cs224d 自然语言处理作业 problem set3 (一) 实现Recursive Nerual Net Work 递归神经网络
1、Recursive Nerual Networks能够更好地体现每个词与词之间语法上的联系
这里我们选取的损失函数仍然是交叉熵函数
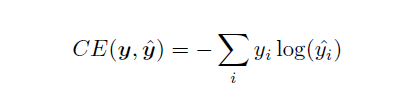
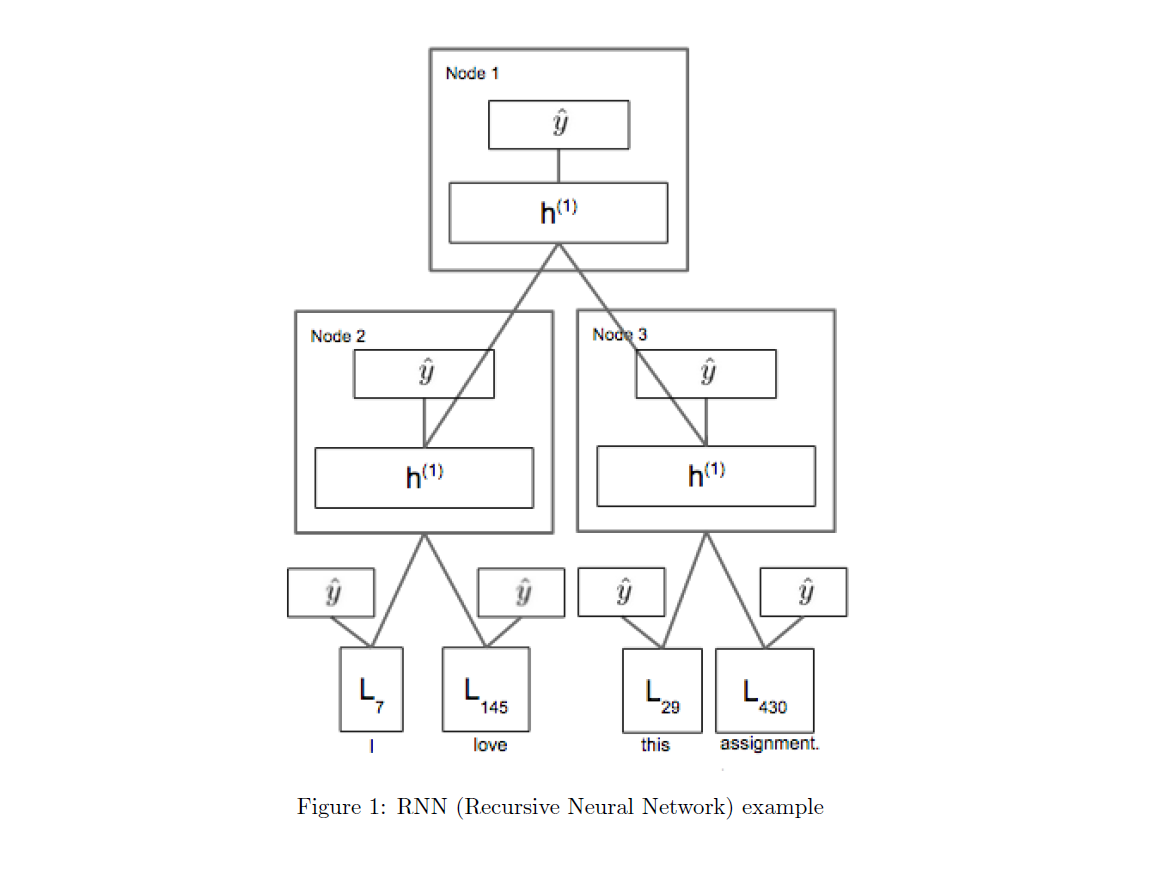
2、整个网络的结构如下图所示:
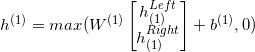

每个参数的更新时的梯队值如何计算,稍后再给大家计算相应的数学公式
这里先列出节点的合并规则
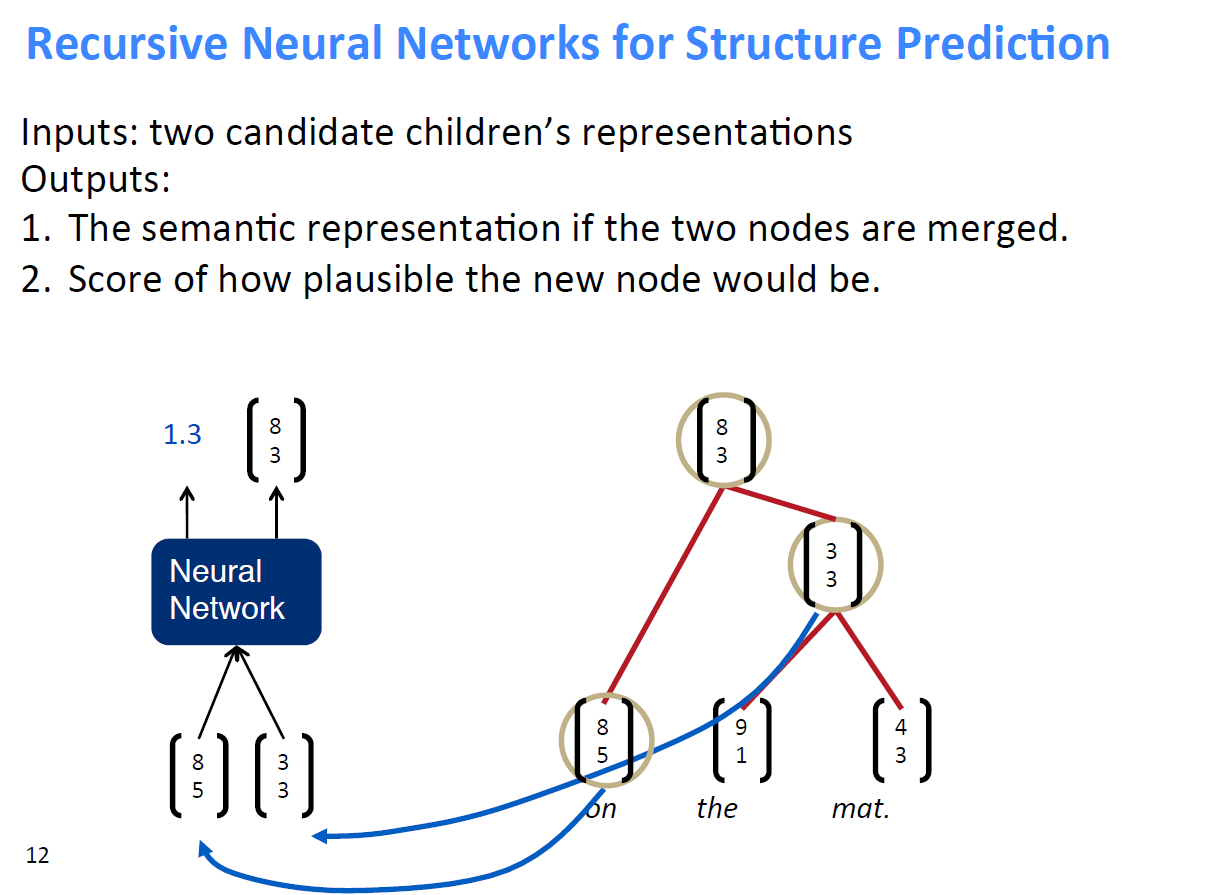

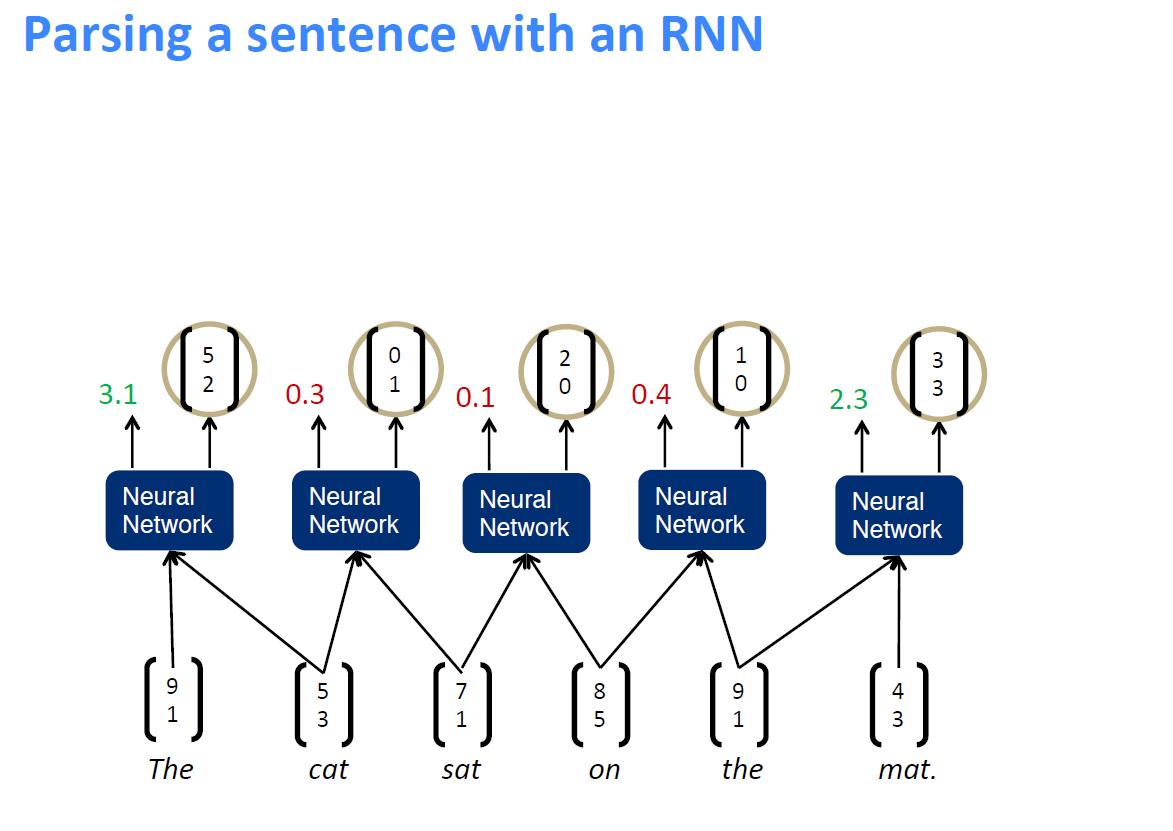
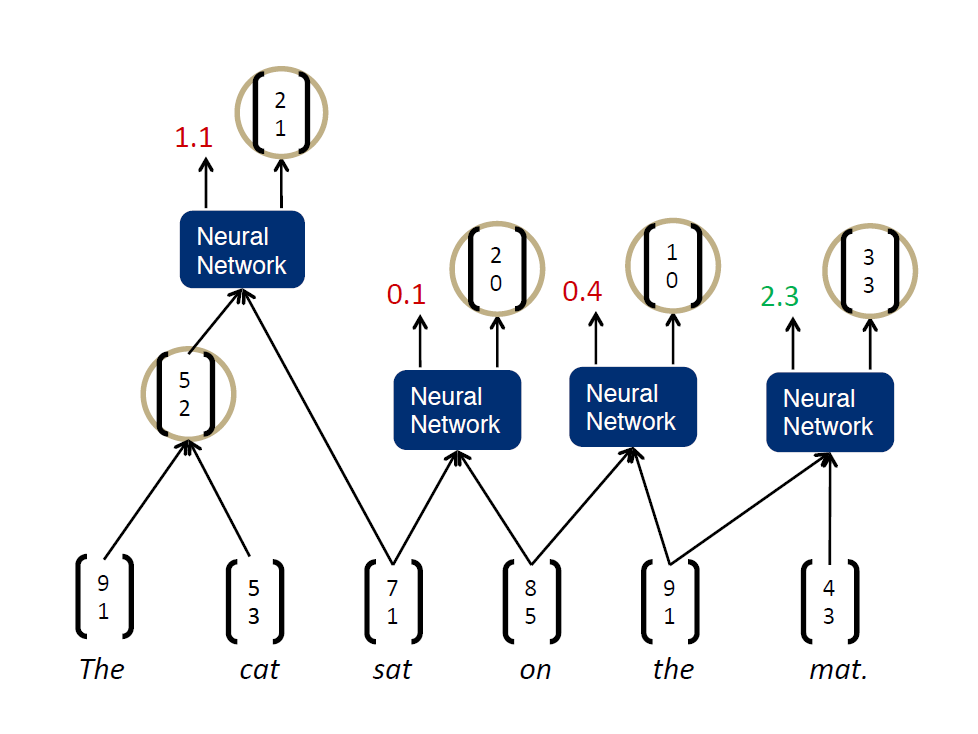
1、即假设将一句话中的词先两个合并,并通过神经网络计算出合并后的得分情况
2、然后找出合并后得分最高的两个词进行真正的合并,得到新的节点,其余节点不合并
3、将得到的新节点加入到下一轮两两合并的计算过程中,直至得到最终节点
下面是计算的代码:
'''
Created on 2017年10月5日 @author: weizhen
'''
# 一个简单的递归神经网络的实现,有着一个ReLU层和一个softmax层
# TODO : 必须要更新前向和后向传递函数
# 你可以通过执行 python rnn.py 方法来执行一个梯度检验
# 插入pdb.set_trace() 在你不确定将会发生什么的地方 import numpy as np
import collections
import pdb
import tree as treeM
import pickle class RNN: def __init__(self, wvecDim, outputDim, numWords, mbSize=30, rho=1e-4):
self.wvecDim = wvecDim
self.outputDim = outputDim
self.numWords = numWords
self.mbSize = mbSize
self.defaultVec = lambda : np.zeros((wvecDim,))
self.rho = rho def initParams(self):
np.random.seed(12341) # Word vectors
self.L = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.wvecDim, self.numWords) # Hidden layer parameters
self.W = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.wvecDim, 2 * self.wvecDim)
