不同gdb,相同数据集合并
众所周知,数据处理是GIS中一项重要且繁琐的工作,处理数据的工具和方法也太多了,在做数据处理的时候,经常会遇到这样的问题:对存储在不同gdb中、并且数据集名称相同的数据进行合并处理:
如图:数据组织如下,每个gdb中都存储了一些列FeatureClass,(但gdb中的FeatureClass数量并不相同)
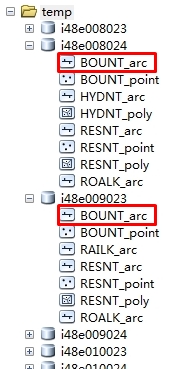
思路是:
1.先对每个gdb中的数据进行处理,使得每个gdb中的featureclass数量和名称相同。由于对Engine比较熟悉,这里我是用Engine进行处理的,具体代码如下:
private function Execute(){ //初始执行函数:
string templatePath = @"F:\testout";
DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(templatePath);
DirectoryInfo[] dirInfo = directoryInfo.GetDirectories();
string yy = dirInfo[].Name;
string FeatureClassName = "ROALK_arc"; //FeatureClass名称,这里可以设置一个数组,存储所有的FeatureClass
for (int i = ; i < dirInfo.Length; i++)
{
string gdbName = dirInfo[i].Name;
//打开filegdb
bool value = oper(@"F:\testout\" + gdbName, FeatureClassName);//判断FeatureClass是否存在
string path = @"F:\testout\" + gdbName;
if (value == false)
{
copyFeatureClass(path, FeatureClassName);
}
}
}
public bool oper(string filename,string featureClassName) //判断FeatureClass是否存在
{
IWorkspace2 workspace = null;
IWorkspaceFactory2 workspaceFactory = new FileGDBWorkspaceFactoryClass();
workspace = workspaceFactory.OpenFromFile(filename, ) as IWorkspace2;
IFeatureWorkspace featureWorkspace = workspace as IFeatureWorkspace;
bool flag = workspace.get_NameExists(ESRI.ArcGIS.Geodatabase.esriDatasetType.esriDTFeatureClass, featureClassName);
return flag;
}
public bool oper(string filename,string featureClassName) //判断是gdb中是否存在某个FeatureClass
{
IWorkspace2 workspace = null;
IWorkspaceFactory2 workspaceFactory = new FileGDBWorkspaceFactoryClass();
workspace = workspaceFactory.OpenFromFile(filename, ) as IWorkspace2;
IFeatureWorkspace featureWorkspace = workspace as IFeatureWorkspace;
bool flag = workspace.get_NameExists(ESRI.ArcGIS.Geodatabase.esriDatasetType.esriDTFeatureClass, featureClassName);
return flag;
}
//拷贝所有的FeatureClass到gdb,并删除里面的数据,保证每个featureclass为空,注:D:\Data\Shapefiles存储了所有的要合并的FeatureClass的空图层,便于拷贝。
private void convert()
{
IWorkspaceName sourceWorkspaceName = new WorkspaceNameClass
{
WorkspaceFactoryProgID = "esriDataSourcesFile.ShapefileWorkspaceFactory",
PathName = @"D:\Data\Shapefiles"
};
IName sourceWorkspaceIName = (IName)sourceWorkspaceName;
IWorkspace sourceWorkspace = (IWorkspace)sourceWorkspaceIName.Open(); // Create a name object for the target (file GDB) workspace and open it.
IWorkspaceName targetWorkspaceName = new WorkspaceNameClass
{
WorkspaceFactoryProgID = "esriDataSourcesGDB.FileGDBWorkspaceFactory",
PathName = @"D:\Data\Public.gdb"
};
IName targetWorkspaceIName = (IName)targetWorkspaceName;
IWorkspace targetWorkspace = (IWorkspace)targetWorkspaceIName.Open(); // Create a name object for the source dataset.
IFeatureClassName sourceFeatureClassName = new FeatureClassNameClass();
IDatasetName sourceDatasetName = (IDatasetName)sourceFeatureClassName;
sourceDatasetName.Name = "BOUNT_arc";
sourceDatasetName.WorkspaceName = sourceWorkspaceName; // Create a name object for the target dataset.
IFeatureClassName targetFeatureClassName = new FeatureClassNameClass();
IDatasetName targetDatasetName = (IDatasetName)targetFeatureClassName;
targetDatasetName.Name = "BOUNT_arc";
targetDatasetName.WorkspaceName = targetWorkspaceName; // Open source feature class to get field definitions.
IName sourceName = (IName)sourceFeatureClassName;
IFeatureClass sourceFeatureClass = (IFeatureClass)sourceName.Open(); // Create the objects and references necessary for field validation.
