The Class Loader Hierarchy--转载
Class loaders in the Application Server runtime follow a delegation hierarchy that is illustrated in the following figure and fully described inTable 2–1.
Figure 2–1 Class Loader Runtime Hierarchy
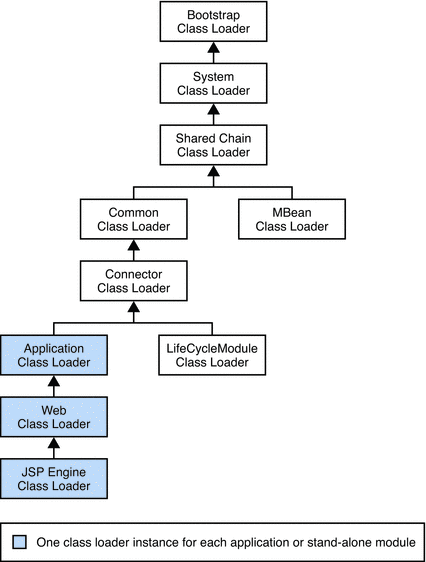
The following table describes the class loaders in the Application Server.
Table 2–1 Sun Java System Application Server Class Loaders
|
Class Loader |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Bootstrap |
The Bootstrap class loader loads the basic runtime classes provided by the JVM, plus any classes from JAR files present in the system extensions directory. It is parent to the System class loader. To add JAR files to the system extensions, directory, see Using the Java Optional Package Mechanism. |
|
System |
The System class loader loads Application Server launch classes. It is parent to the Shared Chain class loader. It is created based on the system-classpath attribute of the java-config element in the domain.xml file. In the Admin Console, select the Application Server component, the JVM Settings tab, and the Path Settings tab, then edit the System Classpath field. See Using the System Class Loader and java-config in Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 9 Administration Reference. |
|
Shared Chain |
The Shared Chain class loader loads most of the core Application Server classes. It is parent to the MBean class loader and the Common class loader. Classes specified by the classpath-prefix and classpath-suffixattributes of the java-config element in the domain.xml file are added to this class loader. In the Admin Console, select the Application Server component, the JVM Settings tab, and the Path Settings tab, then edit the Classpath Prefix or Classpath Suffix field. The environment classpath is included if env-classpath-ignored="false" is set in the java-configelement. Use classpath-prefix to place libraries ahead of Application Server implementation classes in the shared chain. The classpath-prefix is ideal for placing development and diagnostic patches. Use classpath-suffix to place libraries after implementation classes in the shared chain. |
|
MBean |
The MBean class loader loads the MBean implementation classes. See MBean Class Loading. |
|
Common |
The Common class loader loads classes in the domain-dir/lib/classes directory, followed by JAR files in thedomain-dir/lib directory. It is parent to the Connector class loader. No special classpath settings are required. The existence of these directories is optional; if they do not exist, the Common class loader is not created. See Using the Common Class Loader. |
|
Connector |
The Connector class loader is a single class loader instance that loads individually deployed connector modules, which are shared across all applications. It is parent to the LifeCycleModule class loader and the Application class loader. |
|
LifeCycleModule |
The LifeCycleModule class loader is created once per lifecycle module. Each lifecycle-module element’sclasspath attribute is used to construct its own class loader. For more information on lifecycle modules, seeChapter 13, Developing Lifecycle Listeners. |
|
Application |
The Application class loader loads the classes in a specific enabled individually deployed module or Java EE application. One instance of this class loader is present in each class loader universe; see Class Loader Universes. The Application class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load. It is parent to the Web class loader. The Application class loader loads classes in the following order:
The location attribute points to domain-dir/applications/j2ee-apps/app-name or domain-dir/applications/j2ee-modules/module-name. The stubs directory is domain-dir/generated/ejb/j2ee-apps/app-name or domain-dir/generated/ejb/j2ee-modules/module-name. |
|
Web |
The Web class loader loads the servlets and other classes in a specific enabled web module or a Java EE application that contains a web module. This class loader is present in each class loader universe that contains a web module; see Class Loader Universes. One instance is created for each web module. The Web class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load. The classes it loads are in WEB-INF/classes or WEB-INF/lib/*.jar. It is parent to the JSP Engine class loader. |
|
JSP Engine |
The JSP Engine class loader loads compiled JSP classes of enabled JSP files. This class loader is present in each class loader universe that contains a JSP page; see Class Loader Universes. The JSP Engine class loader is created with a list of URLs that point to the locations of the classes it needs to load. |
Note that this is not a Java inheritance hierarchy, but a delegation hierarchy. In the delegation design, a class loader delegates classloading to its parent before attempting to load a class itself. A class loader parent can be either the System class loader or another custom class loader. If the parent class loader cannot load a class, the class loader attempts to load the class itself. In effect, a class loader is responsible for loading only the classes not available to the parent. Classes loaded by a class loader higher in the hierarchy cannot refer to classes available lower in the hierarchy.