self.b = np.zeros((self.wvecDim)) # Softmax weights
# note this is " U "in the notes and the handout...
# there is a reason for the change in notation
self.Ws = 0.01 * np.random.randn(self.outputDim, self.wvecDim)
self.bs = np.zeros((self.outputDim)) self.stack = [self.L, self.W, self.b, self.Ws, self.bs] # Gradients
self.dW = np.empty(self.W.shape)
self.db = np.empty((self.wvecDim))
self.dWs = np.empty(self.Ws.shape)
self.dbs = np.empty((self.outputDim)) def costAndGrad(self, mbdata, test=False):
"""
每一个datum在minibatch里边都是一个树
前向计算每一个树,反向传播到每一个树
返回值:
cost:
梯度:w.r.t W,Ws,b,bs
以上变量的梯度都是在稀疏形式存储的
或者是以测试状态下的
Returns:
cost,correctArray,guessArray,total
"""
cost = 0.0
correct = []
guess = []
total = 0.0 self.L, self.W, self.b, self.Ws, self.bs = self.stack
# 初始化所有梯度都是0
self.dW[:] = 0
self.db[:] = 0
self.dWs[:] = 0
self.dbs[:] = 0
self.dL = collections.defaultdict(self.defaultVec) # 在每一个batch中前向计算每一个tree
for tree in mbdata:
c, tot = self.forwardProp(tree.root, correct, guess)
cost += c
total += tot
if test:
return (1. / len(mbdata)) * cost, correct, guess, total # 在每一个batch上进行反向传播
for tree in mbdata:
self.backProp(tree.root) # 通过mb的大小来计算损失和梯度
scale = (1. / self.mbSize)
for v in self.dL.values():
v *= scale # 添加L2正则化项
cost += (self.rho / 2) * np.sum(self.W ** 2)
cost += (self.rho / 2) * np.sum(self.Ws ** 2) return scale * cost, [self.dL, scale * (self.dW + self.rho * self.W), scale * self.db, scale * (self.dWs + self.rho * self.Ws), scale * self.dbs] def forwardProp(self, node, correct=[], guess=[]):
"""损失应该是一个不断更新的变量,总损失是我们需要用在准确率报告里边的数据"""
cost = total = 0.0
# 下面实现递归神经网络前向传播的函数
# 你应该更新 node.probs, node.hActsl,node.fprop,and cost
# node :你当前节点是在语法树上的
# correct : 这是一个不断更新的标记真值的列表
# guess: 这是一个不断更新的猜测我们的模型会预测为哪一个结果的列表
# (我们会同时使用正确的和猜测的值来构造我们的混淆矩阵)
L = self.L
# 隐藏层的参数
W = self.W
b = self.b # Softmax 权重
Ws = self.Ws
bs = self.bs if node.isLeaf:
node.hActsl = L[:, node.word]
else:
if not node.left.fprop:
cost_left, total_left = self.forwardProp(node.left, correct, guess)
cost += cost_left
total += total_left
if not node.right.fprop:
cost_right, total_right = self.forwardProp(node.right, correct, guess)
cost += cost_right
total += total_right node.hActsl = W.dot(np.hstack((node.left.hActsl, node.right.hActsl))) + b
node.hActsl[node.hActsl < 0] = 0 x = Ws.dot(node.hActsl) + bs
x -= np.max(x)
node.probs = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x)) correct += [node.label]
guess += [np.argmax(node.probs)] cost -= np.log(node.probs[node.label]) node.fprop = True return cost, total + 1 def backProp(self, node, error=None):