IFieldChecker fieldChecker = new FieldCheckerClass();
IFields sourceFields = sourceFeatureClass.Fields;
IFields targetFields = null;
IEnumFieldError enumFieldError = null; // Set the required properties for the IFieldChecker interface.
fieldChecker.InputWorkspace = sourceWorkspace;
fieldChecker.ValidateWorkspace = targetWorkspace; // Validate the fields and check for errors.
fieldChecker.Validate(sourceFields, out enumFieldError, out targetFields);
if (enumFieldError != null)
{
// Handle the errors in a way appropriate to your application.
MessageBox.Show("Errors were encountered during field validation.");
} // Find the shape field. String shapeFieldName = sourceFeatureClass.ShapeFieldName;
int shapeFieldIndex = sourceFeatureClass.FindField(shapeFieldName);
IField shapeField = sourceFields.get_Field(shapeFieldIndex); // Get the geometry definition from the shape field and clone it.
IGeometryDef geometryDef = shapeField.GeometryDef;
IClone geometryDefClone = (IClone)geometryDef;
IClone targetGeometryDefClone = geometryDefClone.Clone();
IGeometryDef targetGeometryDef = (IGeometryDef)targetGeometryDefClone; // Cast the IGeometryDef to the IGeometryDefEdit interface.
IGeometryDefEdit targetGeometryDefEdit = (IGeometryDefEdit)targetGeometryDef;
// Set the IGeometryDefEdit properties.
targetGeometryDefEdit.GridCount_2 = ;
targetGeometryDefEdit.set_GridSize(, 0.75); IFeatureDataConverter featureDataConverter = new FeatureDataConverterClass();
IEnumInvalidObject enumInvalidObject = featureDataConverter.ConvertFeatureClass
(sourceFeatureClassName, null, null, targetFeatureClassName,
targetGeometryDef, targetFields, "", , ); // Check for errors.
IInvalidObjectInfo invalidObjectInfo = null; enumInvalidObject.Reset(); }
2.合并,在ArcGIS中采用Python:
可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/esrichinacd/article/details/14146653
最后需要注意的地方是:在10.2的ArcMap中执行时会如下错误
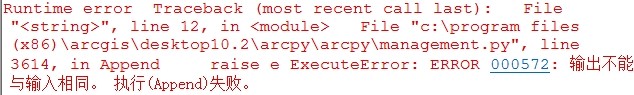
我也是检查了好长时间,原因是10.2的ArcMap中执行结果会自动添加到ArcMap中,即使右键取消“添加至结果”也不行。(导致了第二次循环的时候合并的数据是结果集相同的数据的合并,所以会报上面错误)
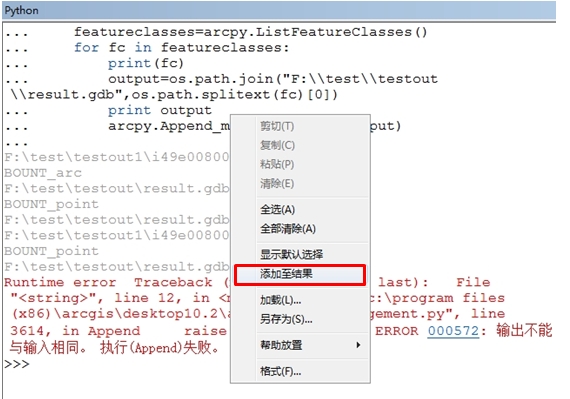
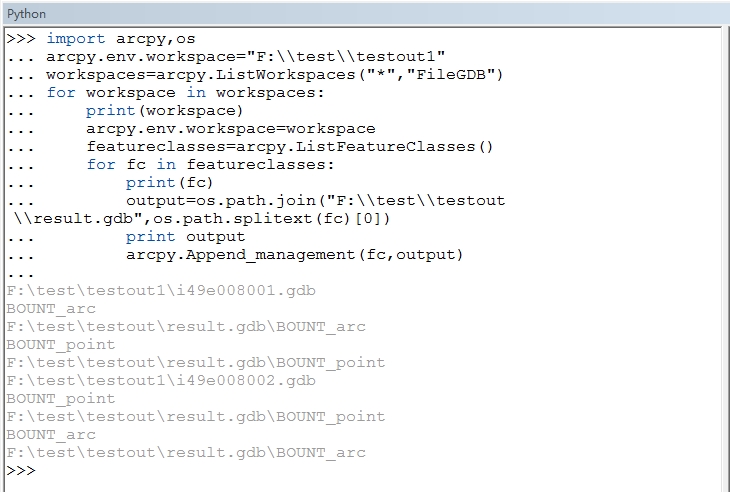
所以这里,我们执行的时候可以到ArcCatalog中执行python脚本:
不同gdb,相同数据集合并的更多相关文章
- R语言数据集合并、数据增减、不等长合并
每每以为攀得众山小,可.每每又切实来到起点,大牛们,缓缓脚步来俺笔记葩分享一下吧,please~ --------------------------- 数据选取与简单操作: which 返回一个向量 ...
