Springboot集成SpringSecurity
一、Spring security 是什么?
Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。
它提供了一组可以在Spring应用上下文中配置的Bean,充分利用了Spring IoC,DI(控制反转Inversion of Control ,DI:Dependency Injection 依赖注入)和AOP(面向切面编程)功能,为应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制功能,减少了为企业系统安全控制编写大量重复代码的工作。
二、Spring security 怎么使用?
使用Spring Security很简单,只要在pom.xml文件中,引入spring security的依赖就可以了。
<!-- spring security依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
什么都不做,直接运行程序,这时你访问任何一个URL,都会弹出一个“需要授权”的验证框,如图:

spring security 会默认使用一个用户名为:user 的用户,密码就是 启动的时候生成的(通过控制台console中查看),如图
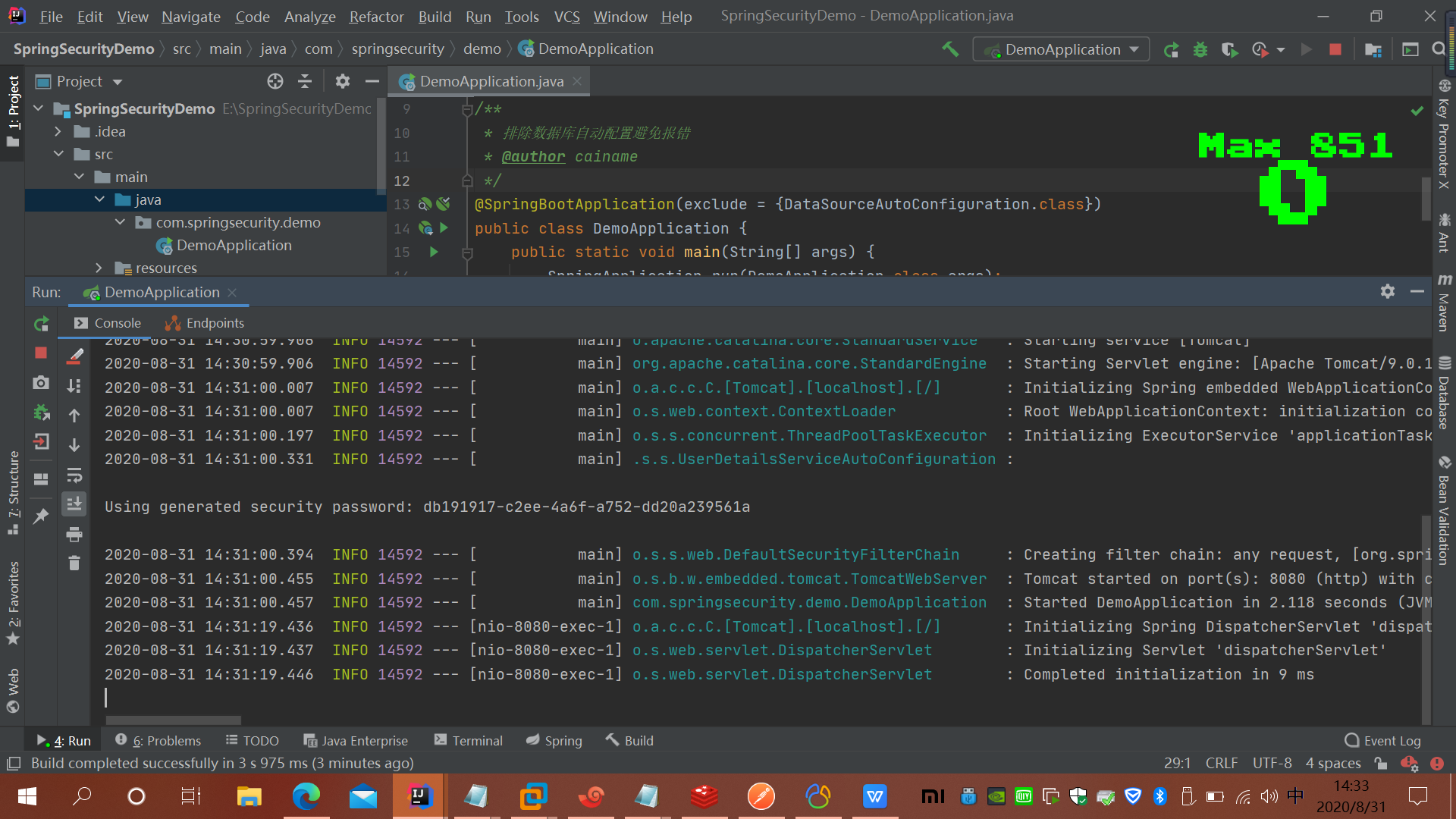
很显然这根本不是我们想要的,接下来我们需要一步一步的改造
改造1 使用页面表单登录
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/**
* loginPage("/login")表示登录时跳转的页面,因为登录页面我们不需要登录认证,所以我们需要添加 permitAll() 方法
* permitAll()表示这个不需要验证 登录页面,登录失败页面
* loginProcessingUrl处理登陆的url
* failureUrl:失败的处理url
*/
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login/form")
.failureUrl("/login-error")
.permitAll().
