JpaRepository 增删改查
Jpa查询
JpaRepository简单查询
基本查询也分为两种,一种是spring data默认已经实现,一种是根据查询的方法来自动解析成SQL。
预先生成方法
spring data jpa 默认预先生成了一些基本的CURD的方法,例如:增、删、改等等
继承JpaRepository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}
使用默认方法
@Test
public void testBaseQuery() throws Exception {
User user=new User();
userRepository.findAll();
userRepository.findOne(1l);
userRepository.save(user);
userRepository.delete(user);
userRepository.count();
userRepository.exists(1l);
// ...
}
自定义的简单查询就是根据方法名来自动生成SQL,主要的语法是findXXBy,readAXXBy,queryXXBy,countXXBy, getXXBy后面跟属性名称:
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
Keyword Sample JPQL snippet And findByLastnameAndFirstname … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 Or findByLastnameOrFirstname … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 Is,Equals findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals … where x.firstname = ?1 Between findByStartDateBetween … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 LessThan findByAgeLessThan … where x.age < ?1 LessThanEqual findByAgeLessThanEqual … where x.age ⇐ ?1 GreaterThan findByAgeGreaterThan … where x.age > ?1 GreaterThanEqual findByAgeGreaterThanEqual … where x.age >= ?1 After findByStartDateAfter … where x.startDate > ?1 Before findByStartDateBefore … where x.startDate < ?1 IsNull findByAgeIsNull … where x.age is null IsNotNull,NotNull findByAge(Is)NotNull … where x.age not null Like findByFirstnameLike … where x.firstname like ?1 NotLike findByFirstnameNotLike … where x.firstname not like ?1 StartingWith findByFirstnameStartingWith … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) EndingWith findByFirstnameEndingWith … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) Containing findByFirstnameContaining … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) OrderBy findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc Not findByLastnameNot … where x.lastname <> ?1 In findByAgeIn(Collection ages) … where x.age in ?1 NotIn findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) … where x.age not in ?1 TRUE findByActiveTrue() … where x.active = true FALSE findByActiveFalse() … where x.active = false IgnoreCase findByFirstnameIgnoreCase … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1)
按照Spring Data的规范,查询方法以find | read | get 开头,涉及查询条件时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,
要注意的是:条件属性以首字母大写。
示例:
例如:定义一个Entity实体类:
class People{
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
}
以上使用and条件查询时,应这样写:
findByLastNameAndFirstName(String lastName,String firstName);
注意:条件的属性名称与个数要与参数的位置与个数一一对应
JpaRepository查询方法解析流程
JPA方法名解析流程
Spring Data JPA框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,比如find、findBy、read、readBy、get、getBy,然后对剩下部分进行解析。
假如创建如下的查询:findByUserDepUuid(),框架在解析该方法时,首先剔除findBy,然后对剩下的属性进行解析,假设查询实体为Doc。
-- 1.先判断userDepUuid (根据POJO(Plain Ordinary Java Object简单java对象,实际就是普通java bean)规范,首字母变为小写。)是否是查询实体的一个属性,
如果根据该属性进行查询;如果没有该属性,继续第二步。
-- 2.从右往左截取第一个大写字母开头的字符串(此处为Uuid),然后检查剩下的字符串是否为查询实体的一个属性,如果是,则表示根据该属性进行查询;如果没有该属性,则重复第二步,继续从右往左截取;最后假设 user为查询实体的一个属性。
-- 3.接着处理剩下部分(DepUuid),先判断 user 所对应的类型是否有depUuid属性,如果有,则表示该方法最终是根据 “ Doc.user.depUuid” 的取值进行查询;否则继续按照步骤 2 的规则从右往左截取,最终表示根据 “Doc.user.dep.uuid” 的值进行查询。
-- 4.可能会存在一种特殊情况,比如 Doc包含一个 user 的属性,也有一个 userDep 属性,此时会存在混淆。可以明确在属性之间加上 "_" 以显式表达意图,比如 "findByUser_DepUuid()" 或者 "findByUserDep_uuid()"。
特殊的参数(分页或排序):
还可以直接在方法的参数上加入分页或排序的参数,比如:
