Gym - 101848C Object-Oriented Programming (树链剖分+线段树+动态开点)
3.0 s
1024 MB
standard input
standard output
Functions overriding, is a well-known concept, when we are using inheritance in Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). For those who are not familiar with OOP, I will recall a few things to perhaps refresh your memory.
- A class has at most one parent class. When they do, they are called subclasses inheriting their parents. Subclasses also inherit all the functions declared in their parent classes, and also, all the functions inherited by parents' parents, and so on. Here, we refer to the ancestors as superclasses.
- Subclasses can, of course, declare new functions, and also override the functions already declared in superclasses. This is called overriding.
- When an instance of the subclass calls a function, it will first try to find the code in its own class body, and then its parent, and then its parent's parent, etc., until it reaches the root (the superclass of all classes). If the function has still not been found yet, a runtime error will be raised.
As you might have guessed, we are interested in finding out in which class the function is written when some instance of a particular class calls it.
The input is in the following format:
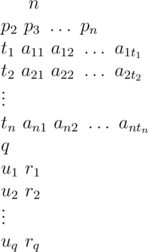
n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105) is the number of classes. Classes are numbered from 1 to n. pi (1 ≤ pi ≤ i - 1) is the parent class of class i. Class 1 is the root class, superclass of all classes. It has no parent.
ti denotes the number of functions written in class i, including both new functions and overriding functions. Then follows ai1, ai2, ..., aiti a list of these functions. Functions are also denoted using positive integers. It's guaranteed that every number will appear at most once in one list. 1 ≤ aij ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ti ≤ 106, 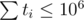 .
.
q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105) is the query number. Then follows q queries. ui, ri (1 ≤ ui ≤ n, 1 ≤ ri ≤ 106) is the i-th query, asking when an instance of class ui calls function ri, in which class is this function written?
For each query, print answer. If it is illegal, that is, a "runtime error" is raised, then output - 1.
5
1 2 3 3
2 2 1
0
2 5 2
2 4 5
1 5
4
3 4
5 2
4 5
1 3
-1
3
4
-1
The sample is equivalent to the following Java code.
class Class1 {
void function2() { System.out.println("1"); }
void function1() { System.out.println("1"); }
}
class Class2 extends Class1 {
}
class Class3 extends Class2 {
void function5() { System.out.println("3"); }
void function2() { System.out.println("3"); }
}
class Class4 extends Class3 {
void function4() { System.out.println("4"); }
void function5() { System.out.println("4"); }
}
class Class5 extends Class3 {
void function5() { System.out.println("5"); }
}
void test() {
new Class3().function4();
new Class5().function2();
new Class4().function5();
new Class1().function3();
}
Some of the tests in the raw problem package have been removed due to the "Maximal summary testset file size exceeded" error on Codeforces.
题意:
题面说的很复杂,但是我们可以将他转换成一个比较直白的模型:
给你n个点,依此输入n-1条边,形成一棵树。然后依此输入n行,依此表示1-n这几个点每个点含有哪几个值(一个点可以包含多个值,也可以不包含值,如果一条路径上,后面的点包含的值如果和前面点包含的值相同,在询问时会覆盖前面的),然后q个询问,每个询问输入两个值:u,r;询问u到根节点路径上哪个点包含r这个值(相同的值后面点覆盖前面点),输出这个点的坐标。
思路:
我们对每个值建一棵树,将包含这些值的点存进树里,点i就将树上点i标为i,然后询问u,r时,我们只要询问第r棵树上1-u上最大值就好了(用个链剖+线段树就好了),建树的话直接动态开点就行了不会超内存,这样的话这道题就很好写了。。
如果想到了思路就很好写,之前想歪了思路,debug了半天都没有得到想要的值。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
const int Max = 3e7+;
const int M = 2e6+;
const int MM = 2e6;
int ls[Max],rs[Max],sum[Max],root[Max],idx,ed[Max];
struct node{
int to,next;
}e[M];
int cnt,cnt1,n;
int son[M],siz[M],head[M],fa[M],top[M],dep[M],tid[M],mx[M],rk[M];
void add(int u,int v){
e[++cnt].to = v;e[cnt].next = head[u];head[u] = cnt;
} void dfs1(int u,int faz,int deep){
dep[u] = deep;
fa[u] = faz;
siz[u] = ;
for(int i = head[u];i;i = e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
if(v == faz) continue;
dfs1(v,u,deep+);
siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]||son[u] == -)
son[u] = v;
}
} void dfs2(int u,int t){
top[u] = t;
mx[u] = cnt1;
tid[u] = cnt1;
rk[cnt1] = u;
cnt1++;
if(son[u] == -) return ;
dfs2(son[u],t),mx[u] = max(mx[u],mx[son[u]]);
for(int i = head[u];i;i=e[i].next){
int v = e[i].to;
if(v != fa[u]&&v != son[u])
dfs2(v,v),mx[u] = max(mx[u],mx[v]);
}
} void update(int &k,int l,int r,int p,int num){
if(!k){
k = ++idx;
sum[k] = num;
}
sum[k] = max(sum[k],num);
if(l == r)
return ;
int m = (l + r) >> ;
if(p <= m) update(ls[k],l,m,p,num);
else update(rs[k],m+,r,p,num);
} int query(int k,int L,int R,int l,int r){
if(!k) return ;
if(L <= l&&R >= r){
return sum[k];
}
int m = (l + r) >> ;
int ans = ;
if(L <= m) ans = max(ans,query(ls[k],L,R,l,m));
if(R > m) ans = max(ans,query(rs[k],L,R,m+,r));
return ans;
} int solve(int x,int y,int rt){
int fx = top[x],fy = top[y];
int ans = ;
while(fx != fy){
if(dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy);
ans = max(ans,query(root[rt],tid[fx],tid[x],,MM));
x = fa[fx]; fx = top[x];
}
if(dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x,y);
ans = max(ans,query(root[rt],tid[x],tid[y],,MM));
return ans;
} int main()
{
int x,k,q,t,n;
idx = ;
cnt1 = ; cnt = ;
root[] = ,sum[] = ;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(son,-,sizeof(son));
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
scanf("%d",&x);
add(x,i); add(i,x);
}
dfs1(,,); dfs2(,);
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int j = ;j <= t;j ++){
scanf("%d",&x);
update(root[x],,MM,tid[i],i);
}
}
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--){
scanf("%d %d",&k,&x);
//cout<<"kk: "<<k<<" "<<root[k]<<endl;
int num = solve(,k,x);
if(num == ) num = -;
printf("%d\n",num);
}
return ;
}
Gym - 101848C Object-Oriented Programming (树链剖分+线段树+动态开点)的更多相关文章
- 【BZOJ-2325】道馆之战 树链剖分 + 线段树
2325: [ZJOI2011]道馆之战 Time Limit: 40 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 1153 Solved: 421[Submit][Statu ...
