[Elementary Mechanics Using Python-02]Feather in tornado
Problem
9.17 Feather in tornado.
In this project you will learn to use Newton’s laws and the force model for air resistance in a wind field to address the motion of a light object in strong winds. We start from a simple model without wind and gradually add complexity to the model, until we finally address the motion in a tornado. Motion without wind:
First, we address the motion of the feather without wind.
(a) Identify the forces acting on a feather while it is falling and draw a free-body diagram for the feather.
(b) Introduce quantitative force models for the forces, and find an expression for the acceleration of the feather. You may assume a quadratic law for air resistance.
(c) If you release the feather from rest, its velocity will tend asymptotically toward the terminal velocity, \(v_T\) . Show that the terminal velocity is \(v_T\) = \(−(mg/D)^{1/2}\), where D is the constant in the air resistance model.
(d) We release the feather from a distance h above the floor and measure the time t until the feather hits the floor. You may assume that the feather falls with a constant velocity equal to the terminal velocity. Show how you can determine D/mg by measuring the time t. Estimate D/mg when you release the feather from a height of 2.4 m above the floor and it takes 4.8 s until it hits the floor.
(e) We will now develop a more precise model where we do not assume that the velocity is constant. You release the feather from the height h at the time t = 0 s. Find the equation you have to solve to find the position of the feather as a function of time. What are the initial conditions?
(f) Write a program that solves this equation to find the velocity and position as a function of time t. Use the parameters you determined above, and test the program by ensuring that it produces the correct terminal velocity.
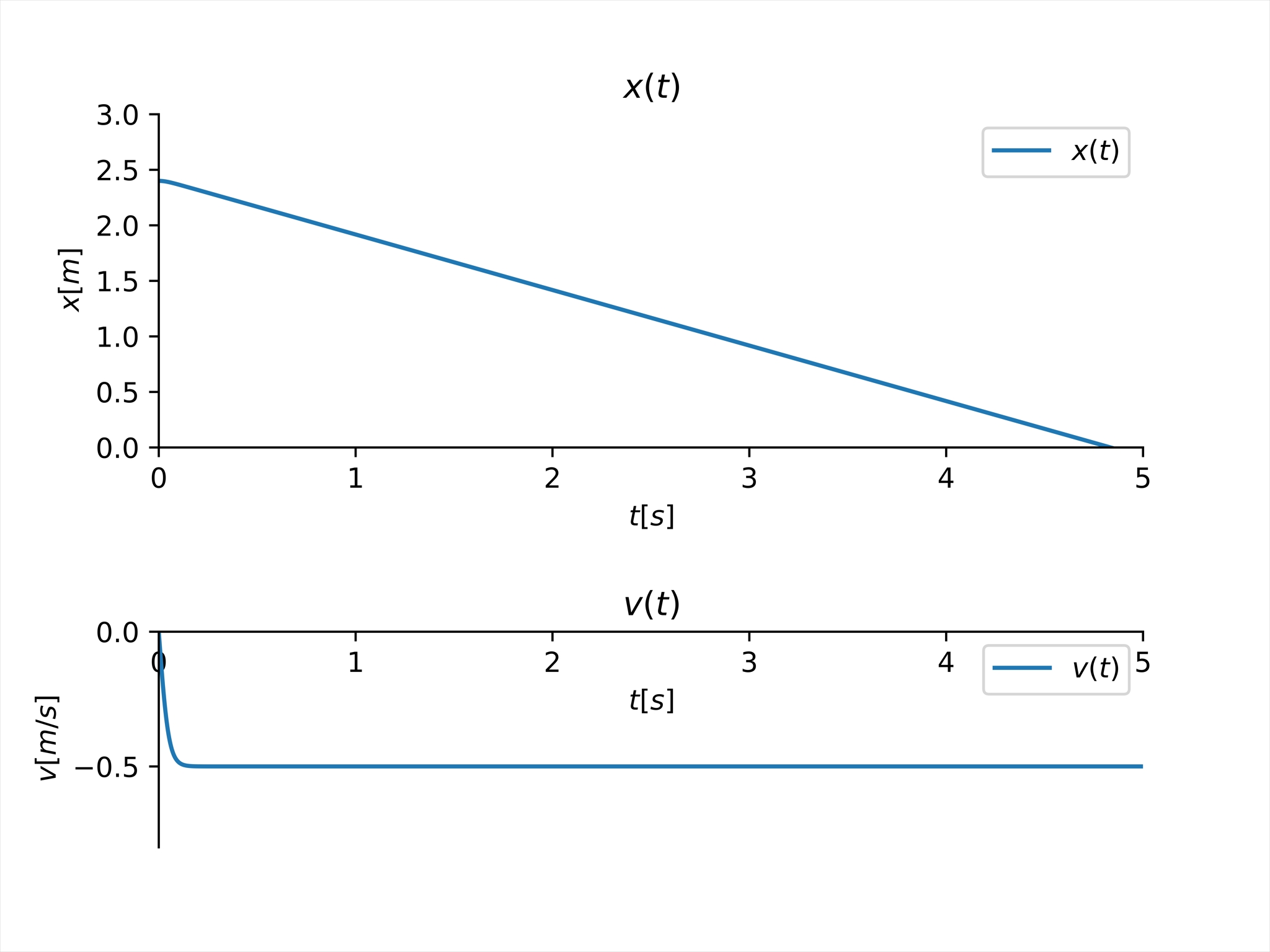