"""
实现递归神经网络的反向传播函数
应该更新 self.dWs, self.dbs, self.dW, self.db, and self.dL[node.word] 相关地
node:你在语法树种的当前节点
error:误差从之前一个迭代过程中传递进来的
"""
# 清空节点
node.fprop = False L = self.L
# 隐藏节点的参数
W = self.W
b = self.b # Softmax层的权重
Ws = self.Ws
bs = self.bs error_this = node.probs
error_this[node.label] -= 1.0
delta = Ws.T.dot(error_this) self.dWs += np.outer(error_this, node.hActsl)
self.dbs += error_this if error is not None:
delta += error delta[node.hActsl == 0] = 0 if node.isLeaf:
self.dL[node.word] += delta
else:
self.dW += np.outer(delta, np.hstack([node.left.hActsl, node.right.hActsl]))
self.db += delta delta = np.dot(self.W.T, delta)
self.backProp(node.left, delta[:self.wvecDim])
self.backProp(node.right, delta[self.wvecDim:]) def updateParams(self, scale, update, log=False):
"""
如下这样更新参数
p:=p-scale*update
如果log是真的,输出根节点的均方误差,并且更新根节点的值
"""
if log:
for P, dP in zip(self.stack[1:], update[1:]):
pRMS = np.sqrt(np.mean(P ** 2))
dpRMS = np.sqrt(np.mean((scale * dP) ** 2))
print("weight rms=%f -- update rms=%f" % (pRMS, dpRMS))
self.stack[1:] = [P + scale * dP for P, dP in zip(self.stack[1:], update[1:])] # 解决词典并且进行稀疏的更新
dL = update[0]
for j in dL.iterkeys():
self.L[:, j] += scale.dL[j] def toFile(self, fid):
pickle.dump(self.stack, fid) def fromFile(self, fid):
self.stack = pickle.load(fid) def check_grad(self, data, epsilon=1e-6):
cost, grad = self.costAndGrad(data) err1 = 0.0
count = 0.0
print("Checking dW...")
for W, dW in zip(self.stack[1:], grad[1:]):
W = W[..., None]
dW = dW[..., None]
for i in range(W.shape[0]):
for j in range(W.shape[1]):
W[i, j] += epsilon
costP, _ = self.costAndGrad(data)
W[i, j] -= epsilon
numGrad = (costP - cost) / epsilon
err = np.abs(dW[i, j] - numGrad)
err1 += err
count += 1
if 0.001 > err1 / count:
print("Grad Check Passed for dW")
else:
print("Grad Check Failed for dW:Sum of Error=%.9f" % (err1 / count)) # check dL separately since dict
dL = grad[0]
L = self.stack[0]
err2 = 0.0
count = 0.0
print("Checking dL...")
for j in dL.keys():
for i in range(L.shape[0]):
L[i, j] += epsilon
costP, _ = self.costAndGrad(data)
L[i, j] -= epsilon
numGrad = (costP - cost) / epsilon
err = np.abs(dL[j][i] - numGrad)
err2 += err
count += 1
if 0.001 > err2 / count:
print("Grad Check Passed for dL")
else:
print("Grad Check Failed for dL: Sum of Error = %.9f" % (err2 / count)) if __name__ == '__main__': train = treeM.loadTrees()
numW = len(treeM.loadWordMap()) wvecDim = 10
outputDim = 5 rnn = RNN(wvecDim, outputDim, numW, mbSize=4)
rnn.initParams() mbData = train[:4]
print("Numerical gradient check...")
