Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 2)A B C 模拟 数学
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You have decided to watch the best moments of some movie. There are two buttons on your player:
- Watch the current minute of the movie. By pressing this button, you watch the current minute of the movie and the player automatically proceeds to the next minute of the movie.
- Skip exactly x minutes of the movie (x is some fixed positive integer). If the player is now at the t-th minute of the movie, then as a result of pressing this button, it proceeds to the minute (t + x).
Initially the movie is turned on in the player on the first minute, and you want to watch exactly n best moments of the movie, the i-th best moment starts at the li-th minute and ends at the ri-th minute (more formally, the i-th best moment consists of minutes: li, li + 1, ..., ri).
Determine, what is the minimum number of minutes of the movie you have to watch if you want to watch all the best moments?
The first line contains two space-separated integers n, x (1 ≤ n ≤ 50, 1 ≤ x ≤ 105) — the number of the best moments of the movie and the value of x for the second button.
The following n lines contain the descriptions of the best moments of the movie, the i-th line of the description contains two integers separated by a space li, ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 105).
It is guaranteed that for all integers i from 2 to n the following condition holds: ri - 1 < li.
Output a single number — the answer to the problem.
2 3
5 6
10 12
6
1 1
1 100000
100000
In the first sample, the player was initially standing on the first minute. As the minutes from the 1-st to the 4-th one don't contain interesting moments, we press the second button. Now we can not press the second button and skip 3 more minutes, because some of them contain interesting moments. Therefore, we watch the movie from the 4-th to the 6-th minute, after that the current time is 7. Similarly, we again skip 3 minutes and then watch from the 10-th to the 12-th minute of the movie. In total, we watch 6 minutes of the movie.
In the second sample, the movie is very interesting, so you'll have to watch all 100000 minutes of the movie.
题意:水 n个期望区间 可跳过x 问需要持续的最短时间
题解:模拟
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#define __int64 ll
using namespace std;
int n,k;
int mp[];
int l,r;
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
mp[i]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&l,&r);
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++)
mp[j]=;
}
int sum=;
int be=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
int j=i;
if(mp[j]==)
{
sum=sum+(j-be)%k;
int s;
for( s=j;s<=;s++)
{
if(mp[s]==)
sum++;
else
break;
}
j=s;
be=j;
}
i=j;
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You have a new professor of graph theory and he speaks very quickly. You come up with the following plan to keep up with his lecture and make notes.
You know two languages, and the professor is giving the lecture in the first one. The words in both languages consist of lowercase English characters, each language consists of several words. For each language, all words are distinct, i.e. they are spelled differently. Moreover, the words of these languages have a one-to-one correspondence, that is, for each word in each language, there exists exactly one word in the other language having has the same meaning.
You can write down every word the professor says in either the first language or the second language. Of course, during the lecture you write down each word in the language in which the word is shorter. In case of equal lengths of the corresponding words you prefer the word of the first language.
You are given the text of the lecture the professor is going to read. Find out how the lecture will be recorded in your notes.
The first line contains two integers, n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 3000) — the number of words in the professor's lecture and the number of words in each of these languages.
The following m lines contain the words. The i-th line contains two strings ai, bi meaning that the word ai belongs to the first language, the word bi belongs to the second language, and these two words have the same meaning. It is guaranteed that no word occurs in both languages, and each word occurs in its language exactly once.
The next line contains n space-separated strings c1, c2, ..., cn — the text of the lecture. It is guaranteed that each of the strings ci belongs to the set of strings {a1, a2, ... am}.
All the strings in the input are non-empty, each consisting of no more than 10 lowercase English letters.
Output exactly n words: how you will record the lecture in your notebook. Output the words of the lecture in the same order as in the input.
4 3
codeforces codesecrof
contest round
letter message
codeforces contest letter contest
codeforces round letter round
5 3
joll wuqrd
euzf un
hbnyiyc rsoqqveh
hbnyiyc joll joll euzf joll
hbnyiyc joll joll un joll 题意:string
题解:模拟
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define __int64 ll
using namespace std;
int n,m;
string a,b;
map<string,string> mp;
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
cin>>a>>b;
if(a.size()<=b.size())
{
mp[a]=a;
mp[b]=a;
}
else
{
mp[a]=b;
mp[b]=b;
}
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
cout<<mp[a]<<" ";
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Crazy Town is a plane on which there are n infinite line roads. Each road is defined by the equation aix + biy + ci = 0, where ai and bi are not both equal to the zero. The roads divide the plane into connected regions, possibly of infinite space. Let's call each such region a block. We define an intersection as the point where at least two different roads intersect.
Your home is located in one of the blocks. Today you need to get to the University, also located in some block. In one step you can move from one block to another, if the length of their common border is nonzero (in particular, this means that if the blocks are adjacent to one intersection, but have no shared nonzero boundary segment, then it are not allowed to move from one to another one in one step).
Determine what is the minimum number of steps you have to perform to get to the block containing the university. It is guaranteed that neither your home nor the university is located on the road.
The first line contains two space-separated integers x1, y1 ( - 106 ≤ x1, y1 ≤ 106) — the coordinates of your home.
The second line contains two integers separated by a space x2, y2 ( - 106 ≤ x2, y2 ≤ 106) — the coordinates of the university you are studying at.
The third line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 300) — the number of roads in the city. The following n lines contain 3 space-separated integers ( - 106 ≤ ai, bi, ci ≤ 106; |ai| + |bi| > 0) — the coefficients of the line aix + biy + ci = 0, defining the i-th road. It is guaranteed that no two roads are the same. In addition, neither your home nor the university lie on the road (i.e. they do not belong to any one of the lines).
