CS229 6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening
PCA
给定一组二维数据,每列十一组样本,共45个样本点
-6.7644914e-01 -6.3089308e-01 -4.8915202e-01 ...
-4.4722050e-01 -7.4778067e-01 -3.9074344e-01 ...

可以表示为如下形式:
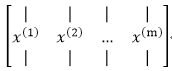
本例子中的的x(i)为2维向量,整个数据集X为2*m的矩阵,矩阵的每一列代表一个数据,该矩阵的转置X' 为一个m*2的矩阵:

假设如上数据为归一化均值后的数据(注意这里省略了方差归一化),则数据的协方差矩阵Σ为 1/m(X*X'),Σ为一个2*2的矩阵:

对该对称矩阵对角线化:

这是对于2维情况,若对于n维,会得到一组n维的新基:
 ,且U的转置:
,且U的转置:

原数据在U上的投影为用UT*X表示即可:
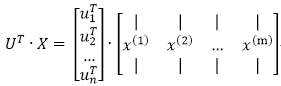
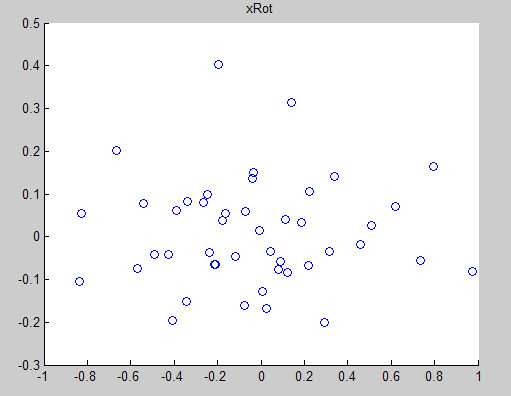
对于二维数据,UT为2*2的矩阵,UT*X会得到2*m的新矩阵,即原数据在新基下的表示XROT,原来的数据映射到这组新基上,便得到可一组在各个维度上不相关的数据,取k<n,把数据映射到 上,便完成的降维过程,下图为XROT:
上,便完成的降维过程,下图为XROT:
对基变换后的数据还可以进行还原,比如得到了原始数据 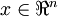 的低维“压缩”表征量
的低维“压缩”表征量 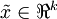 , 反过来,如果给定
, 反过来,如果给定 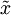 ,我们应如何还原原始数据
,我们应如何还原原始数据 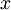 呢?
呢? 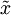 的基为要转换回来,只需
的基为要转换回来,只需 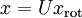 即可。进一步,我们把
即可。进一步,我们把 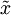 看作将
看作将 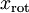 的最后
的最后 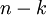 个元素被置0所得的近似表示,因此如果给定
个元素被置0所得的近似表示,因此如果给定 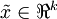 ,可以通过在其末尾添加
,可以通过在其末尾添加 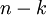 个0来得到对
个0来得到对 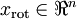 的近似,最后,左乘
的近似,最后,左乘 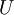 便可近似还原出原数据
便可近似还原出原数据 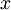 。具体来说,计算如下:
。具体来说,计算如下:

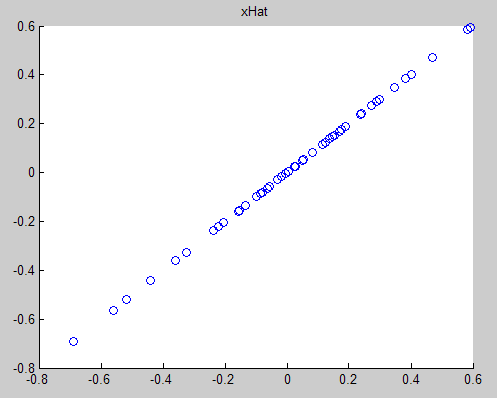
下图为还原后的数据:
下面来看白化,白化就是先对数据进行基变换,但是并不进行降维,且对变化后的数据,每一个维度上都除以其标准差,来达到归一化均值方差的目的。另外值得一提的一段话是:
感觉除了层数和每层隐节点的个数,也没啥好调的。其它参数,近两年论文基本都用同样的参数设定:迭代几十到几百epoch。sgd,mini batch size从几十到几百皆可。步长0.1,可手动收缩,weight decay取0.005,momentum取0.9。dropout加relu。weight用高斯分布初始化,bias全初始化为0。最后记得输入特征和预测目标都做好归一化。做完这些你的神经网络就应该跑出基本靠谱的结果,否则反省一下自己的人品。
对于ZCA,直接在PCAwhite 的基础上左成特征矩阵U即可,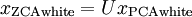