and().authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().
and().csrf().disable();
}
改造2、自定义用户名和密码
很显然,这样改造之后,虽然登录页面是好看了,但还远远不能满足我们的应用需求,所以第二步,我们改造自定义的用户名和密码。
自定义用户名和密码有2种方式,一种是在代码中写死,这也是官方的demo,另一种是使用数据库
/**
* 自定义密码
* @param auth
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("admin").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("USER");
}
spring security的原理就是使用很多的拦截器对URL进行拦截,以此来管理登录验证和用户权限验证
用户登陆,会被AuthenticationProcessingFilter拦截,调用AuthenticationManager的实现,而且AuthenticationManager会调用ProviderManager来获取用户验证信息(不同的Provider调用的服务不同,因为这些信息可以是在数据库上,可以是在LDAP服务器上,可以是xml配置文件上等),如果验证通过后会将用户的权限信息封装一个User放到spring的全局缓存SecurityContextHolder中,以备后面访问资源时使用。
所以我们要自定义用户的校验机制的话,我们只要实现自己的AuthenticationProvider就可以了。
在用AuthenticationProvider 这个之前,我们需要提供一个获取用户信息的服务,实现 UserDetailsService 接口
用户名密码->Authentication(未认证) -> AuthenticationManager ->AuthenticationProvider->UserDetailService->UserDetails->Authentication(已认证)
public class UserInfo implements Serializable, UserDetails {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 用户名
*/
private String username;
/**
* 用户密码
*/
private String password;
/**
* 用户角色
*/
private String role;
private boolean accountNonExpired;
private boolean accountNonLocked;
private boolean credentialsNonExpired;
private boolean enabled;
public UserInfo(String username, String password, String role, boolean accountNonExpired, boolean accountNonLocked,
boolean credentialsNonExpired, boolean enabled) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.role = role;
this.accountNonExpired = accountNonExpired;
this.accountNonLocked = accountNonLocked;
this.credentialsNonExpired = credentialsNonExpired;
this.enabled = enabled;
}
/**
* 权限
* @return
*/
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(role);
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return accountNonExpired;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return accountNonLocked;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return credentialsNonExpired;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
}
然后实现第2个类 UserService 来返回这个UserInfo的对象实例
package com.springsecurity.demo.service; import com.springsecurity.demo.entity.UserInfo;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import sun.security.rsa.RSASignature; /**
* @author cainame
*/ @Component
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { /**
* 这里可以可以通过username(登录时输入的用户名)然后到数据库中找到对应的用户信息,并构建成我们自己的UserInfo来返回
* @param username
* @return
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
if(username.equals("admin"))
{
UserInfo userInfo=new UserInfo("admin", "123456", "ROLE_ADMIN", true,true,true, true);
return userInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
到这里为止,我们自己定义的UserInfo类和从数据库中返回具体的用户信息已经实现,接下来我们要实现的,我们自己的 AuthenticationProvider
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider { @Autowired
private MyUserDetailsService userDetailService; @Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
/**
* 这个获取表单输入中返回的用户名;
*/
String userName = authentication.getName();
/**
* 这个是表单中输入的密码;
*/
String password = (String) authentication.getCredentials(); /**
* 调用服务获取用户信息
*/