(g) Fig. 9.19 shows the position and velocity calculated with the program using the parameters found above. Was the approximation in part (d) reasonable? Explain your answer. Model with wind: We have now found a model that can be used to find the motion of the feather. We will now find the motion of the feather in three dimensions while it is blowing. The velocity of the wind varies in space, so that the wind velocity w is a function of the position r. We write this as w = w(r).
(h) Find an expression for the acceleration of the feather. The expression may include the wind velocity w(r). Let the z-axis correspond to the vertical direction.
(i) Assume that the feather is moving in an approximately horizontal plane—that is you may assume that the vertical acceleration is negligible. How does the wind have to blow in order for the feather to move in a circular orbit of radiusr0 with a constant speed v0?
Motion in a tornado: For a tornado with a center at the origin, the wind velocity is expected to be approximately given by the model:
\[\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{r}) = u_0\boldsymbol{r}e^{−r/R}\hat{u_θ} = u_0(-y, x,0)e^{−r/R}\hat{u_θ} , \space \space (9.79)
\]where u0 is a characteristic velocity for the wind, R is the radius of the tornado, and uˆθ is a tangential unit vector in the horizontal plane (\(\hat{u_\theta}\) is normal to r). Here, r = (x, y,z), and r = |r|. The velocity field is illustrated in Fig. 9.20.
(j) Is is possible to choose an appropriate set of initial conditions so that the feather moves in a circular path in the tornado? Explain your answer.
(k) Rewrite your program to find the velocity and position of the feather as a function of time. For the tornado you may use the values u0 = 100 m/s and R = 20 m.
(l) Find the trajectory for the feather if it is released from rest from a height of 2.4m, and in a position corresponding to r = −R i + hk. (m) The trajectory of the feather is shown in Figs. 9.20 and 9.21. Compare the results with what happended when you dropped the feather without wind. Why does the feather now take longer to reach the ground?