matlab代码:
close all %%================================================================
%% Step : Load data
% We have provided the code to load data from pcaData.txt into x.
% x is a * matrix, where the kth column x(:,k) corresponds to
% the kth data point.Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x.
% You do not need to change the code below. x = load('pcaData.txt','-ascii');
figure();
scatter(x(, :), x(, :));
title('Raw data'); %%================================================================
%% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain U
% Implement PCA to obtain the rotation matrix U, which is the eigenbasis
% sigma. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
u = zeros(size(x, )); % You need to compute this
[n m] = size(x);
p = mean(x,);%按行求均值,p为一个2维列向量
%x = x-repmat(p,,m);%预处理,均值为0
sigma = (./m)*x*x';%协方差矩阵
[u s v] = svd(sigma);%奇异值分解得到特征值与特征向量 % --------------------------------------------------------
hold on
plot([0 u(1,1)], [0 u(2,1)]);%画第一条线
plot([0 u(1,2)], [0 u(2,2)]);%第二条线
scatter(x(1, :), x(2, :));
hold off %%================================================================
%% Step 1b: Compute xRot, the projection on to the eigenbasis
% Now, compute xRot by projecting the data on to the basis defined
% by U. Visualize the points by performing a scatter plot. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xRot = zeros(size(x)); % 初始化一个基变换后的数据
xRot = u'*x; %做基变换 % -------------------------------------------------------- % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure();
scatter(xRot(, :), xRot(, :));
title('xRot'); %%================================================================
%% Step : Reduce the number of dimensions from to .
% Compute xRot again (this time projecting to dimension).
% Then, compute xHat by projecting the xRot back onto the original axes
% to see the effect of dimension reduction % 用投影后的数据还原原始数据
k = ; % Use k = 1 and project the data onto the first eigenbasis
xHat = zeros(size(x)); % 还原原始数据
%[u(:,),zeros(n,)]'*x 代表原数据在新基上的前K维的投影,之后的维度为0
%对降维后的数据进行还原:u * xRot = Xhat,Xhat为还原后的数据
xHat = u*([u(:,1),zeros(n,1)]'*x);%n代表数据的维度 % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xHat(, :), xHat(, :));
title('xHat'); %%================================================================
%% Step : PCA Whitening
% Complute xPCAWhite and plot the results. epsilon = 1e-;
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
% s为对角阵,diag(s)会返回s主对角线元素组成的列向量
% diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))会返回一个对角阵,
% 对角线元素为 -> ./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon
% 变换后的数据为 : Xrot = u'*x
%这样做对应于Xrot的数据再每个维度除以其标准差
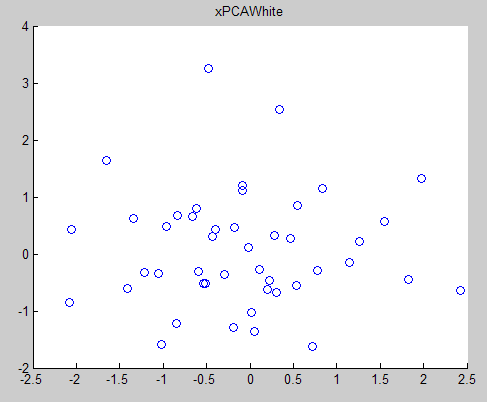
xPCAWhite = diag(1./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xPCAWhite(, :), xPCAWhite(, :));
title('xPCAWhite'); %%================================================================
%% Step : ZCA Whitening
% Complute xZCAWhite and plot the results. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xZCAWhite = u*diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % --------------------------------------------------------
figure(5);
scatter(xZCAWhite(1, :), xZCAWhite(2, :));
title('xZCAWhite'); %% Congratulations! When you have reached this point, you are done!
% You can now move onto the next PCA exercise. :)
PCA与Whitening与ZCA的一个小实验:参考自http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Exercise:PCA_and_Whitening
%%================================================================
%% Step 0a: 加载数据
% 随机采样10000张图片放入到矩阵x里.
% x 是一个 * 的矩阵,该矩阵的第 k列 x(:, k) 对应第k张图片 x = sampleIMAGESRAW();
figure('name','Raw images');
randsel = randi(size(x,),,); % A random selection of samples for visualization
display_network(x(:,randsel)); %%================================================================
%% Step 0b: -均值(Zero-mean)这些数据 (按行)
% You can make use of the mean and repmat/bsxfun functions.
[n m] = size(x);
p = mean(x,);
x = x - repmat(p,,m);
%%================================================================
%% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain xRot
