shell script 编程入门
参考 《linux shell scripting cookbook》
控制台输出
结构化输出
#!/bin/bash
#Filename: printf.sh
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4s\n" No Name Mark
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 1 Sarath 80.3456
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 2 James 90.9989
printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 3 Jeff 77.564
结果:
No Name Mark
1 Sarath 80.35
2 James 91.00
3 Jeff 77.56
输出彩色文字
echo -e "\e[1;33m This is red text \e[0m"
\e[1;31m 是设置颜色为红色 \e[0m 是重置颜色 , 这样就不会影响后面的输出
前景色:
reset = 0, black = 30, red = 31,
green = 32, yellow = 33, blue = 34, magenta = 35, cyan = 36, and white = 37
背景色:
reset = 0, black = 40, red = 41, green = 42, yellow = 43, blue = 44,
magenta = 45, cyan = 46, and white=47
字符替换
cat c1.sh
eqeqeqweqe eqeweqwewqe eqwewqeqweq wqeqweqwewqe
eqwewqe;wqewqewqewqqdfewfr;erqrqrqwrwq;
空格或者; 替换为换行符
cat c1.sh | tr ' |;' '\n'
eqeqeqweqe
eqeweqwewqe
eqwewqeqweq
wqeqweqwewqe
eqwewqe
wqewqewqewqqdfewfr
erqrqrqwrwq
字符串的长度
root@kali:~# content='hello world'
root@kali:~# echo ${#content}
11
识别当前的shell
root@kali:~# echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
root@kali:~# echo $0
bash
检测当前脚本执行用户是不是超级用户
#!/bin/bash
if [ $UID -ne 0 ]; then
echo Non root user. Please run as root.
else
echo Root user
fi
root@kali:~/shell# ./c1.sh
Root user
kali@kali:/root/shell$ ./c1.sh
Non root user. Please run as root.
文件操作
0: stdin (standard input)
1: stdout (standard output)
2: stderr (standard error)
正常的输出重定向到文件
root@kali:~# echo aa > stdout.txt
root@kali:~# cat stdout.txt
aa
异常的输出重定向到文件
这种写不进去
root@kali:~# ls + > stderr.txt
ls: cannot access '+': No such file or directory
root@kali:~# cat stderr.txt
root@kali:~#
这样可以
root@kali:~# ls + 2> stderr.txt
root@kali:~# cat stderr.txt
ls: cannot access '+': No such file or directory
也可以
root@kali:~# ls + &>> stderr.txt
root@kali:~# cat stderr.txt
ls: cannot access '+': No such file or directory
ls: cannot access '+': No such file or directory
输入重定向
root@kali:~/shell# cat domains.txt
www.baidu.com
root@kali:~/shell# exec 3< domains.txt
root@kali:~/shell# cat <&3
www.baidu.com
root@kali:~/shell#
输出重定向
root@kali:~/shell# exec 4> output.txt
root@kali:~/shell#
root@kali:~/shell# cat output.txt
root@kali:~/shell# echo haha >&4
root@kali:~/shell# cat output.txt
haha
root@kali:~/shell#
数组
root@kali:~/shell# array_var=(a b c d e f)
root@kali:~/shell#
root@kali:~/shell# echo ${array_var[*]}
a b c d e f
root@kali:~/shell# echo ${array_var[2]}
c
root@kali:~/shell# echo ${#array_var[*]}
6
root@kali:~/shell# echo ${array_var[@]}
a b c d e f
root@kali:~/shell#
别名
del 替换 rm 防止误操作
alias rm='echo "rm is disabled, use del instead."'
