Flink – window operator
参考,
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/05/25/flink-internals-window-mechanism/
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/06/06/flink-internals-session-window/
WindowOperator
window operator通过WindowAssigner和Trigger来实现它的逻辑
当一个element到达时,通过KeySelector先assign一个key,并且通过WindowAssigner assign若干个windows,这样这个element会被放入若干个pane
一个pane会存放所有相同key和相同window的elements
/**
* An operator that implements the logic for windowing based on a {@link WindowAssigner} and
* {@link Trigger}.
*
* <p>
* When an element arrives it gets assigned a key using a {@link KeySelector} and it gets
* assigned to zero or more windows using a {@link WindowAssigner}. Based on this, the element
* is put into panes. A pane is the bucket of elements that have the same key and same
* {@code Window}. An element can be in multiple panes if it was assigned to multiple windows by the
* {@code WindowAssigner}.
*
* <p>
* Each pane gets its own instance of the provided {@code Trigger}. This trigger determines when
* the contents of the pane should be processed to emit results. When a trigger fires,
* the given {@link InternalWindowFunction} is invoked to produce the results that are emitted for
* the pane to which the {@code Trigger} belongs.
*
* @param <K> The type of key returned by the {@code KeySelector}.
* @param <IN> The type of the incoming elements.
* @param <OUT> The type of elements emitted by the {@code InternalWindowFunction}.
* @param <W> The type of {@code Window} that the {@code WindowAssigner} assigns.
*/
@Internal
public class WindowOperator<K, IN, ACC, OUT, W extends Window>
extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, InternalWindowFunction<ACC, OUT, K, W>>
implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT>, Triggerable, InputTypeConfigurable { // ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Configuration values and user functions
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ protected final WindowAssigner<? super IN, W> windowAssigner; protected final KeySelector<IN, K> keySelector; protected final Trigger<? super IN, ? super W> trigger; protected final StateDescriptor<? extends AppendingState<IN, ACC>, ?> windowStateDescriptor; /**
* The allowed lateness for elements. This is used for:
* <ul>
* <li>Deciding if an element should be dropped from a window due to lateness.
* <li>Clearing the state of a window if the system time passes the
* {@code window.maxTimestamp + allowedLateness} landmark.
* </ul>
*/
protected final long allowedLateness; //允许late多久,即当watermark已经触发后 /**
* To keep track of the current watermark so that we can immediately fire if a trigger
* registers an event time callback for a timestamp that lies in the past.
*/
protected transient long currentWatermark = Long.MIN_VALUE; protected transient Context context = new Context(null, null); //Trigger Context protected transient WindowAssigner.WindowAssignerContext windowAssignerContext; //只为获取getCurrentProcessingTime // ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// State that needs to be checkpointed
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ /**
* Processing time timers that are currently in-flight.
*/
protected transient PriorityQueue<Timer<K, W>> processingTimeTimersQueue; //Timer用于存储timestamp,key,window, queue按时间排序 /**
* Current waiting watermark callbacks.
*/
protected transient Set<Timer<K, W>> watermarkTimers;
protected transient PriorityQueue<Timer<K, W>> watermarkTimersQueue; // protected transient Map<K, MergingWindowSet<W>> mergingWindowsByKey; //用于记录merge后的stateWindow和window的对应关系
对于window operator而已,最关键的是WindowAssigner和Trigger
WindowAssigner
WindowAssigner,用于指定一个tuple应该被分配到那些windows去
借用个图,可以看出有多少种WindowAssigner
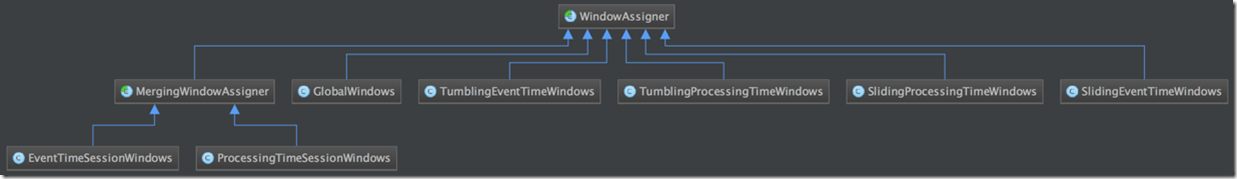
对于WindowAssigner,最关键的接口是,assignWindows
为一个element,分配一组windows, Collection<W>
@PublicEvolving
public abstract class WindowAssigner<T, W extends Window> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /**
* Returns a {@code Collection} of windows that should be assigned to the element.