% Implement PCA to obtain xRot, the matrix in which the data is expressed
% with respect to the eigenbasis of sigma, which is the matrix U. xRot = zeros(size(x)); % 新基下的数据
sigma =(./m)*x*x';
[u s v] = svd(sigma);
XRot = u'*x; %%================================================================
%% Step 1b: Check your implementation of PCA
% 新基U下的数据的协方差矩阵是对角阵,只在主对角线上不为0
% Write code to compute the covariance matrix, covar.
% When visualised as an image, you should see a straight line across the
% diagonal (non-zero entries) against a blue background (zero entries). % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
covar = zeros(size(x, )); % You need to compute this
covar = (./m)*xRot*xRot'; %新基下数据的均值仍然为0,直接计算covariance % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure('name','Visualisation of covariance matrix');
imagesc(covar); %%================================================================
%% Step 2: Find k, the number of components to retain
% Write code to determine k, the number of components to retain in order
% to retain at least 99% of the variance.
% 保留99%的方差比 % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
k = 0; % Set k accordingly
for i = i,n:
lambd = diag(s)%对角线元素组成的列向量
% 通过循环找到99%的方差百分比的k值
for k = 1:n
if sum(lambd(1:k))/sum(lambd)<0.99
continue;
end
%下面是另一种k的求法
%其中cumsum(ss)求出的是一个累积向量,也就是说ss向量值的累加值
%并且(cumsum(ss)/sum(ss))<=0.99是一个向量,值为0或者1的向量,为1表示满足那个条件
%k = length(ss((cumsum(ss)/sum(ss))<=0.99)); %%================================================================
%% Step 3: Implement PCA with dimension reduction
% Now that you have found k, you can reduce the dimension of the data by
% discarding the remaining dimensions. In this way, you can represent the
% data in k dimensions instead of the original 144, which will save you
% computational time when running learning algorithms on the reduced
% representation.
%
% Following the dimension reduction, invert the PCA transformation to produce
% the matrix xHat, the dimension-reduced data with respect to the original basis.
% Visualise the data and compare it to the raw data. You will observe that
% there is little loss due to throwing away the principal components that
% correspond to dimensions with low variation. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
%把x映射到U的前k个基上 u(:,1:k)'*x作为Xrot',Xrot'为k*m维的
%补全整个Xrot'中k到n维的元素为0,然后左乘U变回到原来的基下得到Xhat
% 首先为了降维做一个基变换,降维后要还原到原来的坐标系下,还原后为
%对应的降维后的原始数据 xHat = u*[u(:,1:k)'*x;zeros(n-k,m)]; % Visualise the data, and compare it to the raw data
% You should observe that the raw and processed data are of comparable quality.
% For comparison, you may wish to generate a PCA reduced image which
% retains only % of the variance. figure('name',['PCA processed images ',sprintf('(%d / %d dimensions)', k, size(x, )),'']);
display_network(xHat(:,randsel));
figure('name','Raw images');
display_network(x(:,randsel)); %%================================================================
%% Step 4a: Implement PCA with whitening and regularisation
% Implement PCA with whitening and regularisation to produce the matrix
% xPCAWhite. epsilon = .;
xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % 白化处理
% xRot = u' * x 为白化后的数据
xPCAWhite = diag(1./sqrt(diag(s) + epsilon))* u' * x;
figure('name','PCA whitened images'); display_network(xPCAWhite(:,randsel));
%%================================================================ %%
Step 4b: Check your implementation of PCA whitening
% Check your implementation of PCA whitening with and without regularisation.
% PCA whitening without regularisation results a covariance matrix
% that is equal to the identity matrix. PCA whitening with regularisation
% results in a covariance matrix with diagonal entries starting close to
% and gradually becoming smaller. We will verify these properties here.
% Write code to compute the covariance matrix, covar.
% Without regularisation (set epsilon to or close to ),
% when visualised as an image, you should see a red line across the
% diagonal (one entries) against a blue background (zero entries).