The Java Servlet specification recommends that the Web class loader look in the local class loader before delegating to its parent. You can make the Web class loader follow the delegation inversion model in the Servlet specification by setting delegate="false" in the class-loader element of the sun-web.xml file. It is safe to do this only for a web module that does not interact with any other modules. For details, see class-loader in Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 9 Application Deployment Guide.
The default value is delegate="true", which causes the Web class loader to delegate in the same manner as the other class loaders. You must use delegate="true" for a web application that accesses EJB components or that acts as a web service client or endpoint. For details about sun-web.xml, see The sun-web.xml File in Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 9 Application Deployment Guide.
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19501-01/819-3659/beadf/index.html
The Class Loader Hierarchy--转载的更多相关文章
- Taxonomy of class loader problems encountered when using Jakarta Commons Logging(转)
Acknowledgments I would like to thank Jacob Kjome for reviewing early drafts of this document. His c ...
- slf4j的简单介绍
SLF4J,Simple Logging Facade for JAVA,是一个十分简单的的日志facade,对于不同的日志框架做了一个封装. 对比common logging,Common logg ...
- ssh项目部署到weblogic中问题总结
部署到weblogic还是比较费劲的 ,不过基本上问题全是由于classloader顺序的问题引起的. 首先在web-inf底下添加weblogic.xml文件如下 <?xml version= ...
- tomcat源码剖析
最近看Tomcat的源码的节奏还算是挺紧凑的,给人的感觉,tomcat的代码相对以前读的jetty的代码显得更有条理一些...当然这也是有可能是因为自己看的jetty的版本是比较老的,而看的Tomca ...
- verview of Spring Framework--转
http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/html/overview.html 2. Introduct ...
- FLEX 图片拷贝
在用FLEX做GIS相关的开发的时候,遇到一个问题.因为是监控类的系统,所以需要要求地图上的ICON的实时更新,从而会出现重复加载的情况.就是重复请求相同的图片用做背景,尤其是在加载的ICON较多的时 ...
- tomcat 组件研究一--启动过程总结
作为java 开发者,从开始学习java 便知道tomcat 这个容器了,但是一直却没有怎么研究过它的内部结构,以前对tomcat的认识也仅仅局限在那几个常用的目录放什么东西,那几个常用的配置文件应该 ...
- Spring3.0官网文档学习笔记(二)
1.3 使用场景 典型的成熟的spring web应用 spring使用第三方框架作为中间层 远程使用场景 EJB包装 1.3.1 依赖管理.命名规则(包) spring-*.jar *号代表 ...
- Tomcat启动过程源码解读
根据Tomcat源码来看一下Tomcat启动过程都做了什么 部分代码为主要流程代码,删去了try-catch以及一些校验逻辑,方便理解主流程 先来一张启动过程时序图,了解一下启动顺序 Tomcat启动 ...
- java底层学习
额,马上就要面试了,Java的底层肯定是需要了解的.网上找了找java的底层文章,做个记号.java底层主要是类的加载.连接和初始化. 本文主要分为四个方面: (1)java底层概述 (2)new和n ...
随机推荐
- Druid :大数据实时处理的开源分布式系统(1)
引言 Druid 是一个快速,近实时的查询海量只读数据的系统.Druid 的目标是可用性要达到100%,即使在部署新代码,或者某些节点 down 机的情况下. Druid 目前支持的单表查询方式和 D ...
- 【HDU 1533】 Going Home (KM)
Going Home Problem Description On a grid map there are n little men and n houses. In each unit time, ...
- 高人ozhy111提供的下载资源
特别是有很多手机方面的独创源代码,先记下来,有空挨个看一遍: http://download.csdn.net/user/ozhy111 比如:idtcpserver文件传输xe7PC端及手机端 ht ...
- Android 自定义组件随着手指自动画圆
首先自定义一个View子类: package com.example.androidtest0.myView; import android.content.Context; import andro ...
- [OJ] Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
LintCode 160. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II (Medium) LeetCode 154. Find Minimum in Rotated ...
- JBossESB教程(一)——开发环境的搭建
前言 上篇对SOA的概述里面,在说SOA构建需要考虑什么时,提到了ESB,它作为SOA的基础设施而存在. 从这篇开始,将对ESB的其中一个实现JBossESB进行一个从头开始的讲解,既然是从头开始,那 ...
- Ehcache详细解读(转)
Ehcache 是现在最流行的纯Java开源缓存框架,配置简单.结构清晰.功能强大,最初知道它,是从Hibernate的缓存开始的.网上中文的EhCache材料 以简单介绍和配置方法居多,如果你有这方 ...
- ImageSwitcher 右向左滑动的实现方式
ImageSwitcher is;...is.setInAnimation(this, android.R.anim.slide_in_left);is.setOutAnimation(this, a ...
- Android ---时间工具类
public class DateUtil { // protected static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(DateUtil.class); // 格式:年- ...
- Windows环境下Android NDK环境搭建
前面介绍Windows下Android 开发环境配置,主要是面向JAVA开发环境,对只做APK上层应用开发人员来讲,基本够用了,由于Linux系统的权限限制和Android封装架构限制,很多涉及底层设 ...
