Mini projects #4 ---- Pong
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University
授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott Rixner, John Greiner, Stephen Wong
工具:http://www.codeskulptor.org/, simplegui 模块
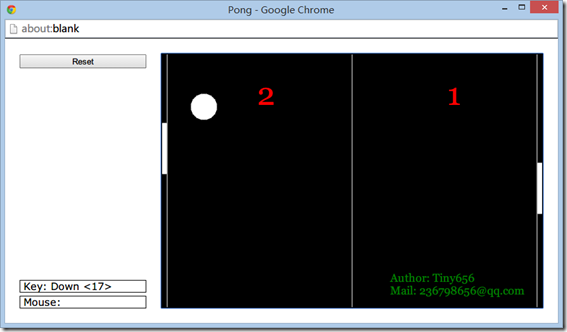
第四次作业,完成一个弹球的游戏,游戏的界面如下,规则也很简单,球不断在两边的paddle之间撞击后速度会不断加快,直到有一名玩家无法将球回击,则另一名玩家得分。
之前得了解一下控制物体移动的方式。
假设物体与点p相对应,第一种方式是直接通过控制点p的坐标来实现移动。
在draw_handler中不用进行更新,只用绘制他的position就可以
坐标的变化放在key_handler中进行修改,比如
key_handler:
Left Arrow –> p[0] –= c
Right Arrow –> p[0] += c
Up Arrow –> p[1] –= c
Down Arrow –> p[1] += c
代码如下:
import simplegui WIDTH = 500
HEIGHT = 300
p = [WIDTH/2, HEIGHT/2] def draw(canvas):
canvas.draw_circle(p, 30, 1, "White", "White") def key_down(key):
c = 4
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
p[1] -= c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['down']:
p[1] +=c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['left']:
p[0] -= c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['right']:
p[0] += c # Create a frame and assign callbacks to event handlers
frame = simplegui.create_frame("Position Control", WIDTH, HEIGHT)
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
frame.set_keydown_handler(key_down) # Start the frame animation
frame.start()
第二种方式通过控制点p的速率(velocity)变化来实现移动。
draw_handler中进行坐标的更新和绘制
在key_handler中进行速率的调整
draw_handler:
p[0] += v[0]
p[1] += v[1]
key_handler:
Left Arrow –> v[0] –= c
Right Arrow –> v[0] += c
Up Arrow –> v[1] –= c
Down Arrow –> v[1] += c
代码如下:
import simplegui WIDTH = 500
HEIGHT = 300
v = [0, 0]
p = [WIDTH/2, HEIGHT/2] def draw(canvas):
p[0] += v[0]
p[1] += v[1]
canvas.draw_circle(p, 30, 1, "White", "White") def key_down(key):
c = 1
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
v[1] -= c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['down']:
v[1] +=c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['left']:
v[0] -= c
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['right']:
v[0] += c # Create a frame and assign callbacks to event handlers
frame = simplegui.create_frame("Position Control", WIDTH, HEIGHT)
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
frame.set_keydown_handler(key_down) # Start the frame animation
frame.start()
这里再提一下碰撞的处理,上下碰撞,只用把v[1]的方向取反,左右碰撞,把v[0]的方向取反。
主要就是边界位置的判断,对于一个假定中心为p,半径为r的求来说:
碰撞如下:
Left Wall:
p[0] <= r
Right Wall:
p[0] >= (width-1)-r
Top Wall:
p[1] <= r
Bottom Wall:
p[1] >= (height-1)-r
下面两张图来自老师的课件,关于定义
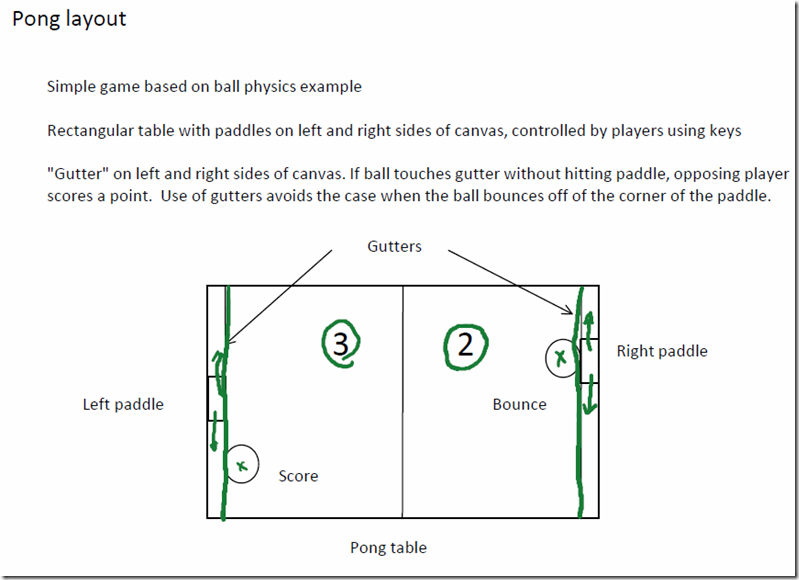
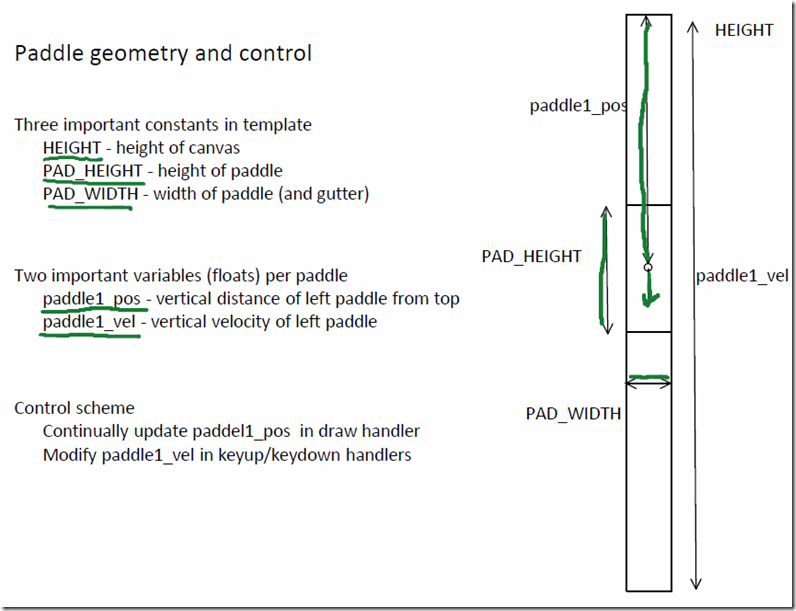
回归到这个游戏,基本要用到的知识也就这么多,移动paddle处理方式稍微特殊一点,keydown_handler进行velocity的正方向增加,那么keyup_handler进行velocity的负方向增加,这样就可以实现,按下按键后paddle持续移动,释放按键后paddle停止移动。
对于小球,初始随机给一个velocity,只要不是垂直或者水平,然后处理碰撞,在进行paddle碰撞后,要给予小球10%velocity上的增量。
