Blink Coordinate Spaces
Blink Coordinate Spaces
Blink Coordinate Spaces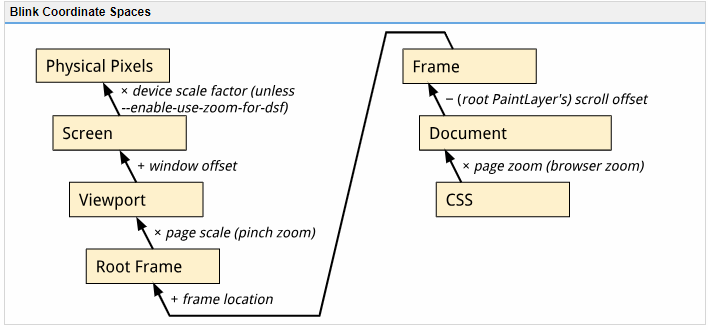
Types of ZoomThere are two types of zoom in Chromium: Browser Zoom and Pinch-Zoom. Browser zoom is what you get by using Ctrl+/- or the zoom buttons in the
 menu. It changes the size of a CSS pixel relative to a device independent pixel and so it will cause page layout to change. Throughout Blink, Browser-zoom is referred to as “Page Zoom” or “Zoom” more generally. menu. It changes the size of a CSS pixel relative to a device independent pixel and so it will cause page layout to change. Throughout Blink, Browser-zoom is referred to as “Page Zoom” or “Zoom” more generally. Pinch-zoom is activated by using a pinch gesture on a touchscreen. It scales the surface the web page is rendered onto and so it does not cause a relayout of the page. Throughout Blink, Pinch-zoom is referred to as “Page Scale”.
Types of PixelsPhysical Pixels: These are the actual pixels on the monitor or screen. Device Independent Pixels (DIPs): Modern devices sport high density displays (e.g. Apple’s Retina). In order to keep the UI at a comfortably readable size we scale it up based on the density of the display. This scaling factor is called the device pixel ratio in web APIs and device scale factor in Chromium code. A UI will always be the same size in DIPs regardless of how many pixels are actually used to display it. To go from physical pixels to DIPs we divide the physical pixel dimensions by the device scale factor.
CSS pixels: CSS defines its own pixel type that is also independent of physical pixels. When there is no Browser-Zoom or Pinch-Zoom applied, CSS pixels and DIPs are equivalent. However, browser zoom can make CSS pixels bigger or smaller relative to DIPs. You may come across the term un-zoomed CSS pixel below and in code. This refers to the fact that these pixels do not have browser zoom applied (but they do have pinch-zoom applied). I.e. Converting from frame-space (which is in un-zoomed CSS pixels) to Viewport using something like FrameView::frameToViewport will not apply the browser zoom.
A note about --use-zoom-for-dsf
The --use-zoom-for-dsf flag is used to have Blink use CSS based browser-zoom (the same kind as applied by Ctrl+/-) for screen-density based UI scaling. When this flag is passed, Blink doesn't scale anything using the device scale factor (and ensures it's set to 1) and instead boosts the page zoom factor by the requested amount.
This flag is currently shipped on all Aura platforms (ChromeOS, Linux, Windows), work is ongoing to bring it to Android, and remains unshipped on Mac.
Coordinate SpacesNote that the conversion methods between these spaces do not apply browser zoom. To go from CSS pixels to Document Content, FrameView Content, or Frame space you must first multiply by the browser-zoom scale factor.
Document
The coordinate space of the current FrameView's document content, in un-zoomed CSS pixels. The origin is the top left corner of the Frame’s document content. In Web/Javascript APIs this is referred to as "page coordinates" (e.g. MouseEvent.pageX) though there it is in CSS pixels (i.e. browser zoom applied). Because coordinates in this space are relative to the document origin, scrolling the frame will not affect coordinates in this space.
Frame
The coordinate space of the current FrameView in un-zoomed CSS pixels. The origin is the top left corner of the frame. Therefore, scrolling the frame will change the "frame-coordinates" of elements on the page. This is the same as document coordinates except that Frame coordinates take the Frame’s scroll offset into account. In Web/Javascript APIs this is referred to as "client coordinates" (e.g. MouseEvent.clientX) though there it is in CSS pixels (i.e. browser zoom applied).
Root Frame
The Frame coordinates of the top level (i.e. main) frame. This frame contains all the other child frames (e.g. elements create frames on a page).
(Visual) Viewport
The coordinate space of the visual viewport as seen by the user, in DIPs. The origin is at the top left corner of the browser view (Window or Screen). The difference between Viewport and RootFrame is the transformation applied by pinch-zoom. This is generally what you'd use to display something relative to the user's Window or Screen.