alias del='/bin/rm'
如果要在其他窗口生效,添加到~/.bashrc
编写高质量的 shell 脚本
cat 输出
root@kali:~/shell# cat in.txt
iinnniniii
root@kali:~/shell# ls -l |cat - in.txt
total 12
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 110 Oct 17 11:34 c1.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Oct 17 15:59 in.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Oct 17 15:55 out.txt
iinnniniii
find 正则查找
root@kali:~/shell# find . -regex ".*\(\.txt\|\.sh\)$"
./c1.sh
./in.txt
./out.txt
文件的类型:
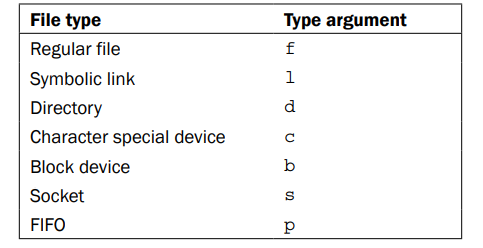
时间类型,单位(天)
Access time (-atime): 访问时间
Modification time (-mtime): 修改时间(内容)
Change time (-ctime): 修改时间(元数据,权限什么的)
单位(分钟)
-amin (access time)
-mmin (modification time)
-cmin (change time)
查找类型为f,最近访问在7天之前的
find . -type f -atime +7
文件大小
b: 512 byte blocks
c: Bytes
w: Two-byte words
k: Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
M: Megabyte (1024 kilobytes)
G: Gigabyte (1024 megabytes)
find . -type f -atime +7 -size +10M
查找并删除
find . -name out.txt -delete
xargs 改变输出的排版
root@kali:~/shell# cat in.txt
iinnniniii
sds
dsds
dsd
dsds
ds
dsd
1 2
3 4 5 678 99 0 0 -fg gd gdfg dfh
dsfdsgdsg ghgf g f
root@kali:~/shell# cat in.txt | xargs
iinnniniii sds dsds dsd dsds ds dsd 1 2 3 4 5 678 99 0 0 -fg gd gdfg dfh dsfdsgdsg ghgf g f
root@kali:~/shell# cat in.txt | xargs -n 3
iinnniniii sds dsds
dsd dsds ds
dsd 1 2
3 4 5
678 99 0
0 -fg gd
gdfg dfh dsfdsgdsg
ghgf g f
root@kali:~/shell# echo "splitXsplitXsplitXsplit" | xargs -d X
split split split split
前面的输出作为后面的输入
find . -type f -name "*.txt" -print | xargs rm -f
tr 转换
大小写
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS" | tr 'A-Z' 'a-z'
hello who is this
替换和删除
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr 'A-Za-z' ' '
123
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr -d 'A-Za-z'
123
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr -d 'A-Za-z '
123
互补性删除(下面就是删除非 0-9 的字符 )
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr -d -c '0-9\n'
123
压缩空格
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr -d ' '
HELLOWHOISTHIS123
root@kali:~/shell#
root@kali:~/shell#
root@kali:~/shell# echo "HELLO WHO IS THIS 123" | tr -s ' '
HELLO WHO IS THIS 123
累加
root@kali:~/shell# cat sum.txt
1
2
3
4
5
root@kali:~/shell# cat sum.txt | echo $[ $(tr '\n' '+' ) 0 ]
15
文件加密解密
base64 sum.txt > sum.txt.b64
root@kali:~/shell# cat sum.txt.b64
MQoyCjMKNAo1Cgo=
root@kali:~/shell# base64 -d sum.txt.b64
1
2
3
4
5
文件操作
排序
root@kali:~/shell# cat a.txt
apple
orange
gold
silver
steel
iron
root@kali:~/shell# sort a.txt
apple
gold
iron
orange
silver
steel
找到公共的内容
首先要把内容排序
root@kali:~/shell# source a.txt -o a.txt
root@kali:~/shell# sort b.txt -o b.txt
root@kali:~/shell# comm a.txt b.txt
apple
carrot
cookies
gold
iron
orange
silver
steel
只显示公共部分
root@kali:~/shell# comm a.txt b.txt -1 -2
gold
orange
不显示公共部分
root@kali:~/shell# comm a.txt b.txt -3
apple
carrot
cookies
iron
silver
steel
联合执行指令
- 结束所有的Windows进程
root@kali:~# ps -aux |grep windows |awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
shell script 编程入门的更多相关文章
- Linux零基础之shell基础编程入门
从程序员的角度来看, Shell本身是一种用C语言编写的程序,从用户的角度来看,Shell是用户与Linux操作系统沟通的桥梁.用户既可以输入命令执行,又可以利用 Shell脚本编程,完成更加复杂的操 ...
- 08 bash特性--shell脚本编程入门
shell脚本编程入门 编程语言介绍 编程语言分为:机械语言.汇编语言和高级语言: 计算机能识别的语言为机械语言,而人类能学习的并且能够方便掌握的为高级语言,所以,我们所编写的程序就要通过编译来转换成 ...
