More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This post builds on a previous post, but can be read and understood independently.
As part of my course on statistical learning, we created 3D graphics to foster a more intuitive understanding of the various methods that are used to relax the assumption of linearity (in the predictors) in regression and classification methods.
The authors of our text (The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd Edition) provide a Mixture Simulation data set that has two continuous predictors and a binary outcome. This data is used to demonstrate classification procedures by plotting classification boundaries in the two predictors, which are determined by one or more surfaces (e.g., a probability surface such as that produced by logistic regression, or multiple intersecting surfaces as in linear discriminant analysis). In our class laboratory, we used the R package rgl to create a 3D representation of these surfaces for a variety of semiparametric classification procedures.
Chapter 6 presents local logistic regression and kernel density classification, among other kernel (local) classification and regression methods. Below is the code and graphic (a 2D projection) associated with the local linear logistic regression in these data:
library(rgl)
load(url("http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tibs/ElemStatLearn/datasets/ESL.mixture.rda"))
dat <- ESL.mixture
ddat <- data.frame(y=dat$y, x1=dat$x[,1], x2=dat$x[,2]) ## create 3D graphic, rotate to view 2D x1/x2 projection
par3d(FOV=1,userMatrix=diag(4))
plot3d(dat$xnew[,1], dat$xnew[,2], dat$prob, type="n",
xlab="x1", ylab="x2", zlab="",
axes=FALSE, box=TRUE, aspect=1) ## plot points and bounding box
x1r <- range(dat$px1)
x2r <- range(dat$px2)
pts <- plot3d(dat$x[,1], dat$x[,2], 1,
type="p", radius=0.5, add=TRUE,
col=ifelse(dat$y, "orange", "blue"))
lns <- lines3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2,1)], 1) ## draw Bayes (True) classification boundary in blue
dat$probm <- with(dat, matrix(prob, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm, levels=0.5))
pls0 <- lapply(dat$cls, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1, color="blue")) ## compute probabilities plot classification boundary
## associated with local linear logistic regression
probs.loc <-
apply(dat$xnew, 1, function(x0) {
## smoothing parameter
l <- 1/2
## compute (Gaussian) kernel weights
d <- colSums((rbind(ddat$x1, ddat$x2) - x0)^2)
k <- exp(-d/2/l^2)
## local fit at x0
fit <- suppressWarnings(glm(y ~ x1 + x2, data=ddat, weights=k,
family=binomial(link="logit")))
## predict at x0
as.numeric(predict(fit, type="response", newdata=as.data.frame(t(x0))))
}) dat$probm.loc <- with(dat, matrix(probs.loc, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.loc <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.loc, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.loc, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.loc, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
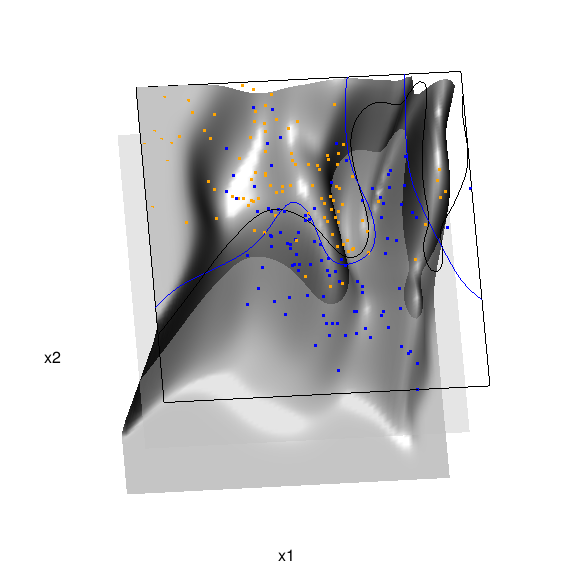
In the above graphic, the solid blue line represents the true Bayes decision boundary (i.e., {x: Pr("orange"|x) = 0.5}), which is computed from the model used to simulate these data. The probability surface (generated by the local logistic regression) is represented in gray, and the corresponding Bayes decision boundary occurs where the plane f(x) = 0.5 (in light gray) intersects with the probability surface. The solid black line is a projection of this intersection. Here is a link to the interactive version of this graphic: local logistic regression.
Below is the code and graphic associated with the kernel density classification (note: this code below should only be executed after the above code, since the 3D graphic is modified, rather than created anew):
## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl) ## kernel density classification
## compute kernel density estimates for each class
dens.kde <-
lapply(unique(ddat$y), function(uy) {
apply(dat$xnew, 1, function(x0) {
## subset to current class
dsub <- subset(ddat, y==uy)
## smoothing parameter
l <- 1/2
## kernel density estimate at x0
mean(dnorm(dsub$x1-x0[1], 0, l)*dnorm(dsub$x2-x0[2], 0, l))
})
}) ## compute prior for each class (sample proportion)
prir.kde <- table(ddat$y)/length(dat$y) ## compute posterior probability Pr(y=1|x)
probs.kde <- prir.kde[2]*dens.kde[[2]]/
(prir.kde[1]*dens.kde[[1]]+prir.kde[2]*dens.kde[[2]]) ## plot classification boundary associated
## with kernel density classification
dat$probm.kde <- with(dat, matrix(probs.kde, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.kde <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.kde, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.kde, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.kde, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
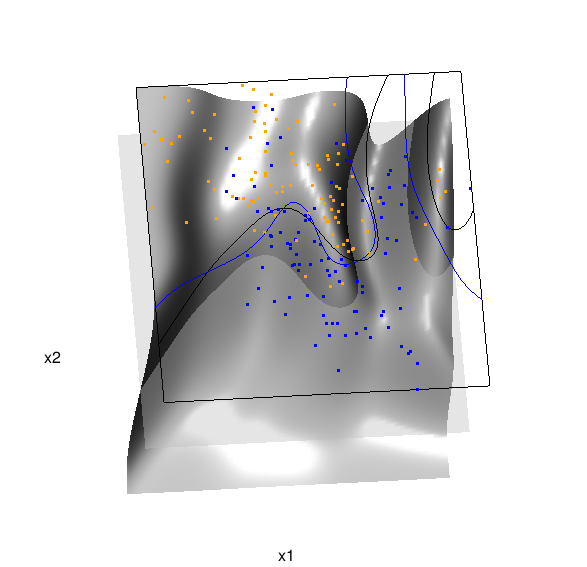
Here are links to the interactive versions of both graphics: local logistic regression, kernel density classification
This entry was posted in Technical and tagged data, graphics, programming, R, statistics on February 7, 2015.
