mysql学习------二进制日志
一.什么是二进制日志
1.记录对数据发生或潜在发生更改的sql语句
2.二进制格式保存
3.用途广泛,包括
a.查看数据库变更历史
b.数据库增量备份
c.数据库灾难恢复
d.mysql replication
二.不重启修改二进制日志配置
1.set @@global.log_bin=1;
2.set @@global.binlog_size=37268 (单位是bytes)
3.其他参数通过以下命令查阅
show variables like '%bin%';
三.常用二进制日志相关参数
修改以下配置后,需要重启数据库服务使其生效
1.log-bin=
开启并指定二进制日志的保存路径及文件名,不设置则使用默认值,默认存放位置为数据库文件所在目录下,名称为hostname-bin.xxxx
2.max-binlog-size=500m
设置单个二进制日志文件的最大值,默认为1G,最大也为1G
3.binlog-do-db与binlog-ignore-db
指定二进制日志文件记录那些数据库操作,不记录那些数据库操作
4.binlog-cache-size=100m
设置二进制日志缓存大小
5.sync-binlog=N
每隔N秒将缓存中的二进制日志记录写回硬盘,默认为0,不过,你经常会陷入group commit函数与I/O之间的二选一矛盾,如果在replication环境中,由于考虑到耐久性及一致性,则需设置为1,同时还需要设置innodb-flush-log-at-trx-commit=1 及 innodb-support-xa=1(默认已开启)
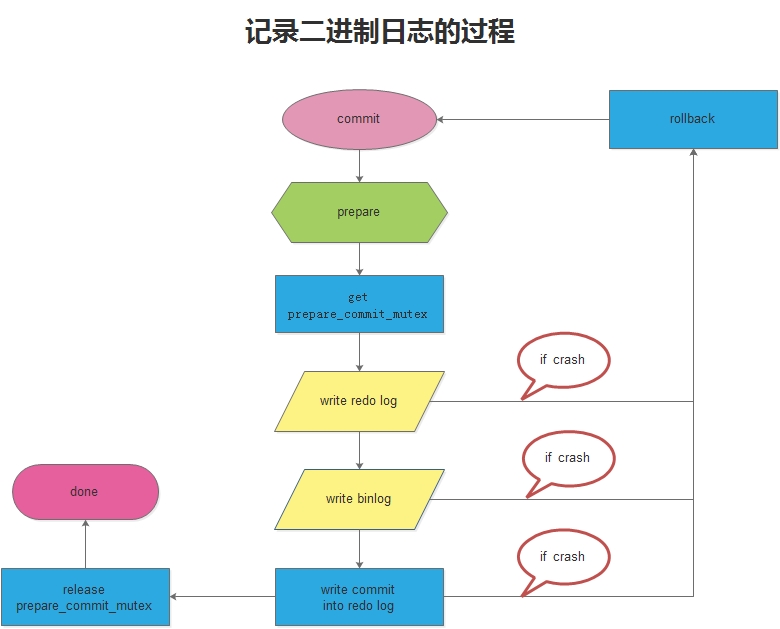
三.二进制的操作及总结
1.暂停二进制日志
set sql_log_bin = {0|1}
2.查看二进制日志
mysqlbinlog master-bin.000001
mysqlbinlog -v master-bin.000001
mysqlbinlog -v master-bin.000001 > test.sql #导出二进制日志到sql脚本
mysqlbinlog -v master-bin.000001 >> test.sql #追加二进制日志到sql脚本
3.mysqlbinlog的命令参数
Usage: mysqlbinlog [options] log-files
-?, --help Display this help and exit.
--base64-output=name
Determine when the output statements should be
base64-encoded BINLOG statements: 'never' disables it and
works only for binlogs without row-based events;
'decode-rows' decodes row events into commented
pseudo-SQL statements if the --verbose option is also
given; 'auto' prints base64 only when necessary (i.e.,
for row-based events and format description events). If
no --base64-output[=name] option is given at all, the
default is 'auto'.
--bind-address=name IP address to bind to.
--character-sets-dir=name
Directory for character set files.
-d, --database=name List entries for just this database (local log only).
--debug-check Check memory and open file usage at exit .
--debug-info Print some debug info at exit.
--default-auth=name Default authentication client-side plugin to use.
-D, --disable-log-bin
Disable binary log. This is useful, if you enabled
--to-last-log and are sending the output to the same
MySQL server. This way you could avoid an endless loop.
You would also like to use it when restoring after a
crash to avoid duplication of the statements you already
have. NOTE: you will need a SUPER privilege to use this
option.
-F, --force-if-open Force if binlog was not closed properly.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-force-if-open to disable.)
-f, --force-read Force reading unknown binlog events.
-H, --hexdump Augment output with hexadecimal and ASCII event dump.
-h, --host=name Get the binlog from server.