UserInfo userInfo = (UserInfo) userDetailService.loadUserByUsername(userName); if (userInfo == null) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("用户名不存在");
} if (!userInfo.getPassword().equals("123456")) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("密码不正确");
} /**
* 获取权限
*/
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = userInfo.getAuthorities(); return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userInfo, password, authorities); } @Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}
}
到此为止,我们的用户信息的获取,校验部分已经完成了。接下来要让它起作用,则我们需要在配置文件中修改,让他起作用。回到我的SecurityConfig代码文件,修改如下:
1、注入我们自己的AuthenticationProvider
2、修改配置的方法:
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(provider);
}
3.获取当前登陆的用户
Object object = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
改造3、自定义登录成功和失败的处理逻辑
在现在的大多数应用中,一般都是前后端分离的,所以我们登录成功或失败都需要用json格式返回,或者登录成功之后,跳转到某个具体的页面。
为了实现这个功能,我们需要写2个类,分别继承SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler和SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler2个类,并重写其中的部分方法即可。
校验成功
@Component("myAuthenticationSuccessHandler")
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
/**
* 登陆成功之后的处理方法
* @param request
* @param response
* @param authentication
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws ServletException, IOException {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "200");
map.put("msg", "登录成功");
map.put("user",SecurityContextHolder.getContext());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
new DefaultRedirectStrategy().sendRedirect(request, response, "/index");
}
}
error:
package com.springsecurity.demo.config; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* @author cainame
*/ @Component("myAuthenticationFailHander")
public class MyAuthenticationFailHander extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler { @Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); @Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
logger.info("登录失败");
//以Json格式返回
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", "201");
map.put("msg", "登录失败");
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(map));
}
}
配置:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
/**
* loginPage("/login")表示登录时跳转的页面,因为登录页面我们不需要登录认证,所以我们需要添加 permitAll() 方法
* permitAll()表示这个不需要验证 登录页面,登录失败页面
* loginProcessingUrl处理登陆的url
* failureUrl:失败的处理url
*/
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login/form")
.failureUrl("/login-error")
.successHandler(myAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(myAuthenticationFailHander)
.permitAll().
and().authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().
and().csrf().disable();
}
改造4、添加权限控制
之前的代码我们用户的权限没有加以利用,现在我们添加权限的用法。
之前的登录验证通俗的说,就是来判断你是谁(认证),而权限控制就是用来确定:你能做什么或者不能做什么(权限)
在讲这个之前,我们简单说下,对于一些资源不需要权限认证的,那么就可以在Config中添加 过滤条件,如:
.and().authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/index").permitAll()
那么我们直接访问 /index 就不会跳转到登录页面,这样我们就可以把一些不需要验证的资源以这种方式过滤,比如图片,脚本,样式文件之类的。
我们先来看第一种:在编码中写死的。
那其实权限控制也是通过这种方式来实现
.antMatchers("/whoim").hasRole("ADMIN")
这个用户的角色哪里来,就是我们自己的UserDetailsService中返回的用户信息中的角色权限信息,这里需要注意一下就是 .hasRole("ADMIN"),那么给用户的角色时就要用:ROLE_ADMIN
.antMatchers 这里也可以限定HttpMethod的不同要求不同的权限(用于适用于Restful风格的API).
