[Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Regression
梯度下降
一、亲手实现“梯度下降”
以下内容其实就是《手动实现简单的梯度下降》。
神经网络的实践笔记,主要包括:
- Logistic分类函数
- 反向传播相关内容
Link: http://peterroelants.github.io/posts/neural_network_implementation_part01/
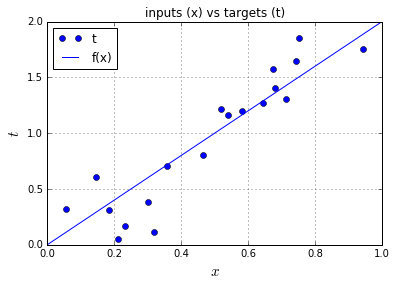
1. 生成训练数据
由“目标函数+随机噪声”生成。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Part 1, create training data
# Define the vector of input samples as x, with 20 values sampled from a uniform distribution
# between 0 and 1
x = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 20) # Generate the target values t from x with small gaussian noise so the estimation won't be perfect.
# Define a function f that represents the line that generates t without noise
def f(x): return x * 2 # Create the targets t with some gaussian noise
noise_variance = 0.2 # Variance of the gaussian noise
# Gaussian noise error for each sample in x
# shape函数是numpy.core.fromnumeric中的函数,它的功能是读取矩阵的长度,比如shape[0]就是读取矩阵第一维度的长度。
# shape[0]得到对应的长度,也即是真实值的个数,以便生成对应的noise值
noise = np.random.randn(x.shape[0]) * noise_variance
# Create targets t
t = f(x) + noise
# Part2, draw the training data # Plot the target t versus the input x
plt.plot(x, t, 'o', label='t')
# Plot the initial line
plt.plot([0, 1], [f(0), f(1)], 'b-', label='f(x)')
plt.xlabel('$x$', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('$t$', fontsize=15)
plt.ylim([0,2])
plt.title('inputs (x) vs targets (t)')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
2. loss与weight的关系
# 定义“神经网络模型“
def nn(x, w): return x*w # 定义“损失函数”
def cost(y, t): return ((t - y) ** 2).sum() # Plot the cost vs the given weight w # Define a vector of weights for which we want to plot the cost
# start 是采样的起始点
# stop 是采样的终点
# num 是采样的点个数
ws = np.linspace(0, 4, num=100) # weight values
cost_ws = np.vectorize(lambda w: cost(nn(x, w) , t))(ws) # cost for each weight in ws # Plot
plt.plot(ws, cost_ws, 'r-')
plt.xlabel('$w$', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('$\\xi$', fontsize=15)
plt.title('cost vs. weight')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
3. 梯度模拟
# define the gradient function. Remember that y = nn(x, w) = x * w
def gradient(w, x, t):
return 2 * x * (nn(x, w) - t) # define the update function delta w
def delta_w(w_k, x, t, learning_rate):
return learning_rate * gradient(w_k, x, t).sum() # Set the initial weight parameter
w = 0.1
# Set the learning rate
learning_rate = 0.1 # Start performing the gradient descent updates, and print the weights and cost:
nb_of_iterations = 4 # number of gradient descent updates
w_cost = [(w, cost(nn(x, w), t))] # List to store the weight,costs values
for i in range(nb_of_iterations):
dw = delta_w(w, x, t, learning_rate) # Get the delta w update
w = w - dw # Update the current weight parameter
w_cost.append((w, cost(nn(x, w), t))) # Add weight,cost to list # Print the final w, and cost