- Shell脚本编程入门(一) 分类: 学习笔记 linux ubuntu 2015-07-09 21:06 29人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
最近在学shell,记录一下. if语句的使用: 1.判断两个参数大小 #!/bin/sh #a test about if statement a=10 b=20 if [ $a -eq $b ]; ...
- Shell脚本编程入门(一)
最近在学shell,记录一下. if语句的使用: 1.判断两个参数大小 #!/bin/sh #a test about if statement a=10 b=20 if [ $a -eq $b ]; ...
- Shell脚本编程入门到放弃
1 区分大小写 UNIX是区分大小写的,因此shell脚本也是区分大小写的 2 特殊字符 UNIX的某些字符都有特殊的意义或功能,如果它们不以其特殊的意义使用必须要进行转义(escaped). 为了转 ...
- 5个Shell脚本编程入门练习例子
例子一:绘制特殊图形 复制代码代码如下: #!/bin/bash MAX_NO=0 echo -n "Enter Number between (5 to 9) : " read ...
- shell脚本编程入门
Linux的Shell种类众多,这里我们关注的重点是Bash. 基本语法 环境变量$PATH IO重定向: 以<改变标准输入 如:tr -d '\r' < dos-file.txt 以& ...
- Shell Script编程——USB挂载/复制文件/查找文件/压缩文件
PS:$引用变量的时候不要加空格.用了case,while的结构. main文件 #!/bin/bash chmod a+x changedate chmod a+x changemod chmod ...
- linux基础之Shell Script入门介绍
本文介绍下,学习shell script编程的入门知识,通过几个入门实例,带领大家走进shell script的神圣殿堂,呵呵,有需要的朋友参考下. 本文转自:http://www.jbxue.com ...
随机推荐
- kotlin 之相等判断
在kotlin 中存在二种相等的判断: 1.引用相等 也就是说,两个引用指向同一个对象,使用===操作 ,相反操作为!==来判断 2.结构相等 使用equals 函数相等和==操作符 a?.equal ...
- 通过OpenCL内核代码猜测设备寄存器个数
在OpenCL标准中,没有给出查看计算设备一共有多少寄存器,至少能分配给每个work-item多少寄存器使用的特征查询.而由于一个段内核代码是否因寄存器紧缺而导致性能严重下降也是一个比较重要的因素,因 ...
- 免费的HTML5版uploadify
转http://www.cnblogs.com/lvdabao/p/3452858.html var defaults = { fileTypeExts:'',//允许上传的文件类型,格式'*.jpg ...
- 阶段5 3.微服务项目【学成在线】_day03 CMS页面管理开发_06-新增页面-前端-新增页面
新建一个添加的页面 复制page_list页面改改名字 page_add 一个标准的页面 <template> <div> 新增页面 </div> </tem ...
- mudos源码分析
错误捕捉相关的代码在simulate.c void throw_error() { )->framekind & FRAME_MASK) == FRAME_CATCH) { LONGJM ...
- nginx访问日志的几个统计命令
nginx日志中得到访问量最高前10个IP: cat access.log.10 | awk '{a[$1]++} END {for(b in a) print b"\t"a[b] ...
- Spring Aop(六)——@DeclareParents介绍
转发:https://www.iteye.com/blog/elim-2395410 6 @DeclareParents介绍 @DeclareParents注解也是Aspectj提供的,在使用基于As ...
- Python扫描器-爬虫基础
0x1.基础框架原理 1.1.爬虫基础 爬虫程序主要原理就是模拟浏览器发送请求->下载网页代码->只提取有用的数据->存放于数据库或文件中 1.1.基础原理 1.发起HTTP请求 2 ...
- 解决Linux:Too many levels of symbolic links
Too many levels of symbolic links 解决:创建链接时使用绝对路径
- 动态中位数-POJ 3784
题目: 依次读入一个整数序列,每当已经读入的整数个数为奇数时,输出已读入的整数构成的序列的中位数. 输入格式 第一行输入一个整数P,代表后面数据集的个数,接下来若干行输入各个数据集. 每个数据集的第一 ...