完整代码如下:
# Implementation of classic arcade game Pong import simplegui
import random # initialize globals - pos and vel encode vertical info for paddles
WIDTH = 600
HEIGHT = 400
BALL_RADIUS = 20
PAD_WIDTH = 8
PAD_HEIGHT = 80
HALF_PAD_WIDTH = PAD_WIDTH / 2
HALF_PAD_HEIGHT = PAD_HEIGHT / 2
LEFT = False
RIGHT = True # initialize ball_pos and ball_vel for new bal in middle of table
# if direction is RIGHT, the ball's velocity is upper right, else upper left
def spawn_ball(direction):
global ball_pos, ball_vel # these are vectors stored as lists
ball_pos = [WIDTH/2, HEIGHT/2]
ball_dir = 1 if direction == RIGHT else -1
ball_vel = [ball_dir * random.randrange(2, 4), -random.randrange(1, 3)] # define event handlers
def new_game():
global paddle1_pos, paddle2_pos, paddle1_vel, paddle2_vel # these are numbers
global score1, score2 # these are ints
spawn_ball(random.choice([LEFT, RIGHT]))
paddle1_pos, paddle2_pos = HEIGHT / 2, HEIGHT / 2
paddle1_vel, paddle2_vel = 0, 0
score1, score2 = 0, 0 def draw(canvas):
global score1, score2, paddle1_pos, paddle2_pos, ball_pos, ball_vel # draw mid line and gutters
canvas.draw_line([WIDTH / 2, 0],[WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT], 1, "White")
canvas.draw_line([PAD_WIDTH, 0],[PAD_WIDTH, HEIGHT], 1, "White")
canvas.draw_line([WIDTH - PAD_WIDTH, 0],[WIDTH - PAD_WIDTH, HEIGHT], 1, "White") # update ball
new_ball_posX = ball_pos[0] + ball_vel[0]
new_ball_posY = ball_pos[1] + ball_vel[1]
if new_ball_posY <= BALL_RADIUS:
ball_pos[1] = BALL_RADIUS
ball_vel[1] *= -1
elif new_ball_posY >= HEIGHT - 1 - BALL_RADIUS:
ball_pos[1] = HEIGHT - 1 - BALL_RADIUS
ball_vel[1] *= -1
else:
ball_pos[1] = new_ball_posY # hit the left gutter
if new_ball_posX <= PAD_WIDTH + BALL_RADIUS:
ball_pos[0] = PAD_WIDTH + BALL_RADIUS
if (ball_pos[1] >= paddle1_pos - HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
and ball_pos[1] <= paddle1_pos + HALF_PAD_HEIGHT):
ball_vel[0] = -(ball_vel[0] + 0.1 * ball_vel[0])
ball_vel[1] = ball_vel[1] + 0.1 * ball_vel[1]
else:
score2 = score2 + 1
spawn_ball(RIGHT) # hit the right gutter
elif new_ball_posX >= WIDTH - PAD_WIDTH - BALL_RADIUS:
ball_pos[0] = WIDTH - PAD_WIDTH - BALL_RADIUS
if (ball_pos[1] >= paddle2_pos - HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
and ball_pos[1] <= paddle2_pos + HALF_PAD_HEIGHT):
ball_vel[0] = -(ball_vel[0] + 0.1 * ball_vel[0])
ball_vel[1] = ball_vel[1] + 0.1 * ball_vel[1]
else:
score1 = score1 + 1
spawn_ball(LEFT)
else:
ball_pos[0] = new_ball_posX # draw ball
canvas.draw_circle(ball_pos, BALL_RADIUS, 1, "White", "White") # update paddle's vertical position, keep paddle on the screen
new_paddle1_pos = paddle1_pos + paddle1_vel
if new_paddle1_pos <= HALF_PAD_HEIGHT:
paddle1_pos = HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
elif new_paddle1_pos >= HEIGHT-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT:
paddle1_pos = HEIGHT-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
else:
paddle1_pos = new_paddle1_pos new_paddle2_pos = paddle2_pos + paddle2_vel
if new_paddle2_pos <= HALF_PAD_HEIGHT:
paddle2_pos = HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
elif new_paddle2_pos >= HEIGHT-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT:
paddle2_pos = HEIGHT-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT
else:
paddle2_pos = new_paddle2_pos # draw paddles
canvas.draw_polygon([[0, paddle1_pos-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[PAD_WIDTH-1, paddle1_pos-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[PAD_WIDTH-1, paddle1_pos+HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[0, paddle1_pos+HALF_PAD_HEIGHT]], 1, "White", "White")
canvas.draw_polygon([[WIDTH-PAD_WIDTH+1, paddle2_pos-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[WIDTH, paddle2_pos-HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[WIDTH, paddle2_pos+HALF_PAD_HEIGHT],
[WIDTH-PAD_WIDTH+1, paddle2_pos+HALF_PAD_HEIGHT]], 1, "White", "White")
# draw scores
canvas.draw_text(str(score1), (WIDTH/4, HEIGHT/5), 50, "Red")
canvas.draw_text(str(score2), (WIDTH/4*3, HEIGHT/5), 50, "Red")
canvas.draw_text("Author: Tiny656", (WIDTH/5*3, HEIGHT/20*18), 18, "Green")
canvas.draw_text("Mail: 236798656@qq.com", (WIDTH/5*3, HEIGHT/20*19), 18, "Green") def keydown(key):
global paddle1_vel, paddle2_vel
acc = 3
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['w']:
paddle1_vel -= acc
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['s']:
paddle1_vel += acc
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
paddle2_vel -= acc
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['down']:
paddle2_vel += acc def keyup(key):
global paddle1_vel, paddle2_vel
acc = 3
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['w']:
paddle1_vel += acc
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['s']:
paddle1_vel -= acc
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
paddle2_vel += acc
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['down']:
paddle2_vel -= acc def reset():
new_game() # create frame
frame = simplegui.create_frame("Pong", WIDTH, HEIGHT)
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
frame.set_keydown_handler(keydown)
frame.set_keyup_handler(keyup)
frame.add_button("Reset", reset, 200) # start frame
new_game()
frame.start()
Mini projects #4 ---- Pong的更多相关文章
- Mini projects #7 ---- Spaceship
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University 授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott ...