Solution
\((a)\)
考虑无风情况,\(\boldsymbol{w} = \boldsymbol{0}\),很容易画出受力分析图
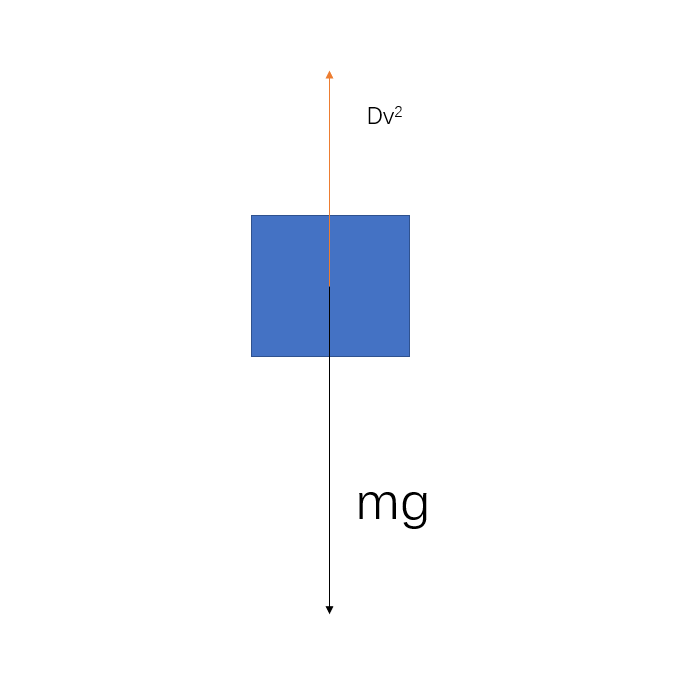
\((b)\)
由受力分析图可以简单的列出动力学方程
\]
\(\Rightarrow\)
\]
\((c)\)
我们令 \(\boldsymbol{a} = \boldsymbol{0}\), 得到方程
\]
\(\Rightarrow\)
\]
\((d)\)
由\((c)\)中公式,我们列出
\]
将\(v_T = -\sqrt[]{\frac{mg}{D}}\)带入求解,得
\]
\((e)\)
此问方程就是\((b)\)中得到的方程
\]
\((f)\)
编程实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = 9.81
H = 2.4
dt = 0.001
C = 4 # D/mg
t = np.arange(0, 5, 0.001)
a = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
v = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
x = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
a[0] = -G
v[0] = 0
x[0] = H
for index in range(1, 5000):
a[index] = (-1 + C*v[index-1]**2)*G
v[index] = v[index-1] + a[index-1]*dt
x[index] = x[index-1] + v[index-1]*dt
plt.subplot('211')
plt.title('$x(t)$')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.plot(t, x, label="$x(t)$")
plt.xlim([0, 5])
plt.ylim([0, 3])
plt.xlabel('$t[s]$')
plt.ylabel('$x[m]$')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot('313')
plt.title('$v(t)$')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.plot(t, v, label="$v(t)$")
plt.xlim([0, 5])
plt.ylim([-0.8, 0])
plt.xlabel('$t[s]$')
plt.ylabel('$v[m/s]$')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('f.jpg', dpi=3000)
\((h)\)
考虑上风力,改为相对于风的速度
\]
\((i)\)
忽略铅锤方向加速度,\(让g \rightarrow 0, 且当\boldsymbol{a}=-\frac{v_0^2}{r_0}\hat{r}时:\\\)
\]
解出\(\boldsymbol{w}\)
\]
\((j)\)
首先列出羽毛的微分方程
\]
找到初值条件
&\boldsymbol{x}(0) = [-20, 0, 2.4] \\
&\boldsymbol{v}(0) = [0, 0, 0] \\
&\boldsymbol{a}(0) = -(\boldsymbol{k} + \frac{D}{mg}|\boldsymbol{v}(0)-\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{x}(0))|(\boldsymbol{v}(0)-\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{x}(0))))g\\
\end{align}\end{matrix}\right.