- hadoop小文件合并
1.背景 在实际项目中,输入数据往往是由许多小文件组成,这里的小文件是指小于HDFS系统Block大小的文件(默认128M), 然而每一个存储在HDFS中的文件.目录和块都映射为一个对象,存储在Nam ...
- R︱高效数据操作——data.table包(实战心得、dplyr对比、key灵活用法、数据合并)
每每以为攀得众山小,可.每每又切实来到起点,大牛们,缓缓脚步来俺笔记葩分享一下吧,please~ --------------------------- 由于业务中接触的数据量很大,于是不得不转战开始 ...
- SAS︱数据索引、数据集常用操作(set、where、merge、append)
代码部分大多来源于姚志勇老师的<SAS编程与数据挖掘商业案例>. 每每以为攀得众山小,可.每每又切实来到起点,大牛们,缓缓脚步来俺笔记葩分享一下吧,please~ ------------ ...
- Hadoop实战项目:小文件合并
项目背景 在实际项目中,输入数据往往是由许多小文件组成,这里的小文件是指小于HDFS系统Block大小的文件(默认128M),早期的版本所定义的小文件是64M,这里的hadoop-2.2.0所定义的小 ...
- spark系列-2、Spark 核心数据结构:弹性分布式数据集 RDD
一.RDD(弹性分布式数据集) RDD 是 Spark 最核心的数据结构,RDD(Resilient Distributed Dataset)全称为弹性分布式数据集,是 Spark 对数据的核心抽象, ...
- Atitit 数据存储视图的最佳实际best practice attilax总结
Atitit 数据存储视图的最佳实际best practice attilax总结 1.1. 视图优点:可读性的提升1 1.2. 结论 本着可读性优先于性能的原则,面向人类编程优先于面向机器编程,应 ...
- Webform Application传值 ViewState
Application:所有的会话共享一个Application空间,任何一个人改变Application的内容,其他人都会发现被改变了.Application中的内容不会被自动释放 存放位置:服务端 ...
- ASP.Net WebForm温故知新学习笔记:二、ViewState与UpdatePanel探秘
开篇:经历了上一篇<aspx与服务器控件探秘>后,我们了解了aspx和服务器控件背后的故事.这篇我们开始走进WebForm状态保持的一大法宝—ViewState,对其刨根究底一下.然后,再 ...
随机推荐
- 海康威视 NET_DVR_FindFile NET_DVR_PlayBackByTime 尝试读取或写入受保护的内存,这通常指示其他内存已损坏
从农民伯伯那下载的代码 NET_DVR_PlayBackByTime NET_DVR_FindFile 这两个方法执行不了 下面是我改的 经过测试了 [DllImport("HCNetSDK ...
- 使用Nginx负载均衡搭建高性能.NETweb应用程序一
一.遇到的问题 当我们用IIS服务器部署了一个web应用以后,当很多用户高并发访问的时候,客户端响应就会很慢,客户的体验就会很差,由于IIS接受到客户端请求的 时候,就会创建一个线程,当线程达到几千个 ...
- cache 浅析
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26817832-id-3244916.html 1. Cache Cache一词来源于法语,其原意是"藏匿处,隐秘的地方&q ...
- OpenCV相机标定和姿态更新
原帖地址: http://blog.csdn.net/aptx704610875/article/details/48914043 http://blog.csdn.net/aptx704610875 ...
- 用thinkphp写的一个例子:抓取网站的内容并且保存到本地
我需要写这么一个例子,到电子课本网下载一本电子书. 电子课本网的电子书,是把书的每一页当成一个图片,然后一本书就是有很多张图片,我需要批量的进行下载图片操作. 下面是代码部分: public func ...
- 【linux】修改文件所属用户和组
使用chown命令可以修改文件或目录所属的用户: 命令:chown 用户 目录或文件名 例如:chown qq /home/qq (把home目录下的qq目录的拥有者改为qq用户) 使用chgrp命 ...
- asp.net 后台实现删除,划掉效果
效果: name = "<S>" + fircon + "</br>" + "</S>"; 增加“< ...
- javascript - 简单实现一个图片延迟加载的jQuery插件
最近在看一本书<Third-Party Javascript>很不错,推荐给大家,下载地址各位自己搜索了. 步骤: 1.打开google,鉴于google基本打不开,那么就打开这个网址吧. ...
- WPF操作ini 文件的读写示例
/// <summary> /// IniFiles 的摘要说明. /// 示例文件路径:C:\file.ini /// [Server] //[*] 表示缓存区 /// name=loc ...
- 【网络——Linux】——IPMI详细介绍【转】
一.IPMI含义 智能平台管理接口(IPMI:Intelligent Platform Management Interface)是一项应用于服务器管理系统设计的标准,由Intel.HP.Dell和N ...