.antMatchers("/whoim").hasRole("ADMIN").antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,"/user/*").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET,"/user/*").hasRole("USER")
Spring Security 的校验的原理:左手配置信息,右手登录后的用户信息,中间投票器。
从我们的配置信息中获取相关的URL和需要的权限信息,然后获得登录后的用户信息
然后经过:AccessDecisionManager 来验证,这里面有多个投票器:
AccessDecisionVoter,(默认有几种实现:比如:1票否决(只要有一个不同意,就没有权限),全票通过,才算通过;只要有1个通过,就全部通过。类似这种的。
WebExpressionVoter 是Spring Security默认提供的的web开发的投票器。(表达式的投票器)
Spring Security 默认的是 AffirmativeBased 只要有一个通过,就通过。
有兴趣的可以 从FilterSecurityInterceptor这个过滤器入口,来查看这个流程。
内嵌的表达式有:permitAll denyAll 等等。
每一个权限表达式都对应一个方法。
如果需要同时满足多个要求的,不能连写如 ,我们有个URL需要管理员权限也同时要限定IP的话,不能:.hasRole("ADMIN").hasIPAddress("192.168.1.1");
而是需要用access方法 .access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasIpAddress('192.168.1.1')");这种。
.antMatchers("/whoim").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasIpAddress('192.168.119.1')")
那我们可以自己写权限表达式吗? 可以,稍后。。。这些都是硬编码的实现,都是在代码中写入的,这样的灵活性不够。所以我们接下来继续改造
改造4、添加基于RBAC(role-Based-access control)权限控制
这个大家可以去百度一下,一般都是由 3个部分组成,一个是用户,一个是角色 ,一个是资源(菜单,按钮),然后就是 用户和角色的关联表,角色和资源的关联表
核心就是判断当前的用户所拥有的URL是否和当前访问的URL是否匹配。
首先我们自己提供一个判断的接口和实现,代码如下:
public interface RbacService {
boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication);
}
实现:
@Component("rbacService")
public class RbacServiceImpl implements RbacService {
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication) {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
boolean hasPermission = false;
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) { //首先判断先当前用户是否是我们UserDetails对象。
String userName = ((UserDetails) principal).getUsername();
Set<String> urls = new HashSet<>();
urls.add("/whoim");// 数据库读取 //读取用户所拥有权限的所有URL
// 注意这里不能用equal来判断,因为有些URL是有参数的,所以要用AntPathMatcher来比较
for (String url : urls) {
if (antPathMatcher.match(url, request.getRequestURI())) {
hasPermission = true;
break;
}
}
}
return hasPermission;
}
}
修改配置文件:
.anyRequest().access("@rbacService.hasPermission(request,authentication)")
其中 @rbacService 就是我们自己声明的bean,在RbacServiceImpl实现类的头部注解中。
改造5、记住我的功能Remeber me
本质是通过token来读取用户信息,所以服务端需要存储下token信息
根据官方的文档,token可以通过数据库存储 数据库脚本
CREATE TABLE persistent_logins (
username VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
series VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
token VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
last_used TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (series)
);
然后,配置好token 的存储 及数据源 引入jdbc启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
增加前端checkbox
<tr>
<td>记住我</td>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="remember-me" value="true"/></td>
</tr>
配置
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository() {
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl tokenRepository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
tokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
return tokenRepository;
}
设置
.rememberMe()
.rememberMeParameter("remember-me").userDetailsService(myUserDetailsService)
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
.tokenValiditySeconds(60)
Springboot集成SpringSecurity的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot 集成SpringSecurity JWT
目录 1. 简介 1.1 SpringSecurity 1.2 OAuth2 1.3 JWT 2. SpringBoot 集成 SpringSecurity 2.1 导入Spring Security ...
- 【使用篇二】SpringBoot集成SpringSecurity(22)
SpringSecurity是专门针对基于Spring项目的安全框架,充分利用了依赖注入和AOP来实现安全管控.在很多大型企业级系统中权限是最核心的部分,一个系统的好与坏全都在于权限管控是否灵活,是否 ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(5)——权限控制
在第一篇中,我们说过,用户<–>角色<–>权限三层中,暂时不考虑权限,在这一篇,是时候把它完成了. 为了方便演示,这里的权限只是对角色赋予权限,也就是说同一个角色的用户,权限是 ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(4)——自定义表单登录
通过前面三篇文章,你应该大致了解了 Spring Security 的流程.你应该发现了,真正的 login 请求是由 Spring Security 帮我们处理的,那么我们如何实现自定义表单登录呢, ...