- 【BZOJ2243】[SDOI2011]染色 树链剖分+线段树
[BZOJ2243][SDOI2011]染色 Description 给定一棵有n个节点的无根树和m个操作,操作有2类: 1.将节点a到节点b路径上所有点都染成颜色c: 2.询问节点a到节点b路径上的 ...
- BZOJ2243 (树链剖分+线段树)
Problem 染色(BZOJ2243) 题目大意 给定一颗树,每个节点上有一种颜色. 要求支持两种操作: 操作1:将a->b上所有点染成一种颜色. 操作2:询问a->b上的颜色段数量. ...
- POJ3237 (树链剖分+线段树)
Problem Tree (POJ3237) 题目大意 给定一颗树,有边权. 要求支持三种操作: 操作一:更改某条边的权值. 操作二:将某条路径上的边权取反. 操作三:询问某条路径上的最大权值. 解题 ...
- bzoj4034 (树链剖分+线段树)
Problem T2 (bzoj4034 HAOI2015) 题目大意 给定一颗树,1为根节点,要求支持三种操作. 操作 1 :把某个节点 x 的点权增加 a . 操作 2 :把某个节点 x 为根的子 ...
- HDU4897 (树链剖分+线段树)
Problem Little Devil I (HDU4897) 题目大意 给定一棵树,每条边的颜色为黑或白,起始时均为白. 支持3种操作: 操作1:将a->b的路径中的所有边的颜色翻转. 操作 ...
- Aizu 2450 Do use segment tree 树链剖分+线段树
Do use segment tree Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://www.bnuoj.com/v3/problem_show ...
- 【POJ3237】Tree(树链剖分+线段树)
Description You are given a tree with N nodes. The tree’s nodes are numbered 1 through N and its edg ...
- HDU 2460 Network(双连通+树链剖分+线段树)
HDU 2460 Network 题目链接 题意:给定一个无向图,问每次增加一条边,问个图中还剩多少桥 思路:先双连通缩点,然后形成一棵树,每次增加一条边,相当于询问这两点路径上有多少条边,这个用树链 ...
- bzoj2243[SDOI2011]染色 树链剖分+线段树
2243: [SDOI2011]染色 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 512 MBSubmit: 9012 Solved: 3375[Submit][Status ...
随机推荐
- 七、Json格式的对象都可以通过遍历来获得里面的value值
- Python学习第三篇——逻辑判定
request_foods=["tomato","beaf","milk"] for elements in request_foods: ...
- TCP粘包问题解析与解决
一.粘包分析 作者本人在写一个FTP项目时,在文件的上传下载模块遇到了粘包问题.在网上找了一些解决办法,感觉对我情况都不好用,因此自己想了个比较好的解决办法,提供参考 1.1 粘包现象 在客户端与服务 ...
- latex中插入eps文件
\documentclass{article} \usepackage{graphicx}\usepackage{epstopdf} \begin{document}\begin{figure} \ ...
- 实现数据结构与算法需要掌握的C语言
我使用C语言并不频繁,一般都是用来实现数据结构与算法,因为面向过程的编程方式容易理解算法的原理,但是呢,如果很长时间没写算法,那么就意味着C语言的某些语法就生疏了,但是总有那么一些,在写算法的时候,特 ...
- nginx强制使用https访问(http跳转到https)
Nginx 的 Location 从零开始配置 - 市民 - SegmentFault 思否https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000009651161 nginx配置loc ...
- Springboot自定义过滤器Filter
前言:自己写了个Springboot项目,最近写的功能越来越多,结合业务已经要写过滤器Filter来过滤处理一些请求. 在网上看了几篇博客,总结如下: 过滤器配置方式有两种: 1.通过@WebFilt ...
- 用Canvas实现一些简单的图片滤镜
1.灰度滤镜 对于灰度滤镜的实现一般有三种算法 1) 最大值法:即新的颜色值R=G=B=Max(R,G,B),通过这种方法处理后的图片看起来亮度值偏高. 2) 平均值法:即新的颜色值R=G=B=(R+ ...
- 区分Python中的可变对象和不可变对象
参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/sun-haiyu/p/7096918.html """不过注意函数传参既不是传值也不是传引用,正确的叫法是传对象 ...
- 详解 RestTemplate 操作
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/itguangit/article/details/78825505 作为开发人员,我们经常关注于构建伟大的软件来解决业务问题.数据只是软件完成工作 ...