Screen
The final screen space on the user's device, relative to the top left corner of the screen (i.e. if we're in a Window, this will include the window's offset from the top left of the screen). Note that this is in DIPs rather than physical pixels.
Web-exposed input co-ordinate spacesTo see exactly how some of the above co-ordinate spaces are exposed to JavaScript in input events see https://rbyers.github.io/inputCoords.html.
|
Blink Coordinate Spaces的更多相关文章
- Input Team
The Chromium Input team (aka input-dev) is a web platform team focused on making touch (P1) and othe ...
- Layout Team
The layout team is a long-term engineering team tasked with maintaining, supporting, and improving t ...
- OpenCASCADE Coordinate Transforms
OpenCASCADE Coordinate Transforms eryar@163.com Abstract. The purpose of the OpenGL graphics process ...
- OpenCASCADE Camera
OpenCASCADE Camera eryar@163.com Abstract. OpenCASCADE introduce a new class Graphic3d_Camera for th ...
- 孙鑫MFC学习笔记11:保存图像
1.CPtrArray指针数组 2.CPtrArray返回void指针,需要做类型转换 3.View类中的OnPaint调用OnPrepareDC和OnDraw,如果覆盖OnPaint,就不会调用On ...
- golang.org/x/mobile/exp/gl/glutil/glimage.go 源码分析
看这篇之前,建议先看之前几篇,这几篇是基础. Go Mobile 例子 basic 源码分析 http://www.cnblogs.com/ghj1976/p/5183199.html OpenGL ...
- 图形变幻矩阵 Transforms
https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/GraphicsImaging/Conceptual/drawingwithquartz2d ...
- Foundations of Game Engine Development Volume 1 Mathematics (Eric Lengyel 著)
http://www.foundationsofgameenginedev.com/ Chapter1 Vectors and Matrices (已看) Chapter2 Transforms (已 ...
- Game Engine Architecture 6
[Game Engine Architecture 6] 1.Data-Parallel Computations A GPU is a specialized coprocessor designe ...
随机推荐
- [雅礼NOIP2018集训 day4]
感觉状态极差啊,今天居然爆零了 主要是以下原因: 1.又是T1看错题肝了两个小时,发现题意理解错误瞬间心态爆炸 2.T2交错了文件名 3.T3暴力子任务和正解(假的)混在一起,输出了两个答案 都想为自 ...
- C# 实现ADSL自动断网和拨号(适用于拨号用户)
using System;using System.Runtime.InteropServices; public struct RASCONN{ public int dwSize; p ...
- 你不知道的JavaScript(五)内置对象模版
尽管JavaScript中有对象的概念,但一般我们并不说JavaScript是面向对象的编程语言,因为它不具备面向对象的一些最基本特征. 在c++/Java等这些面向对象的编程语言中,我们要定义一个对 ...
- (转载)自定义ExpandableListView,实现二级列表效果
先看效果图: 上图是我们要实现的效果,那么现在我们开始着手去做,主要分为以下几步: 一丶我们需要根据效果图去思考该如何动手,从上图分析看,我们可以用一个相对布局RelativeLayout来完成gro ...
- Codeforces 986B. Petr and Permutations(没想到这道2250分的题这么简单,早知道就先做了)
这题真的只能靠直觉了,我没法给出详细证明. 解题思路: 1.交换3n次或者7n+1次,一定会出现一个为奇数,另一个为偶数. 2.用最朴素的方法,将n个数字归位,计算交换次数. 3.判断交换次数是否与3 ...
- A. Amr and Music
解题思路:给出n种乐器学习所需要的时间,以及总共的天数, 问最多能够学多少门乐器,并且输出这几门乐器在原序列中的序号(不唯一) 按照升序排序,为了学到最多的乐器,肯定要选择花费时间最少的来学习 然后用 ...
- ORACLE查询优化之is null和is not null优化
最近工作的时候遇到了比较大的数据查询,自己的sql在数据量小的时候没问题,在数据量达到300W的时候特别慢,只有自己优化sql了,以前没有优化过,所以记录下来自己的优化过程,本次是关于is null和 ...
- git远程仓库变更
查看自己的远程仓库 git remote -v 远程仓库变更 git remote remove origin //移出现有的远程仓库的地址 git remote add origin http:// ...
- 【Computer Vision】图像单应性变换/投影/仿射/透视
一.基础概念 1. projective transformation = homography = collineation. 2. 齐次坐标:使用N+1维坐标来表示N维坐标,例如在2D笛卡尔坐标 ...
- docker系列之一 image和container
docker images往往不知不觉就占满了硬盘空间,为了清理冗余的image,可采用以下方法: 1.进入root权限 sudo su 2.停止所有的container,这样才能够删除其中的imag ...