*
* @param element The element to which windows should be assigned.
* @param timestamp The timestamp of the element.
* @param context The {@link WindowAssignerContext} in which the assigner operates.
*/
public abstract Collection<W> assignWindows(T element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context); /**
* Returns the default trigger associated with this {@code WindowAssigner}.
*/
public abstract Trigger<T, W> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env); /**
* Returns a {@link TypeSerializer} for serializing windows that are assigned by
* this {@code WindowAssigner}.
*/
public abstract TypeSerializer<W> getWindowSerializer(ExecutionConfig executionConfig);
实际看下,具体WindowAssigner的实现
public class TumblingProcessingTimeWindows extends WindowAssigner<Object, TimeWindow> {
@Override
public Collection<TimeWindow> assignWindows(Object element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context) {
final long now = context.getCurrentProcessingTime();
long start = now - (now % size);
return Collections.singletonList(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); //很简单,分配一个TimeWindow
}
@Override
public Trigger<Object, TimeWindow> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env) {
return ProcessingTimeTrigger.create(); //默认给出的是ProcessingTimeTrigger,如其名
}
public class SlidingEventTimeWindows extends WindowAssigner<Object, TimeWindow> {
private final long size;
private final long slide;
@Override
public Collection<TimeWindow> assignWindows(Object element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context) {
if (timestamp > Long.MIN_VALUE) {
List<TimeWindow> windows = new ArrayList<>((int) (size / slide));
long lastStart = timestamp - timestamp % slide;
for (long start = lastStart;
start > timestamp - size;
start -= slide) {
windows.add(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); //可以看到这里会assign多个TimeWindow,因为是slide
}
return windows;
} else {
}
}
@Override
public Trigger<Object, TimeWindow> getDefaultTrigger(StreamExecutionEnvironment env) {
return EventTimeTrigger.create();
}
Trigger, Evictor
下面看看3个主要的接口,分别触发,onElement,onEventTime,onProcessingTime
processElement
处理element到达的逻辑,触发onElement
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows( //通过WindowAssigner为element分配一系列windows
element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext);
final K key = (K) getStateBackend().getCurrentKey();
if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) { //如果是MergingWindow
//.......
} else { //如果是普通window
for (W window: elementWindows) {
// drop if the window is already late
if (isLate(window)) { //late data的处理,默认是丢弃
continue;
}
AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState = getPartitionedState( //从backend中取出该window的状态,就是buffer的element
window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);
windowState.add(element.getValue()); //把当前的element加入buffer state
context.key = key;
context.window = window; //context的设计相当tricky和晦涩
TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onElement(element); //触发onElment,得到triggerResult
if (triggerResult.isFire()) { //对triggerResult做各种处理
ACC contents = windowState.get();
if (contents == null) {
continue;
}
fire(window, contents); //如果fire,真正去计算窗口中的elements
}
if (triggerResult.isPurge()) {
cleanup(window, windowState, null); //purge,即去cleanup elements
} else {
registerCleanupTimer(window);
}
}
}
}
判断是否是late data的逻辑
protected boolean isLate(W window) {
return (windowAssigner.isEventTime() && (cleanupTime(window) <= currentWatermark));
}
private long cleanupTime(W window) {
long cleanupTime = window.maxTimestamp() + allowedLateness; //allowedLateness;
return cleanupTime >= window.maxTimestamp() ? cleanupTime : Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
fire逻辑
private void fire(W window, ACC contents) throws Exception {
timestampedCollector.setAbsoluteTimestamp(window.maxTimestamp());
userFunction.apply(context.key, context.window, contents, timestampedCollector);
}
processWatermark
处理watermark,onEvent触发
@Override
public void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception {
boolean fire;
do {
Timer<K, W> timer = watermarkTimersQueue.peek(); //这叫watermarkTimersQueue,是否有些歧义,叫eventTimerQueue更好理解些
