 维的特征向量,然后我们直接用这个特征向量替代原来的图片,再加若干层全连接的神经网络,对花朵数据集进行训练(属于模型迁移)
基于深度学习和迁移学习的识花实践(转) 深度学习是人工智能领域近年来最火热的话题之一,但是对于个人来说,以往想要玩转深度学习除了要具备高超的编程技巧,还需要有海量的数据和强劲的硬件.不过 Tens ...
- 实战 迁移学习 VGG19、ResNet50、InceptionV3 实践 猫狗大战 问题
实战 迁移学习 VGG19.ResNet50.InceptionV3 实践 猫狗大战 问题 参考博客:::https://blog.csdn.net/pengdali/article/detail ...
- keras系列︱利用fit_generator最小化显存占用比率/数据Batch化
本文主要参考两篇文献: 1.<深度学习theano/tensorflow多显卡多人使用问题集> 2.基于双向LSTM和迁移学习的seq2seq核心实体识别 运行机器学习算法时,很多人一开始 ...
随机推荐
- Objective-C 资源收藏
日志 https://github.com/robbiehanson/CocoaLumberjack 反汇编 otool nm http://stackoverflow.com/questi ...
- 实战Apache+Tomcat集群和负载均衡
实战Apache+Tomcat集群和负载均衡 目录 1. 什么是J2EE集群... 3 1.1. 序言... 3 1.2. 基本术语... 3 伸缩性(Scalability): ...
- django -- 对行的更新只有在save调用后才会入库
python3 manage.py shell Python 3.6.2 (v3.6.2:5fd33b5926, Jul 16 2017, 20:11:06) [GCC 4.2.1 (Apple In ...
- Maven .m2\repository\jdk\tools\1.7 missing
在pom.xml文件中加入: <dependency> <groupId>jdk.tools</groupId> <artifactId>jdk.too ...
- MySql(十):MySQL性能调优——MySQL Server性能优化
本章主要通过针对MySQL Server( mysqld)相关实现机制的分析,得到一些相应的优化建议.主要涉及MySQL的安装以及相关参数设置的优化,但不包括mysqld之外的比如存储引擎相关的参数优 ...
- 如何分析Java程序中的死锁
使用下面方式:产生java的Thread Dump信息 windows平台上:ctrl+break 或者 ctrl+(fn+b)键 Linux平台上:kill -3 pid (查找程序进程id -&g ...
- JS两日期相减
JS两日期相减,主要用到下面两个方法 dateObject.setFullYear(year,month,day) 方法 stringObject.split(separator) 方法 functi ...
- Android基础知识之API等级介绍
原文:http://android.eoe.cn/topic/android_sdk :可以让开发者通过一个表示API级别的整数来描述程序在android平台上的兼容性,系统会将与系统本身提供的API ...
- go 从入门到精通(二)基本数据类型和操作符
一.文件名&关键字&标识符 所有go源码都是以.go结尾 标识符以字母或下划线开头,大小写敏感 下划线_是特殊标识符,用户忽略结果 保留关键字 导入包时可以设置别名 下面是保留关键字: ...
- android:3D垂直翻转动画-FlipAnimation
需求 对ImageView进行相似于翻纸牌的动画 解决 各种Animator的组合 第一步动画: 动画代码文件1,card_flip_left_out.xml <? xml version=&q ...