\]
编程实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
// 定义常量
u0 = 100
R = 20
H = 2.4
G = 9.81
k = np.array([0, 0, 1])
C = 4 # D/mg
def Len(vector):
return np.sqrt(vector[0]**2+vector[1]**2+vector[2]**2)
// 风场函数
def w(xVector, yVector, zVector=0):
rLen = Len([xVector, yVector, zVector])
return np.array([u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*(-yVector), u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*xVector, u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*0])
// 加速度函数
def A(v, r):
W = w(r[0], r[1], r[2])
return -(k+C*(v - W)*Len((v - W)))*G
// 创建网格
xVector, yVector= np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(-101, 101, 100),
np.linspace(-101, 101, 100)
)
// 计算风场
uVector, vVector, wVector = w(xVector, yVector)
M = np.hypot(uVector,vVector)
// 绘制风场
plt.quiver(
xVector, yVector,
uVector, vVector,
M, pivot='mid', width=0.001
)
dt = 0.00001
tMax = 30
t = np.arange(0, tMax, dt)
x = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
v = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
a = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
// 初值条件
v[0,:] = np.array([0, 0, 0])
x[0,:] = np.array([-20, 0, H])
a[0,:] = A(v[0,:], x[0,:])
// 数值积分
i = 0
for index in range(1, 3000000):
a[index,:] = A(v[index-1,:], x[index-1,:])
v[index,:] = v[index-1,:] + a[index-1,:]*dt
x[index,:] = x[index-1,:] + v[index-1,:]*dt
if x[index,2] <= 0:
i = index
print("drop at {} s".format(i*dt))
break
// 绘制羽毛轨迹
plt.plot(x[:i,0], x[:i,1], 'r', linewidth=0.5)
plt.scatter(x[:i:10000,0], x[:i:10000,1], s=0.6)
plt.xlim([-101, 101])
plt.ylim([-101, 101])
plt.axis('equal')
plt.savefig('1.jpg', dpi=3000)
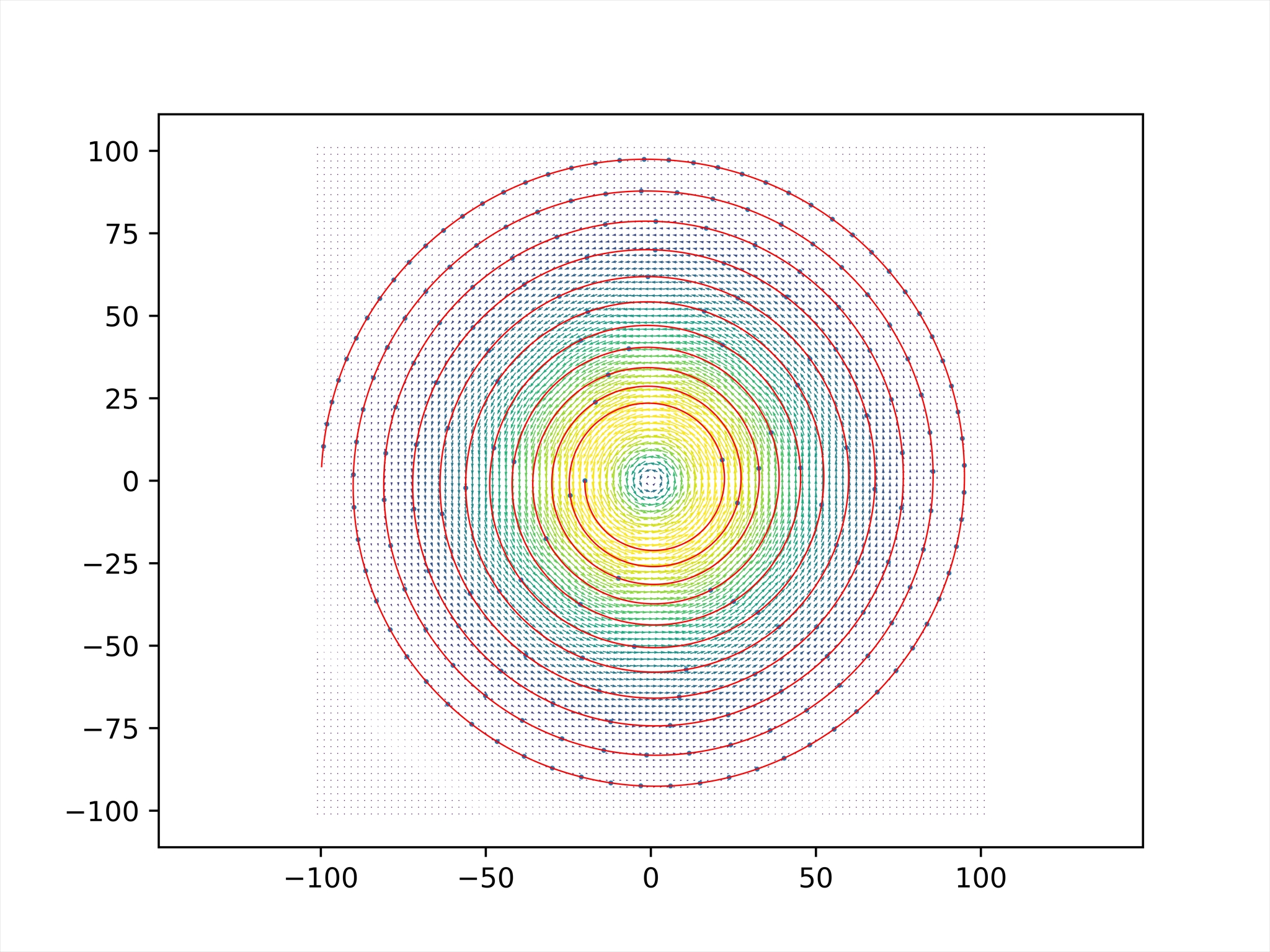
结论
在龙卷风影响下,计算出羽毛要经过 \(20.59065 s\) 落到地面,远大于无风情况下的情况,主要原因是采用了平方模型,使得空气阻力非线性。
[Elementary Mechanics Using Python-02]Feather in tornado的更多相关文章
- Python(九)Tornado web 框架
一.简介 Tornado 是 FriendFeed 使用的可扩展的非阻塞式 web 服务器及其相关工具的开源版本.这个 Web 框架看起来有些像web.py 或者 Google 的 webapp,不过 ...