- Mini projects #8–RiceRocks
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University 授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott ...
- Mini projects #6 ---- Blackjack
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University 授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott ...
- Mini projects #3 ---- Stopwatch: The Game
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University 授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott ...
- Mini projects #5 ---- Memory
课程全名:An Introduction to Interactive Programming in Python,来自 Rice University 授课教授:Joe Warren, Scott ...
- Golang优秀开源项目汇总, 10大流行Go语言开源项目, golang 开源项目全集(golang/go/wiki/Projects), GitHub上优秀的Go开源项目
Golang优秀开源项目汇总(持续更新...)我把这个汇总放在github上了, 后面更新也会在github上更新. https://github.com/hackstoic/golang-open- ...
- A Complete List of .NET Open Source Developer Projects
http://scottge.net/2015/07/08/a-complete-list-of-net-open-source-developer-projects/?utm_source=tuic ...
- Building Xcode iOS projects and creating *.ipa file from the command line
For our development process of iOS applications, we are using Jenkins set up on the Mac Mini Server, ...
- All the Apache Streaming Projects: An Exploratory Guide
The speed at which data is generated, consumed, processed, and analyzed is increasing at an unbeliev ...
随机推荐
- Python3
1.上节内容回顾 递归: 明确的结束条件 问题规模每递归一次都应该比上一次的问题规模有所减少 效率低 高阶函数 文件: rb.wb.ab 一般用在不同系统之间传数据,和传视频流的时候用到,一般以这种形 ...
- 主从LDAP
yum -y install compat-openldap必须得安装这个 1:在主上 备份 cp /etc/openldap/slapd.conf /etc/open ...
- Git相关知识
一些有用的链接: https://www.git-scm.com/ http://nvie.com/posts/a-successful-git-branching-model/ Git开发模式: 建 ...
- 用CSS3在手机上写弹出框,遮盖层
html: 在页面头部要写 <title>网上预约</title> <link href="../App_Themes/default/css/header.c ...
- JQuery源码解析-- 对象的创建
使用 $("a") 返回的对象就不再是一个简单的DOM对象了,而是一个复杂的JQuery对象. 那么JQuery是怎么创建对象的. 为了便于分析,我将JQuery中复杂的代码简化了 ...
- nginx下开启pathinfo模式
第一种方式是通过重写url来实现pathinfo模式: location / { if (!-e $request_filename){ rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php?s=/$ ...
- 有1,2,3一直到n的无序数组,排序
题目:有1,2,3,..n 的无序整数数组,求排序算法.要求时间复杂度 O(n), 空间复杂度O(1). 分析:对于一般数组的排序显然 O(n) 是无法完成的. 既然题目这样要求,肯定原先的数组有一定 ...
- 获取 IP 地址
package j2se.core.net.base; import java.net.InetAddress;import java.net.UnknownHostException; public ...
- HTML可编辑的select
HTML可编辑的select实现原理还是用select和input伪装成的! <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//Dth XHTML 1.0 Transiti ...
- cassandra指定数据库路径
参考 https://docs.datastax.com/en/cassandra/2.1/cassandra/configuration/configCassandra_yaml_r.html 我们 ...