if (timer != null && timer.timestamp <= mark.getTimestamp()) {
fire = true; watermarkTimers.remove(timer);
watermarkTimersQueue.remove(); context.key = timer.key;
context.window = timer.window;
setKeyContext(timer.key); //stateBackend.setCurrentKey(key); AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState;
MergingWindowSet<W> mergingWindows = null; if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) { //MergingWindow
mergingWindows = getMergingWindowSet();
W stateWindow = mergingWindows.getStateWindow(context.window);
if (stateWindow == null) {
// then the window is already purged and this is a cleanup
// timer set due to allowed lateness that has nothing to clean,
// so it is safe to just ignore
continue;
}
windowState = getPartitionedState(stateWindow, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);
} else { //普通window
windowState = getPartitionedState(context.window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor); //取得window的state
} ACC contents = windowState.get();
if (contents == null) {
// if we have no state, there is nothing to do
continue;
} TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onEventTime(timer.timestamp); //触发onEvent
if (triggerResult.isFire()) {
fire(context.window, contents);
} if (triggerResult.isPurge() || (windowAssigner.isEventTime() && isCleanupTime(context.window, timer.timestamp))) {
cleanup(context.window, windowState, mergingWindows);
} } else {
fire = false;
}
} while (fire); //如果fire为true,继续看下个waterMarkTimer是否需要fire output.emitWatermark(mark); //把waterMark传递下去 this.currentWatermark = mark.getTimestamp(); //更新currentWaterMark
}
trigger
首先,这个函数的命名有问题,为何和前面的process…不匹配
这个是用来触发onProcessingTime,这个需要依赖系统时间的定时器来触发,逻辑和processWatermark基本等同,只是触发条件不一样
@Override
public void trigger(long time) throws Exception {
boolean fire; //Remove information about the triggering task
processingTimeTimerFutures.remove(time);
processingTimeTimerTimestamps.remove(time, processingTimeTimerTimestamps.count(time)); do {
Timer<K, W> timer = processingTimeTimersQueue.peek();
if (timer != null && timer.timestamp <= time) {
fire = true; processingTimeTimers.remove(timer);
processingTimeTimersQueue.remove(); context.key = timer.key;
context.window = timer.window;
setKeyContext(timer.key); AppendingState<IN, ACC> windowState;
MergingWindowSet<W> mergingWindows = null; if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) {
mergingWindows = getMergingWindowSet();
W stateWindow = mergingWindows.getStateWindow(context.window);
if (stateWindow == null) {
// then the window is already purged and this is a cleanup
// timer set due to allowed lateness that has nothing to clean,
// so it is safe to just ignore
continue;
}
windowState = getPartitionedState(stateWindow, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);
} else {
windowState = getPartitionedState(context.window, windowSerializer, windowStateDescriptor);
} ACC contents = windowState.get();
if (contents == null) {
// if we have no state, there is nothing to do
continue;
} TriggerResult triggerResult = context.onProcessingTime(timer.timestamp);
if (triggerResult.isFire()) {
fire(context.window, contents);
} if (triggerResult.isPurge() || (!windowAssigner.isEventTime() && isCleanupTime(context.window, timer.timestamp))) {
cleanup(context.window, windowState, mergingWindows);
} } else {
fire = false;
}
} while (fire);
}
EvictingWindowOperator
Evicting对于WindowOperator而言,就是多了Evictor
private void fire(W window, Iterable<StreamRecord<IN>> contents) throws Exception {
timestampedCollector.setAbsoluteTimestamp(window.maxTimestamp());
// Work around type system restrictions...
int toEvict = evictor.evict((Iterable) contents, Iterables.size(contents), context.window); //执行evict
FluentIterable<IN> projectedContents = FluentIterable
.from(contents)
.skip(toEvict)
.transform(new Function<StreamRecord<IN>, IN>() {
@Override
public IN apply(StreamRecord<IN> input) {
return input.getValue();
}
});
userFunction.apply(context.key, context.window, projectedContents, timestampedCollector);
}
关键的逻辑就是在fire的时候,在apply function之前,会先remove需要evict的elements
Flink – window operator的更多相关文章
- Apache Flink - Window
Window: 在Streaming中,数据是无限且连续的,我们不可能等所有数据都到才进行处理,我们可以来一个就处理一下,但是有时我们需要做一些聚合类的处理,例如:在过去的1分钟内有多少用户点击了我们 ...