-l, --local-load=name
Prepare local temporary files for LOAD DATA INFILE in the
specified directory.
-o, --offset=# Skip the first N entries.
-p, --password[=name]
Password to connect to remote server.
--plugin-dir=name Directory for client-side plugins.
-P, --port=# Port number to use for connection or 0 for default to, in
order of preference, my.cnf, $MYSQL_TCP_PORT,
/etc/services, built-in default (3306).
--protocol=name The protocol to use for connection (tcp, socket, pipe,
memory).
-R, --read-from-remote-server
Read binary logs from a MySQL server. This is an alias
for read-from-remote-master=BINLOG-DUMP-NON-GTIDS.
--read-from-remote-master=name
Read binary logs from a MySQL server through the
COM_BINLOG_DUMP or COM_BINLOG_DUMP_GTID commands by
setting the option to either BINLOG-DUMP-NON-GTIDS or
BINLOG-DUMP-GTIDS, respectively. If
--read-from-remote-master=BINLOG-DUMP-GTIDS is combined
with --exclude-gtids, transactions can be filtered out on
the master avoiding unnecessary network traffic.
--raw Requires -R. Output raw binlog data instead of SQL
statements, output is to log files.
-r, --result-file=name
Direct output to a given file. With --raw this is a
prefix for the file names.
--secure-auth Refuse client connecting to server if it uses old
(pre-4.1.1) protocol.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-secure-auth to disable.)
--server-id=# Extract only binlog entries created by the server having
the given id.
--server-id-bits=# Set number of significant bits in server-id
--set-charset=name Add 'SET NAMES character_set' to the output.
-s, --short-form Just show regular queries: no extra info and no row-based
events. This is for testing only, and should not be used
in production systems. If you want to suppress
base64-output, consider using --base64-output=never
instead.
-S, --socket=name The socket file to use for connection.
--start-datetime=name
Start reading the binlog at first event having a datetime
equal or posterior to the argument; the argument must be
a date and time in the local time zone, in any format
accepted by the MySQL server for DATETIME and TIMESTAMP
types, for example: 2004-12-25 11:25:56 (you should
probably use quotes for your shell to set it properly).
-j, --start-position=#
Start reading the binlog at position N. Applies to the
first binlog passed on the command line.
--stop-datetime=name
Stop reading the binlog at first event having a datetime
equal or posterior to the argument; the argument must be
a date and time in the local time zone, in any format
accepted by the MySQL server for DATETIME and TIMESTAMP
types, for example: 2004-12-25 11:25:56 (you should
probably use quotes for your shell to set it properly).
--stop-never Wait for more data from the server instead of stopping at
the end of the last log. Implicitly sets --to-last-log
but instead of stopping at the end of the last log it
continues to wait till the server disconnects.
--stop-never-slave-server-id=#
The slave server_id used for --read-from-remote-server
--stop-never.
--stop-position=# Stop reading the binlog at position N. Applies to the
last binlog passed on the command line.
-t, --to-last-log Requires -R. Will not stop at the end of the requested
binlog but rather continue printing until the end of the
last binlog of the MySQL server. If you send the output
to the same MySQL server, that may lead to an endless
loop.
-u, --user=name Connect to the remote server as username.
-v, --verbose Reconstruct pseudo-SQL statements out of row events. -v
-v adds comments on column data types.
-V, --version Print version and exit.
--open-files-limit=#
Used to reserve file descriptors for use by this program.
-c, --verify-binlog-checksum
Verify checksum binlog events.
--binlog-row-event-max-size=#
The maximum size of a row-based binary log event in
bytes. Rows will be grouped into events smaller than this
size if possible. This value must be a multiple of 256.
--skip-gtids Do not print Global Transaction Identifier information
(SET GTID_NEXT=... etc).
--include-gtids=name
Print events whose Global Transaction Identifiers were
provided.
--exclude-gtids=name
Print all events but those whose Global Transaction
Identifiers were provided.
4.删除二进制日志
a.二进制日志会不断的增长,并产生多个文件,因此需要制定备份计划和管理策略,无用的二进制日志要记得及时删除
b.删除二进制日志有三种方法:
1.操作系统命令直接删除
2.reset master
3.purge
purge {master | binary} logs to 'log_name'
purge {master | binary} logs before 'date'
5.总结
a.日志影响mysql的性能有大量的磁盘空间,因此,往往做采样分析时才打开
b.即使做采样分析,也最好仅在一台测试机器上开启
c.二进制日志由于用途广泛,大多数情况下会开启,需要制定合理的备份计划和管理策略
mysql学习------二进制日志的更多相关文章
- mysql学习------二进制日志管理
MySQL二进制日志(Binary Log) a.它包含的内容及作用如下: 包含了所有更新了数据或者已经潜在更新了数据(比如没有匹配任何行的一个DELETE) 包含关于每个更新数据库( ...