- python web框架——初识tornado
一 Tornado概述 Tornado是FriendFeed使用的可扩展的非阻塞式web框架及其相关工具的开源版本.这个Web框架看起来有些像web.py或者Google的 webapp,不过为了能有 ...
- Python学习笔记17—Tornado
实例 #!/usr/bin/env Python #coding:utf-8 import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornad ...
- python web框架之Tornado
说Tornado之前分享几个前端不错的网站: -- Bootstrap http://www.bootcss.com/ -- Font Awesome http://fontawesome.io/ - ...
- 【Python】linux安装tornado
想写个页面,又不想用tomcat,同事说可以用tornado,试一下 1 我从网上找了个hello world类似的程序,复制粘贴运行,提示 ImportError: No module named ...
- Python Web 框架:Tornado
1.Tornado Tornado:python编写的web服务器兼web应用框架 1.1.Tornado的优势 轻量级web框架 异步非阻塞IO处理方式 出色的抗负载能力 优异的处理性能,不依赖多进 ...
- python web框架之Tornado的简单使用
python web框架有很多,比如常用的有django,flask等.今天主要介绍Tornado ,Tornado是一个用Python写的相对简单的.不设障碍的Web服务器架构,用以处理上万的同时的 ...
- 在学习python的Django\Flask\Tornado前你需要知道的,what is web?
我们都在讲web开发web开发,那到底什么是web呢? 如果你正在学习python三大主流web框架,那这些你必须要知道了 软件开发架构: C/S架构:Client/Server 客户端与服务端 ...
- python 02
函数的参数 默认参数: 函数的基本形参, 可以有默认参数, 什么是基本形参呢, 就是普通变量, 如字符串, 数字等. 并且带有默认参数的形参, 要放在后边. 传参时, 不必将所有的参数都传递, 可以只 ...
随机推荐
- 2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第六场)J Upgrading Technology
传送门 题意: 就是给你n个技能,每个技能最高升到m级,每升一级就是耗费Cij钱,这个Cij可能是负的,如果所有技能都升到或者说超过j等级,就会获得Dj钱,这个Dj也有可能是负值,让你求你最多得到多少 ...
- Java 窗口 绘制图形 #3
写在前面: 高数下学到第二章,突发奇想要写一个程序画二元函数图像 思路分了三层: ①抽象层: 因变量z,自变量x.y,坐标原点x0.y0.z0 ②投影实现层: 屏幕投影坐标px.py,x轴与屏幕水平方 ...
- Triangle War POJ - 1085 极小极大搜索
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/nwpuacmteams/articles/5697873.html 极小极大搜索 的个人理解(alpha-beta剪枝):https://w ...
- 头疼的Python 脚本报错
Python 脚本报错 检查是否用了制表符.变量声明前面不能用制表符,只能用空格,版本为2.7.14
- Dubbo从入门到实践
1 Dubbo出现的背景 随着互联网的发展,网站应用的规模不断扩大,常规的垂直应用架构已无法应对,分布式服务架构以及流动计算架构势在必行,亟需一个治理系统确保架构有条不紊的演进. 我们传统的网站结构为 ...
- K8S(02)管理核心资源的三种基本方法
系列文章说明 本系列文章,可以基本算是 老男孩2019年王硕的K8S周末班课程 笔记,根据视频来看本笔记最好,否则有些地方会看不明白 需要视频可以联系我 管理k8s核心资源的三种基本方法: 目录 系列 ...
- MySQL 语句及其种类
DDL(Data Definition Language) DDL(Data Definition Language),数据定义语言 CREATE:创建数据库和表等对象 DROP:删除数据库和表等对象 ...
- QXDM和QCAT软件使用指南
一.传送门 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i55YXnf 密码:v6nw 二.QXDM,QPST和QCAT的简单说明 QXDM,QPST和QCAT是Qualcomm高通公司针 ...
- git push bug
git push bug fast-forwards $ git push $ git push --help # git pull $ gp To http://git.xgqfrms.xyz:88 ...
- ES6 Arrow Function All In One
ES6 Arrow Function All In One this const log = console.log; const arrow_func = (args) => log(`arg ...