- 【springBoot】springBoot集成redis的key,value序列化的相关问题
使用的是maven工程 springBoot集成redis默认使用的是注解,在官方文档中只需要2步; 1.在pom文件中引入即可 <dependency> <groupId>o ...
- SpringBoot集成security
本文就SpringBoot集成Security的使用步骤做出解释说明.
- springboot集成Actuator
Actuator监控端点,主要用来监控与管理. 原生端点主要分为三大类:应用配置类.度量指标类.操作控制类. 应用配置类:获取应用程序中加载的配置.环境变量.自动化配置报告等与SpringBoot应用 ...
- SpringBoot集成Shiro并用MongoDB做Session存储
之前项目鉴权一直使用的Shiro,那是在Spring MVC里面使用的比较多,而且都是用XML来配置,用Shiro来做权限控制相对比较简单而且成熟,而且我一直都把Shiro的session放在mong ...
- SpringBoot集成redis的key,value序列化的相关问题
使用的是maven工程 springBoot集成redis默认使用的是注解,在官方文档中只需要2步; 1.在pom文件中引入即可 <dependency> <groupId>o ...
随机推荐
- dart系列之:dart语言中的特殊操作符
dart系列之:dart语言中的特殊操作符 目录 简介 普通操作符 类型测试操作符 条件运算符 级联符号 类中的自定义操作符 总结 简介 有运算就有操作符,dart中除了普通的算术运算的操作符之外,还 ...
- 概述C# virtual修饰符
摘要:C#是继C++和Java语言后的又一面向对象的语言,在语法结构,C#有很多地方和C++及Java相似,但是又不同于它们,其中一些关键特别需要引起我们的注意. C# virtual修饰符用于修改方 ...
- 环境(8)Linux用户组权限
一:Linux时间日期-时间同步策略 1.日期与时间 ①时间命令 data:查看当前系统时间 cal :查看日历 cal 2020 修改时间: date -s 11:11:11 ...
- java 获得 微信 UserId
.... public String cs() throws Exception{ /*访问页面,服务器会得到 code(request.getParameter("code")) ...
- 菜鸡的Java笔记第三 - java 自动转换原则
自动转换原则 数据范围保存大的数据类型要转换为数据范围保存小的数据类型,使用强制转换(强制转型就是在变量的前面加括号,在括号里写上需要强制要转的类型.) 数据范围保存小的数据类型可以自动转换为数据范围 ...
- [hdu7076]ZYB's kingdom
不难发现,操作1可以看作如下操作:对于删去$a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{k}$后的每一个连通块(的点集)$V$,令$\forall x\in V,x$的收益加上$s$(其中$s=\sum_{ ...
- SimpleNVR安防监控RTSP/FLV/HLS直播流服务如何分权限添加用户指定通道观看
背景分析 随着SimpleNVR的用户越来越多,很多客户反馈给了我们很宝贵的简易以及用户体验.在此非常感谢大家对我们的支持.其中很多客户不想把所有的视频直播展现出来,想分权限添加新用户,指定通道让其观 ...
- Sentry 监控 - Snuba 数据中台本地开发环境配置实战
系列 1 分钟快速使用 Docker 上手最新版 Sentry-CLI - 创建版本 快速使用 Docker 上手 Sentry-CLI - 30 秒上手 Source Maps Sentry For ...
- Codeforces 997E - Good Subsegments(线段树维护最小值个数+历史最小值个数之和)
Portal 题意: 给出排列 \(p_1,p_2,p_3,\dots,p_n\),定义一个区间 \([l,r]\) 是好的当且仅当 \(p_l,p_{l+1},p_{l+2},\dots,p_r\) ...
- clickhouse使用的一点总结
clickhouse据说是用在大数据量的olap场景列式存储数据库,也有幸能够用到它在实际场景中落地.本篇就来说说简单的使用心得吧. 1. 整体说明 架构啥的,就不多说了,列式存储.大数据量.高性能. ...