More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)的更多相关文章
- Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This semester I'm teaching from Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman's book, The Elements of Statistical ...
- 李宏毅机器学习笔记3:Classification、Logistic Regression
李宏毅老师的机器学习课程和吴恩达老师的机器学习课程都是都是ML和DL非常好的入门资料,在YouTube.网易云课堂.B站都能观看到相应的课程视频,接下来这一系列的博客我都将记录老师上课的笔记以及自己对 ...
- Logistic Regression Using Gradient Descent -- Binary Classification 代码实现
1. 原理 Cost function Theta 2. Python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplo ...
- Classification week2: logistic regression classifier 笔记
华盛顿大学 machine learning: Classification 笔记. linear classifier 线性分类器 多项式: Logistic regression & 概率 ...
- Classification and logistic regression
logistic 回归 1.问题: 在上面讨论回归问题时.讨论的结果都是连续类型.但假设要求做分类呢?即讨论结果为离散型的值. 2.解答: 假设: 当中: g(z)的图形例如以下: 由此可知:当hθ( ...
- Android Programming 3D Graphics with OpenGL ES (Including Nehe's Port)
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/android/Android_3D.html
- Logistic Regression and Classification
分类(Classification)与回归都属于监督学习,两者的唯一区别在于,前者要预测的输出变量\(y\)只能取离散值,而后者的输出变量是连续的.这些离散的输出变量在分类问题中通常称之为标签(Lab ...
- Logistic Regression求解classification问题
classification问题和regression问题类似,区别在于y值是一个离散值,例如binary classification,y值只取0或1. 方法来自Andrew Ng的Machine ...
- 分类和逻辑回归(Classification and logistic regression)
分类问题和线性回归问题问题很像,只是在分类问题中,我们预测的y值包含在一个小的离散数据集里.首先,认识一下二元分类(binary classification),在二元分类中,y的取值只能是0和1.例 ...
随机推荐
- H5学习第四周
本周.我们结束了HTML标签和css样式部分,开始了JS的学习.JS是的内容和css,html基本上没有什么联系而且它比较需要逻辑思考能力,所以要从新开始学习. 使用js的三种方式: 1.html标签 ...
- windows下用cordova构建android app
最近用到cordova打包apk,总结了下,写下来给大家分享. 一.前期准备工作: 1.安装node 6.2.0 *64 下载地址:链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eS7Ts ...
- 图文详解linux如何搭建lamp服务环境
企业网站建设必然离不开服务器运维,一个稳定高效的服务器环境是保证网站正常运行的重要前提.本文小编将会详细讲解Linux系统上如何搭建配置高效的lamp服务环境,并在lamp环境中搭建起企业自己的网站. ...
- Jquery对raido的一些操作方法
raido 单选组radio: $("input[type=radio][checked]").val(); 获 取一组radio被选中项的值 var item = $('i ...
- pixi.js
添加基本文件(库文件) 渲染库 pixi.js pixi.lib.js是pixi.js的子集,依赖class.js,cat.js,event_emiter.js文件 pixi.scroller.js ...
- DOM 以及JS中的事件
[DOM树节点] DOM节点分为三大节点:元素节点,文本节点,属性节点. 文本节点,属性节点为元素节点的两个子节点通过getElment系列方法,可以去到元素节点 [查看节点] 1 document. ...
- Java设计模式:代理模式(二)
承接上文 三.计数代理 计数代理的应用场景是:当客户程序需要在调用服务提供者对象的方法之前或之后执行日志或者计数等额外功能时,就可以用到技术代理模式.计数代理模式并不是把额外操作的代码直接添加到原服务 ...
- THINKPHP3.2 中使用 soap 连接webservice 解决方案
今天使用THINKPHP3.2 框架中开发时使用soap连接webservice 一些浅见现在分享一下, 1.首先我们要在php.ini 中开启一下 php_openssl.dll php_soap. ...
- SQLite数据库_实现简单的增删改查
1.SQLite是一款轻量型的数据库是遵守ACID(原子性.一致性.隔离性.持久性)的关联式数据库管理系统,多用于嵌入式开发中. 2.Android平台中嵌入了一个关系型数据库SQLite,和其他数据 ...
- php头像上传预览
php头像上传带预览: 说道上传图片,大家并不陌生,不过,在以后开发的项目中,可能并不会让你使用提交刷新页面式的上传图片,比如上传头像,按照常理,肯定是在相册选择照片之后,确认上传,而肯定不会通过fo ...