- 一文搞懂Flink Window机制
Windows是处理无线数据流的核心,它将流分割成有限大小的桶(buckets),并在其上执行各种计算. 窗口化的Flink程序的结构通常如下,有分组流(keyed streams)和无分组流(non ...
- 【翻译】Flink window
本文翻译自flink官网:https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-release-1.9/dev/stream/operators/window ...
- flink window的early计算
Tumbing Windows:滚动窗口,窗口之间时间点不重叠.它是按照固定的时间,或固定的事件个数划分的,分别可以叫做滚动时间窗口和滚动事件窗口.Sliding Windows:滑动窗口,窗口之间时 ...
- flink Window的Timestamps/Watermarks和allowedLateness的区别
Watermartks是通过additional的时间戳来控制窗口激活的时间,allowedLateness来控制窗口的销毁时间. 注: 因为此特性包括官方文档在1.3-1.5版本均未做改变,所以 ...
- Flink window机制
此文已由作者岳猛授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. 问题 window是解决流计算中的什么问题? 怎么划分window?有哪几种window?window与时间属 ...
- flink window实例分析
window是处理数据的核心.按需选择你需要的窗口类型后,它会将传入的原始数据流切分成多个buckets,所有计算都在window中进行. flink本身提供的实例程序TopSpeedWindowin ...
- Flink Window窗口机制
总览 Window 是flink处理无限流的核心,Windows将流拆分为有限大小的"桶",我们可以在其上应用计算. Flink 认为 Batch 是 Streaming 的一个特 ...
- Flink Window&Time 原理
Flink 中可以使用一套 API 完成对有界数据集以及无界数据的统一处理,而无界数据集的处理一般会伴随着对某些固定时间间隔的数据聚合处理.比如:每五分钟统计一次系统活跃用户.每十秒更新热搜榜单等等 ...
随机推荐
- Firefox下载自动保存
profile.setPreference("browser.download.folderList", 2); profile.setPreference("brows ...
- Pycharm用Ctrl+鼠标滚轮调节代码字体大小
File --> Setting --> Editor --> General --> 勾选Change font size (zoom) with Ctrl+Mouse W ...
- SQL IN ANY ,(all any) 区别
EXITS 和 IN 的区别: 从效率来看: 1) select * from T1 where exists(select 1 from T2 where T1.a=T2.a) ; T1数据量小而T ...
- MyBatis持久层框架使用总结
MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis . 2 ...
- Pyqt adb 获取Android手机屏幕
adb的全称为Android Debug Bridge,就是起到调试桥的作用.adb的工作方式比较特殊,采用监听Socket TCP 5554等端口的方式让IDE和Qemu通讯,默认情况下adb会da ...
- Redis相关
Redis 持久化 1 why 数据需要持久化,当内存数据库使用的情况 防止缓存失效时候的雪崩效应 2 how 两种方式,快照和日志(aof)方式,各有优缺点. Redis的缓存失效策略 1 what ...
- DS28E01芯片解密DS28E01-100单片机解密多少钱?
DS28E01芯片解密DS28E01-100单片机解密多少钱? DS28E01-100将1024位EEPROM与符合ISO/IEC 10118-3安全散列算法(SHA-1)的质询响应安全认证结合在一起 ...
- python安装库
首先确保安装了pip,并且pip也加入了系统path路径: pip下载:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pip#downloads 下载Python对应的包:(http:// ...
- 浏览器-03 WebKit 渲染1
WebKit是一个渲染引擎,而不是一个浏览器; DOM是对HTML或者XML等文档的一种结构化表示方法,通过这种方式,用户可以通过提供标准的接口来访问页面中的任何元素的相关属性,并可对DOM进行相应的 ...
- WPF,textBox默认是失去焦点绑定值才改变,怎么做到输入框值一改变就改变绑定值. Text="{Binding EvaluationContent,UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"
如果用户提出只要textBox1的文本改变slider1的滑块立刻响应,那就设置Binding的UpdateSourceTrigger属性.它是一个UpdateSourceTrigger类型枚举值,默 ...