Page<UserModel> findByName(String name, Pageable pageable);
List<UserModel> findByName(String name, Sort sort);
Pageable是spring封装的分页实现类,使用的时候需要传入页数、每页条数和排序规则
@Test
public void testPageQuery() throws Exception {
int page=1,size=10;
Sort sort = new Sort(Direction.DESC, "id");
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(page, size, sort);
userRepository.findALL(pageable);
userRepository.findByUserName("testName", pageable);
}
使用JPA的NamedQueries
方法如下:
1:在实体类上使用@NamedQuery,示例如下:
@NamedQuery(name = "UserModel.findByAge",query = "select o from UserModel o where o.age >= ?1")
2:在自己实现的DAO的Repository接口里面定义一个同名的方法,示例如下:
public List<UserModel> findByAge(int age);
3:然后就可以使用了,Spring会先找是否有同名的NamedQuery,如果有,那么就不会按照接口定义的方法来解析。
使用@Query来指定本地查询
只要设置nativeQuery为true,比如:
@Query(value="select * from tbl_user where name like %?1" ,nativeQuery=true)
public List<UserModel> findByUuidOrAge(String name);
注意:当前版本的本地查询不支持翻页和动态的排序
使用命名化参数
使用@Param即可,比如:
@Query(value="select o from UserModel o where o.name like %:nn")
public List<UserModel> findByUuidOrAge(@Param("nn") String name);
创建查询的顺序
Spring Data JPA 在为接口创建代理对象时,如果发现同时存在多种上述情况可用,它该优先采用哪种策略呢?
<jpa:repositories> 提供了query-lookup-strategy 属性,用以指定查找的顺序。它有如下三个取值:
1:create-if-not-found:
如果方法通过@Query指定了查询语句,则使用该语句实现查询;
如果没有,则查找是否定义了符合条件的命名查询,如果找到,则使用该命名查询;
如果两者都没有找到,则通过解析方法名字来创建查询。
这是querylookup-strategy 属性的默认值
2:create:通过解析方法名字来创建查询。
即使有符合的命名查询,或者方法通过@Query指定的查询语句,都将会被忽略
3:use-declared-query:
如果方法通过@Query指定了查询语句,则使用该语句实现查询;
如果没有,则查找是否定义了符合条件的命名查询,如果找到,则使用该
命名查询;如果两者都没有找到,则抛出异常
JpaRepository限制查询
有时候我们只需要查询前N个元素,或者支取前一个实体。
User findFirstByOrderByLastnameAsc();
User findTopByOrderByAgeDesc();
Page<User> queryFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
List<User> findFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Sort sort);
List<User> findTop10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
JpaRepository多表查询
多表查询在spring data jpa中有两种实现方式,第一种是利用hibernate的级联查询来实现,第二种是创建一个结果集的接口来接收连表查询后的结果,这里主要第二种方式。
- 首先需要定义一个结果集的接口类。
public interface HotelSummary {
City getCity();
String getName();
Double getAverageRating();
default Integer getAverageRatingRounded() {
return getAverageRating() == null ? null : (int) Math.round(getAverageRating());
}
}
- 查询的方法返回类型设置为新创建的接口
@Query("select h.city as city, h.name as name, avg(r.rating) as averageRating "
+ "from Hotel h left outer join h.reviews r where h.city = ?1 group by h")
Page<HotelSummary> findByCity(City city, Pageable pageable);
@Query("select h.name as name, avg(r.rating) as averageRating "
+ "from Hotel h left outer join h.reviews r group by h")
Page<HotelSummary> findByCity(Pageable pageable);
- 使用
Page<HotelSummary> hotels = this.hotelRepository.findByCity(new PageRequest(0, 10, Direction.ASC, "name"));
for(HotelSummary summay:hotels){
System.out.println("Name" +summay.getName());
}
在运行中Spring会给接口(HotelSummary)自动生产一个代理类来接收返回的结果,代码汇总使用getXX的形式来获取
JPA更新
支持更新类的Query语句
添加@Modifying即可,比如:
@Modifying
@Query(value="update UserModel o set o.name=:newName where o.name like %:nn")
public int findByUuidOrAge(@Param("nn") String name,@Param("newName") String newName);
注意:
1:方法的返回值应该是int,表示更新语句所影响的行数
2:在调用的地方必须加事务,没有事务不能正常执行
JPA删除
SQL方式-删除
@Query(value = "delete from r_upa where user_id= ?1 and point_indecs_id in (?2)", nativeQuery = true)
@Modifying
void deleteByUserAndPointIndecs(Long uid, List<Long> hids);
注意:
执行delete和update语句一样,需要添加@Modifying注解,使用时在Repository或者更上层需要@Transactional注解。
函数(delete)方式-删除
直接可以使用delete(id),依据id来删除一条数据
也可以使用deleteByName(String name)时,需要添加@Transactional注解,才能使用
Spring Data JPA的deleteByXXXX,是先select,在整个Transaction完了之后才执行delete
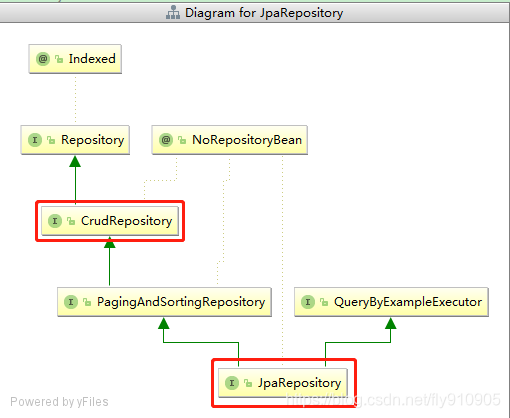
JpaRepository
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
/**
* Deletes the given entities in a batch which means it will create a single {@link Query}. Assume that we will clear
* the {@link javax.persistence.EntityManager} after the call.
*
* @param entities
* 批量解绑多个,优势:只会形成一个SQL语句
*/
void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);
/**
* Deletes all entities in a batch call.
*/
void deleteAllInBatch();
}
CrudRepository
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
/**
* Deletes the entity with the given id.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
void deleteById(ID id);
/**
* Deletes a given entity.
*
* @param entity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
void delete(T entity);
/**
* Deletes the given entities.
*
* @param entities
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@link Iterable} is {@literal null}.
*/
void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
/**
* Deletes all entities managed by the repository.
*/
void deleteAll();
}
JPA添加
利用JpaRepository和CrudRepository中的 save操作
JpaRepository
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository#save(java.lang.Iterable)
*/
<S extends T> List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);
/**
* Flushes all pending changes to the database.
*/
void flush();
/**
* Saves an entity and flushes changes instantly.
*
* @param entity
* @return the saved entity
*/
<S extends T> S saveAndFlush(S entity);
}
CrudRepository
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
/**
* Saves a given entity. Use the returned instance for further operations as the save operation might have changed the
* entity instance completely.
*
* @param entity must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the saved entity will never be {@literal null}.
*/
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
/**
* Saves all given entities.
*
* @param entities must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the saved entities will never be {@literal null}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
<S extends T> Iterable<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);
}
JpaRepository和CrudRepository 的区别
JpaRepository 中的save方法实现源码:
@Transactional
public <S extends T> List<S> save(Iterable<S> entities) {
List<S> result = new ArrayList<S>();
if (entities == null) {
return result;
}
for (S entity : entities) {
result.add(save(entity));
}
return result;
}
CrudRepository 中的save方法源代码
@Transactional
public <S extends T> S save(S entity) {
if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) {
em.persist(entity);//是新的就插入
return entity;
} else {
return em.merge(entity); //不是新的merge
}
}
由源码可知CrudRepository 中的save方法是相当于merge+save ,它会先判断记录是否存在,如果存在则更新,不存在则插入记录
JpaRepository 增删改查的更多相关文章
- springboot(十五):springboot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查示例
这篇文章介绍如何使用jpa和thymeleaf做一个增删改查的示例. 先和大家聊聊我为什么喜欢写这种脚手架的项目,在我学习一门新技术的时候,总是想快速的搭建起一个demo来试试它的效果,越简单越容易上 ...
- springboot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查的示例(转)
这篇文章介绍如何使用jpa和thymeleaf做一个增删改查的示例. 先和大家聊聊我为什么喜欢写这种脚手架的项目,在我学习一门新技术的时候,总是想快速的搭建起一个demo来试试它的效果,越简单越容易上 ...