for i in range(0, len(w_cost)):
print('w({}): {:.4f} \t cost: {:.4f}'.format(i, w_cost[i][0], w_cost[i][1]))
# Plot the first 2 gradient descent updates
plt.plot(ws, cost_ws, 'r-') # Plot the error curve
# Plot the updates
for i in range(0, len(w_cost)-2):
w1, c1 = w_cost[i]
w2, c2 = w_cost[i+1]
plt.plot(w1, c1, 'bo')
plt.plot([w1, w2],[c1, c2], 'b-')
plt.text(w1, c1+0.5, '$w({})$'.format(i))
# Show figure
plt.xlabel('$w$', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('$\\xi$', fontsize=15)
plt.title('Gradient descent updates plotted on cost function')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
w(0): 0.1000 cost: 25.1338
w(1): 2.5774 cost: 2.7926
w(2): 1.9036 cost: 1.1399
w(3): 2.0869 cost: 1.0177
w(4): 2.0370 cost: 1.0086

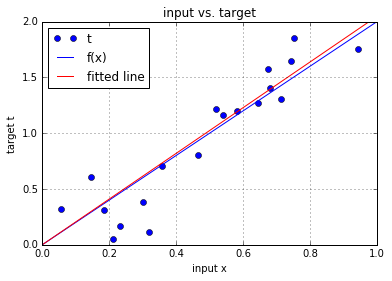
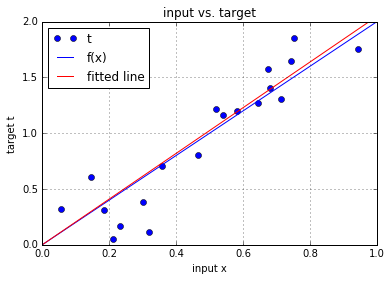
4. 预测的效果
w = 0
# Start performing the gradient descent updates
nb_of_iterations = 10 # number of gradient descent updates
for i in range(nb_of_iterations):
dw = delta_w(w, x, t, learning_rate) # get the delta w update
w = w - dw # update the current weight parameter # Plot the fitted line agains the target line
# Plot the target t versus the input x
plt.plot(x, t, 'o', label='t')
# Plot the initial line
plt.plot([0, 1], [f(0), f(1)], 'b-', label='f(x)')
# plot the fitted line
plt.plot([0, 1], [0*w, 1*w], 'r-', label='fitted line')
plt.xlabel('input x')
plt.ylabel('target t')
plt.ylim([0,2])
plt.title('input vs. target')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
二、封装在API
以上是实现细节,在scikit-learn中被封装成了如下精简的API。
Ref: [Scikit-learn] 1.1. Generalized Linear Models - Neural network models
mlp = MLPClassifier(verbose=0, random_state=0, max_iter=max_iter, **param)
mlp.fit(X, y)
mlps.append(mlp)
随机梯度下降
一、基本介绍
Ref: 1.5. Stochastic Gradient Descent
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is a simple yet very efficient approach to discriminative learning of linear classifiers under convex loss functions such as (linear) Support Vector Machines and Logistic Regression.
- Logistic Regression 是 模型
- SGD 是 算法,也就是 “The solver for weight optimization.” 权重优化方法。
SGD has been successfully applied to large-scale and sparse machine learning problems often encountered in text classification and natural language processing.
Given that the data is sparse, the classifiers in this module easily scale to problems with more than 10^5 training examples and more than 10^5 features.
nlp Feature:
- Loss function: 凸
- 数据大且稀疏(维度高)
The advantages of Stochastic Gradient Descent are:
- Efficiency.
- Ease of implementation (lots of opportunities for code tuning).
The disadvantages of Stochastic Gradient Descent include:
- SGD requires a number of hyperparameters such as the regularization parameter and the number of iterations.
- SGD is sensitive to feature scaling.