rnn.check_grad(mbData)
下面部分是构造节点的python文件tree.py
在进行计算时需要先运行tree.py文件进行tree结构的生成,然后进行合并计算
import collections
import pickle
UNK = 'UNK'
# This file contains the dataset in a useful way. We populate a list of Trees to train/test our Neural Nets such that each Tree contains any number of Node objects. # The best way to get a feel for how these objects are used in the program is to drop pdb.set_trace() in a few places throughout the codebase
# to see how the trees are used.. look where loadtrees() is called etc.. class Node: # a node in the tree
def __init__(self,label,word=None):
self.label = label
self.word = word # NOT a word vector, but index into L.. i.e. wvec = L[:,node.word]
self.parent = None # reference to parent
self.left = None # reference to left child
self.right = None # reference to right child
self.isLeaf = False # true if I am a leaf (could have probably derived this from if I have a word)
self.fprop = False # true if we have finished performing fowardprop on this node (note, there are many ways to implement the recursion.. some might not require this flag)
self.hActs1 = None # h1 from the handout
self.hActs2 = None # h2 from the handout (only used for RNN2)
self.probs = None # yhat class Tree: def __init__(self,treeString,openChar='(',closeChar=')'):
tokens = []
self.open = '('
self.close = ')'
for toks in treeString.strip().split():
tokens += list(toks)
self.root = self.parse(tokens) def parse(self, tokens, parent=None):
assert tokens[0] == self.open, "Malformed tree"
assert tokens[-1] == self.close, "Malformed tree" split = 2 # position after open and label
countOpen = countClose = 0 if tokens[split] == self.open:
countOpen += 1
split += 1
# Find where left child and right child split
while countOpen != countClose:
if tokens[split] == self.open:
countOpen += 1
if tokens[split] == self.close:
countClose += 1
split += 1 # New node
node = Node(int(tokens[1])) # zero index labels node.parent = parent # leaf Node
if countOpen == 0:
node.word = ''.join(tokens[2:-1]).lower() # lower case?
node.isLeaf = True
return node node.left = self.parse(tokens[2:split],parent=node)
node.right = self.parse(tokens[split:-1],parent=node) return node def leftTraverse(root,nodeFn=None,args=None):
"""
Recursive function traverses tree
from left to right.
Calls nodeFn at each node
"""
nodeFn(root,args)
if root.left is not None:
leftTraverse(root.left,nodeFn,args)
if root.right is not None:
leftTraverse(root.right,nodeFn,args) def countWords(node,words):
if node.isLeaf:
words[node.word] += 1 def clearFprop(node,words):
node.fprop = False def mapWords(node,wordMap):
if node.isLeaf:
if node.word not in wordMap:
node.word = wordMap[UNK]
else:
node.word = wordMap[node.word] def loadWordMap():
with open('wordMap.bin','rb') as fid:
return pickle.load(fid) def buildWordMap():
"""
Builds map of all words in training set
to integer values.
""" file = 'trees/train.txt'
print("Reading trees to build word map..")
with open(file,'r') as fid:
trees = [Tree(l) for l in fid.readlines()] print("Counting words to give each word an index..") words = collections.defaultdict(int)
for tree in trees:
leftTraverse(tree.root,nodeFn=countWords,args=words) wordMap = dict(zip(words.keys(),range(len(words))))
wordMap[UNK] = len(words) # Add unknown as word print("Saving wordMap to wordMap.bin")
with open('wordMap.bin','wb') as fid:
pickle.dump(wordMap,fid) def loadTrees(dataSet='train'):
"""
Loads training trees. Maps leaf node words to word ids.
"""
wordMap = loadWordMap()
file = 'trees/%s.txt'%dataSet
print("Loading %sing trees.."%dataSet)
with open(file,'r') as fid:
trees = [Tree(l) for l in fid.readlines()]
for tree in trees:
leftTraverse(tree.root,nodeFn=mapWords,args=wordMap)
return trees if __name__=='__main__':
buildWordMap() train = loadTrees() print("Now you can do something with this list of trees!")
更详细的代码请参考github:
https://github.com/weizhenzhao/cs224d_problem_set3
cs224d 自然语言处理作业 problem set3 (一) 实现Recursive Nerual Net Work 递归神经网络的更多相关文章
- cs224d 作业 problem set3 (一) 实现Recursive Nerual Net Work 递归神经网络
1.Recursive Nerual Networks能够更好地体现每个词与词之间语法上的联系这里我们选取的损失函数仍然是交叉熵函数 2.整个网络的结构如下图所示: 每个参数的更新时的梯队值如何计算, ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (三) 用RNNLM模型实现Language Model,来预测下一个单词的出现
今天将的还是cs224d 的problem set2 的第三部分习题, 原来国外大学的系统难度真的如此之大,相比之下还是默默地再天朝继续搬砖吧 下面讲述一下RNN语言建模的数学公式: 给出一串连续 ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (一) 用tensorflow纯手写实现sofmax 函数,线性判别分析,命名实体识别
Hi Dear Today we will use tensorflow to implement the softmax regression and linear classifier algor ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (二) TensorFlow 实现命名实体识别
神经网络在命名实体识别中的应用 所有的这些包括之前的两篇都可以通过tensorflow 模型的托管部署到 google cloud 上面,发布成restful接口,从而与任何的ERP,CRM系统集成. ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set1 (二) 简单的情感分析
使用在上一篇博客中训练好的wordvector 在这一节进行情感分析. 因为在上一节中得到的是一个词就是一个向量 所以一句话便是一个矩阵,矩阵的每一列表示一个词向量 情感分析的前提是已知一句话是 (超 ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set1 (一) 主要是实现word2vector模型,SGD,CBOW,Softmax,算法
''' Created on 2017年9月13日 @author: weizhen ''' import numpy as np def sigmoid(x): return 1 / (1 + np ...
