PAT_A1018#Public Bike Management
Source:
Description:
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
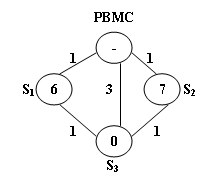
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex S is the current number of bikes stored at S. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
- PBMC -> S1 -> S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
- PBMC -> S2 -> S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: Cmax (≤), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; N (≤), the total number of stations; Sp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to N, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and M, the number of roads. The second line contains N non-negative numbers Ci (,) where each Ci is the current number of bikes at Si respectively. Then Mlines follow, each contains 3 numbers: Si, Sj, and Tij which describe the time Tij taken to move betwen stations Si and Sj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of Spis adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
Sample Input:
10 3 3 5
6 7 0
0 1 1
0 2 1
0 3 3
1 3 1
2 3 1
Sample Output:
3 0->2->3 0
Keys:
Code:
/*
Data: 2019-04-20 19:10:26
Problem: PAT_A1018#Public Bike Management
AC: 34:36 题目大意:
站点最佳状态时,有一半的自行车;
从起点选择最短路径终点,路径上的其他站点同样调整至最佳状态(补充/回收);
多条最短路径时,选择需要携带且回收数量最少的最条路径
输入:
第一行给出,最大容量Cmax,结点数N,Sp终点(默认起点为0),路径数M
第二行给出,各站点现有库存Ci
输出;
携带车辆数,路径,回收车辆数
*/ #include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int M=,INF=1e9;
int grap[M][M],vis[M],d[M],c[M];
int n,m,Cmax,st=,dt,optSent=INF,optBring=INF;
vector<int> temp,opt,pre[M]; void Dijskra(int s)
{
fill(vis,vis+M,);
fill(d,d+M,INF);
d[s]=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
int u=-,Min=INF;
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
{
if(vis[j]== && d[j]<Min)
{
u=j;
Min=d[j];
}
}
if(u==-) return;
vis[u]=;
for(int v=; v<=n; v++)
{
if(vis[v]== && grap[u][v]!=INF)
{
if(d[u]+grap[u][v] < d[v])
{
d[v]=d[u]+grap[u][v];
pre[v].clear();
pre[v].push_back(u);
}
else if(d[u]+grap[u][v]==d[v])
pre[v].push_back(u);
}
}
}
} void DFS(int v)
{
if(v == st)
{
int sent=,bring=;
for(int i=temp.size()-; i>=; i--)
{
int v = temp[i];
if(bring+(c[v]-Cmax/) > )
bring = bring + (c[v]-Cmax/);
else
{
sent += (Cmax/-bring-c[v]);
bring=;
}
}
if(sent < optSent)
{
optSent = sent;
optBring = bring;
opt = temp;
}
else if(sent==optSent && bring<optBring)
{
optBring = bring;
opt = temp;
}
return;
} temp.push_back(v);
for(int i=; i<pre[v].size(); i++)
DFS(pre[v][i]);
temp.pop_back();
} int main()
{
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("Test.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE fill(grap[],grap[]+M*M,INF);
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &Cmax,&n,&dt,&m);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
for(int i=; i<m; i++)
{
int v1,v2;
scanf("%d%d",&v1,&v2);
scanf("%d", &grap[v1][v2]);
grap[v2][v1]=grap[v1][v2];
}
Dijskra(st);
DFS(dt);
printf("%d %d", optSent,st);
for(int i=opt.size()-; i>=; i--)
printf("->%d", opt[i]);
printf(" %d", optBring); return ;
}
PAT_A1018#Public Bike Management的更多相关文章
- 1018. Public Bike Management (30)
时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue There is a public bike service i ...
- PAT 1018. Public Bike Management
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- A1018. Public Bike Management
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- PAT A1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)——最小路径,溯源,二标尺,DFS
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management[难]
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/4b20ed271e864f06ab77a984e71c090f来源:牛客网PAT 1018 Public ...
- PTA (Advanced Level) 1018 Public Bike Management
Public Bike Management There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenie ...
- PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management
PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management 题意: 杭州市有公共自行车服务,为世界各地的游客提供了极大的便利.人们可以在任何一个车站租一辆自行车,并将其送回城市的任何其他车站. ...
- PAT 1018 Public Bike Management(Dijkstra 最短路)
1018. Public Bike Management (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yu ...
随机推荐
- Django搭建简单的站点
1.首先.新建一个项目(project), 名称为 mysite django-admin startproject mysite(假设 django-admin 不行,请用 django-admin ...
- 改动grub默认启动顺序
grub如今有两个版本号,一个grub,一个grub2,两个版本号的操作不太一样. 装centos的朋友非常有可能是grub.我电脑装的是ubuntu14.04,为grub2.我演示grub2的过程. ...
- objc_setAssociatedObject
学习笔记:通过 objc_setAssociatedObject alert 和 button关联 及传值 标签: ios 2013-11-22 16:25 7924人阅读 评论(1) 收藏 举报 ...
- [WebGL入门]二十一,从平行光源发出的光
注:文章译自http://wgld.org/,原作者杉本雅広(doxas),文章中假设有我的额外说明.我会加上[lufy:],另外,鄙人webgl研究还不够深入,一些专业词语.假设翻译有误,欢迎大家指 ...
- LeetCode 706. Design HashMap (设计哈希映射)
题目标签:HashMap 题目让我们设计一个 hashmap, 有put, get, remove 功能. 建立一个 int array, index 是key, 值是 value,具体看code. ...
- hdu3488Tour KM算法
//给一个有向图, //找出若干环,使得这些环覆盖全部点且每一个点仅仅能在一个环中 //问所得的全部环的全部边权值之和的最小值为多少 //对于每一个点仅仅有一个入度和一个出度.那么将每一个点拆成 // ...
- 自己制作Android包括@hide接口的SDK
Android系统存在一些系统级应用与framework代码耦合较深,编译的时候依赖非常多类里面的@hide接口.这类应用怎么来编译呢?首先我们须要制作一份包括Hide接口的SDK,方法例如以下(以a ...
- 1245 最小的N个和(前k小ai+bi)
1245 最小的N个和 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 钻石 Diamond 题解 查看运行结果 题目描述 Description 有两个长度为 N ...
- 浅析Java开发模式—Model1、Model2和三层
"解耦"的思想一直是我们倡导的,但在实际项目中怎样去做?这是需要我们去好好思考的.下面以Model1.Model2.三层为切入点,对比下去了解解耦的思想. Model1 使用JSP ...
- JavaScript Patterns 2.5 (Not) Augmenting Build-in Prototypes
Disadvantage Other developers using your code will probably expect the built-in JavaScript methods t ...