二、函数接口
1.5. Stochastic Gradient Descent
函数名
SGDRegressor 类实现了一个简单的随机梯度下降的学习算法的程序,该程序支持不同的损失函数和罚项 来拟合线性回归模型。 SGDRegressor对于非常大的训练样本(>10.000)的回归问题是非常合适的。- 对于其他问题我们推荐
Ridge, Lasso 或者ElasticNet。
函数参数
具体损失函数可以通过设置 loss 参数。 SGDRegressor 支持以下几种损失函数:
loss="squared_loss": Ordinary least squares, // 可以用于鲁棒回归loss="huber": Huber loss for robust regression, // 可以用于鲁棒回归loss="epsilon_insensitive": linear Support Vector Regression. // insensitive区域的宽度可以 通过参数epsilon指定,该参数由目标变量的规模来决定。
三、模型比较
SGDRegressor 和 SGDClassifier 一样支持平均SGD。Averaging 可以通过设置 `average=True` 来启用。
对于带平方损失和L2罚项的回归,提供了另外一个带平均策略的SGD的变体,使用了随机平均梯度算法(SAG), 实现程序为Ridge 。 # 难道不是直接套公式?而是采用逼近法估参?
问题来了:from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Lasso, Ridge, ElasticNet, SGDRegressor
前四种方法:LinearRegression, Lasso, Ridge, ElasticNet
from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Lasso, Ridge, ElasticNet, SGDRegressor
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston boston = load_boston()
np.set_printoptions(precision=2, linewidth=120, suppress=True, edgeitems=4) # In order to do multiple regression we need to add a column of 1s for x0
x = np.array([np.concatenate((v,[1])) for v in boston.data])
y = boston.target a = 0.3
for name,met in [
('linear regression', LinearRegression()),
('lasso', Lasso(fit_intercept=True, alpha=a)),
('ridge', Ridge(fit_intercept=True, alpha=a)),
('elastic-net', ElasticNet(fit_intercept=True, alpha=a))
]:
met.fit(x,y)
# p = np.array([met.predict(xi) for xi in x])
p = met.predict(x)
e = p-y
total_error = np.dot(e,e)
rmse_train = np.sqrt(total_error/len(p)) kf = KFold(len(x), n_folds=10)
err = 0
for train,test in kf:
met.fit(x[train],y[train])
p = met.predict(x[test])
e = p-y[test]
err += np.dot(e,e) rmse_10cv = np.sqrt(err/len(x))
print('Method: %s' %name)
print('RMSE on training: %.4f' %rmse_train)
print('RMSE on 10-fold CV: %.4f' %rmse_10cv)
print("\n")
Method: linear regression
RMSE on training: 4.6795
RMSE on 10-fold CV: 5.8819 Method: lasso
RMSE on training: 4.8570
RMSE on 10-fold CV: 5.7675 Method: ridge
RMSE on training: 4.6822
RMSE on 10-fold CV: 5.8535 Method: elastic-net
RMSE on training: 4.9072
RMSE on 10-fold CV: 5.4936
Stochastic Gradient Descent 实践
# SGD is very senstitive to varying-sized feature values. So, first we need to do feature scaling.
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(x)
x_s == SGDRegressor(penalty='l2', alpha=0.15, n_iter=200)
sgdreg.fit(x_s,y)
p = sgdreg.predict(x_s)
err = p-y
total_error = np.dot(err,err)
rmse_train = np.sqrt(total_error/len(p)) # Compute RMSE using 10-fold x-validation
kf = KFold(len(x), n_folds=10)
xval_err = 0
for train,test in kf:
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(x[train]) # Don't cheat - fit only on training data
xtrain_s = scaler.transform(x[train])
xtest_s = scaler.transform(x[test]) # apply same transformation to test data
sgdreg.fit(xtrain_s,y[train])
p = sgdreg.predict(xtest_s)
e = p-y[test]
xval_err += np.dot(e,e)
rmse_10cv = np.sqrt(xval_err/len(x)) method_name = 'Stochastic Gradient Descent Regression'
print('Method: %s' %method_name)
print('RMSE on training: %.4f' %rmse_train)
print('RMSE on 10-fold CV: %.4f' %rmse_10cv)
Method: Stochastic Gradient Descent Regression
RMSE on training: 4.8119
RMSE on 10-fold CV: 5.5741
End.
[Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Regression的更多相关文章
- [Scikit-learn] 1.5 Generalized Linear Models - SGD for Classification
NB: 因为softmax,NN看上去是分类,其实是拟合(回归),拟合最大似然. 多分类参见:[Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Logist ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Bayesian Ridge Regression
1.1.10. Bayesian Ridge Regression 首先了解一些背景知识:from: https://www.r-bloggers.com/the-bayesian-approach- ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - Logistic regression & Softmax
二分类:Logistic regression 多分类:Softmax分类函数 对于损失函数,我们求其最小值, 对于似然函数,我们求其最大值. Logistic是loss function,即: 在逻 ...
- 广义线性模型(Generalized Linear Models)
前面的文章已经介绍了一个回归和一个分类的例子.在逻辑回归模型中我们假设: 在分类问题中我们假设: 他们都是广义线性模型中的一个例子,在理解广义线性模型之前需要先理解指数分布族. 指数分布族(The E ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习公开课笔记 -- Generalized Linear Models
网易公开课,第4课 notes,http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes1.pdf 前面介绍一个线性回归问题,符合高斯分布 一个分类问题,logstic回 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 1.1 Generalized Linear Models - from Linear Regression to L1&L2
Introduction 一.Scikit-learning 广义线性模型 From: http://sklearn.lzjqsdd.com/modules/linear_model.html#ord ...
- Popular generalized linear models|GLMM| Zero-truncated Models|Zero-Inflated Models|matched case–control studies|多重logistics回归|ordered logistics regression
============================================================== Popular generalized linear models 将不同 ...
- Regression:Generalized Linear Models
作者:桂. 时间:2017-05-22 15:28:43 链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6890048.html 前言 本文主要是线性回归模型,包括: ...
- Generalized Linear Models
作者:桂. 时间:2017-05-22 15:28:43 链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6890048.html 前言 主要记录python工具包:s ...
随机推荐
- *p 和p[i] 区别
注意:*(arr+ n -1)指向的 是原来&a[n-1]是个地址 与arr[n-1]不同 !!重点!
- iis深入学习资源
iis站点:https://www.iis.net/overview/reliability/richdiagnostictools 感兴趣可以深入学习下iis
- Python3+Appium学习笔记07-元素定位工具UI Automator Viewer
这篇主要说下如何使用UI Automator Viewer这个工具来定位元素.这个工具是sdk自带的.在sdk安装目录Tools目录下找到uiautomatorviewer.bat并启动它 如果启 ...
- golang 2 ways to delete an element from a slice
2 ways to delete an element from a slice yourbasic.org/golang Fast version (changes order) a := []st ...
- hexo主题next 7.X版本配置美化
我们主要对next主题进行了如下配置操作.效果可以前往https://www.ipyker.com 查看. 也可以前往https://github.com/ipyker/hexo-next-theme ...
- .Net优秀应用界面大PK!DevExpress年度大赛,群雄逐鹿花落谁家
DevExpress 优秀界面图片火热征集中! 只要您晒出来,慧都就为您颁奖! 角逐前三,百度AI音箱.小米行李箱等惊喜大礼等您Pick! 活动时间:12月1日-12月31日 立即参与 活动详情 活动 ...
- 2、python--第二天练习题
#1.有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中. #即: {'k ...
- PHP mysqli_error_list() 函数
返回最近调用函数的最后一个错误代码: <?php // 假定数据库用户名:root,密码:123456,数据库:RUNOOB $con=mysqli_connect("localhos ...
- PHP mysqli_data_seek() 函数
mysqli_data_seek() 函数调整结果指针到结果集中的一个任意行. // 假定数据库用户名:root,密码:123456,数据库:RUNOOB $con=mysqli_connect(&q ...
- Navicat permium快捷键
Ctrl + F 搜索本页数据 Ctrl + Q 打开查询窗口 Ctrl + / 注释sql语句 Ctrl + Shift + / 解除注释 Ctrl + R 运行查询窗口的sql语句 Ctrl + ...