% With regularisation, you should see a red line that slowly turns
% blue across the diagonal, corresponding to the one entries slowly
% becoming smaller.
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
% Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a red line across the
% diagonal against a blue background. figure('name','Visualisation of covariance matrix'); imagesc(covar);
%%================================================================ %
% Step : Implement ZCA whitening % Now implement ZCA whitening to produce the matrix xZCAWhite.
% Visualise the data and compare it to the raw data. You should observe
% that whitening results in, among other things, enhanced edges.
xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x));
% ZCA处理
xZCAWhite = u*xPCAWhite;
% Visualise the data, and compare it to the raw data.
% You should observe that the whitened images have enhanced edges.
figure('name','ZCA whitened images');
display_network(xZCAWhite(:,randsel)); figure('name','Raw images'); display_network(x(:,randsel));
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/03/21/2973231.html
CS229 6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening的更多相关文章
- (六)6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening
PCA 给定一组二维数据,每列十一组样本,共45个样本点 -6.7644914e-01 -6.3089308e-01 -4.8915202e-01 ... -4.4722050e-01 -7.4 ...
- CS229 6.10 Neurons Networks implements of softmax regression
softmax可以看做只有输入和输出的Neurons Networks,如下图: 其参数数量为k*(n+1) ,但在本实现中没有加入截距项,所以参数为k*n的矩阵. 对损失函数J(θ)的形式有: 算法 ...
- CS229 6.11 Neurons Networks implements of self-taught learning
在machine learning领域,更多的数据往往强于更优秀的算法,然而现实中的情况是一般人无法获取大量的已标注数据,这时候可以通过无监督方法获取大量的未标注数据,自学习( self-taught ...
- CS229 6.13 Neurons Networks Implements of stack autoencoder
对于加深网络层数带来的问题,(gradient diffuse 局部最优等)可以使用逐层预训练(pre-training)的方法来避免 Stack-Autoencoder是一种逐层贪婪(Greedy ...
- CS229 6.5 Neurons Networks Implements of Sparse Autoencoder
sparse autoencoder的一个实例练习,这个例子所要实现的内容大概如下:从给定的很多张自然图片中截取出大小为8*8的小patches图片共10000张,现在需要用sparse autoen ...
- (六)6.10 Neurons Networks implements of softmax regression
softmax可以看做只有输入和输出的Neurons Networks,如下图: 其参数数量为k*(n+1) ,但在本实现中没有加入截距项,所以参数为k*n的矩阵. 对损失函数J(θ)的形式有: 算法 ...
- CS229 6.1 Neurons Networks Representation
面对复杂的非线性可分的样本是,使用浅层分类器如Logistic等需要对样本进行复杂的映射,使得样本在映射后的空间是线性可分的,但在原始空间,分类边界可能是复杂的曲线.比如下图的样本只是在2维情形下的示 ...
- CS229 6.16 Neurons Networks linear decoders and its implements
Sparse AutoEncoder是一个三层结构的网络,分别为输入输出与隐层,前边自编码器的描述可知,神经网络中的神经元都采用相同的激励函数,Linear Decoders 修改了自编码器的定义,对 ...
- CS229 6.6 Neurons Networks PCA主成分分析
主成分分析(PCA)是一种经典的降维算法,基于基变换,数据原来位于标准坐标基下,将其投影到前k个最大特征值对应的特征向量所组成的基上,使得数据在新基各个维度有最大的方差,且在新基的各个维度上数据是不相 ...
随机推荐
- 1. docker 在 macOS 中的架构 2. 在macOS系统中,docker pull 下来的镜像存储在哪里?
docker 在 macOS 中的架构: 在macOS中,docker的实现跟在其它Linux系统中略有不同,在其它Linux系统中,操作系统本身就是docker容器的宿主机,docker镜像都是直接 ...
- 记一次shell脚本编写及执行
首先cd进一个目录下 tauch tset.sh //新建一个test.sh文件 vim test.sh 编辑脚本 i 插入 #!/bin/bash data 按Esc键 再按ctrl+: wq + ...
- 解决iScroll横向滚动区域无法拉动页面的问题
近期项目中使用iScroll遇到一个问题,在设定wrapper为横向滚动时,如果你手指放在该区域,将无法拉动页面,也就是说该区域取消了默认事件.这个体验是实在是无法接受,特别是页面中有多个横向滚动区域 ...
- windows服务命令 转载
OnCustomCommand executes when the Service Control Manager (SCM) passes a custom command to the servi ...
- Could not write to output file 'c:\Windows\Microsoft.NET ASP.NET Files\xx' -- 'Access is denied
网上有IIS7的解决方法,是给"C:\Windows\Temp"文件夹加上添加用户IIS_IUSRS的完全控制权限. 但我这个老机器是IIS6的,没有IIS_IUSERS用户,只能 ...
- 微信h5支付demo微信H5支付demo非微信浏览器支付demo微信wap支付
服务项目 新手技术咨询 企业技术咨询 定制开发 服务说明 QQ有问必答 QQ.微信.电话 微信开发.php开发,网站开发,系统定制,小程序开发 价格说明 200元/月 1000/月 商议 ...
- spring AOP的学习
1.Spring常用的概念 Joinpoint(连接点): 所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点.在spring中,这些点指的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点. Pointcut(切入点): ...
- 持续集成(Continuous Integration)基本概念与实践
本文由Markdown语法编辑器编辑完成. From https://blog.csdn.net/inter_peng/article/details/53131831 1. 持续集成的概念 持续集成 ...
- C++中函数的形参为数组时,实质形参是指针
C++中函数的形参如果为数组的话,那么进行实参传递时,实参实际上换转化成指针.参考下面的例子: #include<iostream> using namespace std; void f ...
- PAT 乙级 1043 输出PATest(20) C++版
1043. 输出PATest(20) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue 给定一个长度不超过10000 ...