- 【NLP】自然语言处理:词向量和语言模型
声明: 这是转载自LICSTAR博士的牛文,原文载于此:http://licstar.net/archives/328 这篇博客是我看了半年的论文后,自己对 Deep Learning 在 NLP 领 ...
- Deep Learning in NLP (一)词向量和语言模型
原文转载:http://licstar.net/archives/328 Deep Learning 算法已经在图像和音频领域取得了惊人的成果,但是在 NLP 领域中尚未见到如此激动人心的结果.关于这 ...
- Deep Learning In NLP 神经网络与词向量
0. 词向量是什么 自然语言理解的问题要转化为机器学习的问题,第一步肯定是要找一种方法把这些符号数学化. NLP 中最直观,也是到目前为止最常用的词表示方法是 One-hot Representati ...
随机推荐
- linux环境下安装nginx步骤
开始前,请确认gcc g++开发类库是否装好,默认已经安装. ububtu平台编译环境可以使用以下指令 apt-get install build-essential apt-get install ...
- 【Java数据结构学习笔记之二】Java数据结构与算法之队列(Queue)实现
本篇是数据结构与算法的第三篇,本篇我们将来了解一下知识点: 队列的抽象数据类型 顺序队列的设计与实现 链式队列的设计与实现 队列应用的简单举例 优先队列的设置与实现双链表实现 队列的抽象数据类型 ...
- LINUX服务器上新增用户名
最近所里的机群停了,需要用老板的服务器跑程序,这里首先得在老板的服务器上新增一些用户名.新增用户名方法如下: 1.利用useradd添加用户名,并指定用户名目录.脚本解释器.用户名 sudo user ...
- ZXing生成条形码、二维码、带logo二维码
采用的是开源的ZXing,Maven配置如下,jar包下载地址,自己选择版本下载,顺便推荐下Maven Repository <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/art ...
- NullpointerException处理
毫无疑问,空指针NullpointerException是我们最常遇到异常,没有之一! 在刚进入编程职业时,我想,大部分刚进入的同学肯定会受到前辈们的叮咛:一定要防止空指针,这是个低级错误.你们不是? ...
- 201521123016 《Java程序设计》第8周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 2. 书面作业 本次作业题集集合 1.List中指定元素的删除(题目4-1) 1.1 实验总结 1.删除元素的时候从最后一个元素开始,避免删除元素后位置发生变化而导致有些元素没有删 ...
- 201521123042《Java程序设计》 第7周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 网上看了很多资料,发现这一张图总结的还不错就引用过来了.但是最上面的Map和Collection之间的关系应该是依赖,不是Produces. ①概述:Java集合框架主要包括两种类 ...
- 201521123052《Java程序设计》第6周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 1.1 面向对象学习暂告一段落,请使用思维导图,以封装.继承.多态为核心概念画一张思维导图,对面向对象思想进行一个总结. 注1:关键词与内容不求多,但概念之间的联系要清晰,内容覆盖 ...
- 201521123032 《Java程序设计》第4周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 1.1 尝试使用思维导图总结有关继承的知识点. 1.2 使用常规方法总结其他上课内容. 本周学习了继承,了解其中的父类与子类.了解到类,以及如何识别类,对于名词可以考虑是否创建相应 ...
- Java课程设计+购物车WEB页面
1. 团队名称(keke) 徐婉萍:网络1511 201521123006 2. 项目git地址 3. 项目git提交记录截图 4. 项目功能架构图与主要功能流程图 项目功能架构图 项目主要功能流程图 ...