- sssp-springmvc+spring+spring-data-jpa增删改查
环境:IDE:eclipse.jdk1.7.mysql5.7.maven 项目结构图 上面目录结构你可以自己创建 搭建框架 首先加入maven依赖包以及相关插件 <dependencies> ...
- spring-data-rest的魔力 10分钟实现增删改查
目录 创建项目 启动项目 添加person 查看person 及 person 列表 条件查询 分页查询 controller 去哪里了 自定义 spring-data-rest 魔力之外的contr ...
- (转)Spring Boot (十五): Spring Boot + Jpa + Thymeleaf 增删改查示例
http://www.ityouknow.com/springboot/2017/09/23/spring-boot-jpa-thymeleaf-curd.html 这篇文章介绍如何使用 Jpa 和 ...
- spring boot2+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查例子
参考这遍文章做了一个例子,稍微不同之处,原文是spring boot.mysql,这里改成了spring boot 2.Oracle. 一.pom.xml引入相关模块web.jpa.thymeleaf ...
- Spring Boot + Jpa + Thymeleaf 增删改查示例
快速上手 配置文件 pom 包配置 pom 包里面添加 Jpa 和 Thymeleaf 的相关包引用 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframe ...
- SpringBoot JPA + H2增删改查示例
下面的例子是基于SpringBoot JPA以及H2数据库来实现的,下面就开始搭建项目吧. 首先看下项目的整体结构: 具体操作步骤: 打开IDEA,创建一个新的Spring Initializr项目, ...
- Spring Boot(十五):spring boot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查示例
Spring Boot(十五):spring boot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查示例 一.快速上手 1,配置文件 (1)pom包配置 pom包里面添加jpa和thymeleaf的相关包引用 ...
随机推荐
- [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(3) ----- DataParallel(下)
[源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(3) ----- DataParallel(下) 目录 [源码解析] PyTorch 分布式(3) ----- DataParallel(下) 0x00 摘要 0 ...
- 设计模式学习-使用go实现装饰模式
装饰器模式 定义 代码实现 优点 缺点 适用范围 装饰器模式和桥接模式的区别 参考 装饰器模式 定义 装饰模式:动态的给一些对象添加额外的职责,就增加功能来说,装饰模式比生成子类更灵活. 举个栗子: ...
- 关于Python中用户输入字符串(与变量名相同)无法作为变量名引用的理解以及解决方案
在用户登录账号时,我需要在字典中查找是否存在其账号名称以及密码是否正确. 所以,我想将用户输入的账号赋值给变量,在字典中查找是否有此指值. 代码如下: 1 Ya = {'姓名': 'Ya', 'pas ...
- 自由导入你的增量数据-根据条件将sqlserver表批量生成INSERT语句的存储过程实施笔记
文章标题: 自由导入你的增量数据-根据条件将sqlserver表批量生成INSERT语句的存储过程增强版 关键字 : mssql-scripter,SQL Server 文章分类: 技术分享 创建时间 ...
- go微服务框架Kratos笔记(六)链路追踪实战
什么是链路追踪 借用阿里云链路追踪文档来解释 分布式链路追踪(Distributed Tracing),也叫 分布式链路跟踪,分布式跟踪,分布式追踪 等等,它为分布式应用的开发者提供了完整的调用链路还 ...
- js 函数和函数的参数
/* * 函数 function * - 函数也是一个对象 * - 函数中可以封装一些功能(代码),在需要时可以执行这些功能(代码) * - 函数中可以保存一些代码在需要的时候 ...
- [hdu7099]Just Another Data Structure Problem
不难发现,问题即求满足以下条件的$(i,j)$对数: 1.$1\le i<j\le n$且$a_{i}=a_{j}$ 2.$\min_{i\le k\le j}y_{k}\ge l$且$\max ...
- char数据可以放入int[]中会自动转换
int[] ary ={'b','c','a','d','e','f'};System.out.println(ary[0]);//98String str = new String(ary, 2, ...
- 多线程05.thread不知道的知识
Thread thread = new Thread(); // init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0); //init( ...
- Trie树(字典树,单词查找树)详解+题目
什么是字典树? 叫前缀树更容易理解 字典树的样子 Trie又被称为前缀树.字典树,所以当然是一棵树.上面这棵Trie树包含的字符串集合是{in, inn, int, tea, ten, to}.每个节 ...