Output the answer to the problem.
1 1
-1 -1
2
0 1 0
1 0 0
2
1 1
-1 -1
3
1 0 0
0 1 0
1 1 -3
2
Pictures to the samples are presented below (A is the point representing the house; B is the point representing the university, different blocks are filled with different colors):
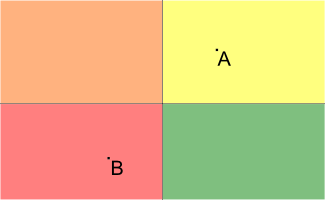
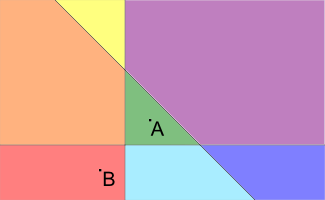
题意:给你起点与终点 以及n条直线将平面分成若干个块 问由起点到终点最少要经过几次跨越
(两个块之间的跨越只能通过边)
题解:数学 通过判断起点与终点相对与每一条的边的位置 若在不同侧 需要记录答案
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#define ll __int64
#define eps 1e-15
using namespace std;
ll x1,y1;
ll x2,y2;
int n;
ll a[],b[],c[];
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d %I64d",&x1,&y1);
scanf("%I64d %I64d",&x2,&y2);
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%I64d %I64d %I64d",&a[i],&b[i],&c[i]);
int sum=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
ll exm1;
ll exm2;
exm1=a[i]*x1+b[i]*y1+c[i];
exm2=a[i]*x2+b[i]*y2+c[i];
if(exm1>)
exm1=;
else
exm1=;
if(exm2>)
exm2=;
else
exm2=;
if(exm1^exm2==)
sum++;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 2)A B C 模拟 数学的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) C. Pythagorean Triples(数学)
Pythagorean Triples 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/C Description Katya studies in a ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) B. Bakery (模拟)
Bakery 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/B Description Masha wants to open her own bak ...
- Codeforces Round #622 (Div. 2) B. Different Rules(数学)
Codeforces Round #622 (Div. 2) B. Different Rules 题意: 你在参加一个比赛,最终按两场分赛的排名之和排名,每场分赛中不存在名次并列,给出参赛人数 n ...
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A B C 模拟 stl 拓扑排序
A. Contest time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 2)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/499 A. Watching a movie You have decided to watch the best moment ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 1) A. Crazy Town 计算几何
A. Crazy Town 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/498/problem/A Description Crazy Town is a plane on ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 1) C. Array and Operations 二分图最大匹配
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/498/C C. Array and Operations time limit per test1 se ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 2) C题(计算几何)解题报告
题目地址 简要题意: 给出两个点的坐标,以及一些一般直线方程Ax+B+C=0的A.B.C,这些直线作为街道,求从一点走到另一点需要跨越的街道数.(两点都不在街道上) 思路分析: 从一点到另一点必须要跨 ...
- Codeforces Round #284 (Div. 1)
A. Crazy Town 这一题只需要考虑是否经过所给的线,如果起点和终点都在其中一条线的一侧,那么很明显从起点走点终点是不需要穿过这条线的,否则则一定要经过这条线,并且步数+1.用叉积判断即可. ...
随机推荐
- app上传到App Store的快捷方法及步骤
跳过证书的申请及配置概要文件的设置, 现在根据已有的配置概要文件及发布证书开始: 1.先在Xcode上的PROJECT和TARGETS->Build Setting->Code Signi ...
- lnmp 设置ci pathinfo和去掉index.php
LNMP上各个版本pathinfo各个版本的设置基本一样: lnmp v1.1上,修改对应虚拟主机的配置文件去掉#include pathinfo.conf前面的#,把try_files $uri = ...
- Java Mysql分页显示
public class View { private int currentPage; private int pageSize; private int recordCount; public V ...
- http Content-type对照表
http://tools.jb51.net/table/http_content_type Content-Type,内容类型,一般是指网页中存在的Content-Type,用于定 义网络文件的类型和 ...
- 在Ubuntu环境把PPT和Word转换为swf文件
项目需要一个在线浏览文档的功能,于是参照网上的代码写了一份利用Microsoft Office 2010和swftools-2013-04-09-1007.exe转换的程序 思路:调用电脑本机的off ...
- [转]ZendFramework数据库操作总结
Zend_Db数据库知识 例子: Model文件: $this->fetchAll("is_jian=1","id DESC",0,2)->toAr ...
- rocksDB 安装问题简单介绍
前一段时间准备测试rocksdb,按照帖子和官网的例子,在安装过程中遇到一些问题.这里给出的是在Ubuntu下安装python使用的版本. 首先,要感谢这些帖子对我的帮助: 1:http://tech ...
- 使用Quartz.NET进行任务调度管理
1.Quartz.NET 介绍 Quartz.NET是一个开源的作业调度框架,是OpenSymphony 的 Quartz API的.NET移植,它用C#写成,可用于winform和asp.net应用 ...
- AngularJS的学习笔记(一)
声明:单纯作为我自己的学习笔记,纯是为了自己学习,上面的话都是从各处粘贴,如有冒犯,请原谅我这个小菜鸟~ AngularJS使用了不同的方法,它尝试去补足HTML本身在构建应用方面的缺陷. 使用双大括 ...
- Asp.net MVC与Javascript
特性验证 首先:在web.config文件中<appSettings>节点内添加<add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value= ...