- 如何通过Mysql的二进制日志恢复数据库数据
经常有网站管理员因为各种原因和操作,导致网站数据误删,而且又没有做网站备份,结果不知所措,甚至给网站运营和盈利带来负面影响.所以本文我们将和大家一起分享学习下如何通过Mysql的二机制日志(binlo ...
- MySQL使用二进制日志恢复数据库
一.二进制日志简介 MySQL有不同类型的日志,其中二进制文件记录了所有对数据库的修改,如果数据库因为操作不当或其他原因丢失了数据,可以通过二进制文件恢复. 在my.ini文件中设置了log-bin, ...
- mysql删除二进制日志文件
一.RESET MASTER 这个语句可以验证首次配置主机备机是否成功.步骤如下: 1. 启动master和 slave,开启replication (即 复制) 注:replication (复制) ...
- mysql使用二进制日志恢复数据
一.恢复到某个二进制文件 1.开启二进制日志 在mysqld的配置节点下添加如下配置 log-bin="E:/Mysql57BinLog/binlog"(windows下的路径,l ...
- MYSQL使用二进制日志来恢复数据
mysqlbinlog工具的使用,大家可以看MySQL的帮助手册.里面有详细的用, 在这个例子中,重点是--start-position参数和--stop-position参数的使用. ·--star ...
- Mysql清理二进制日志的技巧
1:二进制日志 二进制日志记录了所有的DDL(数据定义语言)语句和DML(数据操作语言)语句,但是不记录包括数据查询的语句.语句以"事件"的形式保存,它描述了数据的更改过程,此日志 ...
- mysql学习------错误日志和通用查询日志
一.启动错误日志 1.在不同情况下,错误日志会记录在不同的位置.如果没有在配置文件中指定文件名,则文件名默认为hostname.err 2.在mysql5.6的rpm发布方式中,错误的日志默认的放置在 ...
- Mysql binlog二进制日志
Mysql binlog日志有三种格式,分别为Statement,MiXED,以及ROW! 1.Statement:每一条会修改数据的实际原sql语句都会被记录在binlog中. 优点:不需要记录每一 ...
随机推荐
- Alpha 冲刺五
团队成员 051601135 岳冠宇 051604103 陈思孝 031602629 刘意晗 031602248 郑智文 031602234 王淇 会议照片 项目燃尽图 项目进展 暂无实质性进展. 项 ...
- C# 项目迁移 Microsoft.VisualStudio.Tools.Office.BuildTasks 生成解决方法报错:请确认 <UsingTask> 声明正确,该程序集及其所有依赖项都可用
问题定位: 1.在Server2003上使用vs2010开发的项目,移到Win8上,同样使用vs2010打开.在生成解决方案的时候有如下报错: 未能从程序集 Microsoft.VisualStudi ...
- python进阶:Python进程、线程、队列、生产者/消费者模式、协程
一.进程和线程的基本理解 1.进程 程序是由指令和数据组成的,编译为二进制格式后在硬盘存储,程序启动的过程是将二进制数据加载进内存,这个启动了的程序就称作进程(可简单理解为进行中的程序).例如打开一个 ...
- poj2559 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram(单调栈)
Description A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base l ...
- 【设计模式】—— 组合模式Composite
前言:[模式总览]——————————by xingoo 模式意图 使对象组合成树形的结构.使用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性. 应用场景 1 表示对象的 部分-整体 层次结构 2 忽略组合对 ...
- C++11 初始化
C++11 初始化 统一初始化语法 C++11新添加初始化列表 std::initializer_list<>类型,可以通过{}语法来构造初始化列表 .初始化列表是常数:一旦 ...
- 【题解】 [SCOI2010]传送带 (三分法)
题目描述 在一个2维平面上有两条传送带,每一条传送带可以看成是一条线段.两条传送带分别为线段AB和线段CD.lxhgww在AB上的移动速度为P,在CD上的移动速度为Q,在平面上的移动速度R.现在lxh ...
- PHP使用serialize和json_encode序列化数据并通过redis缓存文件和$GLOGALS缓存资源对象
PHP常用缓存方式:第一种,把需要缓存的数据进行处理,形成PHP可以直接执行的文件.在需要缓存数据的时候,通过include方式引入,并使用.第二种,把需要的数据通过serialize函数序列化后直接 ...
- (转)eclipse 报错 :The method list(String, Object[]) is ambiguous for the type BaseHibernateDao
背景:在开发过程中,经常遇到各种各样的编译问题,不断的总结,才能更好的提高效率. 描述 [报错] :The method list(String, Object[]) is ambiguous for ...
- Golang的字符编码介绍
Golang的字符编码介绍 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. Go里面内建仅支持UTF8字符串编码,因此如果你用fmt.Printf之类的函数无法将GBK,GB2312 ...
